8 Benefits Of Beetroot Juice, Side Effects, & How To Make It
A large sip of this nutritious drink is all you need to pump your athletic performance.

Image: Shutterstock
Beetroots are fast becoming popular for their wonderful nutrient profile. In addition to eating beets, you may also relish their juice. The super-healthy beverage can easily be absorbed by your body.
Studies show that beetroot juice can help lower blood pressure levels (1). This is important to note, as 1 in every 3 adults in the US has high blood pressure (2).
There are other important benefits of beetroot juice for your health. In this post, we will discuss them at length.
 Know Your Ingredient: Beetroot Juice
Know Your Ingredient: Beetroot JuiceWhat Is It?
A healthy vegetable juice made from fresh beetroot.
What Are Its Benefits?
Improves stamina, lowers blood pressure levels, and improves blood flow.
Who Can Consume It?
People can safely eat beetroot or drink its juice for good health except for people who have a history of kidney stones or are at risk.
How Often?
It can be consumed daily in moderation.
Caution
Avoid consuming this juice if you are on blood pressure-lowering medication.
In This Article
What Are The Health Benefits Of Beetroot Juice?
According to Mary Sabat, MS, RD, LD, “Beet juice, in moderation, could become part of a healthy diet. Beet juice has been reported to have many potential health benefits, such as cleansing the gut, reducing inflammation, and improving athletic performance.” She adds, “Some studies suggest that beetroot juice may be beneficial for people with arthritis.”
The nitrates in the juice help lower blood pressure and protect the heart. While the anti-inflammatory properties of the juice help fight cancer, the betalains it contains can help lower blood sugar. Let’s look at how beetroot juice benefits you in detail.
1. May Promote Heart Health

Beetroot juice is a powerful source of nitrates. Nitrates dilate the blood vessels, lowering blood pressure. This is beneficial to the heart (3).
The juice also reduces overstimulation of the sympathetic nervous system, which may elevate blood pressure levels and lead to heart disease (3).
In another study, participants consuming beetroot juice saw a considerable decrease in their blood pressure levels in just 30 minutes (4). This effect subsided in 24 hours, though.
Beetroot juice supplements may improve health in patients who had heart failure (5).
The juice might also lower total cholesterol levels. In a rat study, beetroot extract lowered triglyceridesi A common type of fat (lipid) in the blood that stores excess calories the body does not immediately need to use. and total cholesterol levels. It also increased the levels of HDL (the good cholesterol). This effect could be attributed to the flavonoidsi A group of plant compounds like anthocyanins and flavones with anti-inflammatory and disease-fighting properties. in beets (6).
2. May Help Fight Cancer
The most important antioxidant in beetroot juice is betacyanin, which fights free radicals.
This is one way the juice can contribute to cancer prevention (7).
The anti-inflammatory properties of beetroot juice can also help treat chronic lymphocytic leukemia (cancer of the blood and bone marrow) (8). The betacyanin in the juice also plays a major role here.
Beetroot juice was also found to have anticancer effects comparable with doxorubicin, an anticancer drug (9).
The juice reduces cancer cell proliferation and inflammation and stimulates cell death in cancers of the skin, liver, lungs, and the esophagus (10).
3. May Aid Diabetes Treatment
(11). The betalains in the juice (powerful antioxidant compounds) are responsible for this effect.
Similar effects were observed in obese individuals. Obese individuals who consumed the juice along with carbs showed lower insulin resistance compared to their non-obese counterparts who did not drink the juice (12).
The nitrates in the juice help lower blood pressure. This effect was more accentuated in people with type 2 diabetes (13).
However, moderation is key. Sabat adds, “Beetroot juice is low in calories, but unlike whole beets, it does not contain the fiber which would slow down the insulin effect from the sugar. Beets do contain sugar, so when we take out the fiber, it is going to have a higher glycemic load on the body and might not be the best option for someone wishing to lose weight or those with diabetes who need to watch their sugar content.”
4. May Help Treat Erectile Dysfunction
There is no strong evidence that beetroot juice can treat erectile dysfunction. But a majority of the affected men seem to swear by it.
Some sources suggest that nitric oxide may have a role to play in treating erectile dysfunction (14). The compound relaxes the blood vessels and improves blood flow. This property, apart from lowering blood pressure, also enhances penile blood flow.
Since erectile dysfunction occurs due to lack of proper blood flow to the penile muscles, nitric oxide in beet juice might help facilitate it.
Another important compound involved with erection is cGMP (cyclic guanosine monophosphate). This compound relaxes the arteries and increases blood flow to the penis. A study shows that foods rich in nitrates (which convert to nitric oxide in the body) can increase the levels of cGMP (15).
5. May Boost Athletic Performance
Beetroot juice intake has been linked to improvements in several parameters associated with the cardiovascular and respiratory systems
(16).
The juice showed desirable effects in elite runners as well. Fifteen days of beetroot juice supplementation improved the time to exhaustion in these runners (17). But it didn’t seem to improve other physical parameters, like maximum physical uptake.
Another study reports no improvement in physical performance and stamina after the intake of beetroot juice (18). However, it was conducted with only one shot of beetroot juice.
Khalil, research scientist in nutrition and content creator, drank beetroot juice for 21 days. According to him, beetroot juice helped improve his athletic performance. In one of his vlogs, he states, “On the days I drank beetroot juice prior to working out, I felt really good. I felt like I got a little bit more out of my workouts. I even think that on one of the days I ran farther than I typically run now (i)”.
6. May Reduce Risk Of Dementia
There is less research to support this fact. Some sources suggest that dietary nitrate can improve blood flow to the brain, thereby cutting the risk of dementiai A group of diseases or conditions characterized by loss of brain function that affect thinking, memory, language, and daily functioning. or other forms of cognitive decline (19).
7. May Promote Liver Health
Betaine in beetroot juice might help treat non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. However, this was proven only in animal studies (20).
In another rat study, dietary betaine was found to improve liver function. The compound protected the livers of rats from toxins (21).
8. Can Be Used As A Hair Dye
Though this is not a health benefit of beetroot per se, the juice is often used as a hair dye. If you want a deeper red tint to your hair, here’s how you can use the juice:
- Mix beetroot juice with a carrier oil (like coconut oil).
- Apply this mixture liberally to your hair. Cover your hair with a plastic wrap.
- Leave it on for about an hour.
- Remove the plastic wrap and wash your hair.
 Quick Tip
Quick TipBeetroot juice is fast becoming a superfood, and all for good reason.
Some anecdotal evidence also suggests the juice can help aid weight loss and ease constipation. However, there is no research to support this statement. Hence, consult your doctor if you want to prepare beetroot juice for weight loss, as they can instruct you on how much of the vegetable you need to use and if you need to pair it with any other ingredients.
Beetroot juice is replete with potent compounds. In the following section, we will look at the detailed nutritional profile.
Key Takeaways
- Beetroot juice may help support liver and heart function, regulate blood pressure, and aid digestion.
- It may help maintain blood sugar levels and improve cognitive function.
- Excess consumption of beetroot juice may cause beeturia and increase the risk of kidney stones.
What Is The Nutritional Profile Of Beetroot Juice?
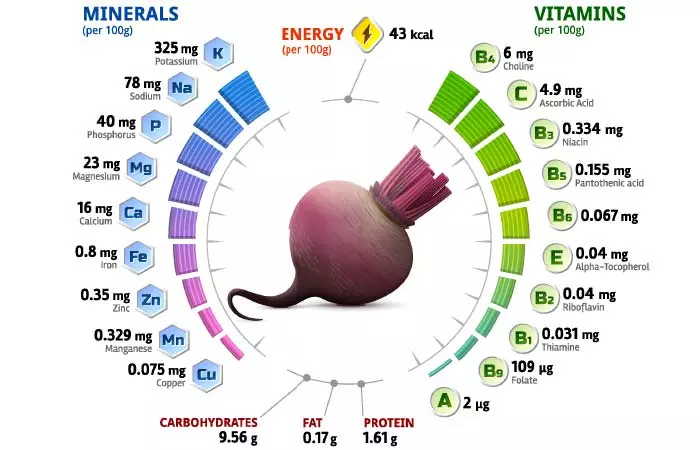

The following table shows the nutritional profile of beetroot. The juice, in the same quantity, would have the same nutrients.
| Nutrient | Unit | 1 cup = 136.0g | 1 beet (2″ dia) = 82.0g |
|---|---|---|---|
| Water | g | 119.11 | 71.82 |
| Energy | Kcal | 58 | 35 |
| Protein | g | 2.19 | 1.32 |
| Total lipid (fat) | g | 0.23 | 0.14 |
| Carbohydrate, by difference | g | 13 | 7.84 |
| Fiber, total dietary | g | 3.8 | 2.3 |
| Sugars, total | g | 9.19 | 5.54 |
| Minerals | |||
| Calcium | mg | 22 | 13 |
| Iron | mg | 1.09 | 0.66 |
| Magnesium | mg | 31 | 19 |
| Phosphorus | 0mg | 54 | 33 |
| Potassium | mg | 442 | 266 |
| Sodium | mg | 106 | 64 |
| Zinc | mg | 0.48 | 0.26 |
| Vitamins | |||
| Vitamin C, total ascorbic acid | mg | 6.7 | 4 |
| Thiamin | mg | 0.042 | 0.025 |
| Riboflavin | mg | 0.054 | 0.033 |
| Niacin | mg | 0.454 | 0.274 |
| Vitamin B-6 | mg | 0.091 | 0.055 |
| Folate, DFE | μg | 148 | 89 |
| Vitamin A, RAE | μg | 4 | 2 |
| Vitamin A, IU | IU | 45 | 27 |
| Vitamin E (alpha-tocopherol) | mg | 0.05 | 0.03 |
| Vitamin K (phylloquinone) | μg | 0.3 | 0.2 |
| Lipids | |||
| Fatty acids, total saturated | g | 0.037 | 0.022 |
| Fatty acids, total monounsaturated | g | 0.044 | 0.026 |
| Fatty acids, total polyunsaturated | g | 0.082 | 0.049 |
*values sourced from USDA, beets, raw
Beetroot juice is a brightly colored beverage that brims with antioxidants. Hence, having it every day is a wonderful idea. But how do you make it?
How Do You Make Beetroot Juice At Home?

What You Need
- 2-4 medium-sized beetroots with their tops on
- A container
- A juicer
Directions
- Wash the beets thoroughly. You can use a brush specifically purchased for this purpose.
- Peel the skin.
- Cut the beets and the tops into manageable pieces.
- Place the beets in the juicer and place the container under the spout of the juicer.
- You can serve the juice chilled. You can sweeten the juice by adding the juice of half an apple.
Beetroot juice naturally tastes earthy. You can improve its taste by adding a dash of lemon.
Here is a quick, flavorful beetroot juice recipe you can try at home:
What You Need
- 2 beetroots, peeled
- 1 green apple
- 1/2 lemon, peeled
- 1-inch ginger
- A pinch of salt
Directions
- Wash and prepare the ingredients.
- Juice the beetroots, apple, lemon, and ginger and mix them in a glass.
- Add a pinch of salt and stir.
- Serve immediately and savor the uniqueness!
While the apple offers sweetness, the lemon and ginger add in a balanced, refreshing flavor. The salt brings a touch of freshness to the exquisite tangy blend. You can also freeze the blend before serving it if you prefer chilled juices.
Here are a few tips you can follow to retain the flavor and nutrient composition of beetroot when juicing it:
- Store the beets in a cool, dry place before juicing to maintain its freshness.
- Juice beets with their skin on for added fiber and vitamins.
- Avoid overheating the juice as it may reduce nutrient levels.
- Drink beetroot juice on an empty stomach to maximize nutrient absorption.
- Drink the juice immediately after making it to preserve nutrients.
- If you are not consuming the juice immediately, limit its exposure to light and air by storing the juice in a sealed container.
Note: Homemade beet juice can be refrigerated for 3-5 days. Store it in an airtight container and keep it at or below 40°F (4°C) to extend its freshness and prevent contamination. However, consume the juice within 24 hours to maintain its freshness and nutrient retention.
 Quick Tip
Quick TipDrinking the juice along with the fiber offers you the benefits discussed in the earlier section. But before you go ahead, you need to be aware of a few side effects of beetroot juice.
What Are The Side Effects Of Beetroot Juice?
• Can Cause Beeturia
Beeturia is the discoloration of urine following the consumption of beetroots/beetroot juice or foods made with them. The pigments in beets, which belong to the family of betacyaninsi A class of red and yellow pigments found in plants that act against the formation of reactive oxygen species (highly reactive chemicals). , are responsible for this (22).
Beeturia is a harmless condition. Reducing beetroot juice intake can rectify it. But be careful as this condition is often observed in people who are deficient in iron.
• Can Increase Risk Of Kidney Stones
Beets/beetroot juice contain(s) oxalates, which are largely responsible for kidney stones (23). Consuming too much of foods high in oxalates can increase the risk of kidney stones.
If you have a history of kidney stones or are at risk, please avoid beetroot juice.
• May Lower Blood Pressure Way Too Much
Beetroot juice can lower blood pressure levels. If you are already on medications to lower blood pressure, please check with your doctor. They might adjust the dosage of your medication accordingly.
Infographic: Beet Lemonade Recipe
Beetroot has an excellent nutrient profile with many health benefits. From improving heart health to reducing the risk of dementia, it helps improve your overall health. Thankfully, you can prepare easy yet healthy beetroot drinks at home. Check out the infographic below to learn how to make some delicious beet lemonade. Illustration: StyleCraze Design Team

Beetroot juice is gaining wide popularity as a superfood for its rich nutrient content. Its anti-inflammatory and anti-oxidative properties not only help cleanse your system and boost your overall health and immune system but also improve your cardiovascular and digestive health as well. So, it is great for body detoxification as well. It is also known to boost your athletic performance and may also be effective in the treatment of erectile dysfunction. It improves your liver health and may reduce the risks of cancer and diabetes. You can easily make it at home and include it in your regular diet routine to reap the many benefits of drinking beetroot juice.
Frequently Asked Questions
How much beetroot juice is too much?
There are no official dosage recommendations. But 250 ml of the juice daily should be ideal as it also helps regulate blood pressure (24). Anything beyond that, over longer periods, may cause issues.
What is the best time to drink beetroot juice?
Drinking it the first thing in the morning can work best as it can help in better absorption. You can also drink the juice at any other time of the day.
How long does beetroot juice take to work?
Beetroot juice takes two to three hours to work and may have an effect after 24 hours.
Is beetroot anti-aging?
Yes. A study examined the impact of beet extract on skin elasticity in female volunteers with dry skin. The findings suggested that oral consumption of beet may positively impact the extracellular matrix (a large network of proteins that give structure to the body’s tissues, including the skin) (25). It may, in fact, be one of the most effective juices for glowing skin.
Is beetroot good for eyesight?
Possibly. Dietary nitrates in beetroot may protect the eyes against age-related macular degeneration (AMD) (26). However, further research is warranted in this regard.
Illustration: Benefits Of Beetroot Juice Side Effects & How To Make It

Image: Stable Diffusion/StyleCraze Design Team
Discover more about drinking beetroot juice every day by checking out the video below. Learn how it can benefit your health and what potential risks you should be aware of.
Personal Experience: Source
StyleCraze's articles are interwoven with authentic personal narratives that provide depth and resonance to our content. Below are the sources of the personal accounts referenced in this article.
i. I Drank Beetroot Juice for 21 DAYS and THIS Happened!https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=hUDvHOGFNGg
References
Articles on StyleCraze are backed by verified information from peer-reviewed and academic research papers, reputed organizations, research institutions, and medical associations to ensure accuracy and relevance. Read our editorial policy to learn more.
- “Dietary Nitrate from Beetroot Juice for Hypertension: A Systematic Review.” Biomolecules, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
- “Hypertension Management: An Update, ” American Health & Drug Benefits, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
- “Acute beetroot juice supplementation on sympathetic nerve activity: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled proof-of-concept study” American Journal of Physiology-Heart and Circulatory Physiology
- “A Double-Blind Placebo-Controlled Crossover Study of the Effect of Beetroot Juice Containing Dietary Nitrate on Aortic and Brachial Blood Pressure Over 24 h” Frontiers in Physiology, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
- “Dietary Nitrate Increases VO2peak and Performance but Does Not Alter Ventilation or Efficiency in Patients With Heart Failure With Reduced Ejection Fraction” Journal of Cardiac Failure
- “Effect Of Beta Vulgaris L. On Cholesterol Rich Diet-Induced Hypercholesterolemia In Rats” Farmacia.
- “Beetroot juice” National Cancer Institute.
- “Beetroot-Carrot Juice Intake either Alone or in Combination with Antileukemic Drug ‘Chlorambucil’ As A Potential Treatment for Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia” Open Access Macedonian Journal of Medical Sciences, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
- “Cytotoxic effect of the red beetroot (Beta vulgaris L.) extract compared to doxorubicin (Adriamycin) in the human prostate (PC-3) and breast (MCF-7) cancer cell lines.” Anti-cancer Agents in Medicinal Chemistry, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
- “Beet Root Juice Promotes Apoptosis in OncogenicMDA-MB-231 Cells While Protecting CardiomyocytesUnder Doxorubicin Treatment” CiteSeerX.
- “Effects of a beetroot juice with high neobetanin content on the early-phase insulin response in healthy volunteers” Journal of Nutritional Science, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
- “Concurrent Beet Juice and Carbohydrate Ingestion: Influence on Glucose Tolerance in Obese and Nonobese Adults” Journal of Nutrition and Metabolism, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
- “Dietary nitrate from beetroot juice selectively reduces central blood pressure in type 2 diabetes: the randomized, controlled VaSera trial” The Nutrition Society, Cambridge University Press.
- “The role of nitric oxide in penile erection” Journal of Expert Opinion on Pharmacotherapy.
- “Antiplatelet effects of dietary nitrate in healthy volunteers: Involvement of cGMP and influence of sex” Free Radical Biology & Medicine, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
- “Effects of Beetroot Juice Supplementation on Cardiorespiratory Endurance in Athletes. A Systematic Review” Nutrients, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
- “The effects of beetroot juice supplementation on exercise economy, rating of perceived exertion and running mechanics in elite distance runners: A double-blinded, randomized study” PloS One, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
- “Effects of a single dose of beetroot juice on cycling time trial performance at ventilatory thresholds intensity in male triathletes” United States Department of Agriculture, National Agricultural Library.
- “Acute effect of a high nitrate diet on brain perfusion in older adults” Nitric Oxide, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
- “Betaine for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: Results of a randomized placebo‐controlled trial” Hepatology, American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases.
- “Betaine in human nutrition” The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition.
- “Beeturia” National Center for Biotechnology Information.
- “Nutritional management of kidney stones” Clinical Nutrition Research, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
- “Dietary nitrate provides sustained blood pressure lowering in hypertensive patients: a randomized, phase 2, double-blind, placebo-controlled study” Hypertension, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
- Double-Blind Study on Effects of Glucosyl Ceramide in Beet Extract on Skin Elasticity and Fibronectin Production in Human Dermal Fibroblasts
https://www.researchgate.net/publication/228622792_Double-Blind_Study_on_Effects_of_Glucosyl_Ceramide_in_Beet_Extract_on_Skin_Elasticity_and_Fibronectin_Production_in_Human_Dermal_Fibroblasts - Association of Dietary Nitrate Intake with the 15-Year Incidence of Age-Related Macular Degeneration
https://www.jandonline.org/article/S2212-2672(18)30276-4/fulltext
Read full bio of Dr. Geeta Dharmatti
- Mary Sabat, MS, RDN, LD, is a registered dietitian and a certified in personal training by the American Council of Exercise. She has 30 years of experience in nutrition education, wellness coaching, fitness training, holistic health, and weight loss coaching. She obtained her bachelor's degree in Dietetics and Nutrition from the University of Delaware and master’s degree in Human Nutrition with an emphasis on Exercise Science from Rutgers University.
 Mary Sabat, MS, RDN, LD, is a registered dietitian and a certified in personal training by the American Council of Exercise. She has 30 years of experience in nutrition education, wellness coaching, fitness training, holistic health, and weight loss coaching. She obtained her bachelor's degree in Dietetics and Nutrition from the University of Delaware and master’s degree in Human Nutrition with an emphasis on Exercise Science from Rutgers University.
Mary Sabat, MS, RDN, LD, is a registered dietitian and a certified in personal training by the American Council of Exercise. She has 30 years of experience in nutrition education, wellness coaching, fitness training, holistic health, and weight loss coaching. She obtained her bachelor's degree in Dietetics and Nutrition from the University of Delaware and master’s degree in Human Nutrition with an emphasis on Exercise Science from Rutgers University.
Read full bio of Ravi Teja Tadimalla
Read full bio of Arshiya Syeda
Read full bio of Aparna Mallampalli



























Community Experiences
Join the conversation and become a part of our empowering community! Share your stories, experiences, and insights to connect with other beauty, lifestyle, and health enthusiasts.