13 Home Remedies To Lower Creatinine Levels
Small changes, big impact. Improve your kidney health with kitchen ingredients.

Image: shutterstock
Our bodies have natural ways of eliminating waste, but sometimes these processes can malfunction. High creatinine levels can be a sign of kidney dysfunction and may pose serious health risks. If you are seeking information on how to lower creatinine levels naturally, this guide can help. In this article, we explore the causes, symptoms, and risk factors associated with high creatinine levels. We also look into effective home remedies that may help you manage your condition and improve your well-being. Continue reading to learn how to take a proactive approach to lowering creatinine levels and promoting optimal kidney function.
In This Article
How To Lower Creatinine Levels Naturally
Medical solutions to lower creatinine levels like dialysis and other treatments and medications can be daunting. However, if you want to go the natural route, we have some suggestions that may help. Here’s how you can try lowering your creatinine levels with natural remedies.
1. Apple Cider Vinegar
Kidney stone formation may slightly elevate serum creatinine levels (1). Apple cider vinegar contains acetic acid, which may lower the risk of kidney stone formation (2). Its antimicrobial properties may help ward off bacterial infections and may prevent your blood creatinine levels from increasing. But, scientific research is lacking in this aspect.
Add a tablespoon of apple cider vinegar to a glass of warm water and mix well. Add some honey to this solution. Drink this solution once daily, preferably with a high-carbohydrate diet.
2. Bitter Gourd
Bitter gourd is a rich source of various minerals, vitamins, antioxidants, and fiber. Anecdotal evidence suggests that it may act as a natural diuretici Water pills that help discharge excess water from the body via the kidneys by inducing increased urine production. , The most prominent bitter gourd benefits include, improving blood circulation, cleansing kidneys, and helping lower blood creatinine levels naturally. However, limited research is available in this regard.
Drink half a cup of bitter gourd juice once daily.
Caution
Do not consume bitter gourd or its juice in excess. A study on mice has shown that 4000 mg/kg is the tolerable range. Any dose exceeding this is nephrotoxici The sudden deterioration in the function of kidneys due to the poisonous effect of chemical substances or medications. (3). However, human studies are to be conducted in this regard.
3. Cinnamon

Cinnamon is thought to be a natural diuretic. Some believe it may also improve the kidneys’ filtration abilities – though more research is warranted to understand this. But cinnamon does regulate the body’s creatinine levels (4).
Mix ½ a tablespoon of cinnamon in warm water or food and consume once a day.
4. Chamomile Tea
Ingestion of chamomile tea may lower high creatinine levels (5).
Add chamomile herb to a cup of hot water. Allow it to steep for at least 10 minutes. Strain and add a little honey. You can have chamomile tea 3 to 4 times daily.
5. Green Tea
Green tea is a natural antioxidant and has diuretic properties (6). The diuretic nature of green tea may help improve the filtration ability of your kidneys and increase urine output – thereby lowering creatinine levels (7).
Steep a green tea bag in a cup of hot water for about 10 minutes. Allow it to cool for a while and add some honey. You can drink green tea 2 to 3 times daily.
 Quick Tip
Quick Tip6. Garlic
Garlic is a natural antioxidant and also acts as a diuretic. It helps flush out toxic waste from your body and may help lower blood creatinine levels (8), (9). Garlic also increases the levels of plasma iron and improves hemoglobin levels (10).
You can chew 4 to 5 garlic cloves or you can add minced garlic to your salads and other foods. You must do this 1 to 2 times daily.
7. Ginger

Ginger contains flavonoidsi A large family of natural substances that protects against oxidative damage and renal injuries. and ethanol that exhibit antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties, which can help protect your kidneys from damage and injury and lower the creatinine levels in your body (11), (12).
Add an inch of ginger to a cup of hot water and allow it to steep for at least 10 minutes. Add a little honey and consume immediately. You can drink this ginger tea thrice daily for optimum benefits.
8. Cranberry Juice
Cranberries contain quinic acid that protects your kidneys from stone formation (13), (14).
Drink a medium cup of cranberry juice once a day.
9. Coconut Water
Tender coconut water is a rich source of vitamin C that can lower your creatinine levels and keep your kidneys healthy and stone-free (15).
Have a glass of tender coconut water once a day.
Caution
Avoid consuming more than 1 glass of coconut water in a day. Anecdotal evidence suggests that it may affect your kidneys.
10. Olive oil
Olive oil exhibits antiurolithici The property of an agent that prevents or dissolves the formation of stones in the urinary tract, kidney, or bladder. activities that may help prevent the formation of kidney stones. In fact, drinking olive oil mixed with lemon juice is a popular home remedy for kidney stones. It may also reduce creatinine levels in the blood (16).
Add a tablespoon of olive oil to your salad or pasta once daily.
Caution
Avoid heating olive oil too much while using it in food preparations.
While these natural remedies may help lower your creatinine levels naturally, having a clear understanding of creatinine can help you be cautious. Learn what exactly is this component in the next section.
What Is Creatinine?
Creatinine is a metabolic product of creatine and a by-product of muscle metabolism (17). Creatine is a significant molecule that helps in the production of energy and improves exercise performance (18).
About 2% of your body’s creatine is converted to creatinine and transported to your kidneys via the bloodstream. Your kidneys filter out most of the creatinine and eliminate it from your body through urine.
Low urine creatinine levels may be an indication of high blood creatinine, and it could be a cause for concern in some cases.
The following chart discusses the normal and abnormal ranges of creatinine levels according to one’s age, gender, muscle mass, etc.
Normal Creatinine Levels
The creatinine levels in your body are usually dependent on your muscle mass, gender, age, and other health factors (19), (20). They are often measured in milligrams per deciliter
| CATEGORY | CREATININE LEVELS |
|---|---|
| Adult Males | 0.9 to 1.3 mg/dl |
| Adult Females | 0.7-1.1 mg/dl |
| Infants | 0.2 mg/dl |
| Individuals with only one kidney | 1.8 to 1.9 mg/dl |
Older people have lower creatinine levels than normal adults, and bodybuilders may have higher creatinine levels than most adults. This is because older individuals have diminished muscles while bodybuilders have more muscles as compared to most normal individuals. Also, individuals with any muscle-related disorders may have significantly lower creatinine levels. There are many low creatinine-level treatments and diet recommendations that may help reverse the condition.
Why Should Creatinine Levels Be Lowered?
High blood creatinine can pose the following dangers if left untreated.
- May Damage Kidneys
Elevated creatinine levels, if left untreated, can damage kidneys. Renal failure may also occur if blood creatinine levels exceed the natural limits or with the intake of excess creatine supplements (21).
According to a report by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), chronic kidney disease is more common in people aged 65 years or older (34%) than in people in the age group of 45–64 years (12%) and 18–44 years (6%). It is more common in women (14%) than men (12%). The estimates are based on a single measure of serum creatinine.
- May Increase The Risk Of Cardiovascular Disease
Higher creatinine levels increase your risk of developing cardiovascular disease (22).
- May Lead To Respiratory Disorders
An increase in creatinine levels may lead to respiratory disorders
(23). However, the relationship between elevated creatinine levels and respiratory disorders remains unclear. Read on to know how to lower creatinine levels through some natural measures!
Thus, it is important to lower creatinine levels through some natural measures! Additionally, you may also need to avoid certain foods to maintain an optimal creatinine level. Take a look!
What Foods Should Be Avoided If Creatinine Levels Are High?

- Spinach
Although there are various Spinach benefits, the leafy green veggie has some side effects too. Spinach is high in potassium. Additionally, it is also high in oxalates and may increase the risk of kidney stones (24).
- Canned Foods
Canned foods are high in sodium. It is added as a preservative to increase the shelf life. This sodium may have detrimental effects on kidney function and may also worsen existing symptoms (25).
- Dairy Products
Dairy products are a rich source of phosphorus. Individuals with chronic kidney disease should limit the consumption of dairy as this phosphorus may interfere with calcium balance (26). It also may lead to a buildup of protein waste in the body and exert pressure on the kidneys.
- Beverages
Colored beverages are loaded with phosphorus to enhance their appearance and taste. However, if you are having any kidney complications, it is better to avoid all kinds of artificial beverages as their phosphorus content can burden the kidneys (27).
- Whole Wheat Bread
Whole wheat bread is rich in phosphorus, potassium, and sodium, and may be unsuitable for people with kidney-related ailments. The whole grains in whole wheat bread may have a higher percentage of sodium than that of white bread (28).
In addition to these, processed foods, fried chips, and pickles are also to be avoided because of their high sodium content.
Here is what you can do to reduce the risk of high creatinine levels in your blood and figure out how to control creatinine levels.
Preventive Tips

- Avoid taking creatinine supplements as they may increase the risk of creatinine deposition. However, there is only limited research in this regard.
- Reduce protein intake as it may aggravate protein deposits in the body and spike creatinine levels (29).
- Consume more fiber-rich foods for a healthy kidney like whole grains, legumes, vegetables, and fruits (30).
- Anecdotal evidence suggests that excess intake of salt may have detrimental effects on kidney function. So, it is advised to reduce excessive salt intake.
 Quick Tip
Quick Tip- Practice yoga asanas like Ardha Matsyendrasana (Half Spinal Twist) after consulting your doctor.
Now that you know how to reduce creatinine levels, let us look into the factors that cause its increase.
Causes Of High Creatinine Levels
If the functioning of your kidneys is interrupted or impaired by any condition, it can cause your creatinine levels to go high. Some of the most common causes of chronic kidney diseases or elevated creatinine levels in adults include:
- Diabetes
Diabetes may sometimes lead to an increase in creatinine levels (31).
- High Blood Pressure
Uncontrolled blood pressure levels may result in an elevation of creatinine levels in the body (32).
- Urinary Tract Infections
Urinary tract infections may cause a spike in creatinine levels. However, clear research is lacking in this regard.
- Drugs Like Cimetidine
Cimetidine is used to treat stomach acidity and peptic ulcers. Regular consumption of cimetidine may increase the levels of creatinine (33).
- High-protein Diets
Excessive protein intake can overload your kidneys, leading to increased creatinine levels.
- Dehydration
Insufficient fluid intake can concentrate creatinine in the blood, causing elevated levels.
- Excessive use of creatine supplements
Creatine is a naturally occurring compound found in the body, but excessive supplementation can increase creatinine levels.
Symptoms Of High Creatinine Levels

The high creatinine symptoms and kidney dysfunction often vary widely and may not be correlated with each other. Some individuals may have severe kidney disease and high creatinine levels without displaying any symptoms, while others usually develop symptoms like:
- Swelling or edema
- Shortness of breath
- Dehydration
- Fatigue
- Nausea and vomiting
- Confusion
It is very important to get your kidneys diagnosed periodically if you have high creatinine levels. Some diagnosis methods that can be used to screen your kidneys for any abnormalities are discussed below.
Diagnosis
If your blood test reveals that you have high creatinine levels, you can undergo the following tests:
- Blood Urea Nitrogen Test (BUN): This test checks the functioning of your kidneys by measuring the amount of urea nitrogen in your blood. A very low creatinine level or highly increased BUN and creatinine often hint at kidney problems.
- Glomerular Filtration Rate Test (GFR): This test reveals the filtration rate of the substances through the glomerulus (blood vessels in kidneys). The normal GFR rate is 90 to 120 ml per minute in a healthy adult. Anything less may indicate kidney malfunction and elevated creatinine levels.
- Urine Analysis: In this test, urine is analyzed physically and chemically, revealing the presence of protein, glucose, and red blood cells (34).
How to prepare for a blood test:
You may be asked to fast for a certain period before the blood test, usually 8-12 hours. Inform your doctor about any medications you’re taking, as some of them can interfere with the test results. Avoid excessive fluid intake before the test, as this can affect creatinine levels.
Infographic: Causes And Symptoms Of High Creatinine Levels
Creatinine plays a key role in energy production and helps improve exercise performance. Creatinine is the by-product of creatine. High levels of creatinine may have negative effects on the body.
The following infographic provides information about the causes and symptoms of high creatinine levels. Check it out. Illustration: StyleCraze Design Team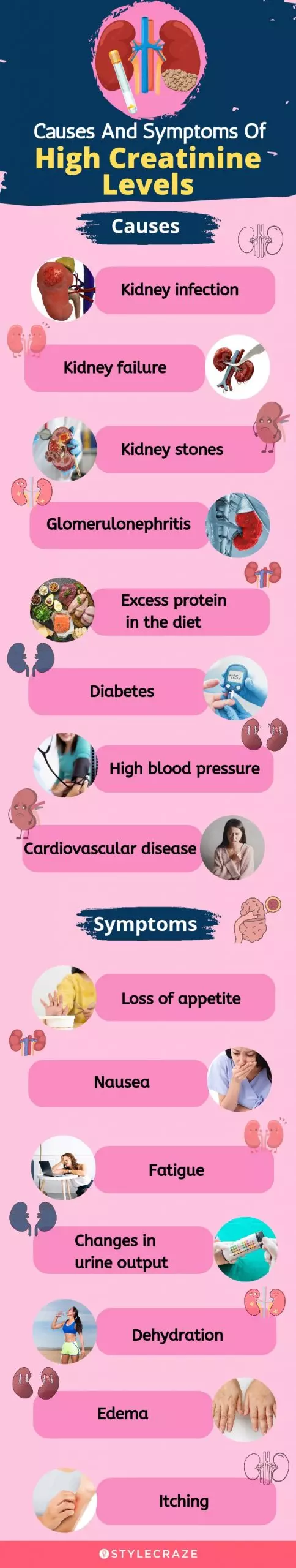
High creatinine levels can be a sign of underlying health problems. Fortunately, there are natural ways to help your body lower its levels and get rid of toxins. Therefore it’s very important to understand how to lower creatinine levels. You can eat more diuretic foods that help your body release water and fight the damage. This way your body might be able to lower creatinine levels and improve kidney health. These natural remedies are a gentle way to maintain balance. Nevertheless, it is important to check your creatinine levels regularly through blood tests and talk to a doctor to ensure proper management and prevent serious complications.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can drinking water lower creatinine?
Jesse Feder, Clinical Dietitian at the Memorial Regional Hospital, says, “If you are dehydrated, your creatinine levels may rise. Therefore, drinking more water can lower your creatinine levels.”
What food can reduce creatinine?
“If you are trying to reduce creatinine levels, it’s important to speak with a doctor, as high creatinine can be a sign of poor kidney function. In this case, you will want to avoid foods high in phosphorus, potassium, and protein. Some foods that can help you lower these levels are cauliflower, cabbage, red bell peppers, berries, fish, garlic, and onion,” says Jesse.
What foods contain high creatinine?
According to Jesse, “Foods do not contain creatinine, as this is a byproduct our bodies produce. However, foods higher in creatine, such as red meats, can be broken down and increase creatinine levels.”
Does vitamin D increase creatinine levels?
Jesse says, “Yes. Higher doses of vitamin D have been associated with increased creatinine levels.”
Is egg good for high creatinine?
“Eggs will not necessarily lower creatinine levels; however, they are typically safe for those with higher creatinine levels,” says Jesse Feder.
Is creatinine 1.5 normal?
No, for most individuals, 1.5 creatinine level is considered high. However, 1.5 creatinine level may be considered normal for a very muscular person.
What is the highest creatinine level recorded?
The highest recorded serum creatinine level is 73.8 mg/dL in a 23-year-old male with a history of pediatric deceased donor kidney transplant (DDKT).
What causes false high creatinine?
False or one-time high creatinine levels may be caused by various factors such as dehydration, intake of protein and creatine supplements over the recommended dosage and consumption of cooked meat.
Does walking reduce creatinine?
Walking is a mild form of exercise that does not generally impact creatinine levels. However, it is considered to be a great form of exercise to prevent kidney damage.
Key Takeaways
- Your body’s creatinine levels are usually determined by your muscle mass, gender, age, and other health factors.
- High blood creatinine levels can harm your kidneys, raise your risk of cardiovascular disease, and cause respiratory problems.
- Apple cider vinegar, chamomile tea, green tea, garlic, and ginger may help lower creatinine levels naturally.
- Spinach, canned foods, dairy products, beverages, and whole wheat bread should be avoided.
Illustration: Remedies To Reduce High Creatinine Levels & Prevention

Image: Stable Diffusion/StyleCraze Design Team
Unlock the key to lowering elevated creatinine levels in your blood with expert guidance. Discover valuable tips on diet, lifestyle changes, and other ways you can maintain a healthy balance in this informative video. Check it out today!
References
Articles on StyleCraze are backed by verified information from peer-reviewed and academic research papers, reputed organizations, research institutions, and medical associations to ensure accuracy and relevance. Read our editorial policy to learn more.
- Kidney Function After the First Kidney Stone Event
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5140038/ - Prevalence of kidney stones in China: an ultrasonography based cross-sectional study
https://bjui-journals.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1111/bju.13828 - Impact of Momordica charantia extract on kidney function and structure in mice
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24644542/ - Efficacy of cinnamon (Cinnamomum burmannii) extract to decrease serum creatinine in acute kidney injury induced male wistar rats
https://www.bioscmed.com/index.php/bsm/article/view/101 - A metabonomic strategy for the detection of the metabolic effects of chamomile (Matricaria recutita L.) ingestion
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15656647/ - Beneficial effects of green tea: A literature review
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2855614/ - The Green Tea Polyphenol(—)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate and its beneficial roles in chronic kidney disease
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5290885/ - Diuretic natriuretic and hypotensive effects produced by Allium sativum (garlic) in anaesthetized dogs
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/2056760/ - Preventive effect of garlic juice on renal reperfusion injury
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21525580/ - Influence of garlic or its main active component diallyl disulfide on iron bioavailability and toxicity
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/20226993/ - Therapeutic Potential of Ginger against Renal Injury Induced by Carbon Tetrachloride in Rats
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3329925/ - The effect of ginger extract on blood urea nitrogen and creatinine in mice
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19090210/ - Effect of blackcurrant- cranberry- and plum juice consumption on risk factors associated with kidney stone formation
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12373623/ - Influence of cranberry juice on the urinary risk factors for calcium oxalate kidney stone formation
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/14616463/ - Prophylactic effect of coconut water (Cocos nucifera L.) on ethylene glycol induced nephrocalcinosis in male wistar rat
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23489503/ - Antiurolithic effect of olive oil in a mouse model of ethylene glycol-induced urolithiasis
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5419107/ - The two sides of creatinine: both as bad as each other?
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4958791/ - International Society of Sports Nutrition position stand: creatine supplementation and exercise
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2048496/ - [Normal ranges of blood urea nitrogen and serum creatinine levels in the community-dwelling elderly subjects aged 70 years or over–correlation between age and renal function]
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/8207875/ - Neonatal and maternal serum creatinine levels during the early postnatal period in preterm and term infants
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5967735/ - Acute renal failure in a young weight lifter taking multiple food supplements including creatine monohydrate
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17046619/ - Serum Creatinine Concentration and Risk of Cardiovascular Disease
https://www.ahajournals.org/doi/full/10.1161/01.STR.28.3.557 - [Significance of serum creatinine levels in respiratory insufficiency conditions]
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/11769441/ - Dietary oxalate and kidney stone formation
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30566003/ - Sodium and phosphorus-based food additives: persistent but surmountable hurdles in the management of nutrition in chronic kidney disease
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3582990/ - Calcium Balance in Chronic Kidney Disease
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5442193/ - Management of Natural and Added Dietary Phosphorus Burden in Kidney Disease
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5797670/ - Differences in the sodium content of bread products in the USA and UK: implications for policy
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29157327/ - False Estimates of Elevated Creatinine
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3383162/ - Dietary fiber effects in chronic kidney disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis of controlled feeding trials
https://idp.nature.com/authorize?response_type=cookie&client_id=grover&redirect_uri=https%3A%2F%2Fwww.nature.com%2Farticles%2Fejcn2014237 - Renal function in diabetic nephropathy
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3083882/ - Prevalence of High Blood Pressure and Elevated Serum Creatinine Level in the United StatesFindings From the Third National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (1988-1994)
https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamainternalmedicine/fullarticle/648077 - A practical approach to glomerular filtration rate measurements: Creatinine clearance estimation using cimetidine
https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Plasma-creatinine-concentrations-Scr-before-and-after-the-administration-of-cimetidine_fig1_11836219 - Renal Function Tests
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK507821/
Read full bio of Dr. Zeel Gandhi
- Jesse Feder, RDN/LDN, is a Clinical Dietitian at the Memorial Regional Hospital. He is also a certified by the American College of Sports Medicine as a personal trainer (ACSM-CPT) and the National Strength and Conditioning Association as a Certified Strength and Conditioning Specialist (NSCA-CSCS).
 Jesse Feder, RDN/LDN, is a Clinical Dietitian at the Memorial Regional Hospital. He is also a certified by the American College of Sports Medicine as a personal trainer (ACSM-CPT) and the National Strength and Conditioning Association as a Certified Strength and Conditioning Specialist (NSCA-CSCS).
Jesse Feder, RDN/LDN, is a Clinical Dietitian at the Memorial Regional Hospital. He is also a certified by the American College of Sports Medicine as a personal trainer (ACSM-CPT) and the National Strength and Conditioning Association as a Certified Strength and Conditioning Specialist (NSCA-CSCS).
Read full bio of Shaheen Naser
Read full bio of Arshiya Syeda
Read full bio of Dipti Sharma


























Community Experiences
Join the conversation and become a part of our empowering community! Share your stories, experiences, and insights to connect with other beauty, lifestyle, and health enthusiasts.