12 Dangerous Food Combinations To Avoid
Think twice before mixing these foods; they could cause you more harm than good.

Image: Midjourney/ StyleCraze Design Team
Mixing several types of food such as meat with cheese and fruits with yogurt is a common and popular practice.
But what several nutritionistsi A professional who advises people on appropriate eating habits and is a specialist in promoting health through food and nutrition. and Ayurvedics claim is that there are certain food combinations that can obstruct digestive channels and inhibit your body from gaining essential nutrients. Understanding food combinations is essential for enhancing digestion as well as avoiding possible health problems. The effects of food pairings on health have long been acknowledged by many cultures, emphasizing the importance of conscious eating habits that are in line with traditional wisdom such as Ayurveda and present nutrition science. In this article, we explore the top 12 food combinations to avoid in your diet.
In This Article
Dangerous Food Combinations To Avoid
A common practice many dieticians and nutritionists advocate for is proper food combining. It is also the practice commonly neglected by most of us. However, It ensures better health and improved digestion.
The principles of food combining revolve around the idea that an incorrect food pairing can have a negative effect on health, digestion, and overall nutrition. A contradictory food item pairing like orange juice with a glass of milk or sugar and fat can hinder digestion. Similarly, combining fresh fruits like bananas with milk may lead to a stomach ache (1). Incompatible food pairings may hinder nutrient uptake like impeding the absorption of iron, calcium, or any essential vitamin.

For instance, combining greens and non-starchy vegetables with foods may seem like a health-conscious choice, but it’s a dangerous food combination that could lead to negative effects when not approached strategically. Non-heme iron, predominantly found in leafy green plant-based sources like spinach and broccoli, has the potential to hinder iron absorption due to the presence of compounds like oxalates and phytates (2).
Alicia Chacha Miller, MS, RD, LDN, adds, “Some foods can alter how medications are processed in the body, which is why understanding a few common interactions can be helpful. Grapefruit juice, for instance, can change how the body breaks down certain medications for blood pressure or cholesterol. Calcium-rich foods might reduce how well iron or certain antibiotics are absorbed. Leafy greens high in vitamin K can affect how blood thinners function, and foods containing tyramine, like cured meats or aged cheeses, can lead to adverse effects when paired with specific antidepressants. Even everyday items like bananas or chocolate may influence how some prescriptions work due to their potassium content or other compounds. The goal in sharing this information isn’t to spark fear but to encourage informed decision-making. Being aware of how food and medicine interact can help people feel more confident in their choices. When in doubt, it’s always best to check in with a healthcare provider to create a plan that supports both your health needs and lifestyle.”
To avoid harmful food combinations that may cause weight gain or stomach bloating, or even lead to the creation of toxins in the digestive tract, it is essential to create a balanced meal with digestion speed in mind.
You can have fast-digesting food with slow-digesting food. However, keep the rules of food combining in mind. Here is a list of food combinations to avoid completely:
Key Takeaways
- Bacon and eggs and other high-protein combinations should be eaten with light proteins first, and meat later.
- Avoid combining water or juice with food.
- Fruits and dairy should be consumed at separate times.
- Avoid consuming cheese and beans at the same time.
- Avoid combining sugar, fat, and salt.
Infographic: 5 Combinations Of Foods To Avoid
Check out the infographic below to learn more about such food pairings that one should avoid consuming to prevent any adverse reactions.
Some thing wrong with infographic shortcode. please verify shortcode syntax
1. Carbs And Animal Protein

When you eat a combination of carbohydrate or starch and lean protein (such as meat with potatoes or bread) they counteract each other: the animal protein putrefiesi The act of slow disintegration of bodies or the rotting of organic matter yielding unpleasant sights and smells. and the carbohydrate (complex carb or simple carb) ferments. This bad combination leads to gas, bloating and flatulencei A condition in which a person suffers from gastric discomfort and passes excess gas contained in their large intestine. (3). Those who have eaten this combination in their diet for years may have developed immunity, but it is better to eat complementary combinations like beans and rice which is a good combination.
2. Two High Proteins
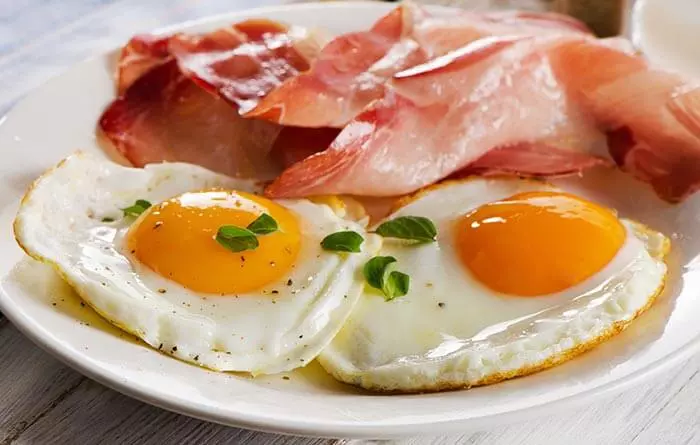

Surf and turf, bacon and eggs – these are all popular combinations containing two high protein sources. Many of these high protein dishes are also processed and fried food combinations that are unhealthy. This improper food combination taxes the digestive system and take a long time to digest.Further, when you eat more protein, your kidneys have to work harder to process it. This may increase the glomerular filtration rate (GFR), a measure of how well your kidneys are filtering waste from your blood. Over time, this extra strain on the kidneys can be harmful, especially for people who already have kidney problems (4).
To avoid this, eat your meals in courses – keeping light proteins first and meat later and never wait more than 10 minutes between each course. Also, avoid processed and fried foods as much as possible. If you have kidney issues, keep your total protein intake to 0.6-0.75 grams per kilogram of body weight per day. If you have no such problems, you stick to a moderate protein intake of 0.8-1.5 grams per kilogram of body weight a day (4). Opt for a sweet fruit and non-starchy vegetable in your diet to offset this bad food combination and ease digestion. You may also combine proteins with probiotics like yogurt and kimchi, as they help improve protein digestion and absorption by supporting the gut microbiota (5).
According to a study, fried food consumption is directly related to coronary artery disease. This study was conducted on 154,663 participants, out of which 90% were men and the mean age was 64 years. Out of these, there were 6,725 CAD events which were associated with fried food consumption, which indicates a linear relationship between fried foods and CAD.
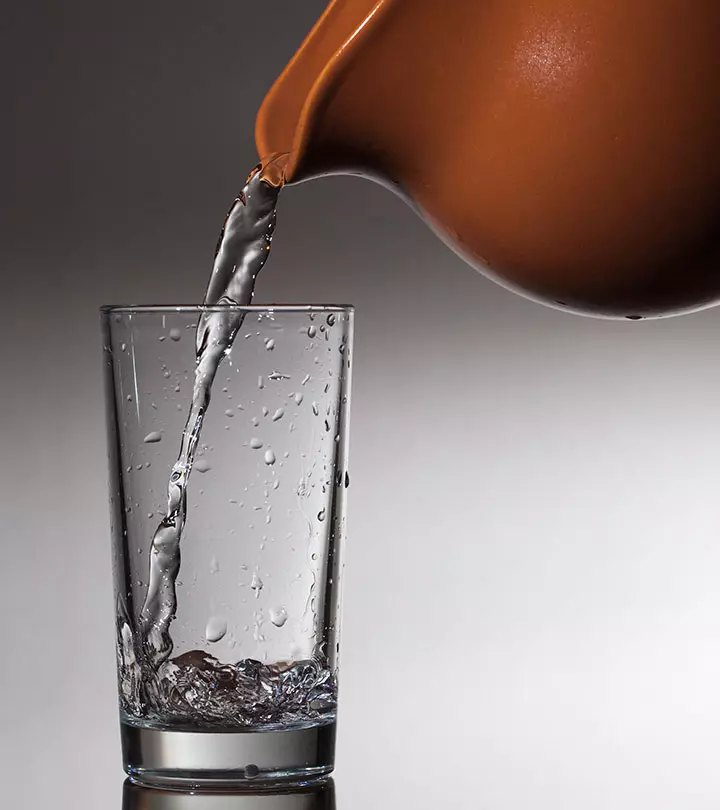
3. Food And Water/Juice

Drinking water or fruit juices like orange juice with your meal is one of the most toxic food combinations. The digestive juice of the stomach is required to digest complex food before it passes on to the intestines for nutrient absorption. Water dilutes your stomach acids and reduces their effectiveness in breaking down proteins, carbohydrates including sugar, and fats, hindering the digestive process. Proponents of the food combining diet prefer drinking water 10 minutes before the meal as it will make you feel fuller for longer (6). This will keep you from overeating or diluting stomach enzymes.
Having food with water is one of the most common food combinations to avoid in Ayurveda, it is important to note that the role of water in diluting stomach acid is not scientifically proven. A study looked at the effect of drinking water during a meal and did not find any evidence supporting the common belief that drinking water while eating could hurt digestion by diluting stomach acids and enzymes (7). So, it is best to consult a doctor if you have any concerns about drinking water during meals.
4. Fruit With Meal
Who doesn’t love some peppy mango salsa with fish or strawberries in their salads. These delicious ingredients, whether it be a tangy acidic fruit or a tropical sweet fruit. are essential in a vegetarian diet. But this is a bad combination as fruit- which otherwise passes quickly through the digestive system- is detained in the system and the sugar in it starts to ferment. However, more research is needed to support this claim.
That said, research published in the International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health suggests that eating fruit before a meal may be more beneficial than after a meal or skipping it altogether(8). It may significantly suppress appetite and support weight management. So, try consuming fruits at least 30 minutes before your meals and not with them.
5. Yogurt With Fruit

Yogurt contains plenty of bacteria that acts on the sugar present in fruits. Anecdotal evidence suggests that this may result in toxins, cold, and may possibly lead to food allergy. Thus, adding this food combo to your diet might result in a negative post digestive effect. You can avoid this problem by using unflavored yogurt at room temperature and mix in honey, cinnamon, or raisins instead of fresh fruit.
Alternatively, some researchers think combining yogurt and fruit might be healthy, as yogurt and fruit are packed with nutrients. Yogurt contains probiotics and fruit contains prebiotics, both of which are important for gut health. However, more research is needed to confirm whether combining these foods is better than eating them separately (9).
 Quick Tip
Quick Tip6. Cereal With Milk And Orange Juice

Milk contains casein and orange juice contains citric acid. Usually, during the formation of cottage cheese, citric acid is used to cause clumping of casein proteins in the milk (10). Due to this, some experts believe that the same may also occur when you consume these foods together. They suggest that dairy and citrus fruit juices are mismatched food combinations. However, more research is needed to back this claim.
Some research also suggests that starchy breakfast cereal and milk also interfere with each other negatively (11). So, you may face negative effects on health like bloating and hindering digestion. To avoid this, have fruit juice at least an hour before or after eating cereal and replace dairy with plant-based milk.
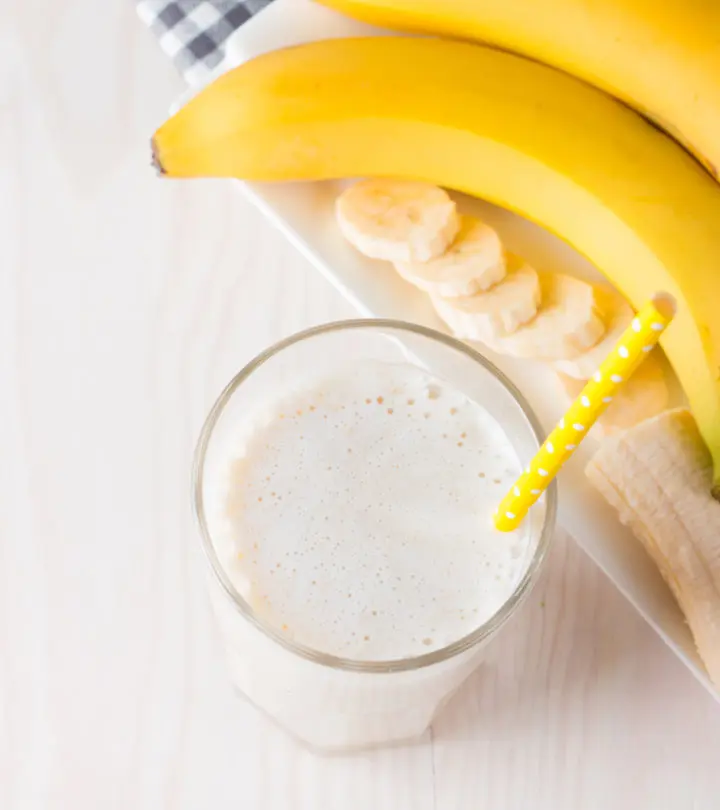
7. Banana And Milk
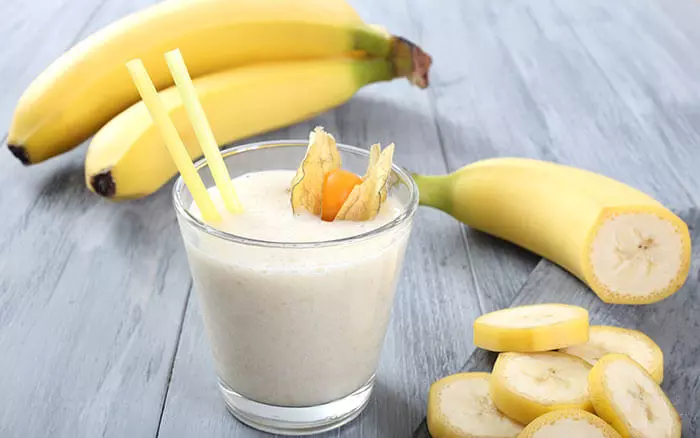

There are very few people on earth who don’t like banana milkshake. A banana milkshake is a common diet drink that keeps you satiated and prevents overheating, leading to weight loss but this also makes for a dangerous food combination, as it sits heavy in your stomach (12).
A study published in the Journal of Ayurveda and Integrative Medicine also explored the potential health risks of consuming bananas and milk together (1). The researchers conducted a 28-day toxicity test on Wistar rats. The results showed significant changes like altered digestion, mild to moderate heart inflammation, and fatty changes in the liver. So, regular consumption of this combination may have mild toxic effects and could harm health over time.
Try to avoid this combination of carbs; if you cannot resist a milkshake, add a pinch of nutmeg or cinnamon to stimulate your digestive system. Alternatively, you can replace regular milk with plant-based options like oat or almond milk.
 Quick Tip
Quick Tip8. Beans And Cheese

This is a very common combination in Mexican cuisine. Beans with cheese are delicious! Beans may help regulate your blood sugar level and manage insulin level (13). Nevertheless, cheese, beans, hot sauce and guacamole- this is a surefire recipe of bloating, gas and other digestion related problems. However, there is no relevant study supporting this claim. Also, unlike the common notion, beans by themselves do not give you gas. Instead, they are rich in dietary fiber that may help promote digestion (14). So try to separate the cheese from beans if you have a weak digestive system.
9. Tomatoes And Pasta

Tomato adds that tangy acidity, making it a must-have choice in pastas. Top it off with a low fat dressing of olive oil and voila! No pasta is complete without tomatoes, cheese sauce, or meat. However, anecdotal evidence suggests all of these wreak havoc on your digestive system. Tomato has acids that weaken the enzyme in starchy pasta and curdles the dairy in cheese. Meat and carbs are also another bad combination that makes this fare very difficult to digest. Since there is limited research on this combination, you can try to stick to pesto sauce to avoid after meal fatigue.
10. Cheese And Meat

Cheesy meatballs, meat in fonduei A meal made up of tiny food pieces, including meat or fruit cooked in or dipped into a hot liquid. , cheese and meat omelet- these all are very high in protein content. Foods obtained from milk are packed with casein that may make the combination of meat and dairy together very difficult to digest. Casein is a protein that gets digested and absorbed very slowly in the body (15). So instead, stick to chopped vegetables in fondue, avoid cheese in meatballs and cut down the meat in omelet.
While there is no study about the combination of cheese and meat, research suggests that both these foods are associated with gastric cancer. The study published in the Food Science and Nutrition journal suggests that eating red meat daily is associated with over three times the risk of gastric cancer compared to those who ate it less (16). Further, consuming dairy products 2–3 times per week doubled the risk. Therefore, it is also a good idea to consume these foods in moderation.
11. Sugar, Fat, And Salt

Any two of these three food combinations can be harmful. Sugar and fat are both foods with a high calorie content. Sugar has no nutritional value, and fat contains saturated fats that may elevate cholesterol levels (17), (18). A high-fat and high-sugar combination of food, if taken in excess, can increase the risk of diabetes and obesity (19), (20). Try cutting back on your sugar intake with a black coffee or opt for low-fat options like low-fat milk.
Salt and fat can be harmful too. This is because salt causes water retention in the body and may elevate blood pressure, while fat may elevate cholesterol levels (21), (18). You can instead try healthier forms of fat, like olive oil.
High-sugar and high-salt is another combination that many people enjoy, but it inevitably leads to weight gain (22). Examples of such foods include certain candy bars and pastries. High-sugar and high-carb baked confectioneries like bread are also not good for your overall health. What you can do instead is make your own granola bars.
12. Wine And Dessert
Combining wine and desserts, particularly sweet ones, is discouraged. The combination creates a contrasting sensory experience. The tannins in wine, especially red wine, interact with the sugars in the desserts. Tannins are compounds found in the skin, seeds, and stems of grapes. These have astringent properties and cause bitter sensations in the mouth (23). This bitterness intensifies when paired with sugary desserts.
Further, desserts can make wine taste overly acidic and diminish its overall flavor. Ideally, desserts are best enjoyed with wines that are sweeter or have a residual sugar content. Opting for a dessert wine or a wine with a low tannin content can enhance the overall dining experience as it helps create a harmony between flavors (24).
Incorporating two different flavors and textures can be an exciting and novel culinary experience. However, nutrition experts and experienced Ayurvedic practitioners do not recommend some food combinations. These may cause digestive problems or impair nutrient absorption. Some of these food combinations to avoid include yogurt with fruit, banana with milk, tomatoes with pasta, and cheese with meat, among others. These may otherwise cause after-meal problems such as gas, bloating, and tiredness. Avoiding such combinations may prevent indigestion and the heavy feeling that follows a large meal. Consider maintaining a food journal to record which combinations suit you best, seek individualized guidance from a nutritionist, and try different pairings to determine what works best for you. Stay away from these combinations for fuller, more satisfying meals.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can I eat banana and apple together?
I can’t eat banana and apple together. The intake of sub-acidic fruits like apples with bananas may hamper the digestion process and cause nausea and headaches.
Is it OK to eat fruits and vegetables together?
Fruits and vegetables may digest differently and should never be mixed. Fruits can digest quickly and hinder the digestion process of veggies due to their high sugar content. When considering easy-to-digest foods, keep in mind that separating fruits and vegetables may support effective digestion.
Can we eat an orange after milk?
We can’t eat oranges after milk. The fruit acid in the orange may combine with the milk protein and possibly affect the absorption of nutrients.
How do food combinations affect long-term health?
Poor food combinations may result in nutrient deficiencies, long-term digestive problems, and a higher risk of developing conditions like diabetes, acid reflux, irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), and obesity. Increasing awareness and practicing mindful eating may greatly improve general health and well-being.
Illustration: Dangerous Food Combinations To Avoid

Image: Stable Diffusion/StyleCraze Design Team
Unveil the nine harmful food combinations that you should steer clear of in this informative video. Explore the potential side effects that you should avoid to achieve optimal digestion. Check out the video now.
References
Articles on StyleCraze are backed by verified information from peer-reviewed and academic research papers, reputed organizations, research institutions, and medical associations to ensure accuracy and relevance. Read our editorial policy to learn more.
- Toxicological evaluation of banana and milk combination as incompatible diet – An experimental exploration of Samyoga viruddha concept
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC8377192/ - Plant-Based Dietary Practices and Socioeconomic Factors That Influence Anemia in India
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC8537570/ - Intestinal gas production from bacterial fermentation of undigested carbohydrate in irritable bowel syndrome
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/2929557/ - Controversies Surrounding High-Protein Diet Intake: Satiating Effect and Kidney and Bone Health
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC4424780/ - Influence of Probiotics on Dietary Protein Digestion and Utilization in the Gastrointestinal Tract
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29769003/ - Effect of Pre-meal Water Consumption on Energy Intake and Satiety in Non-obese Young Adults
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6209729/ - Water intake and obesity: By amount timing and perceived temperature of drinking water
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC11045127/ - Effect of Sequence of Fruit Intake in a Meal on Satiety
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC6888291/ - Potential Health Benefits of Combining Yogurt and Fruits Based on Their Probiotic and Prebiotic Properties
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC5227968/ - Effect of different coagulants at varying strengths on the quality of paneer made from reconstituted milk
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC3931878/ - Effect of food combinations and their co-digestion on total antioxidant capacity under simulated gastrointestinal conditions
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC8866489/ - Viruddha Ahara: A critical view
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3665091/ - Minimal Effective Dose of Beans Required to Elicit a Significantly Lower Glycemic Response Than Commonly Consumed Starchy Foods: Predictions Based on In Vitro Digestion and Carbohydrate Analysis
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC10649573/ - Prebiotic Potential of Dietary Beans and Pulses and Their Resistant Starch for Aging-Associated Gut and Metabolic Health
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC9100130/ - Pre-sleep casein protein ingestion: New paradigm in post-exercise recovery nutrition
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32698256/ - Meat and dairy products intake is associated with gastric cancer: Case–control study findings
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC10345672/ - Added sugars drive nutrient and energy deficit in obesity: a new paradigm
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC4975866/ - Saturated Fatty Acids and Risk of Coronary Heart Disease: Modulation by Replacement Nutrients
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC2943062/ - A high-fat, high-saturated fat diet decreases insulin sensitivity without changing intra-abdominal fat in weight-stable overweight and obese adults
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC5291812/ - A High-Sugar Diet Consumption Metabolism and Health Impacts with a Focus on the Development of Substance Use Disorder: A Narrative Review
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC9323357/ - Sodium Intake and Hypertension
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC6770596/ - High salt intake: independent risk factor for obesity?
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26238447/ - Tannins in Food: Insights into the Molecular Perception of Astringency and Bitter Taste
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC7321337/ - Wine food and health
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7173466/
Read full bio of Reda Elmardi
- Alicia Chacha Miller is a Registered Dietitian specializing in maternal and pediatric nutrition. She obtained her Master's degree in Nutrition Sciences from the University of Southern California. Her work is focused on bridging the gap in health disparities between BIPOC (Black, Indigenous, and People of Color) and other races by making nutrition education available, accessible, and easy to understand. She is the founder of The Cardamom Nutrition, where evidence-based practice, diversity, inclusion, cultural competence, and compassion all collide.
 Alicia Chacha Miller is a Registered Dietitian specializing in maternal and pediatric nutrition. She obtained her Master's degree in Nutrition Sciences from the University of Southern California. Her work is focused on bridging the gap in health disparities between BIPOC (Black, Indigenous, and People of Color) and other races by making nutrition education available, accessible, and easy to understand. She is the founder of The Cardamom Nutrition, where evidence-based practice, diversity, inclusion, cultural competence, and compassion all collide.
Alicia Chacha Miller is a Registered Dietitian specializing in maternal and pediatric nutrition. She obtained her Master's degree in Nutrition Sciences from the University of Southern California. Her work is focused on bridging the gap in health disparities between BIPOC (Black, Indigenous, and People of Color) and other races by making nutrition education available, accessible, and easy to understand. She is the founder of The Cardamom Nutrition, where evidence-based practice, diversity, inclusion, cultural competence, and compassion all collide.
Read full bio of Tanya Choudhary
Read full bio of Ravi Teja Tadimalla
Read full bio of Moksha Gandhi

























Community Experiences
Join the conversation and become a part of our empowering community! Share your stories, experiences, and insights to connect with other beauty, lifestyle, and health enthusiasts.