Agave Syrup: Nutrition, Health Benefits, And Side Effects
Switch the sugar in your pantry with this healthy, plant-based sweetener.

Image: Shutterstock
In the quest of leading a healthy lifestyle, a sizable section of people tend to cut or substitute sugar from their diets. Those who are looking for a substitute, often lean towards sweetening ingredients like maple syrup, honey, jaggery, and stevia. Agave syrup or agave nectar is one such ingredient that is rapidly gaining popularity as a substitute sweetener. If you’re wondering what is agave syrup, how it is made, and what are its health benefits, keep reading this article to find out.
 Know Your Ingredient: Agave Syrup
Know Your Ingredient: Agave SyrupWhat Is It?
A thick and light or dark amber sweetener extracted from the agave plant.
What Are Its Benefits?
It may improve the symptoms of depression and the mother and fetus’ health during pregnancy.
Who Can Consume It?
Anyone can consume this except people with gastrointestinal issues and diabetes.
How Often?
You can use ⅓ to ⅔ of a cup of agave syrup daily.
Caution
Excess intake of agave may increase the risk of heart disease, weight gain, tooth decay, and liver damage.
In This Article
What Is Agave Syrup?
Agave syrup is made from the agave plant, the same plant that is used to make tequila.
It is made by heating the extracts of the agave plant or by using a process called hydrolysis. This syrup has a golden brown color and has a similar consistency as that of honey. Since this is a plant-based sweetener, it is considered to be vegan and gluten-free.
 Did You Know?
Did You Know?A blogger shared his experience with agave syrup as he was searching for a vegan alternative for honey. He wrote, “It’s not exactly like honey; it’s somewhat sweeter, and oddly slightly more… astringent, for lack of a better word, but I’ve grown to like it quite a bit (i).”
Check out the next section to find out the time it takes to grow a mature agave plant.
Key Takeaways
- Agave syrup is rich in fructose, which does not increase blood sugar levels as rapidly as glucose.
- However, prolonged high intake of fructose may increase diabetes and CVD risk. Hence, it is not diabetic-friendly in nature.
- This alternative sweetener contains folate in trace amounts, which is said to improve the health of the fetus and the mother.
How Long Does Agave Take To Grow?
Agave plants typically take several years to reach maturity and flower. The exact time it takes for an agave plant to grow varies depending on multiple factors such as the species of agave, climate, and other growing conditions. In general, it can take anywhere from 8 to 30 years or even longer for an agave plant to mature and produce a flowering stalk.
But is agave healthy? What is it that really makes it a healthy sugar substitute? Let us explore some agave syrup nutritional facts to find out.
Nutritional Information
Nutritional values of agave syrup per 100g (1)
| Name | Amount |
|---|---|
| Water | 22.9g |
| Energy | 310kcal |
| Protein | 0.09g |
| Total Fat | 0.45g |
| Carbohydrates | 76.4g |
| Dietary Fiber | 0.2g |
| Glucose | 12.4g |
| Fructose | 55.6g |
| Potassium | 4mg |
| Selenium | 1.7μg |
| Folate | 30μg |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.234mg |
| Riboflavin | 0.165mg |
| Thiamin | 0.122mg |
From this table, you can see that agave contains some essential minerals like potassium, seleniumi An important trace mineral needed for proper body functioning and health. It prevents cell damage and infections, improves reproductive and thyroid functioning, and helps create DNA. , and folate that may be beneficial for your health. Find out how exactly these might be beneficial for you, in the next section.
& List Of Foods With Their GI”]
The Health Benefits Of Agave Syrup
There is limited research on the health benefits of consuming agave syrup. Some of its potential health benefits are as follows.
- Has A Low Glycemic Index

Research suggests that agave syrup is considered to have a low glycemic index as 90% of it is made up of fructosei It is the sweetest naturally-obtained carb, commonly found in many fruits and hence known as ‘fruit sugar’. It is also found in sugar beets, sugar cane, and vegetables. (2). Fructose in moderation is considered safe and unlike glucose, it does not cause severe spikes in blood sugar levels (3). A study on mice fed with agave nectar revealed that they had lower chances of gaining weight and also had lower blood sugar and insulin levels (4). Given the limited number of studies, the low glycemic level of agave nectar is debatable and requires further research.
- Might Help During Pregnancy

Agave contains trace amounts of folate which is associated with improving the health of the mother and fetus during pregnancy. Studies suggest that consuming folate during pregnancy helps in the proper growth and development of the fetus. It may reduce the risk of neural tube defects (NTDs) that affect that fetus (5).
- May Help With Mental Health Issues

Studies suggest that folate and folic acid may benefit people with mental health issues like depression and dementia. An increase in the intake of food rich in vitamin B6 and folic acid might be able to help with some of these issues (6), (7), (8).
There is limited information available on the health benefits of agave syrup as studies are still being conducted.
 Trivia
TriviaNow that you are aware of the health benefits of agave syrup, there are some practical tips on how to incorporate it into your daily meals and recipes that you should be aware of. Scroll down to know more.
How To Use Agave Syrup Effectively
Agave syrup, a versatile sweetener, can be easily added to a variety of dishes. Here are some useful agave syrup usage tips:
- In most recipes, you can use agave syrup in place of honey, maple syrup, or sugar. Remember that it is sweeter than sugar, so you may want to cut back a little.
- Start with a teaspoon per serving for beverages and adjust to taste. For every cup of sugar in baking, use around two-thirds of a cup of agave syrup.
- Agave syrup works great with savory meals like salad dressings or marinades for meats and vegetables. It also goes well with sweet foods like smoothies, oatmeal, and sweets.
Although agave is a plant-based natural sweetener, it does have a few potential side effects. Let us understand some of these side effects in the next section.
Risk Factors Of Agave

Fructose makes up nearly 90% of the composition of agave syrup and in excess amounts, this may cause a few health complications. Some research states that excess consumption of fructose may affect your metabolism and increase the risk of diabetes and cardiovascular diseases (9).
Another study also suggests that prolonged consumption of fructose may increase LDL cholesterol levels that are linked to an increased risk of heart diseases (10).
 Quick Tip
Quick TipHaving learned the potential benefits and risks of agave syrup, let us look at how this syrup is made and matches up against honey in terms of nutrition and benefits.
How Are Agave Nectar And Honey Made?
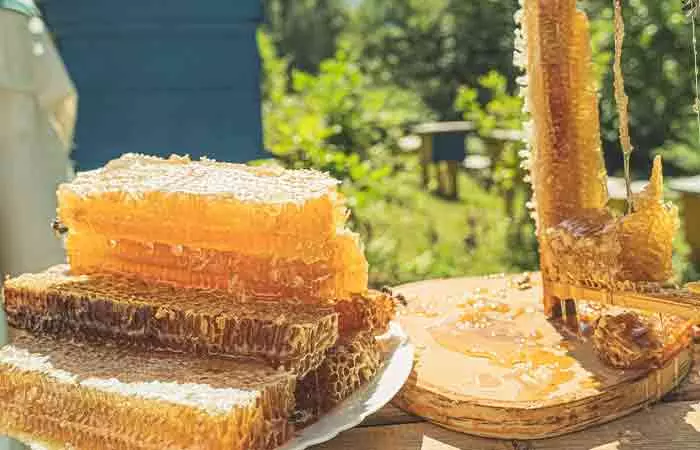

Making agave syrup is a complicated process that requires industrial-grade equipment to process and refine the final product.
The steps to make agave syrup are as follows:
- Ripe agave plants are harvested and their leaves are chopped to extract the juice.
- This juice is then filtered and heated. During this process, it breaks down and releases fructose.
- The end product obtained is agave syrup.
Agave syrup can be made either by heating up the agave juice or by hydrolysis.
Honey on the other hand is made by bees who harvest nectar from a variety of flowers.
- Bees harvest nectar from flowers using an organ called a nectary.
- Inside the bee’s stomach, the nectar is broken down into simple sugars that don’t crystalize.
- It returns to its hive and deposits this in the hexagonal cells of the hive and covers it with a waxy substance called beeswax.
- They reduce the moisture content in the nectar by fluttering their wings. Once the moisture reduces to about 20%, it gets converted to honey.
If you had to pick between honey and agave syrup, or agave syrup and table sugar as a substitute sweetener, which one should you pick? Keep reading to find out the answer to this question.
Honey Vs. Agave Syrup
| Nutrition | Agave Syrup (1) | Honey (11) |
|---|---|---|
| Water | 22.9g | 17.1g |
| Energy | 310kcal | 304kcal |
| Protein | 0.09g | 0.03g |
| Total Fat | 0.45g | 0g |
| Carbohydrates | 76.4g | 82.4g |
| Dietary Fiber | 0.2g | 0.2g |
| Glucose | 12.4g | 35.8g |
| Fructose | 55.6g | 40.9g |
| Potassium | 4mg | 52mg |
| Selenium | 1.7μg | 0.8μg |
| Folate | 30μg | 2μg |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.234mg | 0.024mg |
| Riboflavin | 0.165mg | 0.038mg |
| Thiamin | 0.122mg | 0 |
In terms of calories per 100g, both honey and agave syrup are quite similar. However, honey contains higher levels of potassium and no fat when compared to agave syrup. Besides these nutrients, honey has proven health benefits that make it a better alternative to agave syrup.
Traditionally, honey has been used in numerous home remedies to treat wounds, gastrointestinal issues, and ulcers. It is also known for its antibacterial and anti-inflammatory properties that help relieve cold and flu symptoms (12).
Next up, let us find out if and how agave nectar is better than table sugar.
Agave Nectar Vs. Table Sugar
| Nutrition | Table Sugar (13) | Table Sugar (13) |
|---|---|---|
| Water | 22.9g | 0.02g |
| Energy | 310kcal | 401kcal |
| Protein | 0.09g | 0g |
| Total Fat | 0.45g | 0.32g |
| Carbohydrates | 76.4g | 99.6g |
| Dietary Fiber | 0.2g | NA |
| Glucose | 12.4g | 0g |
| Fructose | 55.6g | 0g |
| Potassium | 4mg | 2mg |
| Selenium | 1.7μg | NA |
| Folate | 30μg | NA |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.234mg | NA |
| Riboflavin | 0.165mg | NA |
| Thiamin | 0.122mg | NA |
From the table, it is quite evident that agave syrup is clearly better than table sugar. Apart from a high calorie and carbohydrate content, table sugar does not have any useful micro and macronutrients like that in agave syrup.
You can make a simple agave syrup at home in a few simple steps as mentioned below.
Easy Agave Syrup Recipe
Ingredients
- 1 cup of agave nectar
- 1/4 cup of water
How To Prepare
- Heat the agave nectar in a saucepan.
- Add water to thin it and keep stirring.
- When the texture thickens, cool it and store it in a container.
You can use this agave-based simple syrup for preparing beverages and cocktails.
In conclusion, agave syrup is made from agave plants that are commonly grown in South America. There are limited studies to suggest that some of the nutrients like folate present in agave syrup have potential health benefits. Since the majority of this syrup is made up of fructose, consuming this in large quantities and for prolonged durations may have health issues. If you are looking at a healthy alternative for sugar, you may consider agave syrup. However, in comparison to honey, agave nectar would be an inferior choice.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is healthier – honey or agave?
Honey is healthier than agave syrup due to its high antioxidant levels.
Is agave good for weight loss?
No. Agave is higher in calories and fructose than honey, which is why it is not good for weight loss.
Which is better for diabetics: honey or agave?
While agave has a low glycemic index, it is high in calories. Hence, honey is a better option for diabetes due to its antioxidants and high nutritional value.
How does agave syrup taste?
It has a similar taste to honey but it is more mild in flavor.
Is agave syrup safe for children to consume?
Yes, it is considered safe for children and babies both.
Illustration: Agave Syrup: Nutrition Health Benefits And Side Effects

Image: Stable Diffusion/StyleCraze Design Team
Agave syrup is seen to be a healthy alternative to sugar. Click on the video below to find out if it is actually as healthy as it is claimed to be!
Personal Experience: Source
StyleCraze's articles are interwoven with authentic personal narratives that provide depth and resonance to our content. Below are the sources of the personal accounts referenced in this article.
i. AGAVE SYRUPhttps://veganstuffinbelgium.wordpress.com/2015/10/05/agave-syrup/
References
Articles on StyleCraze are backed by verified information from peer-reviewed and academic research papers, reputed organizations, research institutions, and medical associations to ensure accuracy and relevance. Read our editorial policy to learn more.
- Sweetener Syrup Agave
https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/170277/nutrients - Effect Of Moderate Intake Of Sweeteners On Metabolic Health In The Rat
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/labs/pmc/articles/PMC3258097/ - Fructose Consumption And Consequences For Glycation Plasma Triacylglycerol And Body Weight: Meta-Analyses And Meta-Regression Models Of Intervention Studies
https://academic.oup.com/ajcn/article/88/5/1419/4648852?login=true - Effects Of Agave Nectar Versus Sucrose On Weight Gain Adiposity Blood Glucose Insulin And Lipid Responses In Mice
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25011004/ - Folic Acid Supplementation and Pregnancy: More Than Just Neural Tube Defect Prevention
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/labs/pmc/articles/PMC3218540/ - Folic Acid Ageing Depression And Dementia
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/labs/pmc/articles/PMC1123448/ - The Role Of Folic Acid In Psychiatric Disorders
https://www.researchgate.net/publication/286411267_The_role_of_folic_acid_in_psychiatric_disorders - Vitamin B12 Vitamin B6 Folic Acid and Psychosis: A Review
https://www.researchgate.net/publication/329001451_Vitamin_B12_Vitamin_B6_Folic_Acid_and_Psychosis_A_Review - Adverse Metabolic Effects Of Dietary Fructose: Results From The Recent Epidemiological Clinical And Mechanistic Studies
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23594708/ - How Bad Is Fructose?
https://academic.oup.com/ajcn/article/86/4/895/4649668 - Honey
https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/169640/nutrients - Honey and Health: A Review of Recent Clinical Research
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/labs/pmc/articles/PMC5424551/ - Sugars Granulated
https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/746784/nutrients
Read full bio of Dr. Somi Igbene
Read full bio of Varsha Patnaik
Read full bio of Ravi Teja Tadimalla
Read full bio of Payal Karnik


























Community Experiences
Join the conversation and become a part of our empowering community! Share your stories, experiences, and insights to connect with other beauty, lifestyle, and health enthusiasts.