7 Health Benefits Of Wheat Germ & How To Include In Your Diet
Understand how this nutritious food supplement may make your body healthier.
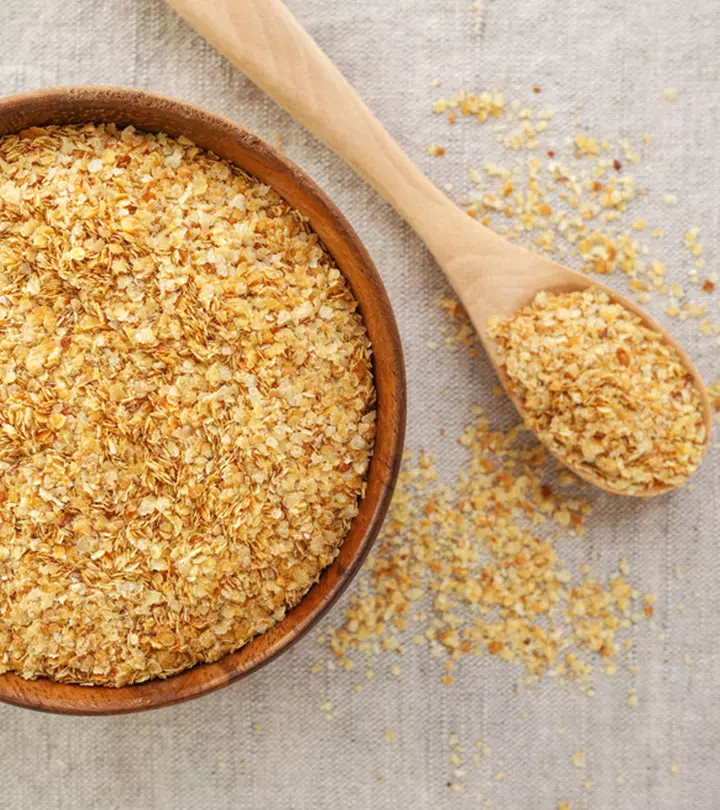

Image: Shutterstock
Wheat germ is a versatile superfood and a great source of fiber and a highly concentrated portion of wheat that is loaded with several nutrients. It is a great source of vitamins, minerals, fat, and proteins. The benefits of wheat germ are numerous and are mainly attributed to its nutrients. Adding wheat germ to your diet can greatly improve your nutritional intake and support overall wellness. It contains antioxidants that help treat many ailments and may aid disease prevention. Wheat germ oil is derived from its extract, which has several applications in the cosmetic industry, thanks to its moisturizing properties. However, the wheat germ is usually discarded during processing due to the presence of polyunsaturated fatty acidsi Healthy dietary fats that decrease the chances of heart disease and play a role in brain and cellular growth. (which are prone to spoilage).
This article explores wheat germ nutrition facts, health benefits, possible adverse effects, and some easy recipes to try. Keep reading.
 Know Your Ingredient: Wheat Germ
Know Your Ingredient: Wheat GermWhat Is It?
It is the breadcrumb-like seed that develops into a wheat plant.
What Are Its Benefits?
It may improve heart health, reduce diabetes and cancer risk, boost muscle and skin health, and reduce menopausal symptoms.
Who Can Use It?
People with diabetes might find wheat germ to be a better alternative to regulate their blood sugar levels.
How Often?
You can consume 1 tablespoon of wheat germ per day.
Caution
Avoid consuming it if you are gluten intolerant or on a low-carb diet.
In This Article
What Is Wheat Germ?
Wheat germ is one of the three parts of a wheat kernel, along with the bran and endospermi Tissue that is rich in nutrients and nourishes the growing embryo during germination. . The wheat germ helps the plant reproduce and spawn new grains. It is removed from the endosperm during the milling process and can be an excellent addition to your diet. You can add wheat germ to your favorite smoothies, protein shakes, muffins, and bread.
 Quick Tip
Quick TipWheat germ is rich in essential nutrients. Below is its nutritional breakdown.
Key Takeaways
- Wheat germ is an excellent source of fiber and high in vitamins, minerals, fats, and proteins.
- It improves heart health, lowers diabetes and cancer risk, boosts muscle function, supports immunity, slows aging, protects the skin from free radical damage, and alleviates menopausal symptoms.
- However, wheat germ can induce weight gain if consumed in excess.
Wheat Germ Nutrition
According to the U.S. Department of Agriculture, 100 grams of crude wheat germ contain (1):
| Calories | 360 |
| Protein | 23.2g |
| Fat | 9.72g |
| Carbohydrates | 51.8g |
| Fiber | 13.2g |
| Calcium | 39 mg |
| Iron | 6.26 mg |
| Magnesium | 239 mg |
| Phosphorous | 842 mg |
| Potassium | 892 mg |
| Thiamin | 1.88 mg |
| Niacin | 6.81 mg |
Wheat germ also contains sodium, zinc, folic acid, and antioxidants that help maintain optimal health. Wheat germ benefits range from promoting heart health to reducing diabetes risk. Know them in detail from the section below.
Wheat Germ Health Benefits
1. May Improve Heart Health
Wheat germ is rich in phytosterols (structurally similar to cholesterol) that have antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. Our body cannot synthesize phytosterols, and they must be obtained through diet. These plant nutrients may help reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease (2). A study conducted by the Harvard School of Public Health (USA) found that consuming whole grains (which include bran and germ) every day may reduce the risk of coronary heart disease (3). Besides, octacosanol (a plant chemical) in wheat germ may help reduce LDL cholesterol levels (4). Wheat germ also contains omega-3 fatty acids that reduce the risk of sudden death from heart disease and all-cause mortality in individuals with such conditions (5).
2. May Reduce Diabetes Risk
Consuming foods rich in dietary fiber may help regulate blood sugar levels (6). A study conducted by the University of Lund (Sweden) also found that dietary fiber may decrease plasma LDL and fasting blood glucose levels (7). Moreover, the presence of alpha-linolenic acidi An omega-3 fatty acid essential for proper growth and development in humans, with the ability to prevent blood clots and heart disease. in wheat germ has been reported to decrease insulin resistance (8). All these factors, in turn, may help reduce the risk of type 2 diabetes.
3. May Reduce The Risk Of Cancer
Studies suggest that wheat germ extract (Avemar) shows anti-cancer activity. It may stimulate natural killer (NK) cell activity and induce apoptosis (programmed cell death of tumor cells) (9), (10). A review published in Nutrients suggests that this fermented wheat germ extract may be an efficient compound in treating cancer. Avemar was found to starve cancer cells of sugar (which they need to survive) and unmask them so that the immune system can act (11). Besides, the anti-proliferative activityi A specific property that tends to suppress cell growth, particularly of cancerous cells, and keeps them from spreading further. of Avemar was found to be effective in treating patients with colon cancer (12). However, more studies are needed to understand this benefit of wheat germ in humans.
4. May Boost Muscle Health

Wheat germ is one of the best sources of plant protein. Coupled with vitamin B and E (present in wheat), it may help build and repair muscles (13). A review published in the International Journal of Molecular Sciences also suggests that a dietary intake of vitamin E-rich foods improves muscle mass and reduces other age-related pathologiesi Diseases whose risks increase with age, such as cancer, metabolic disorders, cardiovascular diseases, neurological disorders, and musculoskeletal decline. (14). However, more studies are warranted to understand this benefit of tocopherolsi A group of fat-soluble substances that comprise vitamin E and are well-known for their antioxidant properties, which protect cells from oxidative damage. in the elderly dealing with sarcopenia (age-related muscle mass).
5. Has Anti-aging Properties
Ferulate, an active and phenolic compound in wheat germ, may slow down aging (by suppressing aging-related gene expression) and act against oxidative stressi An imbalance between the body's antioxidants and free radicals, which damages cells and causes aging and a number of illnesses. (15). Besides, vitamin E present in wheat germ may protect your skin from free radical damage. It may also exhibit photoprotectivei Biological properties that allow organisms to protect themselves from harm caused by over-exposure to sunlight. and anti-photoaging properties and help reduce skin damage (16). In fact, moisturizing creams may contain up to 50 percent of wheat germ oil as it has humectant propertiesi Effects usually found in lotions and shampoos that help keep hair and skin hydrated without making them feel heavy or oily. (17).
6. Reduces Menopausal Symptoms
The anti-inflammatory properties of wheat germ may help reduce the severity of primary dysmenorrhea (painful menstrual periods). Taking three 400 mg capsules of wheat germ extracts daily — between the 16th day of the menstrual cycle to the fifth day of the next menstrual cycle for two consecutive months — showed beneficial results (18). Wheat germ extracts may also relieve the general, psychological, and physical symptoms of premenstrual syndrome (PMS) (19).
7. May Aid Weight Loss
Wheat germ is high in fiber, boasting nearly 13.2g of fiber in a 100g serving (1). Research suggests that increasing your fiber intake in a calorie-restricted diet may help promote weight loss in those dealing with obesity or who are overweight (20). An animal study conducted on mice to determine the efficacy of wheat germ when used alone versus in combination with antibiotics states that the latter was more effective. It led to a significant decrease in food intake, body weight, and fat mass (21). Use wheat germ for weight loss by adding it to your smoothies, oatmeal, and salads. The fiber in it may help keep you full and add an extra crunch to your food.
Is there any specific limit to wheat germ intake? What happens if it is consumed in excess? Scroll down to know in detail.
Wheat Germ Side Effects
Consuming wheat germ is generally considered safe. However, it is rich in calories and may cause weight gain. Hence, check your portions. The same applies to those who are on a low-carb diet. Also, avoid eating wheat germ if you are sensitive to gluten. Some individuals may experience mild side effects like diarrhea, nausea, gas, and dizziness upon intake (22). Therefore, consult your doctor immediately if you experience any of these adverse effects.
Have you ever tried wheat germ in your recipes? If not, here are a few ways to incorporate it into your diet.
How Do You Include Wheat Germ In Your Diet?
- Eat raw wheat germ by topping hot or cold cereal or yogurt with it.
- Use in smoothies or sprinkle over nut butter.
- Add into muffins or casseroles.
- Mix into pancake or waffle batter.
- Add to your favorite soup recipe.
- Use as a crumb topping on desserts or casseroles.
- Stir into the pizza crust.
- Add to pancakes to boost the nutritional value.
- Use as a filler in meatballs or meatloaf.
- Use as a substitute for bread crumbs for a healthier meatloaf.
- Use in your favorite bread-stuffing recipe.
- Sprinkle over Greek yogurt for a nutty flavor.
- Mix into pie fillings and crusts for a nutty flavor.
- Use as a coating for baked fish or chicken.
 Quick Tip
Quick TipAdding wheat germ to your diet takes no great effort. In the next section, we list three easy and delicious recipes with wheat germ. These are not only rich in taste but can also aid proper digestion and provide energy.
Wheat Germ Recipes
1. Wheat Germ Pancakes

What You Need
- Wheat germ – 6 teaspoons
- All-purpose flour – 1 cup
- Whole wheat flour – ½ cup
- Eggs – 2
- Sugar – 3 tablespoons
- Baking powder – 1 tablespoon
- Vanilla extract – ½ teaspoon
- Milk – 1¼ cups
- Mashed banana – 1
- Vegetable oil – 2 tablespoons
Process
- Preheat the griddle or the electric stove to about 350o F.
- Whisk flour, sugar, baking powder, and salt in a medium-sized bowl.
- Mash banana in a large measuring cup.
- Add a little milk and stir. Fill 1¼ of the cup with the milk.
- Add in oil, eggs, and vanilla. Whisk the wet ingredients into the dry ones until just combined.
- Spray the griddle with a non-stick cooking spray. Ladle the pancakes onto it one by one.
- Add ½ a teaspoon of wheat germ to the top of each pancake and cook until the bottoms are brown.
- Flip and cook until golden on the bottom. Serve with syrup.
2. Wheat Germ Cookies
What You Need
- Wheat germ– ¾ cup
- Baking soda – ½ teaspoon
- Butter – 100g
- Brown sugar – ½ cup
- Grated coconut – ½ cup
- Chopped pistachios – ¼ cup
- Egg – 1
- Vanilla extract – 1 teaspoon
- Salt – ¼ teaspoon
Process
- Preheat the oven to 180o F. Line a cookie pan and set it aside.
- Beat butter and sugar until the mixture turns fluffy. Add the egg and vanilla, and beat until they are incorporated.
- Add the dry ingredients and fold until they are combined.
- Fold in the coconut and pistachios.
- Drop spoonfuls of the mixture on the tray at least an inch apart and flatten slightly.
- Bake for 10 minutes if the cookies are small and 15 minutes if they are large. Let them cool in the pan for five minutes before transferring them to a wire rack to cool completely.
3. Wheat Germ Muffins

What You Need
- Wheat germ – ¾ cup
- Whole wheat flour – 1¼ cups
- Milk – 1 cup
- Canola oil – ¼ cup
- Raw sugar – ¼ cup
- Honey – ¼ cup
- Egg – 1
- Baking powder – 3 teaspoons
- Salt – ½ teaspoon
- Flax seeds – 2 tablespoons
Process
- Preheat the oven to 400oF.
- Sift flour in a large bowl and add wheat germ, sugar, salt, and baking powder.
- Beat the egg with a fork in a small bowl. Add honey, vanilla extract, oil, and milk. Mix.
- Pour liquid ingredients in the center of the dry ingredients. Mix well and pour the batter into a greased muffin pan.
- Bake for about 25 minutes until the muffins turn golden brown.
4. Toasted Wheat Germ
What You Need
- 1 cup of wheat germ
Process
- Preheat the oven to 350°F.
- Spread wheat germ evenly on a baking sheet.
- Bake for 5-10 minutes and use a topping for cereal and yogurt.
A blogger shared her obsession with wheat germ on her personal blog: “I have an obsession with wheat germ. I love its aroma and taste, especially when it is toasted and used for bread (i).”
You need to store wheat germ properly to keep it from spoiling. Here are a few tips you can follow.
How To Store Wheat Germ
Store wheat germ in an air-tight container once the seal is opened. It can last up to six to eight months if you store it in the refrigerator. Place it in the freezer to further increase its shelf life. Wheat germ can become rancid quickly if you do not store it properly as it contains unsaturated fat.
Infographic: 5 Reasons To Add Wheat Germ To Your Diet
Wheat germ is a nutrient-packed superfood. It is loaded with vitamins, minerals, protein, and fiber, which benefit your heart and skin health. It may also aid in weight loss and work wonders for your body. This infographic will take you through the most compelling reasons to make wheat germ your new go-to ingredient to give your meals a healthy boost. Check it out!
Illustration: StyleCraze Design Team
Wheat germ is a nutritious by-product formed when wheat is ground into flour. It is packed with dietary fiber, proteins, carbohydrates, vitamins, minerals, and many beneficial bioactive compounds. Wheat germ benefits range from promoting heart health and supporting brain function to improving muscle mass. It is also good for your skin and hair health and may delay early aging. You can reap the benefits of wheat germ by adding it to your smoothies, shakes, and baked goods. However, avoid consuming it in excess as it may hinder weight management and cause weight gain or adversely affect those with gluten sensitivities. Hence, limit its consumption and seek medical advice if you experience any side effects.
Frequently Asked Questions
How much wheat germ should I eat in a day?
It is safe to consume about 3 ounces of wheat germ per day, according to the Dietary Guidelines for Americans, 2020-2025 (23).
Which is better: flaxseed or wheat germ?
Wheat germ. It has a better macronutrient profile than flaxseeds (1), (24).
How can wheat germ be used as a natural supplement for athletic performance?
Wheat germ is recommended by various health enthusiasts due to its ability to boost energy and stamina. It is said to enhance blood flow to the muscles and improve athletic performance. While no one can deny wheat germ’s multiple health benefits, more research is warranted regarding its performance-boosting properties.
Does Atta have wheat germ?
No, the germ is removed from the wheat during the milling process.
Personal Experience: Source
StyleCraze's articles are interwoven with authentic personal narratives that provide depth and resonance to our content. Below are the sources of the personal accounts referenced in this article.
i. Ciabatta with toasted wheat germ and olive oil – wheat germ obsession continueshttps://youcandoitathome.blogspot.com/2011/07/ciabatta-with-toasted-wheat-germ-and.html
References
Articles on StyleCraze are backed by verified information from peer-reviewed and academic research papers, reputed organizations, research institutions, and medical associations to ensure accuracy and relevance. Read our editorial policy to learn more.
- \’Wheat germ\’ crude
https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/168892/nutrients - Phytosterols: Nutritional Health Players in the Management of Obesity and Its Related Disorders
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/labs/pmc/articles/PMC7763348/ - \’Intakes of whole grains\’ \’bran\’ and germ and the risk of coronary heart disease in men
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15585760/ - Octacosanol in Human Health
https://www.sciencedirect.com/sdfe/pdf/download/eid/1-s2.0-S0899900702008699/first-page-pdf - Omega-3 fatty acids and cardiovascular disease
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25720716/ - Effect of soluble fiber intake in lipid and glucose levels in healthy subjects: a randomized clinical trial
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15163472/ - Dietary fiber decreases fasting blood glucose levels and plasma LDL concentration in noninsulin-dependent diabetes mellitus patients
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/2834942/ - Can wheat germ have a beneficial effect on human health? A study protocol for a randomised crossover controlled trial to evaluate its health effects
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/labs/pmc/articles/PMC5129044/ - Avemar (wheat germ extract) in cancer prevention and treatment
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/20155632/ - The effectiveness of fermented wheat germ extract as an adjunct therapy in the treatment of cancer: A systematic review
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27820157/ - The Effects of Adjuvant Fermented Wheat Germ Extract on Cancer Cell Lines: A Systematic Review
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/labs/pmc/articles/PMC6213720/ - Promising cytotoxic activity profile of fermented wheat germ extract (Avemar®) in human cancer cell lines
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/labs/pmc/articles/PMC3104483/ - Nutritional Contents and Medicinal Properties of Wheat: A Review
https://www.researchgate.net/publication/280920597_Nutritional_Contents_and_Medicinal_Properties_of_Wheat_A_Review - Focus on Pivotal Role of Dietary Intake (Diet and Supplement) and Blood Levels of Tocopherols and Tocotrienols in Obtaining Successful Aging
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/labs/pmc/articles/PMC4632695/ - \’Ferulate\’ an \’Active Component of Wheat Germ\’ Ameliorates Oxidative Stress-Induced PTK/PTP Imbalance and PP2A Inactivation
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/labs/pmc/articles/PMC6195880/ - The role of vitamin E in normal and damaged skin
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/7633944/ - Wheat Germ Oil
https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/agricultural-and-biological-sciences/wheat-germ-oil - Effects of Wheat Germ Extract on the Severity and Systemic Symptoms of Primary Dysmenorrhea: A Randomized Controlled Clinical Trial
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/labs/pmc/articles/PMC4222016/ - The Effect of Wheat Germ Extract on Premenstrual Syndrome Symptoms
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/labs/pmc/articles/PMC4277629/ - Fiber intake predicts weight loss and dietary adherence in adults consuming calorie-restricted diets: the pounds lost (preventing overweight using novel dietary strategies) study
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31174214/ - Effects of wheat germ and its combination with antibiotics on metabolic and gut health outcomes in western diet-fed mice
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8181237/ - Wheat/Gluten-Related Disorders and Gluten-Free Diet Misconceptions: A Review
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/labs/pmc/articles/PMC8391170/ - Dietary Guidelines for Americans, 2020-2025
https://www.dietaryguidelines.gov/sites/default/files/2020-12/Dietary_Guidelines_for_Americans_2020-2025.pdf - Flax seeds
https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/1100610/nutrients - Wheat germ: not only a by-product
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22077851/
Read full bio of Jessie Hulsey
Read full bio of Sindhu Koganti
Read full bio of Ravi Teja Tadimalla
Read full bio of Aparna Mallampalli



























Community Experiences
Join the conversation and become a part of our empowering community! Share your stories, experiences, and insights to connect with other beauty, lifestyle, and health enthusiasts.