8 Side Effects Of Apple Cider Vinegar & How To Use It Safely
Keep your intake down a notch; as excessive consumption may prove to be harmful.
Fermentation of apple juice with lactic acid bacteria and yeast are used to make apple cider vinegar (1). Consumption of this healthy tonic at moderate levels has many potential health benefits and is also used as a natural remedy to manage several skin and hair issues. But are there any side effects of apple cider vinegar with excess consumption? Yes, and these may include digestive issues, gastrointestinal problems, hypokalemia (low potassium levels), and tooth decay.
This article explores the possible side effects of apple cider vinegar, the consequences of excess intake, and safer ways of intake. Keep reading.
 Know The Flip Side: Apple Cider Vinegar
Know The Flip Side: Apple Cider VinegarShort-Term Effects
May cause nausea and skin and throat burn.
Long-Term Effects
May severely lower blood sugar and potassium levels and cause tooth decay.
Drug Interactions
May interact with diuretics, laxatives, and diabetes and blood pressure medications.
When To See A Doctor
If you experience very low potassium and blood sugar levels (especially if you have diabetes).
In This Article
Side Effects Of Apple Cider Vinegar
1. May Cause Gastrointestinal Issues

Excess consumption of apple cider vinegar may cause gastrointestinal issues. It may slow down the process of absorption of food in the bloodstream. A study conducted by Lund University found that apple cider vinegar delayed the gastric emptying rate (2). Though this could be beneficial in some cases, it can cause digestion issues in some individuals.
Increased intake of apple cider vinegar may also worsen symptoms of gastroparesis, a common condition in people with type 1 diabetes (3). This highlights the importance of cautious use of apple cider vinegar for diabetes. However, more studies in this line are needed to reach further conclusions.
A blogger shares in one of her blog posts her experience of consuming apple cider vinegar: “I had a gas inflammation problem for 4 days in the beginning as I had an acute gastric [problem]. After that, it started reducing gradually. But it has started again so badly that I release gas every now and then (i).”
2. May Cause Digestive Problems
Apple cider vinegar may help reduce appetite. A study shows that apple cider vinegar acts as an appetite suppressant and promotes feelings of fullness, leading to a natural reduction in food intake. Though this could help with detoxification and weight loss, the vinegar can cause subsequent nausea (4). If you are considering using apple cider vinegar for weight loss, be mindful of this potential side effect.
However, more studies are needed to further understand this side effect of apple cider vinegar.
3. May Cause Hypokalemia
Anecdotal evidence suggests that excessive use of apple cider vinegar may lower the potassium levels in the body
. It may also reduce bone mineral density, which, in turn, makes bones brittle. Hence, individuals with osteoporosis may have to reduce or avoid the intake of apple cider vinegar.
A case of hypokalemia was observed in a 28-year-old woman who had reportedly taken 250 ml of ACV regularly for 6 years (5). More research is needed in this regard.
4. May Cause Tooth Decay

The high acidity of undiluted apple cider vinegar can damage your tooth enamel if consumed in excess. Besides giving a yellowish tinge to your teeth, the vinegar may also increase your dental sensitivity.
A study states that apple cider vinegar may have an erosive potential that may cause tooth decay (6). Another study states the case of a 15-year-old girl who had experienced tooth erosion following the daily intake of apple cider vinegar (7).
5. May Cause Throat Burns
Increased consumption of apple cider vinegar may cause throat burns. Many studies have concluded that the oral overuse of apple cider vinegar can eventually lead to throat irritation. The acetic acid in the vinegar could be the primary cause (8).
A study conducted by the University of Arkansas found that apple cider vinegar tablets may also lead to esophageal injury (8). It is a potent caustic substance, and accidental ingestion of vinegar may lead to esophageal lesions in children (9).
6. May Cause Skin Burns
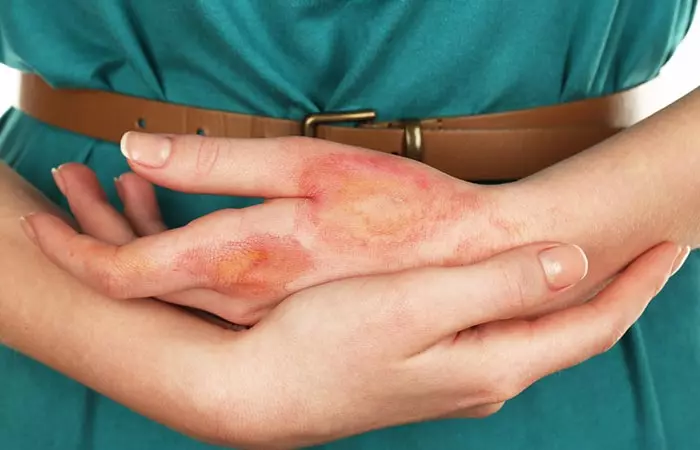
The strong acidic nature of apple cider vinegar may cause skin burns. Applying apple cider vinegar directly to the skin can cause burns and irritation, especially if the vinegar is undiluted.
In a study, a 14-year-old girl developed burns on her nose after applying several drops of apple cider vinegar to remove two moles (10). There are several other anecdotal studies that suggest that apple cider vinegar causes skin burns.
 Quick Tip
Quick Tip7. May Interact with Certain Drugs
There is no sufficient information available in this regard. Since it is acidic, apple cider vinegar may easily react with some drugs including laxatives and diuretics.
Apple cider vinegar may have a direct effect on insulin levels and blood sugar. Taking it along with blood pressure and diabetes medications may cause harm. However, more studies in this line are needed to reach further conclusions. If you are on any medication, consult your doctor before taking apple cider vinegar.
8. May Cause Low Blood Sugar Levels
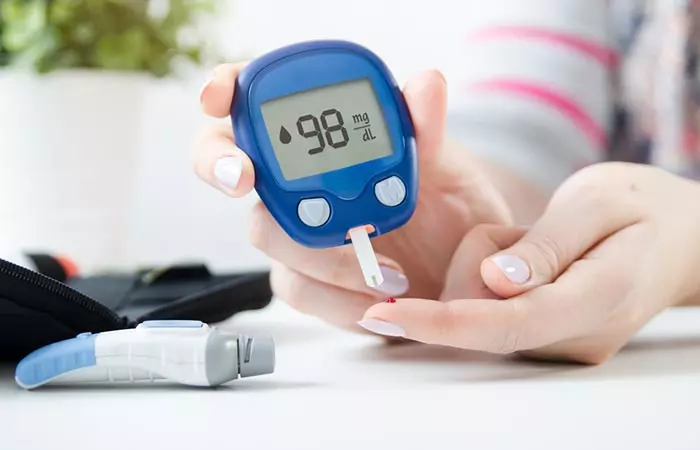

The excessive use of apple cider vinegar may lower blood-sugar levels. The vinegar has an anti-glycemic effect (5), (11). However, taking it along with diabetes medications may cause your blood sugar levels to drop way too low. This, if not treated, may lead to unconsciousness and even coma. More research is needed to further understand this phenomenon.
Apple cider vinegar is also not advised for pregnant/lactating women and those undergoing chemotherapy treatment. It may cause complications. However, there is insufficient information in this regard.
These are the potential adverse effects of apple cider vinegar. Most of these need further research to be thoroughly validated. However, this does not mean one must totally avoid ACV. There is a way to consume it by minimizing the risk of side effects.
Key Takeaways
- The side effects of ACV include gastrointestinal issues, digestive problems, hypokalemia, and tooth decay.
- It may also cause throat and skin burns and low blood sugar levels and react with some medications.
- A daily intake of just 15 ml of ACV is recommended to gain its benefits.
How To Consume Apple Cider Vinegar Safely
The intake of excess and undiluted apple cider vinegar daily may cause possible adverse effects.
To minimize these effects, you can try:
- Diluting the apple cider vinegar with water.
- Reducing the quantity of vinegar intake.
- Limiting contact with the teeth by drinking vinegar through a straw.
- Reducing the amount of time vinegar touches the skin.
- Rinsing your mouth with water after consumption to prevent further damage to the teeth.
 Quick Tip
Quick TipYou can also ensure you consume ACV in the recommended doses to potentially avoid side effects.
Dosage
The recommended dose of apple cider vinegar varies depending on your individual needs. However, a daily intake of 15 ml of apple cider vinegar is enough to enjoy its potential health benefits (12).
Before you apply apple cider vinegar to your skin, dilute it with water. Also, do a patch test.
Infographic: Health Benefits Of Apple Cider Vinegar
Apple cider vinegar is fermented apple juice infused with apple and probiotics. While its excess intake does cause side effects, moderate consumption offers important benefits. Thanks to its acetic acid content, it can help address many health issues and promote good health. Discover more about the benefits of apple cider vinegar in the infographic below.

Illustration: StyleCraze Design Team
Apple cider vinegar has been lauded for its many health benefits in recent years. However, it may prove to be harmful if consumed in excessive amounts. The side effects of apple cider vinegar range from increased risk of osteoporosis to dental problems. Furthermore, it may cause gastrointestinal and digestive issues. In some cases, apple cider vinegar may trigger allergic reactions or interfere with the functioning of certain medications, especially diuretics and those for diabetes. Therefore, it is advised that you only consume ACV as directed by your doctor.
Frequently Asked Questions
Does apple cider vinegar make you sleepy?
There is a lack of scientific evidence to suggest that apple cider vinegar (ACV) makes you sleepy.
Is apple cider good for the bladder?
There is a lack of scientific evidence to suggest that ACV is good for your bladder or the urinary system.
Is apple cider vinegar good for high blood pressure?
Possibly. Studies have shown that the acetic acid in apple cider vinegar can help lower blood pressure levels in hypertensive rats (14).
Is apple cider vinegar good for arthritis?
There is a lack of scientific evidence suggesting that ACV is good for relieving arthritis.
Is apple cider vinegar good for your cholesterol?
Possibly. A study showed that consumption of ACV may reduce total cholesterol levels (15).
Discover the surprising truth about apple cider vinegar! Before you reach for that bottle, watch this eye-opening video to learn which conditions may make it a risky choice for you.
Personal Experience: Source
StyleCraze's articles are interwoven with authentic personal narratives that provide depth and resonance to our content. Below are the sources of the personal accounts referenced in this article.
i. My experience: Benefits and side effects of apple cider vinegar;https://masteradviser.blogspot.com/2016/10/side-effects-of-apple-cider-vinegar-on-liver-kidney-hair-and-other.htmlReferences
Articles on StyleCraze are backed by verified information from peer-reviewed and academic research papers, reputed organizations, research institutions, and medical associations to ensure accuracy and relevance. Read our editorial policy to learn more.
- Cousin, Fabien J et al. “Microorganisms in Fermented Apple Beverages: Current Knowledge and Future Directions.” Microorganisms vol. 5,3 39. 25 Jul. 2017.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5620630/ - Liljeberg H, Björck I. Delayed gastric emptying rate may explain improved glycaemia in healthy subjects to a starchy meal with added vinegar. Eur J Clin Nutr. 1998;52(5):368–371.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/9630389/ - Hlebowicz, Joanna et al. “Effect of apple cider vinegar on delayed gastric emptying in patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus: a pilot study.” BMC gastroenterology vol. 7 46. 20 Dec. 2007.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2245945/ - Darzi J, Frost GS, Montaser R, Yap J, Robertson MD. Influence of the tolerability of vinegar as an oral source of short-chain fatty acids on appetite control and food intake. Int J Obes (Lond). 2014;38(5):675–681.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23979220/ - Johnston, Carol S, and Cindy A Gaas. “Vinegar: medicinal uses and antiglycemic effect.” MedGenMed : Medscape general medicine vol. 8,2 61. 30 May. 2006.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1785201/ - Willershausen I, Weyer V, Schulte D, Lampe F, Buhre S, Willershausen B. In vitro study on dental erosion caused by different vinegar varieties using an electron microprobe. Clin Lab. 2014;60(5):783–790.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24839821/ - Gambon DL, Brand HS, Veerman EC. Ongezond afslanken. Erosie door appelazijn [Unhealthy weight loss. Erosion by apple cider vinegar]. Ned Tijdschr Tandheelkd. 2012;119(12):589–591.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23373303/ - Hill LL, Woodruff LH, Foote JC, Barreto-Alcoba M. Esophageal injury by apple cider vinegar tablets and subsequent evaluation of products. J Am Diet Assoc. 2005;105(7):1141–1144.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15983536/ - Nuutinen M, Uhari M, Karvali T, Kouvalainen K. Consequences of caustic ingestions in children. Acta Paediatr. 1994;83(11):1200–1205.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/7841737/ - Feldstein S, Afshar M, Krakowski AC. Chemical Burn from Vinegar Following an Internet-based Protocol for Self-removal of Nevi. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2015;8(6):50.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26155328/ - Siddiqui, Fahad Javaid et al. “Diabetes Control: Is Vinegar a Promising Candidate to Help Achieve Targets?.” Journal of evidence-based integrative medicine vol. 23 (2018): 2156587217753004.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5954571/ - Samad, Anuar, Azrina Azlan, and Amin Ismail. “Therapeutic effects of vinegar: a review.” Current Opinion in Food Science 8 (2016): 56-61.
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S2214799316300479?via%3Dihub - Nazıroğlu M, Güler M, Özgül C, Saydam G, Küçükayaz M, Sözbir E. Apple cider vinegar modulates serum lipid profile, erythrocyte, kidney, and liver membrane oxidative stress in ovariectomized mice fed high cholesterol. J Membr Biol. 2014;247(8):667–673.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24894721/ - Antihypertensive Effects of Acetic Acid and Vinegar on Spontaneously Hypertensive Rats
https://www.jstage.jst.go.jp/article/bbb/65/12/65_12_2690/_article - The effect of apple cider vinegar on lipid profiles and glycemic parameters: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8243436/
Read full bio of Staci Gulbin
Read full bio of Sindhu Koganti
Read full bio of Ravi Teja Tadimalla
Read full bio of Himanshi Mahajan



























Community Experiences
Join the conversation and become a part of our empowering community! Share your stories, experiences, and insights to connect with other beauty, lifestyle, and health enthusiasts.