Everything You Need to Know About Using Biotin For Your Skin
Harness the less-known magic of biotin for skin to get youthful and clear skin.

Image: Shutterstock
Biotin is a nutrient that helps promote hair and nail health. However, many use biotin for skin-related issues, owing to its claim to improve skin texture. But how does it work? How to use biotin? Are these claims true? In this article, we will answer all your queries. Keep reading to know more.
In This Article
What Is Biotin?
The word “biotin” originates from the Greek word “biotos,” which stands for “life” or “sustenance.” It is also known as vitamin B7 or vitamin H, with H standing for “Haar und Haut,” which is German for “hair and skin.”
Biotin is one among the eight vitamins that constitute the B complex vitamins. These assist the body in converting food into energy. It is a key ingredient in the enzymes that break down carbohydrates, fats, and amino acids to form fatty acids and glucose. Biotin also supports a range of other bodily functions like supporting your nervous system health and maintaining embryonic growth during pregnancy.
 Did You Know?
Did You Know?Biotin is primarily known for its skin benefits. It is one of the vital vitamins for glowing skin and can enhance your skincare routine.
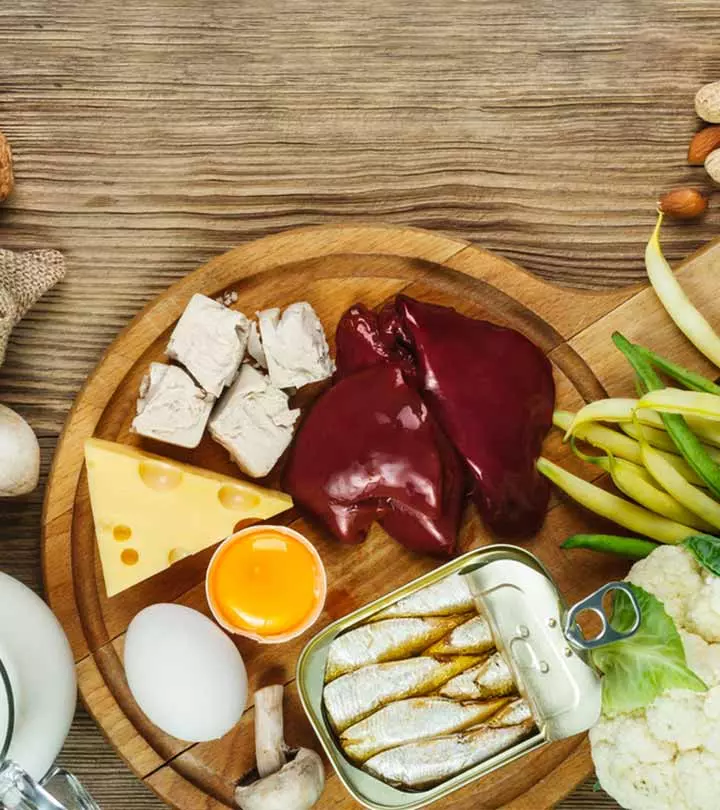
Biotin is readily available in naturally occurring foods. You can meet your daily requirement of the nutrient by consuming a varied diet. Some of the best sources of biotin include:
- Whole eggs, especially the yolk
- Legumes like beans, peas, soybeans, and lentils
- Organ meats, like liver and kidneys
- Nuts like almonds, peanuts, pecans, and walnuts
- Seeds like sunflower and pumpkin seeds
- Fatty fish like salmon and tuna
- Sweet potatoes
- Mushrooms
- Bananas
- Broccoli
- Nutritional and Brewer’s yeast
- Avocados
- Dairy and dairy products like cheese and yogurt
- Oatmeal
- Apples
Biotin for skin is also commercially available in different forms:
- Biotin oil
- Biotin supplements
- Biotin pills or tablets
- Dissolvable biotin powder
- Biotin serum
Understand more about biotin deficiency in the next section.
Key Takeaways
- Biotin is a B complex vitamin that helps smoothen the skin and combat signs of aging and acne.
- Pregnancy, medications, alcohol consumption, and genetic conditions may result in biotin deficiency.
- You can include whole eggs, legumes, mushrooms, bananas in the diet to obtain the required biotin.
- You can also take biotin supplements with a doctor’s advice.
Causes And Effects Of Biotin Deficiency
Biotin deficiency, albeit rare, can be caused due to:
- Medications like antibiotics, anti-seizure drugs, beta-blockers, retinoids, and blood thinners that can impair the body’s ability to absorb vitamins correctly
- Pregnancy, where biotin levels may drop temporarily (1)
As per the worldwide neonatal screening survey, biotin deficiency is prevalent in pregnancy, and it affects half of the pregnant women in the US despite sufficient dietary intake. Profound biotinidase deficiency occurs in 1 in 112,271 births, while partial deficiency occurs in 1 in 129,282. The global incidence rate is 1 in 60,089 live births, but it varies based on genetics and alcohol consumption.
- Chronic gastrointestinal conditions such as colitis and Crohn’s disease that hamper vitamin uptake ( 2)
- Excessive consumption of raw egg whites, which contain avidin, a protein that blocks biotin absorption (3)
- Alcohol abuse and resultant cirrhosis (4)
- Intravenous feeding
- Long-term dieting where rich sources of vitamins and minerals are off the plate
- Deficiency of biotinidase, a hereditary disorder that prevents the body from reusing biotin (5)
- Other genetic conditions like phenylketonuria, biotin transport deficiency, and holocarboxylase synthetase deficiency (6), (7)
This deficiency in biotin could lead to symptoms like (3):
- Red, scaly rashes, especially around the eyes, nose, and mouth
- Parched and flaky skin
- Brittle nails
- Dry skin
- Depression symptoms
- Conjunctivitis
- Numbness and pins and needles in the arms and legs
- Constant fatigue
- Hallucinations
How Is Biotin Good For The Skin?
As discussed, biotin deficiency could lead to scaly red rashes and make skin dry and flaky. Several enzymes rely on biotin to function correctly. The energy produced by the vitamin plays a crucial role in nourishing the skin.
Biotin has multiple skin benefits. Let us explore them now.
1. May Smoothen Skin Texture
Those with a biotin deficiency may experience red and scaly rashes. But one may reverse such symptoms with adequate biotin intake. A study discovered that infants with dermatitis, rash, and alopecia showed remarkable improvements after taking 100 mcg to 10 mg of biotin daily. In another study, daily supplementation of 1 mg of biotin had improved the symptoms of dermatitis in infants (8). However, more studies in adult humans are warranted to further understand this benefit.
2. May Improve Skin Barrier Function
Carboxylase enzymes are responsible for metabolizing fatty and amino acids, which are dependent on biotin (9). Biotin triggers the release of carboxylase enzymes that then digest lipids to improve the skin permeability barrier and its antimicrobial barrier function (10). Biotin also is believed to support the mucous membrane and further strengthen the skin against environmental aggressors.
3. May Help Clear Acne
Biotin may be useful to treat comedonal acne (11). It also may help control skin flaking and irritation associated with acne. However, more information in this regard is warranted.
4. May Promote Younger Skin
While the correlation between biotin and collagen is yet to be well studied, some believe the nutrient helps boost skin cell turnover rate. This could result in youthful skin. However, more research is warranted in this regard.
How To Use Biotin For The Skin?
You can obtain your recommended dose of biotin by consuming a balanced diet. Hence, your first line of action should be to review your diet and incorporate biotin-rich foods like whole grains, cheeses, liver, etc. Also, consume foods in a raw or minimally-processed manner.
You can also consider biotin supplements available as over-the-counter tablets or capsules. It is highly recommended that you first consult a physician rather than self-administering any supplement. It also is vital that you read the information available on the package and only purchase from established and authentic suppliers. Typically, biotin supplements are taken with food.
Frequency Of Using Biotin For The Skin
The recommended daily intake of biotin is around 30 mcg per day ( 12). However, the dosage largely depends on the individual’s age, sex, and dietary patterns. For instance, the average diet of the Western population delivers 35 to 70 mcg of biotin per day.
The Food and Nutrition Board (FNB) suggests that the adequate intake of biotin be around (13):
- 5 mcg between birth and 6 months
- 6 mcg between 7 to 12 months
- 8 mcg between 1 to 3 years
- 12 mcg between 4 to 8 years
- 20 mcg between 9 to 13 years
- 25 mcg between 14 to 18 years
- 30 mcg for those over 19 years of age
Pregnant women should take 30 mcg of biotin, which should increase to 35 mcg during lactation. Higher doses of biotin may be prescribed by dermatologists for nail and hair problems.
While biotin has important benefits for the skin, it may also cause some adverse effects.
Side Effects Of Biotin
Biotin is a water-soluble vitamin. Hence, higher concentrations of biotin are usually flushed out from the body. Biotin toxicity is extremely rare.
However, unmonitored biotin supplementation may cause acne breakouts, a drop in blood glucose levels, and an upset stomach. But these side effects are sporadic and are based on anecdotal evidence. It is nonetheless important to follow the right dosage while taking biotin supplements.
Crystal Smith, a YouTuber, shared her experience with consuming biotin supplements daily. She used the supplement mainly to improve the condition of her hair but suffered from severe breakouts. In her vlog, she said, “Every couple of days I would have a group of acne everywhere on my face, and when they went away, they didn’t just go away silently as if they were never there. I would always have the scars (i).”
How Long Does Biotin Take To Show Results?
Even though research is quite limited, studies suggest that biotin may take anywhere between 90 to 180 days to show results (improved skin smoothness and moisture, and better hair shine) (14).
 Pro Tip
Pro TipHowever, this is only a rough estimate. Most individuals may not see any significant changes in their skin condition until a few good months since they have upped their biotin intake. The key to achieving more effective results is maintaining consistency.
Biotin is an essential vitamin with several benefits for your skin, hair, and nails. You can use biotin for skin-related issues as it helps improve skin texture, strengthen the skin barrier, clear acne, and promote youthful skin. To incorporate biotin into your lifestyle, you can start consuming biotin-rich foods, supplements, powder, serum, or oil. Always consult a doctor before taking supplements, as it will help you decide the dosage and administration method. If you are consistent and patient, you may begin to see the results within a few months.
Frequently Asked Questions
Will biotin cause facial hair growth?
Biotin may cause facial hair growth. However, if you do not have facial hair, it will not contribute to new growth. It may increase the rate of growth in people who already have facial hair.
Does biotin help with wrinkles?
Yes, biotin may help reduce wrinkles and improve the appearance of the skin (15).
Is biotin the same as collagen?
No. Collagen is a protein, and biotin is an essential vitamin. While the body can naturally produce collagen, it cannot produce biotin.
Does biotin increase weight?
There is no scientific evidence that biotin increases weight.
Is biotin good for thyroid?
It is seen that biotin has no impact on thyroid hormonal levels or its function in the body. However, research indicates that it can interfere with laboratory results associated with thyroid tests. It may give wrong results by showing high levels of T3 (triiodothyronine) and T4 (thyroxine) and low levels of thyroid-stimulating hormone that may lead to wrong diagnosis (16).
Can biotin cause dandruff?
Lack of biotin may affect the health of the scalp and turn it dry and flaky. However, biotin cannot cause dandruff. Dandruff is caused by the proliferation of Malassezia yeast and biotin contains antifungal properties which in turn may help improve the condition (17).
Taking biotin for promoting skin health is fine, but taking them may lead to adverse effects such as acne. The following video explains the reasons and explores certain tips to taking biotin in the correct way. Check it out to now!
Personal Experience: Source
StyleCraze's articles are interwoven with authentic personal narratives that provide depth and resonance to our content. Below are the sources of the personal accounts referenced in this article.
(i) ✨My Experience Taking Biotin✨https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=EpLxAr3wV2I
References
Articles on StyleCraze are backed by verified information from peer-reviewed and academic research papers, reputed organizations, research institutions, and medical associations to ensure accuracy and relevance. Read our editorial policy to learn more.
- Marginal biotin deficiency during normal pregnancy1,2,3
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1426254/ - Micronutrient Deficiency in Inflammatory Bowel Diseases: Cause or Effect?
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7212480/ - Biotin Deficiency
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK547751/ - Inhibition of intestinal biotin absorption by chronic alcohol feeding: cellular and molecular mechanisms
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3064116/ - Biotinidase Deficiency
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK1322/ - Nutritional therapy for selected inborn errors of metabolism
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/2681328/ - HOLOCARBOXYLASE SYNTHETASE DEFICIENCY
https://omim.org/entry/253270 - Biotin deficiency in an infant fed with amino acid formula
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15863846/ - Structure and function of biotin-dependent carboxylases
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3508090/ - The outer frontier: the importance of lipid metabolism in the skin
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2674689/ - Biotin: overview of the treatment of diseases of cutaneous appendages and of hyperseborrhea
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31638351/ - Biotin
https://ods.od.nih.gov/factsheets/Biotin-HealthProfessional/ - Dietary Reference Intakes for Thiamin, Riboflavin, Niacin, Vitamin B6, Folate, Vitamin B12, Pantothenic Acid, Biotin, and Choline
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK114310/pdf/Bookshelf_NBK114310.pdf - A Double-blind, Placebo-controlled Study Evaluating the Efficacy of an Oral Supplement in Women with Self-perceived Thinning Hair
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3509882/ - A Randomized Double-Blind Evaluation of a Novel Biotin and Silicon Ingredient Complex on the Hair and Skin of Healthy Women
https://www.longdom.org/open-access/a-randomized-doubleblind-evaluation-of-a-novel-biotin-and-silicon-ingredient-complex-on-the-hair-and-skin-of-healthy-women-61185.html - Biotin induced biochemical hyperthyroidism: a case report and review of the literature
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC10304644/ - Ketoconazole beyond antifungal activity: Bioinformatics-based hypothesis on lipid metabolism in dandruff and seborrheic dermatitis
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34816495/
Read full bio of Dr. Sameeksha Chand
Read full bio of Arshiya Syeda
Read full bio of Ramona Sinha
Read full bio of Monomita Chakraborty





















Community Experiences
Join the conversation and become a part of our empowering community! Share your stories, experiences, and insights to connect with other beauty, lifestyle, and health enthusiasts.