Diffuse Hair Loss: 6 Major Causes And Treatment Guide
Learn the A-Z of hair loss and prevent your beautiful mane from shedding.

Image: Midjourney/ StyleCraze Design Team
Hair shedding is common. Irrespective of gender and age, everyone experiences hair shedding. However, excessive hair loss is concerning. Diffuse hair loss or diffuse alopecia commonly affects women and is a cause for concern.
Hair loss or alopecia is of two types – localized (hair loss in patches) or diffused (hair thinning and loss throughout the scalp). Diffuse hair loss is a troubling issue is triggered by multiple factors. One common form of this condition is female pattern baldness, which is characterized by a gradual thinning of hair on the crown and top of the head. Mostly, it goes away when you address the underlying condition. This article explores the causes of diffuse alopecia, signs, possible treatments, and ways to manage it. Keep reading to know more.
In This Article
What Is Diffuse Hair Loss?
Diffuse hair loss or diffuse alopecia affects the entire scalp (1). The scalp hair grows in cycles:
- Anagen (active hair growth stage that may last 2- 8 years)
- Catagen (involution stage that may last 4-6 weeks)
- Telogen (the resting stage that may last 2-3 months)
The exogen phase is when the hair finally falls out, marking the end of the telogen phase.
Each hair follicle may undergo 10-30 cycles during its lifetime. Diffuse hair shedding or diffuse alopecia occurs when any phase of the hair growth cycle is disrupted (1).
A review conducted on 18,368 patients found the prevalence of alopecia increased from 0.012% to 0.0199% from 2016 to 2019. Furthermore, it was reported that the incidence of alopecia was 87.39 per 100,000 in 2017 to 92.90 per person in 2019.

Losing your hair can really take a toll on your mental health. It is normal to feel worried, down, or even depressed when you are dealing with hair loss. It can be tough to feel confident and happy when you are worried about how you look. Remember, it is important to address these feelings. Talking to a doctor can help you have a better understanding of the reasons behind your hair loss and the ways to address that. This may help you feel better.
Remember that multiple factors may disrupt the hair cycle and cause diffuse hair loss. Let’s take a look.
Key Takeaways
- Diffuse hair loss refers to hair loss that occurs equally across the scalp.
- It is caused by several factors such as telogen effluviumm, anagen effluvium, anemia, stress, and medical conditions.
- Taking supplements, steroids, topical minoxidil, and scalp cooling are some treatment options.
- Thyroid issues, family history of the disorder, pregnancy, surgeries, and other factors all increase the risk of diffuse alopecia.
What Causes Diffuse Hair Loss?
1. Telogen Effluvium
This is the most common cause of diffuse hair loss. Telogen effluvium is a temporary hair loss that may last for several months. Fever, a major surgery, childbirth, psychological stress, nutritional deficiency – anything can trigger telogen effluvium and cause hair loss. Other factors, like low serum ferritin levels caused by iron deficiency and thyroid disorders may also trigger telogen effluvium(2), (1).
 Did You Know?
Did You Know?2. Anagen Effluvium
Diffuse hair loss may also be caused by Anagen effluvium – loss of hair during its growth phase. Anagen hair loss is often triggered by (1):
- Chemotherapy Or Radiation Therapy: It can be seen a week or two after treatment. It affects 80 to 90% of the body, including the eyebrows and eyelashes.
- Heavy Metal Poisoning: Selenium, colchicine, and thalium poisoning may also trigger anagen effluvium.
- Alopecia Areata: This autoimmune condition may cause hair loss in patches(focal alopecia), complete hair loss on the scalp (alopecia totalis), or complete scalp and body hair loss (alopecia totalis).
3. Stress (Physiological And Emotional)
Physiological stress, such as trauma, childbirth, injury, illness, and major surgery, may cause telogen effluvium. However, it is reversible. Emotional stress may cause some hair loss, but the relationship between emotional stress and chronic diffuse hair loss is controversial, and more studies are needed to arrive at a conclusion (1).
 Quick Tip
Quick Tip4. Medical Conditions
Medical conditions like hyperthyroidism, hypothyroidism may trigger telogen effluvium
. However, the hair grows back once the condition is managed. Other medical issues like chronic renal failure, lymphoproliferative disorderi A group of diseases characterized by uncontrolled growth of lymphocytes, a type of white blood cells). , lupusi A long-term autoimmune disease that occurs when the body’s immune system attacks its own tissues or organs. , psoriasisi A long-lasting autoimmune condition that causes itchy, scaly patches and inflammation in your skin. , seborrheic dermatitisi A common skin condition that causes itchy, scaly patches but does not spread by contact. It especially affects the scalp. , and allergic contact dermatitisi An itchy skin rash or inflammation triggered by direct contact with a particular substance or irritant. may also cause telogen effluvium and diffuse hair loss (1).
M. Elizabeth Blair discovered the link between her hair loss and Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) in her mid-20s. Recalling her struggle, she wrote, “When I was about 25, I finally found out what was going on…I appeared to have Polycystic Ovary Syndrome. For a few years, I hoped that my hair would come back, but it never did. It just got worse over the years (i).”
5. Anemia
Extensive research has investigated the relationship between diffuse hair loss, or alopecia, and iron deficiency, with a predominant focus on women experiencing noncicatricial hair loss (hair loss without scarring). Various types of hair loss, such as alopecia areata, androgenic alopecia, and telogen effluvium, have been examined for potential links to iron deficiency. However, there is no conclusive evidence supporting that iron deficiency universally causes hair loss in individuals. Similarly, prescribing iron supplementation to hair loss patients without iron deficiency anemia relies on clinical judgment. While treating iron deficiency anemia is crucial, addressing iron deficiency without anemia remains a subject of debate, emphasizing the need for personalized assessments to avoid excessive iron supplementation (3).
6. Environmental Factors
Sometimes, it is not just what’s going on inside your body that affects your hair, but also the world around you. Pollution, harsh chemicals in hair products, and extreme weather can all take a toll on your locks.
To keep your hair healthy, try to use gentle products and avoid exposing it to too much pollution or harsh weather. Think of it like protecting your skin from the sun. The healthier your environment, the happier your hair will be.
There are specific ways to identify diffuse hair loss. Here are the signs and symptoms to look for.
What Are The Signs Of Diffuse Hair Loss?
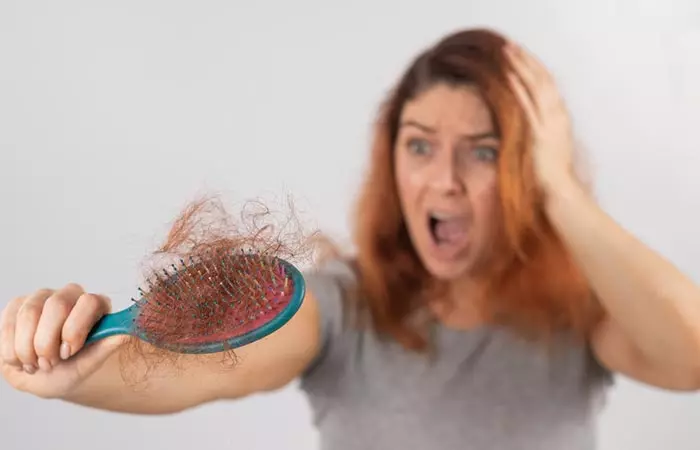

Diffuse hair loss can affect anyone. You may experience:
- Excessive Shedding: Losing 50-150 strands of hair is normal. However, if you are experiencing hair loss in clumps, consult a doctor immediately.
- Hairline Recession: Hair thinning in the central part of the scalp, widening of the hair parting, and hair loss from the frontal part (female pattern hair loss) without any apparent cause are signs of diffuse hair loss triggered by telogen effluvium (2).
- Changes In Hair Texture: Does your hair feel different lately? Maybe it is thinner, weaker, or just not as strong as it used to be. These changes could be an early sign of diffuse hair loss and you should talk to your doctor to understand the reason behind it.
If you notice these signs and symptoms, consult a doctor immediately for a proper diagnosis. They may run a few tests to confirm diffuse hair loss and the underlying reason.
How Is Diffuse Hair Loss Diagnosed?
1. History and Examination
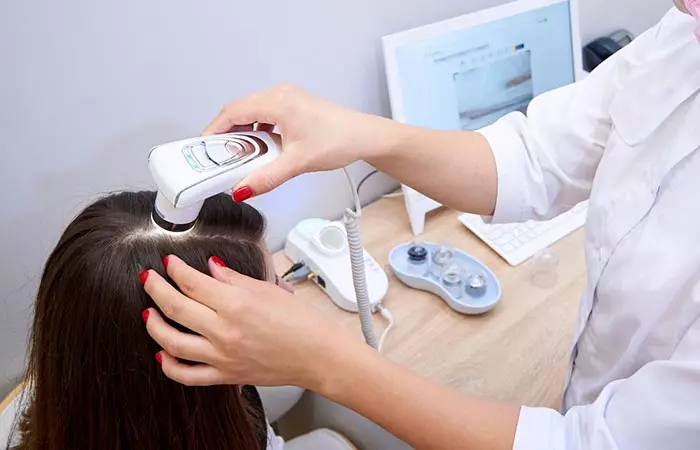
The doctor may conduct:
- Scalp Examination: The scalp health is assessed for the degree of hair loss and the pattern. The doctor may check for signs of scarring, scaling, redness, or inflammation.
- Hair Shaft Examination: The doctor may check the length, strength, and diameter of the hair shafts.
- Trichoscopy: The doctor may examine the scalp using a trichoscope for a more in-depth analysis.
- Ultrasonogram (USG): The doctor may conduct an USG to check for polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOSi A hormonal imbalance that happens during reproductive years that cause enlarged ovaries with small cysts. ).
2. Blood Test
The following tests may be required:
- Complete Blood Count And Ferritin: To identify iron deficiency and anemia.
- Thyroid Function Tests: To determine hyperthyroid or hypothyroid.
- Serum Zinc Level Tests: To check for zinc deficiency.
- Renal and liver function tests: To determine kidney and liver functions as these issues may also cause hair loss.
- Antinuclear Antibodies (ANA) Test: To determine any autoimmune condition.
- Hormonal Evaluation: This would include prolactin, free androgen index, hormone-binding globulin for women suspected of having hyperandrogenismi A medical condition commonly observed in women, caused by excessive male sex hormones (androgens) in their bodies. .
3. Hair Pull Test
The dermatologist may grab a small section of hair that may have about 40-50 strands from different parts of the scalp and gently tug. If six or more strands fall out of each section, it may indicate active hair loss. This test is often done to determine alopecia areata, telogen, and anagen effluvium.
4. Trichogram
This is conducted to analyze the hair. The dermatologist may pluck 25 or 50 hair strands from different parts of the scalp and examine them under a microscope to determine the number of anagen and telogen hairs.
- If more than 80% of the hairs are in the anagen phase and less than 20% are in the telogen phase, your hair loss is normal.
- If 25% of hairs are in the telogen phase, you have telogen effluvium.
5. Scalp Biopsy
It is also called “punch” biopsy. The dermatologist uses a sharp pencil-like device to puncture the scalp and remove tissue for examination. This test is often done to diagnose scarring and cicatricial alopeciai An inflammatory skin condition that destroys the hair follicles and causes scarring and permanent hair loss. .
6. Family History Assessment
Sometimes, hair loss runs in the family. If your mom, dad, or other family members have experienced thinning hair, you might be more likely to experience it.
When you see your doctor, they would want to know about your family’s hair history. This information can help them figure out what is causing your hair loss and choose the best treatment for you.
Once the reason for diffuse hair loss is diagnosed, the doctor may suggest the following treatment options.
What Are The Treatment Options For Diffuse Hair Loss?
1. Topical Minoxidil
Applying 2% and 5% minoxidil (Rogaine) on the scalp may promote hair growth. This is a common treatment option for hair loss caused by telogen effluvium (4).
2. Supplements
Doctors may recommend biotin, amino acids, proteins, and zinc supplements for acute telogen effluvium, chronic diffuse hair loss, and chronic repetitive telogen effluvium (5).
3. Steroids And Other Medications
Oral finasteride and anti-androgens like spironolactone are also used off-label for treating androgenetic alopecia or male pattern baldness (6). If there are any other underlying issues, like dandruff and scalp infection, the doctor may suggest medicated shampoos and topical solutions for treating them.
4. Scalp Cooling
If chemotherapy or radiation therapy has triggered diffuse alopecia, it could be managed with scalp cooling (7).
Along with these, you also have to take care of nutritional deficiencies (if any). Fortunately, there are several treatments available to help restore hair texture, and hair density and promote hair regrowth. You can try homeopathic treatments for hair loss and see if they bring any results. Another option is hair restoration using advanced techniques like hair transplant surgery, which involves moving healthy hair follicles from one area of the body to the balding spot of the body. Follow a balanced diet and take the hair vitamin supplements suggested by your doctor. Choosing gentle hair products and avoiding excessive hair styling can help prevent damage to the hair follicles. Telogen effluvium and diffuse hair loss triggered by physiological stress go away once the stress factor is eliminated. You may also try home remedies to take care of your scalp and hair at home.
Treating Diffuse Alopecia At Home
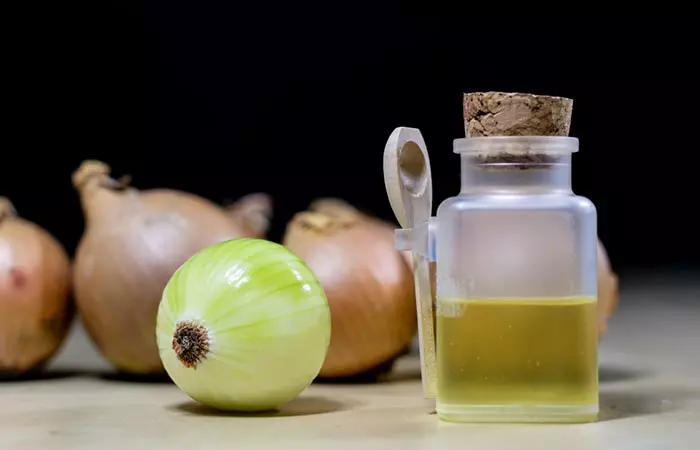

Besides taking care of the hair and following the doctor’s prescription, you may also follow home remedies to prevent hair loss and manage the underlying causes of hair loss (like stress).
- Onion Juice: You can rub fresh onion juice on the affected area. This home remedy is said to promote hair growth (8).
- Aromatherapy: Essential oils help calm your mind and reduce stress levels. This may also help minimize hair fall (9).
- Garlic Gel: Evidence suggests that applying garlic gel and topical betamethasone on bald patches promote hair growth (10).
- Saw Palmetto: This popular herbal remedy is said to reverse hair loss. You can apply saw palmetto extract on the affected area (11).
- Caffeine Extract: A study found that caffeine may stimulate hair growth (12).
Certain factors may increase the risk factor of developing diffuse alopecia. Let’s take a look at them.
What Are The Risk Factors Of Diffuse Alopecia?
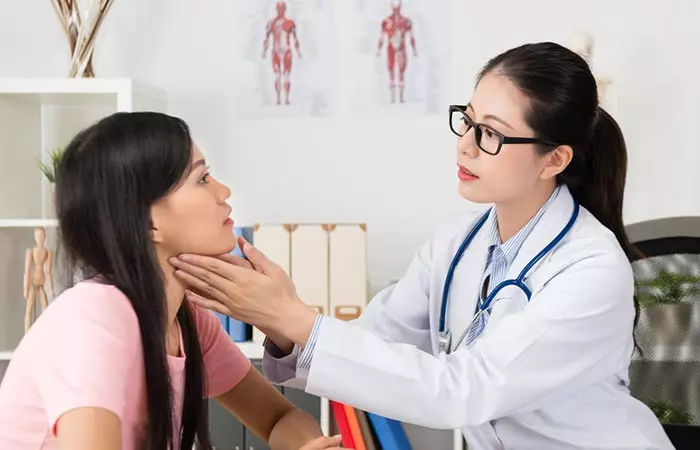
You may develop any form of alopecia if you have:
- A family history of the condition
- Other autoimmune conditions like vitiligo and discoid lupus erythematosus
- Thyroid issues
- A history of atopy (genetic tendency to develop allergic diseases)
Pregnancy, childbirth, surgeries, and physiological stress may also increase your chances of developing telogen effluvium and diffuse alopecia.
Infographic: Dos and Don’ts Of Managing Hair Health
Diffuse hair loss is caused by factors such as nutritional deficiencies, stress, and hormonal imbalance. It may also be a sign of an underlying medical condition. You can use medical treatment or home remedies to promote hair growth. However, there are certains tips you must follow while managing your hair health.
Check out the infographic below to know more!
Some thing wrong with infographic shortcode. please verify shortcode syntax
You may experience diffuse hair loss due to multiple underlying factors and health conditions. However, don’t worry, as diffuse hair loss can be reversed, and normal hair growth will resume once the underlying factor is treated. Therefore, if you notice hair loss all over your head, consult a doctor to determine the exact reason for the issue and follow the prescribed treatment. Also, follow a regular hair care routine, take hair supplements (after consulting the doctor), and consume a healthy diet to maintain your hair health.
Frequently Asked Questions
How do you treat diffuse alopecia?
Diffuse alopecia can be treated with medications like Minoxidil and Finasteride, which stimulate the growth of hair follicles and elongate the growth cycle of the hair.
Is diffuse thinning permanent?
No, diffuse thinning is not permanent. It can be managed and reversed effectively with medical interventions.
Is diffuse thinning genetic?
Yes, diffuse thinning can be genetic. A study found that androgenetic alopecia, which affects 80% of males and 50% of women, is the most prevalent type of hair loss. In this type of alopecia, genetic factors and age-related causes have an impact on the androgen mechanism, which is what causes vellus hair to develop into terminal hair that is longer, thicker, and darker (13).
How long does diffuse thinning last?
The duration of diffuse thinning can vary depending on the underlying cause and the effectiveness of the treatment.
Illustration: Diffuse Hair Loss (Alopecia): Causes, Signs, And Treatments
_causes_signs_and_treatments_illustration.jpg.webp)
Image: Stable Diffusion/StyleCraze Design Team
Read full bio of Dr. Shruti Chavan
Read full bio of Ramona Sinha
Read full bio of Anjali Sayee
Read full bio of Monomita Chakraborty

























Community Experiences
Join the conversation and become a part of our empowering community! Share your stories, experiences, and insights to connect with other beauty, lifestyle, and health enthusiasts.