10 Foods High In Choline, Health Benefits, & Deficiency Effects
Strengthen your body and improve its health by consuming some choline-rich food items.

Image: Shutterstock
The micronutrient choline plays a vital role in improving cardiovascular health, enhancing cognitive ability, and reducing cancer risk.
Including choline-rich foods is a way to get this nutrient as our body produces it in limited amounts. It is found in many animal and plant foods. Keep reading to know which foods are rich in choline, the benefits of this nutrient, and how much choline you need for your body. Scroll down to know what foods have choline.
In This Article
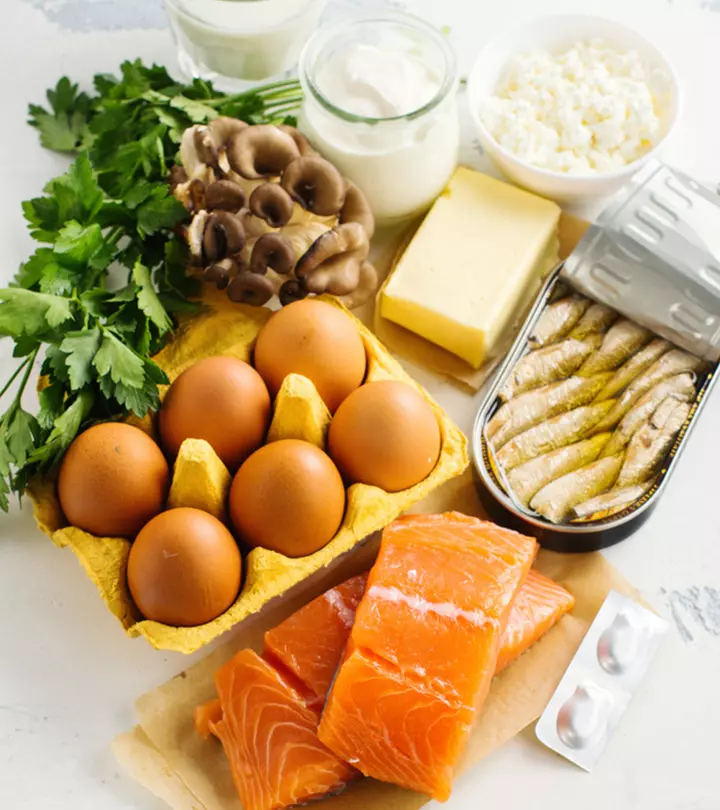
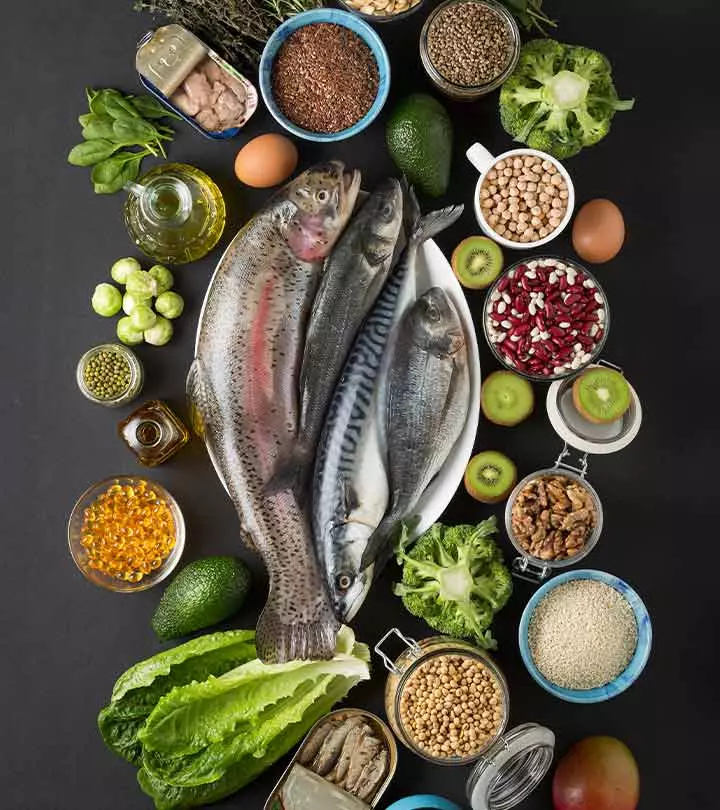
Choline-Rich Foods
1. Whole Eggs
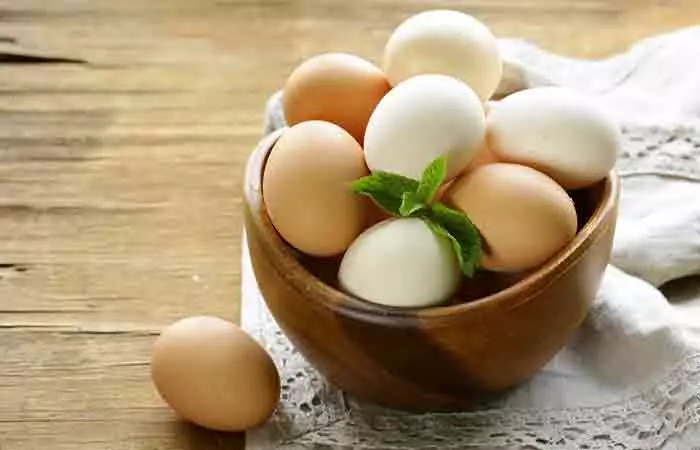

Eggs are the best and primary source of choline. One large egg with yolk contains 147 mg of choline, which is more concentrated in the yolk (680 mg/100g) than the egg white (1 mg/100 g) (1 ),(2). This essential nutrient gets absorbed more easily when consumed in its natural form (bound to phospholipids) than as a supplement. Studies suggest that phospholipids in egg yolk improve choline absorption (3). Higher choline intake can, in turn, improve cognitioni It includes all conscious and unconscious processes by which knowledge is acquired and understood through experience and senses. function in humans (4).
 Quick Tip
Quick Tip2. Fish
Seafood is a rich source of several nutrients like choline. Fish like tuna, salmon, and haddock have high choline content — and three ounces of smoked salmon contain 187 mg of choline (5). A study by the Child and Family Research Institute, Canada, found that higher fish intake improves blood concentrations of vitamin D, choline, and DHA (omega-3 fatty acid) (6).
 Quick Tip
Quick Tip
3. Organ Meat
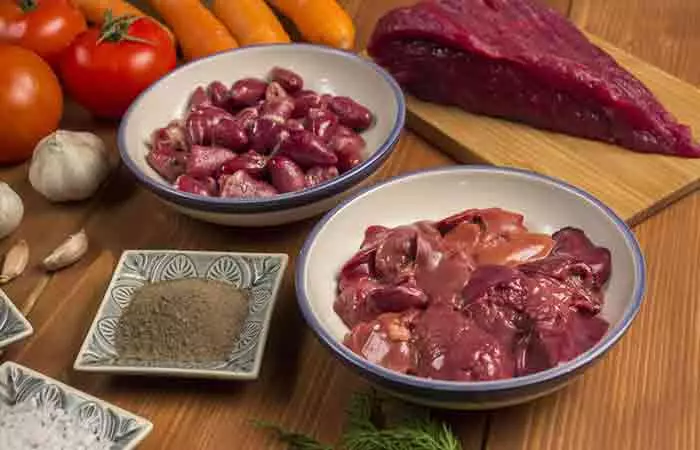

Organ meat is one of the best choline sources. Consuming at least 90g of meat per day along with eggs (one per three days) and milk products helps meet the daily choline requirement in children (7). One slice (85g) of beef liver contains 359 mg of choline (8). Beef was shown to improve iron content in blood and enhance cognitive function in young women. However, it had no specific benefit over non-beef protein with regard to iron levels ( 9). Three ounces of chicken liver, chicken broiler, and turkey contain 247 mg, 56 mg, and 71.7 mg of choline, respectively (1),(9).
4. Soy
Raw soybeans (100g) contain 116 mg of choline (10). They can be the ultimate source of choline for vegetarians. Such individuals can also take soy products like tofu, soy milk, tempeh, and edamame.
5. Cruciferous Vegetables
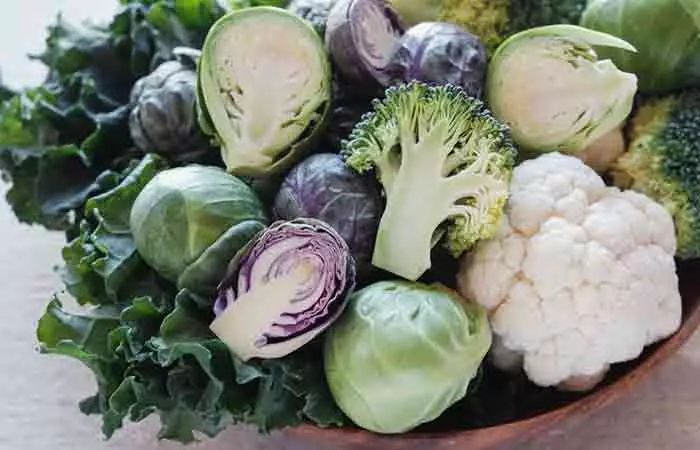

Green vegetables like broccoli and cauliflower are rich sources of choline. One cup each of chopped broccoli (91g) and chopped cauliflower (107g) contains 17 mg and 47.4 mg of choline, respectively (11 ),(12). Besides, one cup (160g) of cooked Brussels sprouts provides 31.2 mg of choline (13 ).
iQuell, a blogger, shared his journey of becoming a vegetarian and embraced many vegetables as a part of his diet. He says, “Most of the time I eat broccoli in salads or stir fry because I don’t like it overcooked. I don’t even know if it taste good or bad I’m just used to it now. It’s high in vitamin K and choline and improves your memory (i)”.
6. Potatoes
One medium potato (173g) contains 24.9 mg of choline (14 ). Red potatoes are another great source of choline with carbs. One baked small red potato (138g) provides 26.1 mg of choline (15).
7. Beans
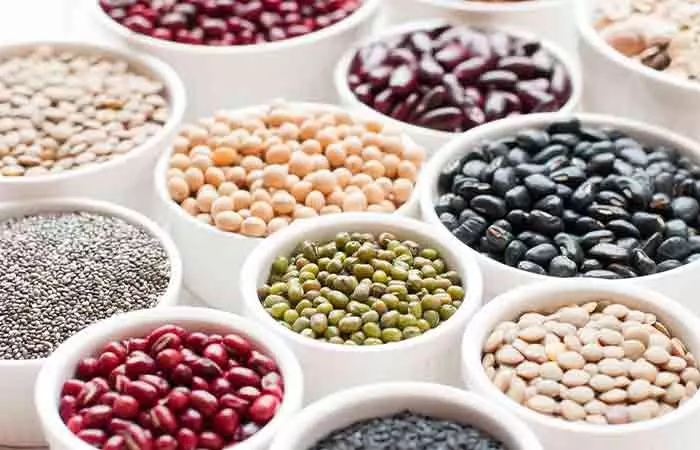

Studies suggest that immature lima beans are the best source of choline for vegans (16). One cup (170g) of lima beans contains 75 mg of choline (17). Also, 100g of kidney beans provides 30.5 mg of choline (18).
8. Shiitake Mushrooms
Shiitake mushrooms are rich in flavor. Cooked shiitake mushrooms (100g) provide 36.8 mg of choline, and these can be added to your soups, pasta, or stir-fries (19 ). Their regular intake can help improve immunity and reduce inflammatory markers (20). They also have anti-oxidative and anti-atherosclerotic properties that help reduce cardiovascular diseases (21).
9. Cottage Cheese
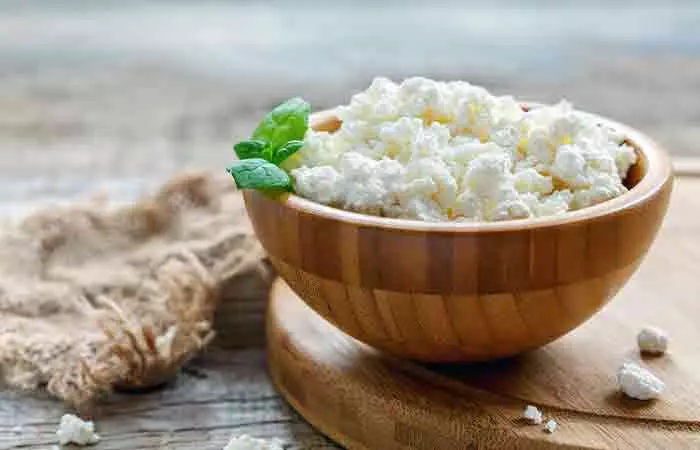

Dairy products like low-fat milk and cottage cheese are excellent sources of choline. One cup (210g) of cottage cheese contains 38.6 mg of choline (22). It is also rich in calcium, which is essential for maintaining bone health and weight loss (23), (24). Besides, it has a mild taste and is easy to incorporate into your diet. Add it to your salads, baked items, smoothies, or use it as an alternative to sour cream.
10. Almonds
Almonds are highly nutritious tree nuts with many health benefits. One cup (141g) of unroasted almonds contains 73.5 mg of choline (25). You can have them in your breakfast or blend them to make smoothies.
Besides, fruits like kiwi and apples are also rich sources of choline. A half-cup each of raw kiwi and chopped raw apples contain 7 mg and 2 mg of choline, respectively (26).
Consuming choline-rich foods is associated with many health benefits. Keep scrolling to know them.
Key Takeaways
- Choline is a nutrient found in various animal and plant foods, including eggs, fish, organ meat, soy, green vegetables, potatoes, beans, shiitake mushrooms, cottage cheese, and almonds.
- Foods high in choline have been linked to various health benefits, including improved brain function, enhanced heart health, and a lower risk of cancer.
- However, remember that people with a choline deficiency may develop muscle damage and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease.
What Are The Health Benefits Of Choline?
- May Improve Brain Function
Choline-containing foods, such as eggs, liver, and salmon as well as choline supplements, are considered brain-boosting foods. You can consider them memory-enhancing foods, cognitive function foods, or nerve function foods as well. This is because choline is an essential nutrient that produces acetylcholine (neurotransmitter). Loss of cholinergic neurons is associated with impaired cognitive function, particularly memory loss and Alzheimer’s diseasei A progressive disease that impairs cognitive functions as a result of damage to brain cells and dementia. . Higher choline intake is found to improve cognitive performance. A review published in the American Journal of Clinical Nutrition suggests that dietary choline intake has neuroprotective effects and can improve cognitive function (27). Choline intake during pregnancy can also improve fetal brain development (28).
- May Support Heart Health
Choline-rich foods can also be considered heart health foods. Long-term choline intake may reduce the risk of inflammatory conditions and cardiovascular diseases (29). A study by Wageningen University, The Netherlands, on post-menopausal women found that high choline intake can lower homocysteine (an amino acid) levels. High homocysteine levels are associated with an increased risk of CVD ( 30). It may also protect the heart by reducing blood pressure and changing lipid profiles.
However, certain studies have shown no association between choline intake and a reduced risk of CVD. Therefore, more research needs to be done. Moreover, if you are planning to start a low-cholesterol diet, you can add choline-rich food to your routine, such as eggs, broccoli, etc., which may help enhance your heart health.
- May Reduce Risk Of Breast Cancer
High choline intake may help prevent the development of breast cancer in post-menopausal women. Choline may also help reduce breast cancer mortality once diagnosed (31),( 32). However, limited studies are available to support this claim.
Inadequate intake of choline can impact your health. Let’s discuss the negative effects of choline deficiency in the following section.
Effects Of Choline Deficiency
Choline is a key nutrient in maintaining the integrity of cell structure, DNA synthesis, and metabolism. The signs and symptoms of its deficiency include muscle aches, restlessness, fatigue, anxiety, poor glucose metabolism, memory impairment, and weight gain (33). A study by the March of Dimes in Berkley, California, suggests that low dietary intake of choline in pregnant women significantly increases the risk of neural tube and oral cleft defects in babies (34). Choline deficiency in people is also associated with liver and muscle dysfunction (and damage) and increases the risk of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (choline plays an important role in fat transportation from the liver and its deficiency may cause fat accumulation in the liver), apoptosisi A biological process of programmed cell death in multicellular organisms to get rid of abnormal or damaged cells. , and increased DNA strand breaks (35). Thus, the intake of liver health foods like choline-rich ingredients is necessary to avoid these complications.
You must now be willing to include choline in your diet. But how much choline should you take to meet your dietary needs?
How Much Choline Does A Human Body Need?
Adequate choline requirements for different age groups include (26):
| Age | Male | Female |
|---|---|---|
| 0-6 months | 125 mg/day | 125 mg/day |
| 7-12 months | 150 mg/day | 150 mg/day |
| 1-3 years | 200 mg/day | 200 mg/day |
| 4-8 years | 250 mg/day | 250 mg/day |
| 9-13 years | 375 mg/day | 375 mg/day |
| 14-18 years | 550 mg/day | 400 mg/day |
| 19+ years | 550 mg/day | 425 mg/day |
Pregnant women should take 450 mg/day of choline and increase it to 550 mg/day during breastfeeding.
While it is possible to get choline from your diet, some people may need to supplement its intake with outside sources. Check the next section for some of the best supplements for choline in your diet.
Best Choline Supplements
1. Choline Alfoscerate
This supplement is also known as alpha-glycerophosphocholine (GPC) and has a high choline content (41% by weight) and is one of the most used food supplements for choline (36). Moreover, due to its ability to cross the blood-brain barrier, it may help enhance cognitive function and aid in the treatment of diseases like Alzheimer’s and dementia (36).
2. Lecithin
It is a mixture of fats found in foods like egg yolk and nuts that may have positive effects on diseases like hypercholesterolemia and cardiovascular disorders (36).
3. Citicoline
A naturally occurring chemical in human and animal cells that may help enhance brain metabolism, and help improve memory and conditions like dementia and Parkinson’s (36).
Infographic: Choline: Risk Groups For Deficiency & Toxicity
Choline is one of the most essential nutrients the human body needs. However, according to many studies, the dietary choline intake of most humans has been found to be below par. In the following infographic, we list the groups that are at risk of choline deficiency. We have also provided insight into choline toxicity and its symptoms. Check it out!
Some thing wrong with infographic shortcode. please verify shortcode syntax
Choline is an important vitamin that can be present in both animal and plant sources. Its consumption may aid in boosting heart and brain health and lessen the risk of cancer. Conversely, its absence can result in muscle damage as well as non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. It’s important to keep in mind that pregnant women need enough choline to ensure that the fetal brain develops properly. To ensure your body gets adequate choline, eat choline-rich foods such as cruciferous vegetables, eggs, organ meats, fish, almonds, and beans.
Frequently Asked Questions
Are bananas high in choline?
No, a medium sized banana contains only about 12 mgs of choline.
Do lemons have choline?
Lemons have small quantities of choline and are not considered a good source.
Does cooking eggs destroy choline?
No,cooking eggs does not destroy any significant quantity of choline.
Do avocados have choline?
Avocados contain moderate amounts of choline, around 14.2 mg per 100 g.
Can choline reverse fatty liver?
While fatty liver disease is associated with choline deficiency, there is no evidence to support that consuming choline can reverse the condition.
What happens if you have too much choline?
Consuming choline in very large quantities may lead to liver toxicity, low blood pressure, increase the risk of cardiovascular issues and cause side effects such as vomiting, nauseai An uneasy feeling in the stomach that causes an urge to vomit but does not always lead to vomiting. , fishy odor and excessive sweating (1).
Check out a certified dietitian’s top tips on getting more choline in your diet. Watch this video to learn how to add choline-rich foods into your meals and snacks for optimal health.
Personal Experience: Source
StyleCraze's articles are interwoven with authentic personal narratives that provide depth and resonance to our content. Below are the sources of the personal accounts referenced in this article.
i. You May Not Be Trash But You Should Take Out Your Garbage (Pt. 3)https://medium.com/@iquell/you-may-not-be-trash-but-you-should-take-out-your-garbage-pt-3-60f08b3f08fe
References
Articles on StyleCraze are backed by verified information from peer-reviewed and academic research papers, reputed organizations, research institutions, and medical associations to ensure accuracy and relevance. Read our editorial policy to learn more.
- Choline
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6259877/ - The Golden Egg: Nutritional Value, Bioactivities, and Emerging Benefits for Human Health
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6470839/ - Natural Choline from Egg Yolk Phospholipids Is More Efficiently Absorbed Compared with Choline Bitartrate; Outcomes of A Randomized Trial in Healthy Adults
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6893749/ - A Comprehensive Review of Eggs, Choline, and Lutein on Cognition Across the Life-span
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29451849/ - Choline: An Essential Nutrient for Public Health
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2782876/ - Low fish intake is associated with low blood concentrations of vitamin D choline and n-3 DHA in pregnant women
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22691303/ - Choline Intake and Its Food Sources in the Diet of Romanian Kindergarten Children
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5579689/ - Beef liver braised
https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/1098653/nutrients - Improvements in Iron Status and Cognitive Function in Young Women Consuming Beef or Non-Beef Lunches
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3916851/ - Turkey, whole, breast, meat only, cooked, roasted
https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/171496/nutrients - Soybeans, mature seeds, raw
https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/174270/nutrients - Broccoli raw
https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/170379/nutrients - Choline and betaine intakes are associated with reduced risk of nasopharyngeal carcinoma in adults: a case–control study
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3915107/ - Cauliflower, raw
https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/169986/nutrients - Brussels sprouts, NS as to form, cooked
https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/1103467/nutrients - Potatoes, white, flesh and skin, baked
https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/170434/nutrients - Potatoes, red, flesh and skin, baked
https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/170435/nutrients - Choline, Neurological Development and Brain Function: A Systematic Review Focusing on the First 1000 Days
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7352907/ - Lima beans, immature seeds, cooked, boiled, drained with salt
https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/169316/nutrients - Beans, kidney, red, mature seeds, cooked, boiled, with salt
https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/175242/nutrients - Mushrooms, shiitake, cooked, without salt
https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/168437/nutrients - Consuming Lentinula edodes (Shiitake) Mushrooms Daily Improves Human Immunity: A Randomized Dietary Intervention in Healthy Young Adults
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25866155/ - Lentinula edodes (shiitake mushroom): An assessment of in vitro anti-atherosclerotic bio-functionality
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6302894/ - Cheese, cottage, creamed, large or small curd
https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/1098045/nutrients - Calcium- and Phosphorus-Supplemented Diet Increases Bone Mass after Short-Term Exercise and Increases Bone Mass and Structural Strength after Long-Term Exercise in Adult Mice
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27008546/ - Role of dietary calcium and dairy products in modulating adiposity
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12733746/ - Almonds, unroasted
https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/1100508/nutrients - Choline
https://ods.od.nih.gov/factsheets/Choline-HealthProfessional/ - The relation of dietary choline to cognitive performance and white-matter hyperintensity in the Framingham Offspring Cohort
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3252552/ - Choline: Critical Role During Fetal Development and Dietary Requirements in Adults
Choline: Critical Role During Fetal Development and Dietary Requirements in Adults – PMC (nih.gov) - Dietary Choline and Betaine Intakes and Risk of Cardiovascular Diseases: Review of Epidemiological Evidence
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3347848/ - Prospective study on dietary intakes of folate, betaine, and choline and cardiovascular disease risk in women
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17375117/ - Dietary choline intake is necessary to prevent systems‐wide organ pathology and reduce Alzheimer’s disease hallmarks
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC9924938/ - Choline metabolism and risk of breast cancer in a population-based study
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2430758/ - Dietary choline deficiency causes DNA strand breaks and alters epigenetic marks on DNA and histones
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22041500/ - Choline supplements: An update
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC10025538/
Read full bio of Bulelani Makapela
Read full bio of Sindhu Koganti
Read full bio of Ravi Teja Tadimalla
Read full bio of Himanshi Mahajan















Community Experiences
Join the conversation and become a part of our empowering community! Share your stories, experiences, and insights to connect with other beauty, lifestyle, and health enthusiasts.