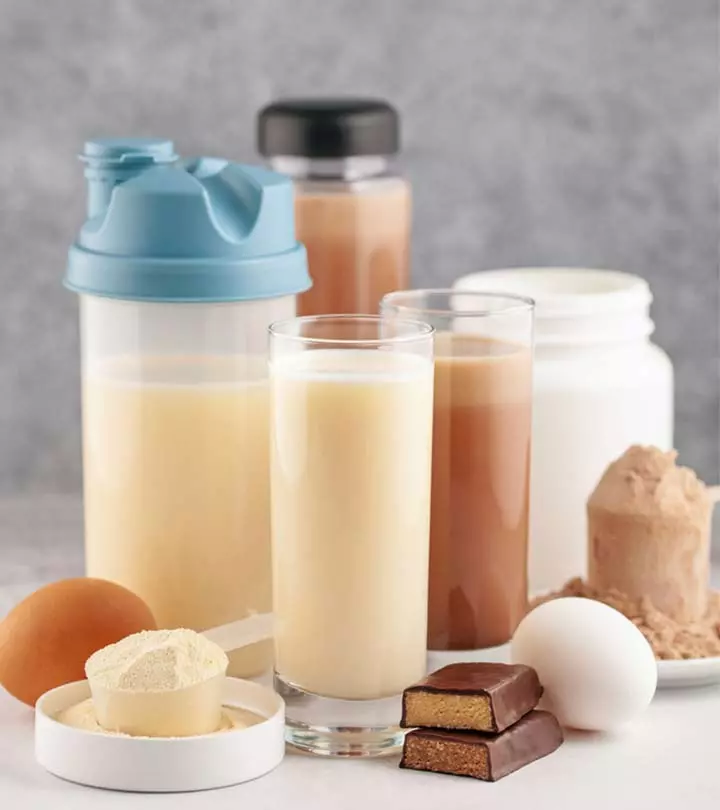
Whey Protein Benefits: 24 Ways To Boost Muscle, Skin & Health
Everything you need to know about this popular dietary protein and amino acid supplement

Image: iStock
If you are here wondering about whey protein’s benefits, we have got you covered! Proteins are rightly known as the building blocks of our body. They help build muscles and connective tissues in our bodies and aid in important metabolic pathways as well. Whey is an important dietary source of these essential proteins and amino acids (1). Athletes and fitness enthusiasts commonly use whey protein for muscle recovery and as a dietary supplement. This versatile ingredient can be easily incorporated into your daily diet, whether it’s in a post-workout shake or a protein-packed meal. In this article, we will explore the benefits of whey protein and how you can easily include it in your diet. Continue reading!
 Know Your Ingredient: Whey Protein
Know Your Ingredient: Whey ProteinWhat Is It?
Whey is the watery milk residue of the curds while creating cheese; therefore, whey protein is the protein from this component.
What Are Its Benefits?
Whey protein helps with weight loss, body composition, and strengthens the muscles.
Who Can Consume It?
Those who need to increase their strength and muscle mass while also shedding fat, such as athletes or bodybuilders.
How Often?
You can consume 1 to 2 scoops daily.
Caution
High doses can cause acne, reduced appetite and increased bowel movements.
In This Article
What Is Whey Protein?
Whey is the purest form of protein. It is obtained from cow’s milk. It is a by-product of milk, obtained during the processing of cheese. Whey is processed into more concentrated forms. Some of its different forms are whey protein, whey protein isolates, whey protein concentrate, whey protein hydrolysate and hydrolyzed proteini A protein type made by splitting its compounds into smaller amino acids to promote its absorption and better muscle repair and growth. . Protein powders are becoming extremely popular these days, owing to their health benefits. It contains a higher amount of protein than all the natural foods (1). Whey protein is highly recommended for women who need more protein in their diet.

Key Takeaways
- Whey is the purest form of milk protein which has numerous benefits for skin, hair, and health.
- It is available in various forms like concentrate, isolate, and hydrolysate, among which whey protein hydrolysate is the most soluble and expensive. You can have it as powder, bars, and supplements.
- The antioxidant and hydrating action of whey protein helps reduce fine lines and wrinkles.
- Whey protein promotes hair growth, reduces hair fall, and helps maintain a healthy scalp.
- The body quickly digests it, thus improving muscle mass, aiding in weight loss, lowering blood sugar levels, and boosting immunity.
Types Of Whey Protein
There are three main types of whey protein supplements: Whey Protein Concentrate, Whey Protein Isolate and Whey Protein Hydrolysate.
- Whey Protein Concentrate (WPC) is the cheapest of all three whey protein powders. It has the lowest amount of protein, around 58 to 89%. The rest is composed of fat, lactose and immune-enhancing peptides like alpha-lactalbumin and immunoglobulin. The percentage of WPC depends on how concentrated it is. Lower end concentrates have 50% protein, while higher end ones have up to 90% protein.
- Whey Protein Isolate contains 95% of the protein, with a minimum amount of lactose and fat. It is regarded as the purest type of whey protein, making it a popular choice for individuals who are lactose intolerant or looking to lower their carbohydrate consumption.
- Whey Protein Hydrolysate has 99% of protein and is the most expensive of all the whey protein powders. It is considered the “pre-digested” form of whey protein, as it undergoes partial hydrolysis- a process necessary for the body to absorb protein. It is the most soluble form of protein and gets quickly digested in the body. This is considered the best whey protein supplement by many.
 Did You Know?
Did You Know?Whey Protein Benefits
Check out here some of the best benefits of whey protein for women:
1. Body Composition
Whey protein is very beneficial for women and may improve body composition without leading to ‘bulking’
(2). Moreover, whey protein is the most soluble and richest form of protein. It is much more nutritious than egg whites, soy and meat.
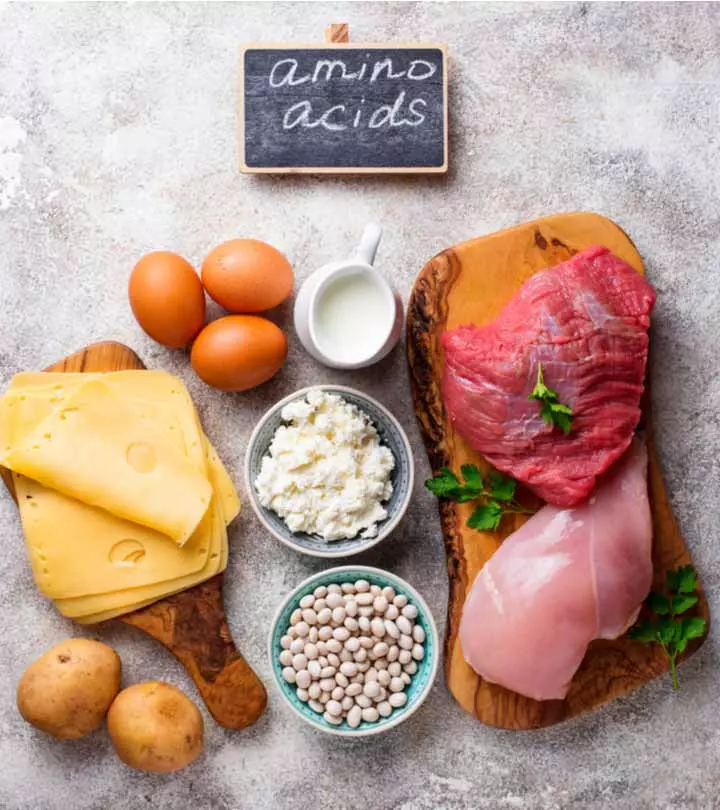
2. Amino Acids
Amino acids are the chemical units which are not produced naturally in our body. Whey protein is a good source of amino acids. They work together to repair our bones, muscles, organs and almost every part of the tissue in the human body. Specific amino acids are needed for specific purposes. Whey protein is high in Branched Chain Amino Acids (BCAA’s). They are useful for muscle repair and preservation. Leucine, another amino acid, stimulates protein synthesis and sends signals to the body to increase its storage of amino acid (3).
3. Aging
Whey protein contains glutathione. This is an antioxidant which scavenges free radicals and delays the signs of aging. Glutathione is made from three main amino acids; cysteine, glutamic acid and glycine. Whey protein also slows down the degeneration of muscles and keeps them strong during old age (4), (5).
4. Weight Loss

Whey protein for weight loss? Yes, according to a study, women who consumed a specialized form of whey protein lost more body fat. They also showed a greater preservation of lean muscle than those who didn’t. Whey protein is low in carbohydrates and high in protein. This speeds up the metabolism to burn excess fat from the body. Researchers have concluded that whey protein can easily control appetite for up to two hours. It contains very little fat, low cholesterol and lactose. This makes it excellent for people on a low-carbohydrate diet (6), (7).
5. Cancer
Cancer, mainly breast and cervical cancer, is the second leading cause of death in women.
Whey concentrate and glutathione modulation is used in cancer treatment. Consumption of whey powder during chemotherapy can help inhibit the growth of cancer cells. It is also an excellent meal for cancer patients as it is easy to digest. It also gets easily absorbed in the body. It provides energy and increases immunity (8), (9).
6. Heart Health
Heart stroke causes paralysis, loss of speech and poor memory. It is also the third leading cause of death in women. Whey protein lowers the LDL cholesterol (which is a contributing factor to cardiovascular diseases such as strokes). It reduces blood pressure and also reduces the risk of heart diseases and stroke (10), (11).
7. Immunity
One of the best whey protein benefits is boosting immunity. Whey protein improves immune response and helps fight infections in women. It boosts the immune system by increasing the production of glutathione. This is a powerful antioxidant which helps in detoxification. Women suffering from asthma should be supplemented with whey protein to improve their cytokine responsei An excessive immune response where too many immune-system-modulating cells are released into the bloodstream, causing harm to the body. (12), (13).
8. Strengthening Muscles
Whey protein is required for repairing, strengthening, and muscle building. Workout and daily exercises deplete the energy levels in the body, leading to muscle deterioration. Whey protein comes from cow’s milk and is a great natural protein for building and repairing muscles (14).
9. Healthy Nails And Skin:

A woman’s body requires protein to generate healthy skin and nails. Whey protein may help the body to create hormones and vital enzymes to keep them running efficiently.
10. Gets Absorbed Quickly
Whey protein shakes are recommended more than any other form of whey protein. Protein shakes contain high amounts of nutrients in the form of soy, whey or caseini A tasteless, odorless white solid used in food, medicine, and cosmetics, which is the main protein in cow's milk and cheese. . It gets easily digested in the body than the protein in foods. It also contains the highest Biological Valuei The measure of how effectively protein is utilized in the body for growth and maintenance on the basis of consumption and absorption. (BV) (15).
11. Blood Sugar Level
Whey protein gives the body a positive nitrogen balance. It also prevents fluctuations in the blood sugar levels which can lead to overeating. Whey protein has low levels of fats and is very effective for diabetes management. This is very beneficial for managing glucose levels. It also prevents the onset of diabetes. This form of protein also improves insulin resistance in the body to keep its levels steady (16).
12. Well-toned Figure
Whey protein tones the muscles and accelerates metabolism. This gives you a healthy and toned figure.
13. Bone Health
More than 65% of the women suffer from osteoporosis, a condition which causes thinning and increased brittleness of bones. To build and maintain healthy bones, women need to consume calcium-rich healthy food. Whey protein improves absorption of calcium which prevents bone loss and keeps them strong (17).
14. Liver
Whey protein, when taken in moderate quantities, supports the functioning of the liver and when consumed in moderation, may have a protective effect on it (18). The liver carries about 500 functions in the body. This would be impossible without the presence of amino acids in it.
15. Healing
Whey protein is an excellent protein choice for women. This is especially true for those who have undergone surgeries. It assists in healing wounds and gets absorbed easily into the body (19).
Whey Protein For Healthy Hair And Skin
Here are the top benefits for your skin and hair.
16. Promotes Hair Growth:
The importance of protein for hair growth cannot be overstated, as it forms a very important constituent of hair, as the hair itself is made up of protein. A deficiency in protein can result in major hair loss problems. Whey protein is a convenient way to increase protein intake in your diet. Having high amounts of protein on a regular basis prevents hair loss and promotes hair growth. Taking whey shakes helps overcome hair problems like bald patches and receding hairlines (20).
17. Helps Strengthen Skin
Collagen is a structural tissue which provides elasticity to the skin. It comprises 30 percent of the body’s total protein and helps strengthen skin, blood vessels, bones and teeth. Consuming whey protein may improve collagen synthesis to keep your skin firm and healthy (21).
18. Promotes Healthy Scalp:
Regular consumption of whey nourishes and strengthens the hair to give you thick, healthy and shiny hair. The acidic properties of whey cure dandruff and scalp psoriasis. This helps to improve the health of the scalp. However, there is a lack of scientific studies and evidence in this regard.
.
19. Maintains Skin Elasticity:
Amino acids in whey protein help maintain the elasticity and firmness of the skin.
20. Acts As Conditioner:

You can also use whey powder in place of your shampoo. Just rub some powder thoroughly on the scalp. Wash it off with lukewarm water to get a clean and oil-free scalp. Alternatively, you can shampoo first and follow it with a whey rinse. Leave it for 10 minutes and then wash off. Whey conditioner will add great texture and body to the hair. It is very useful for fine and limp hair, as it does not weigh down the hair like other hair products.
21. Homemade Toner:
Whey can be used on the skin as a cleanser, toner and moisturizer. Several cosmetic companies incorporate this protein-rich supplement for its amazing skin benefits. Soak a cotton ball in whey. Apply it on the face using gentle strokes. This will work as an amazing homemade toner.
22. Fights Acne:
The anti-microbial properties of whey works amazingly on acne and pimples. It also helps lighten pigmentation and age spots.
23. Restore Skin’s pH Value:
Add 2 cups of whey in your bathtub and soak yourself in it for 20 minutes. The acidity in whey will restore the pH value of the skin to rejuvenate the skin cells and provide effective inflammation reduction properties.
24. Good For Eyes:
For tired or puffy eyes, wet a tea bag with cold whey and place it over on the eyes. Leave it for 20 minutes to get refreshed eyes.
Whey Protein Uses

Whey protein is available in various forms like whey protein bars, whey protein shakes and whey drinks. Whey itself does not have a very appealing taste. Hence it is mixed with other foods like fruits and nuts to make the taste more appealing. Check out whey protein uses here:
- A whey protein shake with raspberries and avocado is the perfect way to start your day. Make sure that the whey protein you get is from grass fed cows and not corn-fed cows. The latter can cause allergies.
- Add a teaspoon of whey powder to your cookies while baking. This will increase the protein levels in your body. You can also add chocolate whey to your coffee to make a delicious mocha.
- It takes a minute to prepare this protein rich drink. Mix one scoop of whey protein into 6 ounces or 200 ml of water. Leave aside the mixed protein for a few minutes. This will help the powder get completely dissolved. Drink this water.
- Whey protein is best consumed immediately after a tiring workout. This will provide your muscles and cells the proper nutrition they need to repair. You can add whey protein to your oats, cereals and pancakes for a protein rich breakfast.
- If you’re looking for a quick snack at work, prepare a whey protein shake with some nuts, fruits and ice cubes for a nutritious and delicious shake.
- Stir one scoop of protein powder to your yoghurt and top it with fruits, nuts and chocolates for a tasty treat. You can also mix whey powder with your favorite ice-cream.
- Use whey, instead of water, while cooking pasta or soups to give it a distinct taste. You can also use whey to make bread. This will give it a wonderful brown crust and aroma.
 Quick Tip
Quick TipThis was about whey protein benefits and uses, now let’s look into some of the side effects of whey protein.
Whey Protein Side Effects
Like other supplements, whey protein has some health risks associated with it. Here are a few side effects of whey protein.
- Most of the side-effects associated with whey protein are related to digestive issues like gastritis, bloating, headaches, cramps, reduced appetite, nausea and fatigue. Rocco, a fitness blogger shared his experience after using whey protein in his blog. He mentioned that his gut had not been in the healthiest state and whey protein didn’t agree with him. Talking about consuming a high-calorie diet with whey protein, he said, “That much food in one day only puts more stress on my stomach too, I felt groggy in the morning and going into my workout I felt sluggish (i).” He went on to add, “A weight gainer every morning was not agreeing with my body.”
- If you’re experiencing any of these symptoms, it is most likely to be either due to the lactose or artificial sweeteners present in whey protein.
- Excess consumption of protein can even exacerbate kidney problems.
- Too much of the protein can deplete a body’s store of calcium, leading to brittle bones and teeth.
- Also, high amounts of protein can cause a woman’s body to produce excess ammonia.
- Women should not consume more than two servings of protein shakes per day.
- Extreme high dosage can also overload the liver, causing serious health problems.
Therefore, before adding whey protein to your diet, particularly if you have existing health conditions or are on medication, consult a healthcare professional to ensure it meets your specific health needs.
Whey and casein are two very popular protein supplements. But how are they different from one another? Find out in the next section.
Whey Vs. Casein Protein
| Whey Protein | Casein |
|---|---|
| It is rapidly digested, making it a favorite post-workout option for muscle repair and growth. | It is slow-digesting and gradually releases amino acids to ensure a prolonged protein supply, making it ideal for nighttime or between meals. |
| Whey protein is rich in branched-chain amino acids (BCAAs) like leucine that stimulates muscle protein synthesis (22), (23). | Casein releases amino acids over an extended period due to its clotting property in the stomach (24), (25). |
| It is used for quick muscle recovery within hours. | It is used in overnight recovery products. |
While whey provides immediate protein replenishment, casein offers a sustained release, making them both valuable for muscle building and recovery.
Infographic: How To Prepare Whey Protein Shake
Whey protein is one of the purest forms of protein that has several benefits for your health. It helps reduce the signs of aging, aids in weight loss, lowers cholesterol levels, and improves immunity. Check out the infographic below to learn how to prepare a whey protein shake to reap its maximum benefits.
Some thing wrong with infographic shortcode. please verify shortcode syntax
Whey protein benefits are numerous. It can positively affect health, hair, and skin. It can improve hormone levels in women and also aid in muscle repair and recovery. It slows down the signs of aging and aids in weight loss by promoting satiety. Whey protein also reduces cancer risk and boosts heart and bone health. It also improves immunity. It promotes hair growth, strengthens the skin, maintains skin elasticity, and promotes a healthy scalp. However, excess consumption may trigger a few undesirable effects like digestive issues, kidney problems, and brittle bones. Hence, moderate consumption is advised for maintaining skin health, cardiovascular health, and digestive health.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can I drink whey protein without working out?
Yes, you can take whey protein without engaging in an intense workout. Ensure that you take it in moderation and as per your nutritional needs.
Does whey protein make your face fat?
Consuming whey protein in moderation along with physical exercise will not make your face fat.
How long does it take for whey protein to leave your system?
It may take between 2 to 4 hours for whey protein to be digested.
What happens when I stop taking whey protein?
When you stop taking whey protein and continue with physical exercise, you will start to lose weight.
Discover the scientific truth behind the benefits and side effects of whey protein with this informative video. Also learn how to maximize your gains and stay safe.
Personal Experience: Source
StyleCraze's articles are interwoven with authentic personal narratives that provide depth and resonance to our content. Below are the sources of the personal accounts referenced in this article.
i. My Experience with whey proteinhttps://rlosurdo97.wordpress.com/2015/12/06/my-experience-with-whey-protein/
References
Articles on StyleCraze are backed by verified information from peer-reviewed and academic research papers, reputed organizations, research institutions, and medical associations to ensure accuracy and relevance. Read our editorial policy to learn more.
- Protein – Which is Best?
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3905294/ - Effect of whey protein supplementation on body composition changes in women: a systematic review and meta-analysis
https://academic.oup.com/nutritionreviews/article/76/7/539/4982765?login=true#117877726 - Branched chain amino acids and their importance in nutrition
https://www.researchgate.net/publication/282332420_Branched_chain_amino_acids_and_their_importance_in_nutrition - The biological activity of undenatured dietary whey proteins: role of glutathione
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/1782728/ - Glutathione and its antiaging and antimelanogenic effects
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5413479/ - Whey Protein Supplementation Enhances Body Fat and Weight Loss in Women Long After Bariatric Surgery: a Randomized Controlled Trial
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27885532/ - A whey-protein supplement increases fat loss and spares lean muscle in obese subjects: a randomized human clinical study
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2289832/ - Whey protein in cancer therapy: A narrative review
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31005617/ - Clinical Impact of Highly Purified Whey Proteins in Patients Affected With Colorectal Cancer Undergoing Chemotherapy: Preliminary Results of a Placebo-Controlled Study
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6681246/ - Acute effects of whey protein isolate on cardiovascular risk factors in overweight post-menopausal women
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/20561625/ - The effects of whey protein on cardiometabolic risk factors
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23167434/ - Dietary Whey Protein Supplementation Increases Immunoglobulin G Production by Affecting Helper T Cell Populations after Antigen Exposure
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7835905/ - Glutathione Fine-Tunes the Innate Immune Response toward Antiviral Pathways in a Macrophage Cell Line Independently of Its Antioxidant Properties
https://www.frontiersin.org/journals/immunology/articles/10.3389/fimmu.2017.01239/full - Whey protein supplementation and muscle mass: current perspectives
https://www.dovepress.com/whey-protein-supplementation-and-muscle-mass-current-perspectives-peer-reviewed-fulltext-article-NDS - Whey protein
https://www.researchgate.net/publication/313715199_Whey_protein - Effect of whey on blood glucose and insulin responses to composite breakfast and lunch meals in type 2 diabetic subjects
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16002802/ - Functional food relevance of whey protein: A review of recent findings and scopes ahead
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1756464615004570 - Protective effect of whey proteins against nonalcoholic fatty liver in rats
https://www.researchgate.net/publication/51047831_Protective_effect_of_whey_proteins_against_nonalcoholic_fatty_liver_in_rats - Wound healing: time to look for intelligent ‘natural’ immunological approaches?
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5499069/ - Diet and hair loss: effects of nutrient deficiency and supplement use
https://www.researchgate.net/publication/316012307_Diet_and_hair_loss_effects_of_nutrient_deficiency_and_supplement_use - Contraction mode and whey protein intake affect the synthesis rate of intramuscular connective tissue
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27603578/ - Isolated branched-chain amino acid intake and muscle protein synthesis in humans: a biochemical review
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6718193/ - Elucidating the underlying mechanism of amino acids to regulate muscle protein synthesis: Effect on human health
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0899900722002106 - Formation of a structured clot during the gastric digestion of milk: Impact on the rate of protein hydrolysis
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0268005X15300333 - Casein Protein Processing Strongly Modulates Post-Prandial Plasma Amino Acid Responses In Vivo in Humans
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7468913/
Read full bio of Bulelani Makapela
Read full bio of Tanya Choudhary
Read full bio of Ravi Teja Tadimalla
Read full bio of Moksha Gandhi

























Community Experiences
Join the conversation and become a part of our empowering community! Share your stories, experiences, and insights to connect with other beauty, lifestyle, and health enthusiasts.