25 Best Vitamin E-Rich Foods You Should Include In Your Diet
Boost your health by consuming ingredients high in this powerful antioxidant.

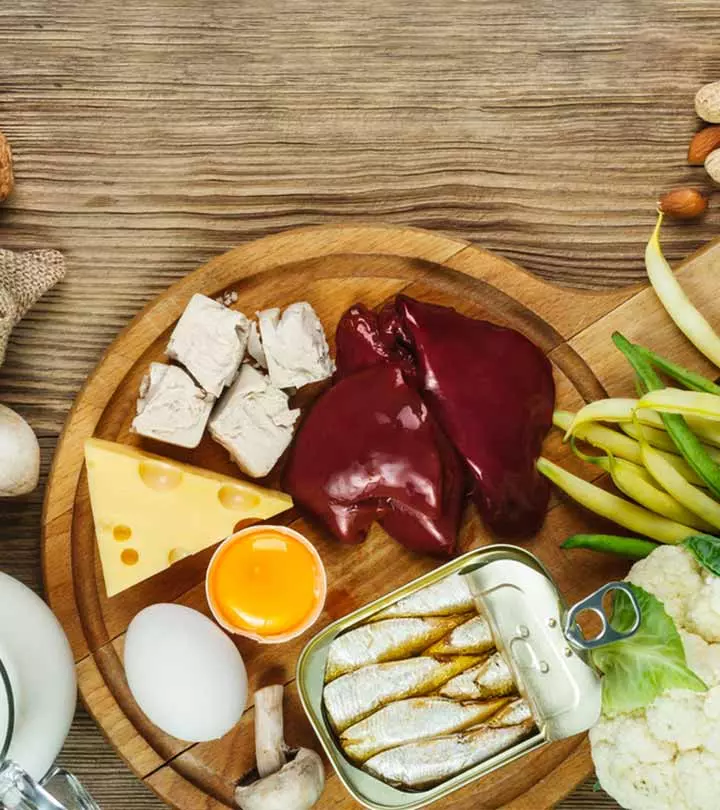
Image: Shutterstock
Vitamin E plays a vital role in many bodily functions. But many of us often neglect to include this nutrient in our diet and end up with a deficiency. You can add vitamin E-rich foods to your diet to prevent this deficiency and boost your health. You can also combat this deficiency by making minor adjustments in your diet along with including these foods with vitamin E.
Scroll down to find out which foods have the most vitamin E, the benefits this nutrient offers, and its recommended intake. Keep reading!
In This Article
What Is Vitamin E? Why Is It Essential?
This vitamin is a group of compounds that include tocopherols and tocotrienols – these two constitute the many different forms of vitamin E. Being a fat-soluble antioxidant, vitamin E fights free radicals and promotes overall health.
Vitamin E has numerous functions – apart from acting as a fat-soluble antioxidant, it also regulates enzyme activity and plays a role in smooth muscle growth. The vitamin also affects gene expression and contributes to eye and neurological health.
Vitamin E comes from various food sources, the most abundant of them being oils (wheat germ, almond, sunflower, etc.) – we will discuss them in this post.
 Did You Know?
Did You Know?And now, we get to the actual deal. the best sources of vitamin e – the everyday foods that are naturally rich in vitamin E.
Key Takeaways
- Vitamin E is an antioxidant that improves enzyme action and maintains the health of muscles, nerves, and eyes.
- The recommended daily intake of Vitamin E is 15 mg.
- Vitamin E contains eight different components, which you can easily take through food rather than supplements.
- Colored vegetables like turnip greens, broccoli, tomato, capsicum, and oregano are rich sources of vitamin E and are perfect items to add to salads or sandwiches.
- Seeds and nuts are healthy snacking alternatives that are rich in vitamins and minerals.
What Are The Top Vitamin E Rich Foods?
We have covered what vitamin E is and why we need it, but do you know the best sources of vitamin E are lying around in your kitchen? That’s right. The graph below shows foods rich in vitamin E and the amount of vitamin E you get with each serving. Wheat germ oil is one of its best sources and provides over 20 mg of vitamin E per tablespoon.

Food Sources of Vitamin E
Source: Production area of rye in specified countries in 2019/2020Check out here the list of top foods high in vitamin E:
- Wheat Germ Oil
- Almonds
- Avocado
- Sunflower Seeds
- Spinach
- Peanut Butter
- Hazelnuts
- Pine Nuts
- Dried Apricots
- Kiwi
1. Wheat Germ Oil

- Serving size – 218 grams
- Vitamin E – 326 milligrams
- DV% – 1628%
All plant oils are rich in vitamin E, and among them, wheat germ oil has the highest content.
Other plant oils rich in vitamin E include sunflower oil, cottonseed oil, olive oil, and coconut oils. You can buy the cold-pressed, unrefined, and organic versions of these oils.
How To Include In Your Diet
You can ideally use these oils for cooking.
2. Almonds
- Serving size – 95 grams
- Vitamin E – 24.9 milligrams
- DV% – 125%
As soon as we think of vitamin E, we think of almonds. They are among the richest natural sources of this vitamin. Almonds are rich in fiber that aid digestion and prevent any digestive issues.
How To Include In Your Diet
Although it’s always advisable to consume raw almonds, you can consume almond oil or almond milk as well.
3. Peanut Butter (Smooth Style)

- Serving size – 258 g
- Vitamin E – 23.2 mg
- DV% – 116%
Though a little high in calories, peanut butter also contains fiber that aids weight loss.
Peanut butter is also rich in magnesium which helps build bones. It also contains good fat.
How To Include In Your Diet
You can apply peanut butter over whole grain bread and have it for breakfast. But if you are avoiding grains or gluten, you can apply the nut butter to fruit or celery sticks. You can also take nut-based crackers.
4. Hazelnuts
- Serving size – 115 grams
- Vitamin E – 17.3 milligrams
- DV% – 86%
Hazelnuts are also rich in B vitamins and folate. The former aids cell and energy metabolism, while the latter helps in DNA synthesis and repair. The nuts are also a rich source of magnesium, calcium, and potassium.
How To Include In Your Diet
You can add hazelnuts to salads and baked goods.
5. Sunflower Seeds

- Serving size – 46 grams
- Vitamin E – 15.3 milligrams
- DV% – 76%
Sunflower seeds are excellent sources of vitamin E. They also help prevent heart disease and cancer – due to their high antioxidant content.
How To Include In Your Diet
Either consume the seeds as a snack or garnish on salads and soups.
6. Pine Nuts
- Serving size – 135 grams
- Vitamin E – 12.6 milligrams
- DV% – 63%
The nutrients in pine nuts also boost energy. They are exceptionally good in magnesium as well, the low levels of which can lead to fatigue.
How To Include In Your Diet
You can use pine nuts in your pasta or as a sandwich spread. You can also add toasted pine nuts to salads for that extra crunch.
7. Dried Apricots

- Serving size – 130 grams
- Vitamin E – 5.6 milligrams
- DV% – 28%
Dried apricots contain moderate amounts of edible fiber as well as a number of essential vitamins, including vitamin E. The fiber in them aids in cholesterol regulation and digestion. And the vitamin E enhances hair and skin health.
How To Include In Your Diet
You can blend dried apricots in a fruit salad.
8. Granola
- Serving size – 45 grams
- Vitamin E – 3.5 milligram
- DV% – 18%
Granola is a good source of fiber as well, a nutrient that helps fight heart disease, diabetes, and obesity. It also contains omega-3 fatty acids (thanks to the nuts), which have a host of other benefits – ranging from improved heart and brain health to healthier skin.
How To Include In Your Diet
You can have grain-free granola for breakfast.
9. Kiwi

- Serving size – 177 g
- Vitamin E – 2.6 mg
- DV% – 13%
Kiwis are also rich in vitamin C that helps boost immunity. They also contain serotonin, which helps treat insomnia by inducing sleep.
How To Include In Your Diet
You can add kiwis to a fruit salad after mixing with yogurt.
10. Taro Root
- Serving size – 104 grams
- Vitamin E – 2.5 milligrams
- DV% – 12%
Taro root is also rich in various antioxidants (beta-carotene and cryptoxanthin) that boost vision health. The high level of vitamin C also helps boost the immune system.
How To Include In Your Diet
You can substitute potato with taro root or sweet potato in your vegetable salad.
11. Red (Or Green) Bell Peppers

- Serving size – 149 grams
- Vitamin E – 2.4 milligrams
- DV% – 12%
Red bell peppers also contain lutein and zeaxanthin, two antioxidants that contribute to eye health. They are also decent sources of iron and are rich in vitamin C (this nutrient helps in iron absorption), both of which help prevent anemia.
How To Include In Your Diet
You can add finely chopped red bell peppers to your grain or leafy salads. You might even add them to your breakfast omelet.
12. Paprika
- Serving size – 7 g
- Vitamin E – 2 mg
- DV% – 10%
Paprika is also rich in iron that plays a role in energy generation. And the capsaicin in paprika is known to relax the blood vessels and lower blood pressure.
How To Include In Your Diet
You can add a spoonful of paprika to your favorite hummus for extra flavor. You can also season homemade soups with paprika.
13. Turnip Greens

- Serving size – 55 grams
- Vitamin E – 1.6 milligrams
- DV% – 8%
While turnip greens taste a little bitter, they have a great share of vitamin E and several other vital nutrients – one of them being vitamin C, which largely promotes hair and skin health. Moreover, it provides sufficient folate as well.
How To Include In Your Diet
You can add raw turnip greens in sandwiches or salads. You can also take them boiled or add to your favorite soups. You can also toss in some beet greens and spinach in this salad bowl as they are also rich in vitamin E.
14. Mustard Greens
- Serving size – 56 grams
- Vitamin E – 1.1 milligrams
- DV% – 6%
Just like Swiss chard, mustard greens are highly nutritious, providing many health benefits. They are one of the top carriers of vitamin E, folate, and vitamins A, C, and K.
How To Include In Your Diet
Although they taste best when well cooked, we recommend using them in salads or considering par-cooking them to retain most of their benefits.
15. Margarine

- Serving size – 14 g
- Vitamin E – 1.3 mg
- DV% – 6%
Margarine is rich in vitamin E as it is made from vegetable oils. It also contains high levels of healthy unsaturated fats and lower levels of saturated fats. These could be beneficial to your heart. But certain brands of margarine might also contain trans fats, so check the labels before you buy. Also, go for those brands containing corn oil as it provides an extra dose of vitamin E.
How To Include In Your Diet
You can replace butter with margarine on your breakfast toast.
16. Wheat (Whole Grain)
- Serving size – 120 grams
- Vitamin E – 1 milligram
- DV% – 5%
Whole grain wheat is also associated with healthy weight loss and a reduced risk of metabolic syndromei A cluster of five conditions, mainly elevated blood sugar and obesity, that can cause heart disease, diabetes, and other health issues. . It also is rich in magnesium, which plays an important role in diabetes treatment.
How To Include In Your Diet
You can prepare whole grain salads (including whole wheat) and have for breakfast.
17. Papaya

- Serving size – 140 grams
- Vitamin E – 1 milligram
- DV% – 5%
Papaya also has powerful antioxidant properties that prevent numerous diseases. It can even fight inflammation and combat indigestion.
How To Include In Your Diet
You can add fresh papaya to your fruit smoothie for added healthfulness.
18. Broccoli
- Serving size – 91 grams
- Vitamin E – 0.7 milligrams
- DV% – 4%
Broccoli is one of the healthiest foods rich in vitamin E. It also is rich in vitamins C and K, which aid in skin and bone health, respectively.
How To Include In Your Diet
You can simply have steamed broccoli for breakfast or make it a part of your meal.
19. Tomatoes

- Serving size – 149 g
- Vitamin E – 0.8 mg
- DV% – 4%
Call it a fruit or a vegetable, the tomato invariably makes its way into our diet in some form. They are exceptionally rich in lycopene, an antioxidant known to combat cancer and numerous other diseases.
How To Include In Your Diet
You can add sliced tomatoes to your sandwich, or even prepare tomato soup for your evening meal.
20. Swiss Chard
- Serving size – 36 grams
- Vitamin E – 0.7 milligrams
- DV% – 3%
This green leafy vegetable replenishes your body with several essential vitamins, including vitamin E. Swiss chard is also an excellent source of vitamins A, C, and K. It also is rich in potassium, magnesium, fiber, and iron.
How To Include In Your Diet
You can enjoy Swiss chard raw in salads or sandwiches. You can also add it to soups.
21. Grass-Fed Butter
- Serving size – 14 g
- Vitamin E – 0.4 mg
- DV% – 2%
Grass-fed butter is one of the few sources of butyric acid, which is known to fight inflammation. In addition to vitamin E, the butter contains vitamin A – a nutrient essential for your vision and skin.
How To Include In Your Diet
You can add grass-fed butter to your breakfast toast.
22. Parsley
- Serving size – 60 grams
- Vitamin E – 0.4 milligrams
- DV% – 2%
Parsley helps fight other dangerous ailments like cancer and diabetes. It is also rich in vitamin K that contributes to bone health. Though fresh parsley is better, you can also use dried ones readily available in the market.
How To Include In Your Diet
You can simply throw a few sprigs of parsley in your salad.
23. Olives

- Serving size – 8 grams
- Vitamin E – 0.1 milligram
- DV% – 1%
Use it as a fruit or oil, olive is a great way of getting your daily vitamin E dose. Olives also contain oleic acid that regulates cholesterol levels and ultimately improves heart health.
How To Include In Your Diet
Add them to pizzas, salads, or pasta or consider using them alone with bread.
24. Oregano
- Serving size – 1 g
- Vitamin E – 0.2 mg
- DV% – 1%
Oregano is known to exhibit anticancer activity. It also contains compounds that can aid in diabetes treatment.
How To Include In Your Diet
You can use oregano as a salad topping or even incorporate it in sandwiches.
25. Abalone
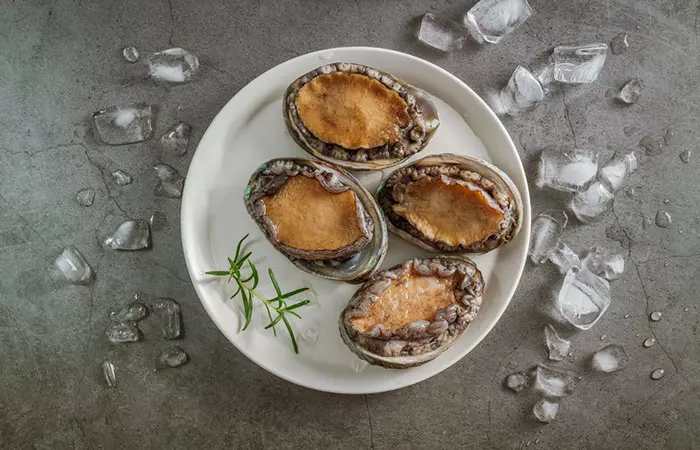

- Serving size – 84.9 g
- Vitamin E – 3.4 mg
- DV% – 23%
Abalone is a seafood widely consumed in Asian countries. It is rich in bioactive compounds that have antioxidant, anti-thrombotic, anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial, and anti-cancer properties (2). It is also rich in vitamin E in abalone, proteins, and fatty acids that may help combat various diseases like asthma, oxidative stress, and cataract (3).
How To Include In Your Diet
You can season abalone with garlic, pepper, oyster sauce, soy sauce, or lemon. You can even steam or pan-fry abalone and eat it with a side of salad.
Well, that’s with the list of vitamin e rich foods. But what about meat – you ask. There’s good news for people who prefer meat. Chicken thigh is known to have the highest vitamin E content. This is followed by chicken breast and pork shoulder (4).
The benefits of vitamin E (of the supplements, especially) can largely be seen only in those who suffer a deficiency. And by the way, what are these benefits?
What Are The Benefits Of Vitamin E?
One of the most important benefits of vitamin E is heart health. The vitamin balances cholesterol levels, thereby contributing to cardiovascular health. As per studies, certain isomers of vitamin E help fight cholesterol oxidationi Excessive build-up of LDL cholesterol in the arteries causing them to be oxidized, resulting in cell damage, plaque formation, and inflammation. (5). The tocotrienol isomers of vitamin E can even prevent atherosclerosisi A condition in which fat and cholesterol accumulate as plaque on artery walls causing them to narrow, block blood flow, and result in a clot. .
Vitamin E, being an antioxidant, fights free radicalsi Unstable molecules formed during cell metabolism can damage DNA, lipids, and proteins, elevating the risk of cancer and other diseases. and inflammation – which consequently results in enhanced immunity (6). The vitamin also fights inflammation on the skin, and hence, improves skin health (7). The antioxidant properties of vitamin E help protect against skin cancer.
Vitamin E oil has also been found to accelerate wound healing and treat other skin ailments like itching, eczema, scars, burns, and psoriasis. It even improves the lifespan of cells. It also prevents dryness by helping skin retain its natural moisture.
Vitamin E also promotes blood circulation to the scalp, thereby improving hair health. A daily dose of the vitamin can help alleviate the symptoms of hot flashes in menopausal women.
Vitamin E has a role in the formation of red blood cells and muscle function, and this can help improve your overall fitness. This might, in a way, aid weight loss.
That’s about some of the benefits of vitamin E. All said and done, one must be aware if they are getting enough of this crucial nutrient. What do you think?
What Is The Recommended Daily Allowance Of Vitamin E?
As we have seen, vegetable oils are the major sources of vitamin E. Among nuts, almonds are the richest sources. But what we need to know is that most of the foods rich in vitamin E are also high in calories – hence, if you are trying to cut calories, you might be avoiding these foods.
Vitamin E is very important. We have seen that already. But how do you know if you are getting enough of it?
Following is the table that gives you the details.
Category (Children & Adults) | Vitamin E (alpha-tocopherol): Recommended Dietary Allowance (RDA) in millimgrams (mg) and International Units (IU) | |||||
CHILDREN | ||||||
1 – 3 Years | 6 mg/day (9 IU) | |||||
| 4 – 8 Years | 7 mg/day (10.4 IU) | |||||
| 9 – 13 Years | 11 mg/day (16.4 IU) | |||||
FEMALES | ||||||
14 years and up | 15 mg/day (22.4 IU) | |||||
Pregnant | 15 mg/day (22.4 IU) | |||||
Breastfeeding | 19 mg/day (28.5 IU) | |||||
MALES | ||||||
14 years and up | 15 mg/day (22.4 IU) | |||||
And then, we have the tolerable upper intake of vitamin E. This is the maximum amount of vitamin E you can take without worrying about the side effects.
Category (Children & Adults) | Tolerable Upper Intake Levels (UL) of Vitamin E (alpha-tocopherol) in milligrams (mg) and International Units (IU) | |||||
| 1 – 3 years | 200 mg/day (300 IU) | |||||
4 – 8 years | 300 mg/day (450 IU) | |||||
9 – 13 years | 600 mg/day (900 IU) | |||||
| 14 – 18 years | 800 mg/day (1200 IU) | |||||
19 years and up | 1000 mg/day (1500 IU) | |||||
And now, we have another important question.
How To Increase Your Vitamin E Intake?
Simple. Include all the foods we spoke of in your diet. You can start cooking with the vegetable oils. Replace your evening pack of chips with fresh fruit and vegetable salad, and toss in the foods we spoke of. You can also have a fruit smoothie plus toast with peanut butter for your daily breakfast.
Or if you are too busy to do all of this, you probably can take supplements.
Or, can you?
What About Natural Vitamin E Supplements?
Let us make this clear.
Natural vitamin E is a family of 8 different compounds – 4 tocopherols and 4 tocotrienols. Which means, if you consume certain wholesome foods, you will get all of these 8 compounds. But a synthetic vitamin E supplement contains just 1 of these 8 supplements (alpha-tocopherol). So, a vitamin E pill is not a good idea. The capsules can’t give you what the natural sources can (1).
A couple of known vitamin E supplements are vitamin E acetate and vitamin E succinate. Though the latter is known to prevent heart disease as well, we still recommend you to go the natural way.
Nalini, a blogger and cancer survivor, shared her experience of taking vitamin E supplements for menopause. She explained the benefits she reaped from them, “Vitamin E reverted my skin to its healthy state. It is like a natural moisturizer which keeps the skin moist in the most natural way (i).”
Well, if you can’t find time to consume vitamin E the natural way, what do you do?
You make time. As simple as that.
We also would like to talk about vitamin E suppositories. This is when you ingest vitamin E through your vagina or anus to soothe symptoms like dryness, itching, or other symptoms of menopause.
They also have their share of benefits and disadvantages. Vitamin E helps lubricate dry skin. It also helps relieve other symptoms of menopause like hot flashes or heart palpitations. Suppositories are absorbed into the bloodstream faster than when taken orally, which is one big advantage.
The disadvantages could be that you might feel sick to the stomach and even vomit. Nausea is another common side effect. Diarrhea can also occur if your body is adjusting to taking the suppositories. Headaches, blurred vision, and mild rashes are the other possible side effects.
 Quick Tip
Quick TipBut you can use vitamin E ointments or creams for treating common skin ailments like rashes or dryness (9). Consult your doctor, though. You can also use vitamin E capsules for skin (the capsules contain the oil). Vitamin E is a nutrient for the skin. It protects the skin cells from damage from reactive oxygen species and ultraviolet radiation.
Talking about pregnancy, it is always better to consult your doctor first before using any vitamin E supplements (though we recommend you don’t). This is because orally administered supplements can cause mild side effects during pregnancy. These can include headache, fatigue, rashes, weakness, and diarrhea. Topical application of the oil is regarded as safe.
What Are The Health Risks Associated With Vitamin E Deficiency?
A deficiency of vitamin E can cause numerous problems. They include:
- Neuromuscular and neurological issues
- Anemia
- Impairment of the immune response
- Cataracts
- Decrease in sex drive
And excess vitamin E can lead to vitamin E toxicity. Though the symptoms are not severe, they include muscle weakness, nausea, fatigue, and diarrhea. The most significant risk is bleeding, although it is uncommon at doses below 1000 mg per day.

Infographic: Vitamin E – Everything You Need To Know About It
Vitamin E is one of the important vitamins required by the body. Since it is an antioxidant, it protects the body from oxidative damage. It also contributes to growth and development and is found in various foods.
Check out the infographic below to learn more about vitamin E, its role in the body, how it is obtained, and what its excess intake can do to your body. Illustration: StyleCraze Design Team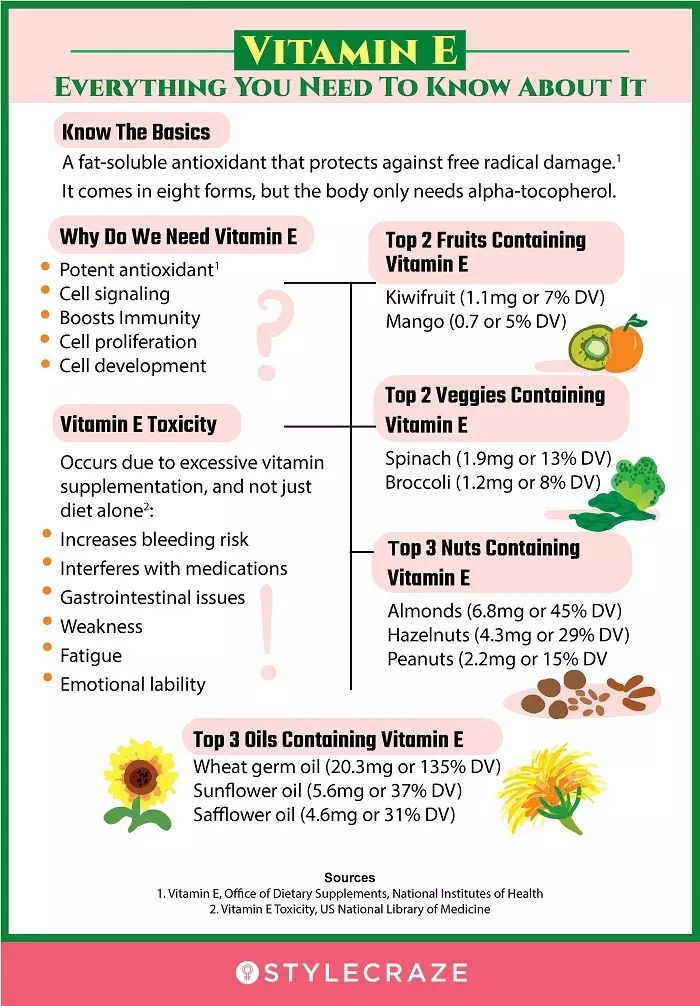
In case you have more questions…
Frequently Asked Questions
Does vitamin E have blood thinning property?
Yes. Hence, don’t take vitamin E along with other blood thinning medications like warfarin.
Is vitamin E water-soluble?
No. It is fat-soluble.
How does vitamin E benefit eye health?
Vitamin E has α-tocopherol which helps protect cells from free radical damage. This antioxidant helps boost the immune system, reduces inflammation, improves blood flow, and prevents platelets from sticking together, all of which support better eye health (10).
What are some vitamin E facts?
Some of the facts include:
• Vitamin E was discovered in 1922 by Dr. Herbert Evans and Katherine Bishop. And in 1936, Dr. Evans isolated alpha-tocopherol.
• Vitamin E was proposed as an antioxidant in 1945.
• Since vitamin E is fat-soluble, it can be stored in the body.
• Vitamin E deficiency is usually uncommon, except in people with a rare genetic disorder, malnourished children, or preterm infants.
What is the best form of vitamin E?
The natural form of vitamin E, called D-alpha tocopherol, which is mixed with natural tocopherols and tocotrienols, is the best form of vitamin E.
What are the eight forms of vitamin E?
We discussed this in brief already.
Are bananas high in vitamin E?
No. Vitamin E is not present in bananas.
Are eggs high in vitamin E?
Eggs contain a small amount of vitamin E. 100 g egg contains around 1.05 mg of vitamin E (11).
Is milk high in vitamin E?
No, milk contains a small amount of vitamin E. 100 g of milk contains around 0.07 mg of vitamin E (12).
Do carrots have vitamin E?
Yes. 100 g of carrot has around 0.66 mg of vitamin E (13).
Do walnuts have vitamin E?
Yes. 100 g of walnuts have around 0.7 mg of vitamin E (14).
Tocopherols consist of 4 types of vitamin E – alpha, beta, gamma, and delta.
And the tocotrienols also consist of 4 types of vitamin E – alpha, beta, gamma, and delta.
Vitamin E can help improve your health with its anti-inflammatory and anti-oxidant properties. Including it in your diet would not only help protect your body from the damage of toxic free radicals but also boost your overall health and immunity. Almonds, peanut butter, spinach, kiwi, or dried apricots are a few of the many options listed above that can help you stock up on vitamin E. Having a balanced diet including the above vitamin E-rich food options would help you see a visible difference in your skin, hair, and overall health over a period of time.
Illustration: Best Vitamin E-Rich Foods You Should Include In Your Diet

Image: Stable Diffusion/StyleCraze Design Team
Learn about 21 vitamin E-rich foods that you must add to your diet for a healthier lifestyle! Click on the video below to learn about their nutritional facts now!
Personal Experience: Source
StyleCraze's articles are interwoven with authentic personal narratives that provide depth and resonance to our content. Below are the sources of the personal accounts referenced in this article.
i. My Post-menopausal Friend – Vitamin E!https://vedvyash.wordpress.com/2018/01/24/my-post-menopausal-friend-vitamin-e/
References
Articles on StyleCraze are backed by verified information from peer-reviewed and academic research papers, reputed organizations, research institutions, and medical associations to ensure accuracy and relevance. Read our editorial policy to learn more.
- Vitamin E
https://ods.od.nih.gov/factsheets/VitaminE-HealthProfessional/ - Therapeutic potential of abalone and status of bioactive molecules: A comprehensive review
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26114550/ - The Role of Vitamin E in Human Health and Some Diseases
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3997530/ - Vitamin E content of different animal products: influence of animal nutrition
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/9095536/ - Effect of supplemental vitamin E for the prevention and treatment of cardiovascular disease
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15061748/ - Vitamin E and immunity
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/10714244/ - The role of vitamin E in normal and damaged skin
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/7633944/ - Vitamin E Toxicity
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK564373/ - Vitamin E ointment at high dose levels suppresses contact dermatitis in rats by stabilizing keratinocytes
https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/PL00012416 - Nutrients for the aging eye
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3693724/ - Egg, Whole, Raw, Fresh
https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/171287/nutrients - Milk, Whole, 3.25% Milkfat, with Added Vitamin D
https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/171265/nutrients - Carrots, Raw
https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/170393/nutrients - Nuts, Walnuts, English
https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/170187/nutrients
Read full bio of Dr. Abby Kramer
Read full bio of Ravi Teja Tadimalla
Read full bio of Arshiya Syeda
Read full bio of Aparna Mallampalli

























Community Experiences
Join the conversation and become a part of our empowering community! Share your stories, experiences, and insights to connect with other beauty, lifestyle, and health enthusiasts.