Flaxseed Oil Benefits: 12 Proven Ways To Boost Health
Discover powerful wellness tips, hidden nutrients, safe usage, and potential risks inside.
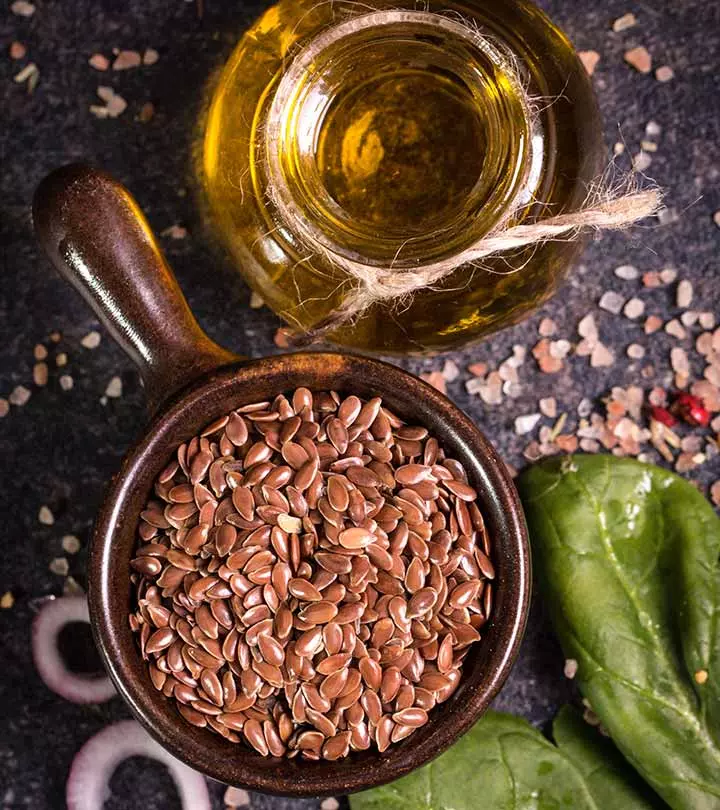

Image: Shutterstock
From reducing inflammation to promoting skin health, the benefits of flaxseed oil are quite impressive – and all credit goes to their nutrient-rich profile!
This oil, extracted from the beneficial flaxseeds, is also thought to help with weight loss and enhance hair growth. It is available commercially in the form of pills or capsules, which are found to be highly effective as well.
In this article, we look at these benefits in detail, the nutritional profile of flaxseed oil, how to use it in cooking, and its recommended dosage. Keep reading!
In This Article
What Makes Flaxseed Oil Good For Your Health?
Alpha-linolenic acid (ALA) is the answer.
Flaxseed oil is one of the richest sources of ALA (about 7 g/tablespoon). Flaxseeds (Linum usitatissimum L.) are a bounty of essential fats, lipids, and fiber. The highest concentration of flax fats is in flax oil. This oil has active cardioprotective, anticancer, anti-inflammatory, and laxative properties (1). It is more bioavailable in the oil than in the milled and whole seeds (1).
This oil also has other fatty acids like linoleic, palmitic, stearic, and oleic acids. Here are their proportions (1):
| Fatty acids | Percentage (%) (Range) |
|---|---|
| Palmitic acid (C16:0) | 4.90–8.00 |
| Stearic acid (C18:0) | 2.24–4.59 |
| Oleic acid (C18:1) | 13.44–19.39 |
| Linoleic acid (C18:2) (?-6) | 12.25–17.44 |
| a-Linolenic acid (C18:3) (?-3) | 39.90–60.42 |
The flaxseed ALA is the precursor to the pivotal omega-3, long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFA) – Eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and Docosahexaenoic acid (DHA). A fraction of dietary ALA (about 10% -15%) can get converted into these two long-chain PUFAs (2) .
This is why flaxseed oil is becoming popular as a vegan substitute for fish oil. Though fish oil is rich in EPA and DHA, the amount of converted EPA and DHA and the energy you get from flaxseed oil is much more. Fish oil also may carry a risk of mercury contamination, which is not the case with flaxseed oil (1). This replacement comes with some ambiguity and apprehension.
What is important is that ALA helps in the transport of DHA to the brain cells (neurons). It may also be involved in the functions of skin and fur in mammals (2).
Anecdotal evidence suggests that flaxseed oil may also promote hair health. This could be attributed to the presence of omega-3 fatty acids in the oil. The oil also contains vitamin E that may fight free radical damage and reduce hair fall. However, there is less information to support this.
Some believe the oil may also aid weight loss. But there is less research here as well. However, flaxseed fibers, when taken as supplements, may suppress appetite (3). This could aid in weight loss.
There is a long list of benefits that ALA has. Let’s take a look at what flaxseed oil offers in detail.
The flaxseed ALA is the precursor to the pivotal omega-3, long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFA) – Eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and Docosahexaenoic acid (DHA). A fraction of dietary ALA (about 10% -15%) can get converted into these two long-chain PUFAs (2).
This is why flaxseed oil is becoming popular as a vegan substitute for fish oil. Though fish oil is rich in EPA and DHA, the amount of converted EPA and DHA and the energy you get from flaxseed oil is much more. Fish oil also may carry a risk of mercury contamination, which is not the case with flaxseed oil (1). This replacement comes with some ambiguity and apprehension.
What is important is that ALA helps in the transport of DHA to the brain cells (neurons). It may also be involved in the functions of skin and fur in mammals (2).
Anecdotal evidence suggests that flaxseed oil may also promote hair health. This could be attributed to the presence of omega-3 fatty acids in the oil. The oil also contains vitamin E that may fight free radical damage and reduce hair fall. However, there is less information to support this.
Some believe the oil may also aid weight loss. But there is less research here as well. However, flaxseed fibers, when taken as supplements, may suppress appetite (3). This could aid in weight loss.
There is a long list of benefits that ALA has. Let’s take a look at what flaxseed oil offers in detail.
Did You Know?
- A 2018 study revealed that eating 10 g of flaxseed-baked cookies daily for 12 weeks was useful for those with diabetes (4) .
- It improved symptoms of constipation, glycemic control, and body weight. When lactating women took flaxseed oil supplements, it resulted in an increase of ALA content in breast milk. There is not enough evidence to explain if the infants are benefited from this ALA boost.
- On the other hand, supplementing infants with flaxseed oil or ALA-fortified formula improved their DHA levels (5) .
Benefits of Flaxseed Oil
1. May Lower Cholesterol And Prevent Heart Disease
Hypercholesterolemia is a primary cause of cardiovascular diseases. A study involving hemodialysis patients reported the positive effects of daily flaxseed oil intake (6).
The patient group on flaxseed oil supplementation (6 g/day) showed about 23% reduction in serum triglyceride concentration when compared to the control group (6).
This oil may also lower LDL (bad cholesterol) and boost HDL (good cholesterol) levels in hypercholesterolemic individuals (individuals with high cholesterol levels). The oil can have short-term benefits in those with mild hypercholesterolemia, especially in individuals with increased blood pressure .
A few studies demonstrate the anti-hypertensive and anti-atherosclerotic activity of flaxseed oil. But some studies report the ineffectiveness of this oil in altering serum lipids .
2. May Help Manage Eye Disorders
The deficiency of dietary fats can cause inflammation in different parts of the eye, including the cornea, conjunctiva, and lacrimal glands. It can also affect tear quality and quantity. One common ophthalmic disorder is dry eye disease (7), (8).
Research says that the oral administration of omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids can mitigate such a deficiency. This is because these fatty acids are responsible for the synthesis of anti-inflammatory compounds (7), (8).
Flaxseed oil counters the inflammatory effects of arachidonic acid and its derivatives. It triggers the synthesis of non-inflammatory mediators, PGE1 and TXA1. These molecules reduce inflammation of lacrimal glands (glands that secrete the aqueous layer of the tear film in the eye), cornea, and conjunctiva (7) .
In rabbit studies, oral and topical administration of linseed/flaxseed oil could improve dry eye disease and restore vision functionality (7).
5. May Improve Menstrual Health
Flaxseeds also contain good amounts of compounds that convert into lignans. The predominant of those is secoisolariciresinol diglucoside (SDG). SDG gets converted to enterodiol and enterolactone (8).
These lignans act as phytoestrogens. They are structurally and functionally similar to the estrogen in your body . They can weakly interact with estrogen receptors in your liver, brain, heart, and bones (9) .
Flaxseed oil might help relieve menopause symptoms, and menstrual cramps and treat infertility. Some research states that these compounds may prevent bone diseases (osteoporosis) and cancers of the breast, ovaries, and prostate to an extent. However, the exact role of lignans in this aspect is yet to be totally understood (9).
Interestingly, flaxseed oils do not typically provide lignans unless ground flaxseeds have been added to the oil (9).
6. May Possess Anticancer Properties
The high lignan content in flaxseeds may explain their oil’s anticancer and antiproliferative properties (10) .
Studies also link omega-3 fatty acids to cancer protection (8). Diets rich in omega-3 fatty acids – like the ALA in flaxseed oil – may suppress the growth and proliferation of breast and colon cancer cells (8), (11).
It is not just the fatty acids. Flaxseed oil is also rich in several other micronutrients, which contribute to these benefits.
But before we proceed, let me clear a doubt that could be lurking in your mind.
What Is The Difference Between Flaxseed And Linseed?
Flaxseed is being cultivated since the beginning of human civilization. Almost every part of it is of industrial or economic importance.
Flaxseed is used to describe flax that is consumed as food by humans. Linseed is used to describe flax that is used in the industry and livestock .
Flax was initially grown by the US colonists to produce high-quality fiber, linen, and paper. But recent times have seen flax growing increasingly famous in the food and health sectors.
Flaxseed oil is now a health fad. For those of you looking for the numbers to believe this fact, the next section might seem impressive.
Nutritional Profile Of Flaxseed Oil
| Nutrition Table for Flaxseed Oil | ||
|---|---|---|
| Nutrient | Unit | Serving size (1 tbsp or 13.6 g) |
| Water | g | 0.02 |
| Energy | kcal | 120 |
| Energy | kJ | 503 |
| Protein | g | 0.01 |
| Total lipid (fat) | g | 13.60 |
| Vitamins | ||
| Vitamin E (alpha-tocopherol) | mg | 0.06 |
| Tocopherol, beta | mg | 0.07 |
| Tocopherol, gamma | mg | 3.91 |
| Tocopherol, delta | mg | 0.22 |
| Tocotrienol, alpha | mg | 0.12 |
| Tocotrienol, gammal | mg | 0.12 |
| Vitamin K (phylloquinone) | µg | 1.3 |
| Lipids | ||
| Fatty acids, total saturated | g | 1.221 |
| 10:0 | g | 0.001 |
| 12:0 | g | 0.002 |
| 14:0 | g | 0.010 |
| 15:0 | g | 0.004 |
| 16:0 | g | 0.695 |
| 17:0 | g | 0.007 |
| 18:0 | g | 0.458 |
| 20:0 | g | 0.018 |
| 22:0 | g | 0.015 |
| 24:0 | g | 0.010 |
| Fatty acids, total monounsaturated | g | 2.508 |
| 14:1 | g | 0,001 |
| 16:1 undifferentiated | g | 0.008 |
| 16:1 c | g | 0.008 |
| 18:1 undifferentiated | g | 2.491 |
| 18:1 c | g | 2.487 |
| 18:1 t | g | 0.004 |
| 22:1 undifferentiated | g | 0.004 |
| 22:1 c | g | 0.002 |
| 22:1 t | g | 0.002 |
| 24:1 c | g | 0.003 |
| Fatty acids, total polyunsaturated | g | 9.227 |
| 18:2 undifferentiated | g | 1.948 |
| 18:2 n-6 c,c | g | 1.937 |
| 18:2 CLAs | g | 0.004 |
| 18:2 t not further defined | g | 0.007 |
| 18:3 undifferentiated | g | 7.258 |
| 18:3 n-3 c,c,c (ALA) | g | 7.258 |
| 20:2 n-6 c,c | g | 0.004 |
| 20:3 undifferentiated | g | 0.013 |
| 20:3 n-6 | g | 0.002 |
| 22:4 | g | 0.002 |
| Fatty acids, total trans | g | 0.013 |
| Fatty acids, total trans-monoenoic | g | 0.006 |
| Stigmasterol | g | 4 |
| Campesterol | g | 13 |
| Beta-sitosterol | g | 28 |
Source: USDA
Cooking with flaxseed oil is the best way to get these micronutrients. Here are a few ways you can do that.
How To Use Flaxseed Oil In Cooking
You can use flaxseed oil for dressing those lunch salads, upping your yogurt game, or even whipping creamy meal smoothies.
Remember that flaxseed oil rapidly oxidizes because of its abundant fats. Don’t use it directly for cooking. Instead, add it to pre-heated or cooked food.
Check out a super-quick and lip-smacking recipe using flaxseed oil below.
Zesty Lemon-Flax Oil Dressing
Here’s a simple and uplifting vegan vinaigrette for you. You can drizzle this dressing on salads, pasta, garlic breadsticks, tarts, and roasted or grilled chicken.
What You Need
- Fresh lemon juice: ¼ cup
- Flaxseed oil: ¼ cup
- White balsamic vinegar: ¼ cup
- Dijon mustard: 1 tablespoon
- Garlic: 1 clove, minced
- Salt and pepper: to taste
- Mixing bowl: large-medium
Let’s Make It!
- Add all the ingredients to a clean mixing bowl.
- Whisk them together thoroughly.
- Drizzle generously over a choice of dishes.
- Enjoy the goodness of vegan fat!
You may also want to take a look at supplements.
Flaxseed oil is available as softgels/capsules. These supplements fulfill the essential fatty acid requirement.
Wondering how much to take? Scroll down!
What Is The Recommended Dose Of Flaxseed Oil?
One tablespoon of flaxseed oil contains 7.3 g of alpha-linolenic acid (ALA) and about 120 calories. This could mean a lot of piled pounds!
Keeping this in mind, the Institute of Medicine recommends 1.6 g/day of ALA for men and 1.1 g for women. Generally, the amount in a flaxseed oil supplement is about 6.2 grams – this is within the safety limits (12).
However, if you have heart issues, we recommend you consult with a physician for the right dosage. It is better to use these supplements under strict medical supervision.
This is because flaxseed oil may have mild side effects. You should read the next section to know more.
What Are The Safety Concerns And Side Effects Of Flaxseed Oil?
Flaxseed oil, flaxseeds, and their supplements are well tolerated in small amounts. There are not many proven side effects of flaxseed oil.
However, keep the following points in mind while consuming flaxseed oil or supplements (13) :
- Avoid flaxseed oil and the seeds during pregnancy and lactation. As flaxseeds have phytoestrogens, the oil may have mild yet unfavorable hormonal effects.
- Large quantities of flaxseed oil might cause constipation, leading to intestinal blockage. Make sure you keep yourself hydrated while taking it.
- The phytoestrogens in flaxseed oil may affect fertility in young men and women.
- Only 0.5%-1% of ALA in flaxseed oil gets converted to EHA, DPA, and other essential fatty acids. You may end up consuming a lot more of this oil to cater to your body’s fatty acid needs. Such high doses might backfire.
- Flaxseed derivatives may interfere with blood thinners, anticoagulants, and similar medications. Please use this oil under medical supervision.
The health benefits of flaxseed oil stem from its rich nutritional profile of essential fatty acids, dietary fiber, and vitamins E and K. New research indicates that it boosts levels of EPA, DHA, and secoisolariciresinol diglucoside (SDG). These elements play a key role in the proper functioning of the ocular, renal, cardiovascular, nervous, and immune systems. Aside from its powerful cardioprotective and anticancer properties, this oil is also an anti-inflammatory. But as its safety standards have not been determined yet, pregnant and breastfeeding women should consult a doctor before consuming flaxseed oil.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can you take flaxseed oil at night?
Yes. You can take both flaxseeds and their oil at night. Some believe it may promote sleep by boosting levels of serotonin. Though more research is warranted here, taking the oil at night does not seem to cause any harm.
Can you mix flaxseeds in water?
Yes. You can mix flaxseeds with water and stir and take it as tea. Adding some lemon can improve its taste.
References
Articles on StyleCraze are backed by verified information from peer-reviewed and academic research papers, reputed organizations, research institutions, and medical associations to ensure accuracy and relevance. Read our editorial policy to learn more.
- Flax and flaxseed oil: an ancient medicine & modern functional food
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4152533/ - What is the role of alpha-linolenic acid for mammals?
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12617463/ - Flaxseed dietary fiber supplements for suppression of appetite and food intake
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22245724/ - A randomized trial of the effects of flaxseed to manage constipation, weight, glycemia, and lipids in constipated patients with type 2 diabetes
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5944250/ - Flaxseed
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK501895/ - Effects of Flaxseed Oil on Serum Lipids and Lipoproteins in Hemodialysis Patients: a Randomized Controlled Trial
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27904000/ - Use of linseed oil to treat experimentally induced keratoconjunctivitis sicca in rabbits
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3589208/ - The Effect of Flaxseed in Breast Cancer: A Literature Review
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5808339/ - Dietary Lignans: Definition, Description and Research Trends in Databases Development
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6321438/ - The benefits of flaxseed
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4152533/ - Chemopreventive effects of dietary flaxseed oil on colon tumor development
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15749630/ - Omega-3 Fatty Acids
https://ods.od.nih.gov/factsheets/Omega3FattyAcids-HealthProfessional/ - Flaxseed and Flaxseed Oil
https://www.nccih.nih.gov/health/flaxseed-and-flaxseed-oil
Read full bio of Heather M. Duquette-Wolf
Read full bio of Ravi Teja Tadimalla































Community Experiences
Join the conversation and become a part of our empowering community! Share your stories, experiences, and insights to connect with other beauty, lifestyle, and health enthusiasts.