Bulking Diet: What To Eat And Avoid, Meal Plans, And Recipes
Discover the secrets of bulking up your muscles with precision nutrition.

Image: Shutterstock
Bulking is a popular term in the fitness world often associated with gaining muscles to add size. Usually, athletes and bodybuilders go on a bulking diet for muscle growth, strength gains, and overall physique enhancement. This diet aims at providing your body with additional calories and specific nutrients and is ideal for anyone who wants to gain muscles and increase their body size.
In this article, we discuss the different types of bulking diets, foods you need to eat and avoid, recipes, additional tips, and more. Keep reading to learn more.
 At A Glance: The Bulking Diet
At A Glance: The Bulking Diet- Principle: Emphasizes consuming foods at a strategic calorie surplus but avoiding excess unhealthy fats.
- Purpose: To gain muscle mass.
- Who It Is For: Professional bodybuilders, athletes, and individuals who want to bulk up and gain lean muscle.
- Duration: Short-term
- Who Should Avoid: Individuals with excess body fat
- Cons: May increase body fat and lead to risks of cardiovascular diseases and diabetes.
In This Article
What Is Bulking?
Bulking is a strategic way of strength training and building your muscles. It is a phase where bodybuilders and athletes aim to promote muscle growth by going on a calorie surplus. The bulking diet helps increase muscle mass, build strength, and achieve a more muscular appearance. Let’s learn more about it in the next section.
Key Takeaways
- The bulking diet involves consuming surplus calories to promote muscle growth and strength.
- There are three types of bulking diets – clean, big, and dirty, each with varying caloric and food recommendations.
- Maintain an ideal macronutrient ratio during the bulking diet. Consume 55-60% carbs, 25-30% proteins, and 5-20% fats for bulking.
- Prioritize nutrient-dense foods, avoid excessive junk food, and adjust calorie intake for effective and healthy bulking.
What Is A Bulking Diet?

A bulking diet is about consuming calorie-dense foods to gain weight and muscle mass. The diet and meal plan may differ based on the individual’s preferences and health requirements. A bulking diet is a specialized form of a bodybuilding diet, aimed at increasing muscle mass by providing higher calorie intake, rich in proteins, fats, and carbohydrates.
A study involving male bodybuilders found that increased calorie intake combined with resistance training increases muscle mass and body fat. The study observed that increasing the total daily calorie intake by 10-20% and consuming a surplus of 500 calories per day gave significant results (1).
The surplus calories above your regular calorie intake will differ according to your gender, fitness goals, and nutritional requirements. Depending on that, you may go for any of the three bulking dites – clean bulking, big bulking, and dirty bulking. They differ in terms of diet quality and food choices. Check out the next section to learn more about them.
Types Of Bulking Diets
1. Clean Bulking
This dietary approach prioritizes the quality of food over the calories. In this diet, you consume moderate amounts of extra calories from whole foods. It helps reduce body fat and promotes slower and steady weight gain compared with other bulking diets. Individuals who prefer to stay lean, like gymnasts, boxers, and athletes, usually prefer this diet. It involves the intake of lean protein, complex carbohydrates, healthy fats, and other nutritious foods. One may steadily gain 0.5 to 1 pound per week when on this diet.
2. Big Bulking
Big bulking is also known as regular, aggressive, or conventional bulking. The key is to maximize muscle growth by consuming more calories than your daily requirements. However, it may also lead to quick fat accumulation. You may try big bulking if you have a fast metabolism and tend to lose weight more quickly than gain it.
3. Dirty Bulking
Just as it sounds, dirty bulking involves gaining maximum size in minimum time. It encourages consuming as many calories as possible. Sometimes these calorie-rich foods lack healthy nutrition. These dirty bumps may accelerate weight gain and promote muscle growth. However, this approach also results in significant fat accumulation as you are eating high-calorie, low-nutrient “junk food” on this diet.
When selecting a bulking diet, it is best to consult a registered dietitian to ensure you are getting the recommended portions and learning the proper diet techniques.
A bulking diet is often part of a larger weight gain diet plan, specifically tailored to help individuals increase muscle mass while managing fat gain. You can distribute the surplus calories among different macronutrients such as protein, carbs, and fats. Check out the next section to know what foods to include in your bulking diet.
Foods To Eat On A Bulking Diet

A well-structured bulking diet focuses on incorporating high calorie foods for weight gain to ensure you’re consuming enough energy to support muscle growth and recovery. According to one study, the ideal macronutrient ratio for a bulking diet for bodybuilders is roughly as follows (2):
- Carbohydrates: 55-60%
- Proteins: 25-30%
- Fats: 15-20%
This ratio may differ slightly based on your body and health goals.
Protein
Proteins are essential for building tissues, regulating hormones, transporting molecules in the body, supporting the immune system, and more functions in the body (3).
Building muscles requires sufficient protein intake. You may consume at least 0.8 g of protein for every 1 kg of your body weight (4). However, for an extensive bulking diet, you may need to consume about 1.6-2.2 g of protein per kg of your body weight (5).
Include these protein-rich foods in your healthy bulking diet:
- Lean meats: Beef, lamb, veal, and pork.
- Fish and seafood: Fish, crab, lobster, prawns, oysters, mussels, scallops, clams, etc.
- Poultry: Chicken, eggs, turkey, duck, emu, goose, and bush birds.
- Nuts and seeds: Peanuts, walnuts, almonds, pine nuts, macadamias, hazelnuts, cashews, sesame seeds, pumpkin seeds, sunflower seeds, etc.
- Dairy products: Greek yogurt, milk, and cottage cheese.
- Legumes and beans: All beans, chickpeas, lentils, split peas, soy, and soy products such as tofu.
 Pro tip
Pro tipCarbohydrates
Carbohydrates are essential macronutrients that provide energy for the body, support brain and muscle function, help regulate metabolism, and may influence blood sugar control (6).
Consume at least 3–5 g of carbohydrates per kilogram of your body weight per day to meet your energy needs during resistance exercise while bulking up (5). Include these carbohydrate-rich foods in your diet for bulking:
- Grains: Buckwheat, amaranth, wild rice, quinoa, barley, and oats.
- Fruits: Apples, berries, mangoes, bananas, melons, oranges, etc.
- Dairy products: Milk and yogurt.
- Legumes: Lentils, dried beans, peas, etc.
- Starchy vegetables: Potatoes, corn, and peas.
Fats
Fats are essential nutrients that provide energy, support cell growth, and help absorb certain vitamins in the body (7).
Consume fat in a moderate quantity when bulking up, keeping it in the range of 0.5–1.5 g per kg of your body weight per day (5). Include these fat-rich foods when trying to gain weight:
- Fish: Atlantic salmon, trevally, mackerel, Southern bluefin tuna, and sardines.
- Fruits: Avocados
- Dairy: Milk, yogurt, cheese, etc.
- Meat: Beef and lamb.
- Oils: Olive oil, coconut oil, etc.
- Nuts and spreads: Peanuts, hazelnuts, cashews, margarine, almonds, etc.
Bulking up may look easy on the surface as all you need to do is consume more calories. However, excessive consumption of unhealthy fats and carbs can cause a lot of health problems. Move to the next section for a list of foods to avoid while on a healthy bulking diet.
Foods To Avoid On A Bulking Diet

Overeating carbs and saturated and trans fatty acids may increase your risk of coronary heart disease (8). Moreover, this may lead to the accumulation of more fat than healthy muscular weight. This is why bodybuilders should limit their consumption of unhealthy fats.
Be careful with the intake of the following foods when on a bulking diet:
- Processed sugary snacks: Candies, pastries, and sugary cereals.
- Sugary beverages: Soda, packaged fruit juices with added sugar, and energy drinks.
- Junk food: Fast foods such as burgers and pizza with excessive cheese and toppings, deep-fried foods, potato chips, etc.
When it is challenging to achieve nutritional demands with whole meals alone, supplements might help you bulk more effectively. Branched-chain amino acids (BCAAs), which help to reduce muscle fatigue and promote recovery, creatine, which increases strength and performance, and whey protein, which stimulates muscle growth and repair, are common supplements. Incorporating these supplements strategically alongside a well-balanced diet can optimize your results and help you achieve your bulking goals more efficiently.
Now that you have curated a list of the foods to include and avoid, it is time to explore the sample meal plans. Keep scrolling for 6-meal sample diet plans for a clean, big, and dirty bulking diet.
Bulking Diet Meal Plans
Meal Plan For Clean Bulking
Meal 1: Breakfast
- 3 scrambled eggs with 1 cup of spinach and tomatoes
- 2 whole-grain toast
- 1 cup of fresh fruit salad
Meal 2: Mid-Morning Snack
- 6 oz of Greek yogurt with ½ cup of honey and berries
Meal 3: Lunch
- 4-6 oz of grilled chicken breast
- 2 cups of mixed green salad
- ½ cup of quinoa
- Meal 4: Afternoon Snack
- ½ cup of cottage cheese with pineapple chunks
Meal 6: Evening Snack
- ¼ cup of mixed nuts
Meal 6: Dinn
er
- 4-6 oz of baked salmon with lemon and dill
- 1 cup of steamed broccoli and carrots
- ½ cup of brown rice
Meal Plan For Big Bulking
Meal 1: Breakfast
- 4 eggs (boiled or scrambled)
- 2 slices of whole-wheat toast
- 1 avocado
- 1 banana
Meal 2: Mid-Morning Snack
- 1 cup of Greek yogurt
- 1/2 cup of berries
- 1/4 cup of nuts
Meal 3: Lunch
- 6 oz of grilled chicken breast
- 1 cup of brown rice
- 1 cup of steamed broccoli
Meal 4: Afternoon Snack
- 1 protein shake (whey or vegan)
- 1 cup of fruit
Meal 5: Evening Snack
- 6 oz of grilled salmon
- 1 cup of quinoa
- 1 cup of roasted vegetables
Meal 6: Dinner
- 1 cup of oatmeal
- 1/2 cup of berries
- 1/4 cup of nuts
Meal Plan For Dirty Bulking
Meal 1: Breakfast
- 2 cups of sugary cereal
- 1 cup of whole milk
- 1 banana
Meal 2: Mid-Morning Snack
- 1 peanut butter and jelly sandwich
- 1 bag of chips
- 1 can of soda
Meal 3: Lunch
- 2 slices of pizza
- 1 order of fries
- 1 glass of milkshake
Meal 4: Afternoon Snack
- 1 candy bar
- 1 bag of cookies
- 1 can of soda
Meal 5: Evening Snack
- 1 double cheeseburger
- 5.9 oz of French fries
- 1 chocolate milkshake
Meal 6: Dinner
- 1 bowl of pasta with tomato sauce
- 1 slice of garlic bread
- 1 can of soda
Streamline your bulking diet with efficient meal preparation. Buy high-quality storage containers, cook in bulk, and schedule your meals around your exercise routine. In addition to saving time, this technique guarantees that you always have nutrient-dense meals on hand, which lessens the temptation to go for junk food.
Some essential tips will help with making your bulking process more effective. Explore them in the following section.
Tips For A Bulking Diet

- Distribute protein intake evenly throughout the meals, especially within one hour after the resistance training (9).
- Opt for nutrient-dense whole foods over empty calories.
- Ensure you consume enough calories to support your bulking goals, typically 200-400 calories above maintenance levels.
- Balance fiber intake, as too much fiber, can reduce appetite and make you feel too full when bulking (10).
- Supplement wisely with proven options like creatine and protein powder. Do not take supplements without consulting a doctor (11).
- Consider calorie-dense shakes to increase calorie intake.
- Set realistic goals to avoid stress on the digestive system, as a bulking diet involves eating a lot.
- Combining a bulking diet with exercises to gain weight can help you build muscle mass effectively by providing the necessary nutrients and energy for muscle growth.

Following these dietary guidelines may help speed up your bulking journey. So, it calls for the most important part of this diet – eating! Jump to the next section for some delicious recipes.
Bulking Diet Recipes
1. Grilled Chicken And Rice Bowl
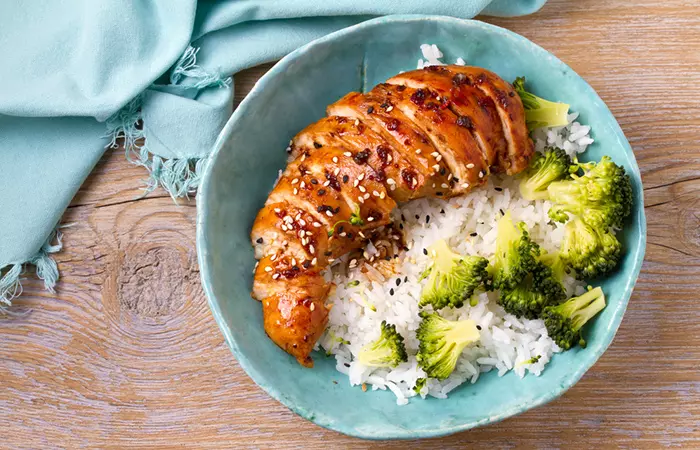

Ingredients
- 6 oz (170g) of boneless, skinless chicken breast
- 1 cup of cooked brown rice
- 1 cup of steamed broccoli
- 2 tablespoons of olive oil
- Salt and pepper to taste
How To Prepare
- Season chicken breast with salt and pepper.
- Grill chicken over medium-high heat for 5-7 minutes per side or until cooked through.
- In a separate pot, cook brown rice according to package instructions.
- Steam broccoli until tender.
- Divide cooked rice, grilled chicken, and steamed broccoli into a bowl.
- Drizzle with olive oil, season with additional salt and pepper if desired, and mix well.
- Serve and enjoy!
2. Beef And Vegetable Stir-Fry
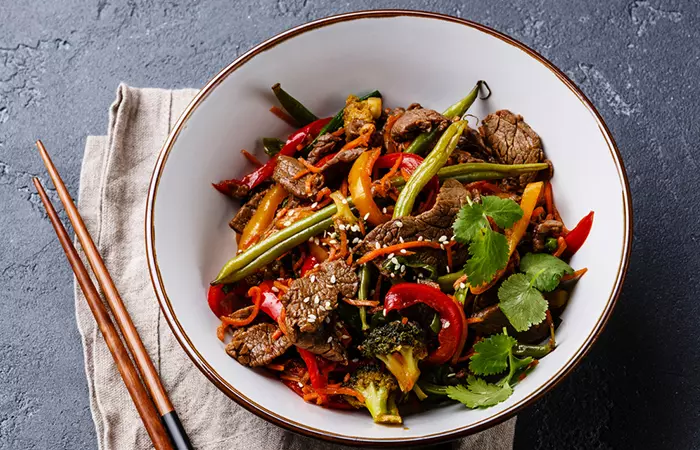

Ingredients
- 8 oz of lean beef (sirloin or flank steak), thinly sliced
- 2 cups of mixed vegetables
- 2 tablespoons of soy sauce
- 1 tablespoon of olive oil
- 1 teaspoon of minced garlic
- Cooked white rice (portion to your preference)
How To Prepare
- Heat olive oil in a pan over medium-high heat.
- Add minced garlic and sliced beef, and stir-fry for 2-3 minutes until beef is browned.
- Add mixed vegetables and continue to stir-fry for 3-5 minutes until they become tender-crisp.
- Pour in soy sauce and stir to coat evenly.
- Serve over cooked white rice.
- Enjoy your beef and vegetable stir-fry!
3. Protein-Packed Oatmeal
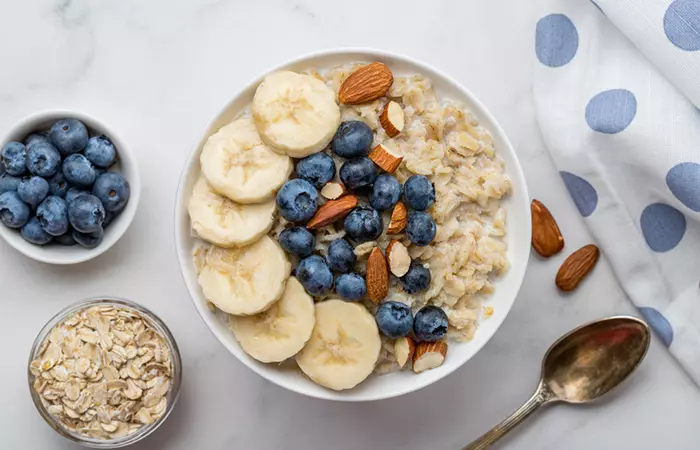

Ingredients
- 1 cup of rolled oats
- 2 cups of milk (dairy or plant-based)
- 1 scoop of your favorite protein powder
- 1 tablespoon of honey or maple syrup
- 1/2 cup of fresh berries
- Sliced bananas and chopped nuts (optional toppings)
How To Prepare
- Combine rolled oats and milk in a saucepan.
- Cook over medium heat, stirring occasionally, until oats are creamy and cooked (about 5-7 minutes).
- Stir in the protein powder and sweeten with honey or maple syrup.
- Top with fresh berries and any optional toppings you prefer.
- Mix everything and serve your protein-packed oatmeal.
A healthy bulking diet is all about having a balanced approach to nutrition. You have to maintain a calorie surplus and include all major nutrients. Avoid processed and junk foods as much as possible and go for healthy fats to up your calorie intake. Consume proteins and carbohydrates to support muscle growth. Moreover, it’s important to work with a registered dietitian to avoid the risk of deficiencies and health issues. Set realistic goals and evaluate your current physique to decide on a complete diet plan suitable for you. Ultimately focus not only on eating, but also on eating better. It will help maximize your muscle growth and reduce fat accumulation.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is 3000 calories a lot for bulking?
No. Consuming 3000 calories can be a suitable starting point for bulking, but adjust based on your individual needs and goals as you progress. Ideally, start with 10-20% more calories in your daily diet (5). Moreover, the metabolism may vary from person to person. Therefore, a 3000-calorie diet might be a lot for some and adequate for others. Consult a doctor before changing your diet.
How long does it take to bulk up?
It may take about 4 weeks of increased energy intake and resistance training to see significant results in bulking up.
Is peanut butter good for adding bulk?
Peanut butter is rich in protein and healthy fats (12). It can be beneficial for bulking if consumed in moderation.
How many months should a beginner bulk?
It may take 6-10 weeks of consistent diet and resistance training for a beginner to start bulking (13). After that, you will need to continue the plan to maintain your body composition.
Can I still do cardio while on a bulking diet?
Cardio exercise may burn more calories than you can afford to lose when trying to bulk up. Therefore, focus on lower-intensity workouts like resistance training.
Should I avoid all junk food while bulking?
You can consume junk foods occasionally when on a bulking diet. However, excess consumption may lead to an increase in bad cholesterol levels and fat accumulation (8).
Illustration: Bulking Diet: What To Eat And Avoid Meal Plans And Recipes

Image: Stable Diffusion/StyleCraze Design Team
The bulking diet is not just about gaining weight and size. It also focuses on improving strength and gaining muscle mass. Watch the video below to learn ways to make the most of this diet.
References
Articles on StyleCraze are backed by verified information from peer-reviewed and academic research papers, reputed organizations, research institutions, and medical associations to ensure accuracy and relevance. Read our editorial policy to learn more.
- Effects of different dietary energy intake following resistance training on muscle mass and body fat in bodybuilders: a pilot study
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6942464/ - Macronutrient considerations for the sport of bodybuilding
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15107010/ - Protein
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6140426/ - Protein for life: Review of optimal protein intake, sustainable dietary sources and the effect on appetite in ageing adults
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5872778/ - Nutrition recommendations for bodybuilders in the off-season: a narrative review
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6680710/ - Physiology, carbohydrates
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK459280/ - Dietary fats
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6628852/ - Saturated and trans fatty acids and coronary heart disease
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/18937892/ - Pre- versus post-exercise protein intake has similar effects on muscular adaptations
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5214805/ - The role of dietary fibers in regulating appetite an overview of mechanisms and weight consequences
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/36193993/ - Creatine in health and disease
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7910963/ - Peanut butter, smooth style, without salt, U.S. Department Of Agriculture
https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/172470/nutrients - Maximizing muscle hypertrophy: a systematic review of advanced resistance training techniques and methods
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6950543/
Read full bio of Mary Sabat
Read full bio of Himanshi Mahajan
Read full bio of Arshiya Syeda
Read full bio of Moksha Gandhi
























Community Experiences
Join the conversation and become a part of our empowering community! Share your stories, experiences, and insights to connect with other beauty, lifestyle, and health enthusiasts.