Moringa Benefits: 15 Science-Backed Health Advantages
This superfood can reduce inflammation and diabetes risk and help you in many different ways.

Image: Midjourney/ StyleCraze Design Team
Moringa’s benefits are slowly gaining popularity all over the world. It is popularly known as drumstick tree, and it offers an array of health benefits. It is called Moringa oleifera scientifically.
Moringa contains many vitamins, essential amino acids, and minerals (1). It is also loaded with many powerful antioxidants and bioactive compounds.
Moringa is used in many medicines, and its usage dates back millennia. Read the article below to get detailed info about what science says about its benefits. Scroll down!
 Know Your Ingredient: Moringa
Know Your Ingredient: MoringaWhat Is It?
A nutrient-dense plant native to south Asia that is used for medicinal purposes.
What Are Its Benefits?
May help manage diabetes, improve heart health, aid digestive and liver function, and strengthen bones.
Who Can Use It?
Generally safe for everyone.
How Often?
As part of a balanced diet, in moderation.
Caution
Might interact with thyroid medication and affect nutrient absorption. Pregnant women and people with low blood sugar and low blood pressure should avoid it.
In This Article
What Are The Health Benefits Of Moringa?
Moringa is replete with important antioxidants that fight oxidative stress and related diseases. The plant can fight inflammation and may aid the treatment of cancer and diabetes. It may also strengthen bones and improve brain health.
1. May Help Prevent Cancer
Moringa root has been found to induce cancer cell death. Though all parts of the moringa plant can help kill cancer cells, the root was found to be the most potent (2).
Moringa also may play a remarkable role in the prevention and treatment of cancers of the breast and colon. Specific compounds in the plant, known as nanocomposites, were found to destroy cancerous cells while sparing the healthy ones (2).
Eugenol (another compound in moringa) was found to prevent cancers of the skin, colon, and prostate (3). The plant prevents the cancer cells from forming colonies in the body. In other words, it inhibits the spread of cancer within the body.
Extracts of moringa may also inhibit cancers of the liver and the lung (4).
2. Can Fight Inflammation
One of the most prominent moringa seeds benefits is its anti-inflammatory activity. The flavonoids in moringa can help fight inflammation in rats and human cell lines (5), (6). This way, the plant also has a role to play in the treatment of inflammatory bowel diseases (including ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s Disease).
Moringa was also effective in blocking certain cytokines that promote inflammation in the human body. The extracts of moringa seeds also have anti-inflammatory properties (5).
The anti-inflammatory properties of moringa may also help relieve rheumatic pain in rats (7), (8). However, more trials in humans are warranted.
The most potent of the phytochemicals in moringa that fight inflammation include flavonoids and isothiocyanates. Their anti-inflammatory potential is so intense that studies emphasize their cancer prevention ability or their ability to treat inflammatory conditions like diabetes, and arthritis (9).
3. May Aid Diabetes Treatment

In certain rat studies, moringa seed powder was found to exhibit antidiabetic properties. Moringa contains fiber, which can help reduce blood glucose levels. Fortification of a diabetes diet with moringa was found to lower fasting blood glucose levels (10).
In another study, post-menopausal women who took 7 grams of moringa leaf powder every day for three months observed a reduction in their fasting blood glucose levels (11).
Another small study showed that including moringa leaves in the diet may lower blood sugar levels. The participants of the study saw a 21% decrease in blood sugar levels, highlighting some of the moringa leaves benefits (12).
Treating diabetic rats with moringa seed powder restored the histology of both the kidneys and the pancreas, thereby improving the symptoms. It is possible that these effects could be observed in humans as well (13).
 Did You Know?
Did You Know?4. May Promote Heart Health
Moringa improved cardiac diastolic functioni The flow of blood into the lower heart chambers (ventricles) that are responsible for the proper functioning of the heart. in hypertensive rats. It also reduced fibrosis (the scarring of connective tissue) in the left ventricle (14).
Moringa also helps lower cholesterol levels, which can help improve heart health. In a study, the plant was found to increase the excretion of fecal cholesterol (15).
Moringa pods are replete with polyunsaturated fatty acids, including linoleic, linolenic, and oleic acids. These have the ability to lower cholesterol. Moringa seed oil contains 76% PUFAs, and it can be an ideal substitute for olive oil (16).
Moringa leaf extract may also lower blood pressure levels. This extract reduced oxidative stress and relieved vascular dysfunction in hypertensive rats (17). This effect can potentially ward off heart disease.
5. Enhances Digestive Health
Moringa was found to modulate the composition of gut bacteria and offer associated benefits in mice. It has a role to play in treating digestive inflammation and preventing high-fat-induced obesity (18).
Moringa increases the concentrations of Bifidobacteria in the gut in rats, which are the major class of bacteria making up the gastrointestinal microbiota (18).
According to animal studies, moringa may also contain active agents with gastroprotective properties that promote digestive health and enhance the mucus lining of the gut (19).
The plant can also treat and prevent ulcers (19).
6. May Strengthen Bones

Moringa is a good source of calcium, magnesium, and phosphorus – nutrients essential for bone health (20). It also contains lysine, an amino acid that promotes calcium absorption (21).
Moringa was found to have a miraculous effect on bone integrity and may prevent osteoporosisi A bone disease responsible for lowering bone mass and density, leading to fragile bones and increased risk of fractures. (22). Specific flavonoids in moringa may also stimulate osteoblastic cells, which are cells that synthesize bones.
However, there are very few studies stressing the bone-protective properties of moringa. Certain other studies are yet to conclude if intake of moringa actually impacts bone health in a positive way (21).
7. May Promote Brain Health
In animal studies, moringa mitigated neurodegeneration and memory impairment (23). Moringa seemed to work by preventing the reduction of neuronal density, a phenomenon that happens to accelerate with age.
The plant also fights oxidative stress, which is a major cause of cognitive decline (23). Studies conclude that moringa could be used as a medicinal food for the treatment of dementiai A cognitive syndrome that causes various symptoms, such as memory loss and difficulty in problem-solving. .
The ability of moringa to fight oxidative stress can also protect the brain during a stroke (24).
Moringa extracts, when taken along with certain antidepressants, were also found to aid depression treatment (25). However, make sure you always speak to your health care provider before taking new supplements alongside medication to avoid contraindications.
8. May Help Treat Anemia
Though more research is needed, one study conducted in rats states that moringa can increase blood iron levels, thereby treating anemia (26). This is especially true with moringa leaves, which are iron-rich. The vitamin C in moringa also increases iron absorption in the body.
9. May Improve Liver Health

Moringa has been found to protect the liver against various toxins. It achieves this by lowering excess cholesterol in the liver. In studies, rats with fatty liver were fed with a diet fortified with moringa. They showed decreased levels of triglycerides. This is an indication of a healthy liver (27).
Moringa (and its leaves) may also prevent hepatic steatosis (infiltration of liver cells by fat), as observed in animal studies. It also helps fight liver inflammation (28).
Moringa may also enhance the recovery of the liver from hepatic damage induced by antitubercular drugs (29).
10. May Help Fight Bacterial Infections
Aqueous extracts of moringa had shown to fight bacteria and fungus, thereby inhibiting certain infections (30).
In another study, moringa exhibited antimicrobial activity against Staphylococcus aureus, Vibrio cholerae, and Escherichia coli, common antibiotic-resistant pathogens (31).
11. Can Prevent Arsenic Toxicity
Arsenic toxicity is a serious concern. It is more prevalent in areas where water contaminated with arsenic is used for irrigation and cooking (32).
Mice studies show that moringa can offer protective effects against arsenic toxicity (33).
Moringa also displays hepatoprotective properties against arsenic toxicity. The plant achieves this by combating the generation of reactive oxygen species and free radicals (34).
12. May Have Anti-Aging Benefits
This is especially true with moringa leaves. They are also replete with antioxidants like vitamins A, B, and C, which can contribute to skin health (35).
In studies, the use of a facial cream with moringa as the primary ingredient significantly improved the skin elasticity and hydration in the participants (35). The plant also enhanced the division of fibroblasts (cells in the connective tissue that produce collagen and other fibers), thereby promoting skin appearance and texture.
The antioxidants in moringa can also offer anti-aging benefits. They work to protect the skin cells from environmental stressors, including UV radiation. These properties make moringa an ingredient of promise in upcoming anti-aging skin care products (36).
13. May Treat Acne And Other Skin Issues
Thanks to its antifungal properties, moringa may also help treat certain skin diseases (37). Its antimicrobial activity against Staphylococcus aureus may help treat pimples, boils, carbuncles, and abscesses.
14. May Aid Weight Loss

The weight loss effects of moringa are not well studied. A small study emphasizes the ability of moringa to prevent weight gain. This effect can be attributed to isothiocyanates, a class of compounds in moringa (38).
More research is warranted pertaining to the ability of moringa to induce weight loss. Hence, consult your doctor before you consume moringa for this purpose.
15. May Help Manage Rheumatoid Arthritis
The unsaturated fatty acids and phytochemicals present in moringa seed oil and leaves exhibit anti-inflammatory and anti-arthritic properties that may help manage rheumatoid arthritis (39). A study published in Frontiers in Pharmacology found that moringa helps alleviate joint inflammation associated with arthritis (40). However, the mechanism behind this is yet to be studied. Additionally, animal studies suggest that the ethanol extract from moringa leaves exhibits analgesic properties and may help prevent chronic inflammation, joint destruction, and soft tissue damage (41). However, more research done on humans is warranted in this regard.
Anecdotal evidence also suggests that the glucosamine present in moringa may help alleviate the symptoms of arthritis.
 Trivia
TriviaThese are the various benefits of moringa. You can have the drumsticks (pods) along with the leaves as well. In the following section, we will look at the nutritional profile of the pods.
Key Takeaways
- Moringa is high in minerals, vitamins, and amino acids, along with a ton of bioactive substances and antioxidants.
- It helps reduce cholesterol levels. This is especially crucial to maintain heart health.
- Nutrients such as calcium, magnesium, and phosphorus are abundant in moringa and vital for nails and bone health.
- An easy way to add moringa to your diet is to add it to your soup or curries as a powder.
What Is The Nutritional Profile Of Moringa?
| Nutrient Data For: Drumstick pods, raw | ||
|---|---|---|
| Nutrient | Unit | Value per 100 g |
| Proximates | ||
| Water | g | 88.2 |
| Energy | kcal | 37 |
| Protein | g | 2.1 |
| Total lipid (fat) | g | 0.2 |
| Carbohydrate, by difference | g | 8.53 |
| Fiber, total dietary | g | 3.2 |
| Minerals | ||
| Calcium, Ca | mg | 30 |
| Iron, Fe | mg | 0.36 |
| Magnesium, Mg | mg | 45 |
| Phosphorus, P | mg | 50 |
| Potassium, K | mg | 461 |
| Sodium, Na | mg | 42 |
| Zinc, Zn | mg | 0.45 |
| Vitamins | ||
| Vitamin C, total ascorbic acid | mg | 141 |
| Thiamin | mg | 0.053 |
| Riboflavin | mg | 0.074 |
| Niacin | mg | 0.62 |
| Vitamin B-6 | mg | 0.12 |
| Folate, DFE | µg | 44 |
| Vitamin A, RAE | µg | 4 |
| Vitamin A, IU | IU | 74 |
| Lipids | ||
| Fatty acids, total saturated | g | 0.033 |
| Fatty acids, total monounsaturated | g | 0.102 |
| Fatty acids, total polyunsaturated | g | 0.003 |
| Fatty acids, total trans | g | 0 |
| Cholesterol | mg | 0 |
Source: USDA, drumstick pods, raw
Moringa is a humble plant with several vital nutrients. It is easily available and inexpensive, and including it in your diet shouldn’t be a problem at all.
How To Include Moringa In Your Diet
Here are a few simple ways:
- Add chopped and cooked moringa drumsticks to your soup/curry.
- Add moringa powder to your salad.
- Mix moringa powder with your morning smoothie for a quick boost of taste and nutrition.
- Add the powder to your brownie or cracker mixture.
You can also make moringa tea, which would be a tasteful way to add the goodness of the plant to your diet. The tea can be prepared using moringa leaves. These leaves are already air-dried.
You can grind them in a blender until you achieve a powdery consistency. Add this ground moringa to tea bags and store them in a cool and dry place. Add this powder to hot water, along with some lemon and sugar. However, avoid adding too much sugar to your diet.
In her blog, the author sheds light on the often-overlooked Vitamin E, emphasizing the importance of incorporating it into our daily diets. She highlights moringa leaves as a rich source of Vitamin E and shares five creative ways to include them. The blogger adds, “The use of moringa leaves is not uncommon in South Indian cuisine, and I try to ensure my family gets enough of this essential nutrient by including the greens in my day-to-day cooking as much as I can (i).”
But before you go ahead with moringa, you need to be aware of its side effects.
What Are The Side Effects Of Moringa?
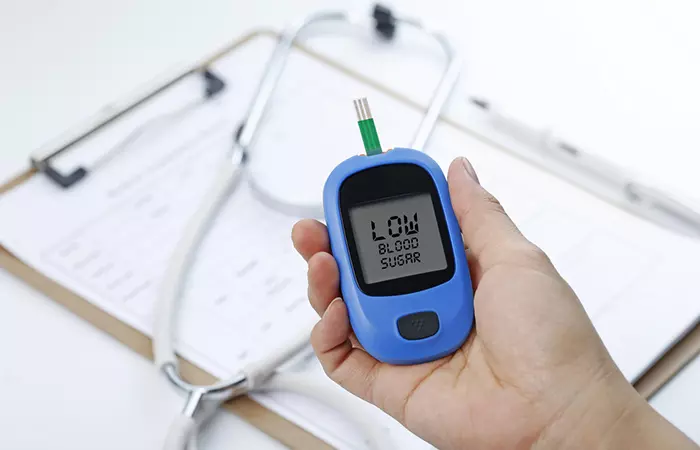
- May Hinder Nutrient Absorption
Moringa leaves may contain antinutrients that can hinder the absorption of certain nutrients (including protein) (42). These antinutrients include tannins, trypsin inhibitors, nitrates, and oxalic acid (43). Hence, if you are taking medications/supplements for nutrient deficiency, please check with your doctor before consuming moringa.
- May Interact With Thyroid Medication
Moringa can have thyroid-like properties (44). Though its interaction with thyroid medication (with hypothyroidism) hasn’t been documented, it is better to check with your doctor before taking moringa regularly.
- May Lower Blood Sugar Levels Way Too Much
We have seen that moringa can help lower blood sugar levels (45). If you are already on medications for treating high blood sugar, moringa might lead to hypoglycemiai A condition in which glucose levels in the body are lower than normal, causing heart palpitations and anxiety. . Hence, please check with your doctor.
- May Lower Blood Pressure Levels Way Too Much
Moringa can also help lower blood pressure levels (17). If you are already on medications for treating high blood pressure, consuming moringa might lead to hypotension. Hence, it is important to talk to your doctor.
- Can Be Harmful During Pregnancy
A study states that moringa may cause violent uterine contractions, possibly leading to abortion (46). However, another report documents the use of moringa leaves to curb malnutrition in pregnant and breastfeeding women (47).
Note: These studies are conflicting. Therefore, it’s important to talk to a healthcare provider before trying any new supplement, especially if you have existing health issues or are taking medication. This can help prevent any unwanted side effects or interactions.
Infographic: 7 Significant Health Benefits Of Moringa
Moringa is a rich source of essential vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants and has remarkable nutritional content for health-conscious individuals. It has been used as a therapeutic and medicinal aid for centuries due to its anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial, and immunity-boosting properties. Check out the infographic below to know more about its top benefits.
Some thing wrong with infographic shortcode. please verify shortcode syntaxMoringa or drumstick is a rich source of many essential vitamins, minerals, and amino acids, therefore it is added to various skin and hair care products. Packed with antioxidants and bioactive compounds, moringa helps fight inflammation and reduce oxidative damage for improved health and wellness. Not only is it beneficial for cardiac, bone, brain, and liver health, but it also helps digestion and regulates your blood sugar and blood pressure levels, aids in weight loss, improves the immune system, and keeps infections at bay. Anecdotal evidence also states its use as a herbal medicine for improving sleep, brain function, and mood. While it is quickly gaining popularity as a superfood, moringa should be consumed in moderation to prevent any possible adverse effects.
Frequently Asked Questions
How to eat dry moringa seeds?
You can add moringa seeds to soups, stews, and sauces. You can also air-dry them and add them to muffin mixes and bread mixes.
Can you take moringa on an empty stomach?
Yes, you can take moringa on an empty stomach.
What is the ideal dosage for moringa?
There is less information on the ideal dosage for moringa. If you have any specific health condition, please consult your doctor on the dosage.
Can moringa cause blood clots?
Yes, moringa extracts have clot hydrolysis properties, which reduce clotting time, ensure that bleeding stops faster, and enhance wound healing (48).
Is it better to take moringa in the morning or at night?
It is believed that the best time to take moringa is in the morning with breakfast as it gives your body the energy that is required for the day.
Does moringa have vitamin D?
Yes, moringa is rich in nutrients and vitamins like A, B, C, and D (49).
Does moringa have omega-3 fatty acids?
Yes, moringa is rich in polyunsaturated fatty acids, which include omega-3 and 6, which help in preventing cardiovascular disease (50)
Illustration: Health Benefits Of Moringa, Nutrition, & Side Effects

Image: Stable Diffusion/StyleCraze Design Team
References
Articles on StyleCraze are backed by verified information from peer-reviewed and academic research papers, reputed organizations, research institutions, and medical associations to ensure accuracy and relevance. Read our editorial policy to learn more.
- Health benefits of Moringa oleifera, Asian Pacific Journal of Cancer Prevention, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25374169/ - Moringa oleifera Root Induces Cancer Apoptosis more Effectively than Leave Nanocomposites and Its Free Counterpart, Asian Pacific Journal of Cancer Prevention, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5697473/ - Moringa oleifera as an Anti-Cancer Agent against Breast and Colorectal Cancer Cell Lines, PloS One, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4545797/ - A potential oral anticancer drug candidate, Moringa oleifera leaf extract, induces the apoptosis of human hepatocellular carcinoma cells, Oncology Letters, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4533244/ - Anti-inflammatory effect of Moringa oleifera Lam. seeds on acetic acid-induced acute colitis in rats, Avicenna Journal of Phytomedicine, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4103706/ - The Flavonoid Quercetin Inhibits Proinflammatory Cytokine (Tumor Necrosis Factor Alpha) Gene Expression in Normal Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells via Modulation of the NF-κβ System https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1391952/
- The Role of Flavonoids in Inhibiting Th17 Responses in Inflammatory Arthritis https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5859886/
- Contribution to the study of the anti-inflammatory activity of Moringa oleifera (moringaceae), Dakar Medical, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15776678/ - Moringa oleifera and inflammation: a mini-review of its effects and mechanisms, United States Department of Agriculture, National Agricultural Library.
https://pubag.nal.usda.gov/catalog/5711988 - Effect of Moringa oleifera consumption on diabetic rats, BMC Complementary & Alternative Medicine, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5894151/ - Effect of supplementation of drumstick (Moringa oleifera) and amaranth (Amaranthus tricolor) leaves powder on antioxidant profile and oxidative status among postmenopausal women, Journal of Food Science and Technology.
https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s13197-012-0859-9 - Effect of some Indian vegetables on the glucose and insulin response in diabetic subjects, International Journal of Food Sciences and Nutrition.
https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/abs/10.3109/09637489309017439 - The Antidiabetic Effect of Low Doses of Moringa oleifera Lam. Seeds on Streptozotocin Induced Diabetes and Diabetic Nephropathy in Male Rats, BioMed Research International.
https://www.hindawi.com/journals/bmri/2015/381040/ - Cardiac Protective Effects of Moringa oleifera Seeds in Spontaneous Hypertensive Rats, American Journal of Hypertension, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26864583/ - Effect of fruits of Moringa oleifera on the lipid profile of normal and hypercholesterolaemic rabbits. Journal of Ethnopharmacology, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12738086/ - Moringa oleifera: A review on nutritive importance and its medicinal application, Food Science and Human Wellness, ScienceDirect.
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2213453016300362 - Moringa oleifera leaf extract lowers high blood pressure by alleviating vascular dysfunction and decreasing oxidative stress in L-NAME hypertensive rats, Phytomedicine, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30668387/ - Investigating of Moringa Oleifera Role on Gut Microbiota Composition and Inflammation Associated with Obesity Following High Fat Diet Feeding, Open Access Macedonian Journal of Medical Sciences, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6108815/ - Histological exhibition of the gastroprotective effect of Moringa oleifera leaf extract, Comparative Clinical Pathology, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5834558/ - Effect of moringa oleifera on bone density in post menopausal women, Furman University.
https://www.semanticscholar.org/paper/Effect-of-Moringa-Oleifera-on-Bone-Density-in-Women-Brown-Merritt/dca50c9db2d549c6b2c1a125c4f9e43aa6f7d118?p2df - Clinical evaluation of cissus quadrangularis and moringa oleifera and osteoseal as osteogenic agents in mandibular fracture, National Journal of Maxillofacial Surgery, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3343389/ - The anti-osteoporotic effect of Moringa oliefera on osteoblasticcells: SaOS 2, Journal of Pharmacy and Biological Sciences.
https://www.semanticscholar.org/paper/The-anti-osteoporotic-effect-of-Moringa-oliefera-on-Patel-Rangrez/7fbc3aa6a5dd399b43b2d792a02058e2b28633a2?p2df - Moringa oleifera Mitigates Memory Impairment and Neurodegeneration in Animal Model of Age-Related Dementia, Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3884855/ - Cerebroprotective Effect of Moringa oleifera against Focal Ischemic Stroke Induced by Middle Cerebral Artery Occlusion, Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity.
https://www.hindawi.com/journals/omcl/2013/951415/ - Evaluation of the antidepressant activity of Moringa oleifera alone and in combination with fluoxetine, Journal of Ayurveda and Integrative Medicine, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4719488/ - Anti-Anemia Effect of Standardized Extract of Moringa Oleifera Lamk. Leaves on Aniline Induced Rats, ResearchGate.
https://www.researchgate.net/publication/303975796_Anti-Anemia_Effect_of_Standardized_Extract_of_Moringa_Oleifera_Lamk_Leaves_on_Aniline_Induced_Rats - Influence of Moringa oleifera on Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver in Adult Albino Rats, Middle East Journal of Applied Sciences.
https://www.semanticscholar.org/paper/Influence-of-Moringa-oleifera-on-Non-Alcoholic-in-Halaby-El-din/31987b349e2bbce24f2cbcdd4c5a67d940b186b4?p2df - Moringa Leaves Prevent Hepatic Lipid Accumulation and Inflammation in Guinea Pigs by Reducing the Expression of Genes Involved in Lipid Metabolism, International Journal of Molecular Sciences, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5535825/ - Hepatoprotective activity of Moringa oleifera on antitubercular drug-induced liver damage in rats, Journal of Medicinal Food, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12495589/ - Impact of Moringa aqueous extract on pathogenic bacteria and fungi in vitro, Annals of Agricultural Sciences, ScienceDirect.
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0570178316300203 - Antibacterial effect (in vitro) of Moringa oleifera and Annona muricata against Gram positive and Gram negative bacteria, Revista do Instituto de Medicina Tropical de São Paulo, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/20602021/ - High levels of inorganic arsenic in rice in areas where arsenic-contaminated water is used for irrigation and cooking, The Science of the Total Environment, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21899878/ - Protective effects of Moringa oleifera Lam. leaves against arsenic-induced toxicity in mice, Asian Pacific Journal of Tropical Biomedicine, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25183111/ - Protective role of Moringa oleifera (Sajina) seed on arsenic-induced hepatocellular degeneration in female albino rats, Biological Trace Element Research, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/20661662/ - Enhancement of human skin facial revitalization by moringa leaf extract cream, Advances in Dermatology and Allergology, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4112252/ - Tropical Plant Called Moringa Shows Promise in Health, Anti-Aging Products, Rutgers Today.
https://www.rutgers.edu/news/tropical-plant-called-moringa-shows-promise-health-anti-aging-products - Antifungal Efficacy of Moringa oleifera Lam. American Journal of Phytomedicine and Clinical Therapeutics.
https://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/viewdoc/download?doi=10.1.1.682.526&&rep=rep1&&type=pdf - Isothiocyanate-rich Moringa oleifera extract reduces weight gain, insulin resistance and hepatic gluconeogenesis in mice, Molecular Nutrition & Food Research, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4456298/ - Antiarthritic, anti-inflammatory activity of Moringa peregrina seed oil and leaves in Freund’s complete adjuvant-induced arthritis in rats, Journal of Kimg Saud University, ScienceDirect.
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1018364721000112 - Moringa oleifera Lam and its Therapeutic Effects in Immune Disorders, Frontiers in Pharmacology, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7773658/ - In vivo anti-arthritic and anti-nociceptive effects of ethanol extract of Moringa oleifera leaves on complete Freund’s adjuvant (CFA)-induced arthritis in rats, Integrative Medicine Research, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5884001/ - Evaluation of nutritional quality of moringa (Moringa oleifera Lam.) leaves as an alternative protein source for Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus L.), Aquaculture, ScienceDirect.
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0044848602004970 - Chemical characteristics and fractionation of proteins from Moringa oleifera Lam. Leaves, Food Chemistry, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24206684/ - Possible Role of Moringa oleifera Lam. Root in Epithelial Ovarian Cancer, Medscape General Medicine, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1924986/ - Effect of Moringa oleifera consumption on diabetic rats https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5894151/
- Powder microscopy of bark–poison used for abortion: moringa pterygosperma gaertn, Journal of the Indian Academy of Forensic Sciences, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12262404/ - Effect of Moringa Oleifera Leaf ExtractsSupplementation in Preventing Maternal DNA Damage, International Journal of Scientific and Research Publications.
https://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/viewdoc/download?doi=10.1.1.652.2403&&rep=rep1&&type=pdf - Moringa oleifera Lam.: Protease activity against blood coagulation cascade, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3250039/ - Moringa oleifera is a Prominent Source of Nutrients with Potential Health Benefits, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8373516/ - Nutritional and Antioxidant Properties of Moringa oleifera Leaves in Functional Foods, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC9030530/
Read full bio of Kelly Mulhall
Read full bio of Ravi Teja Tadimalla
Read full bio of Arshiya Syeda
Read full bio of Sindhu Koganti


























Community Experiences
Join the conversation and become a part of our empowering community! Share your stories, experiences, and insights to connect with other beauty, lifestyle, and health enthusiasts.