Dysphagia Diet: How Does It Work, Diet Plan, & Recipes
Eat and swallow food with ease on this diet!
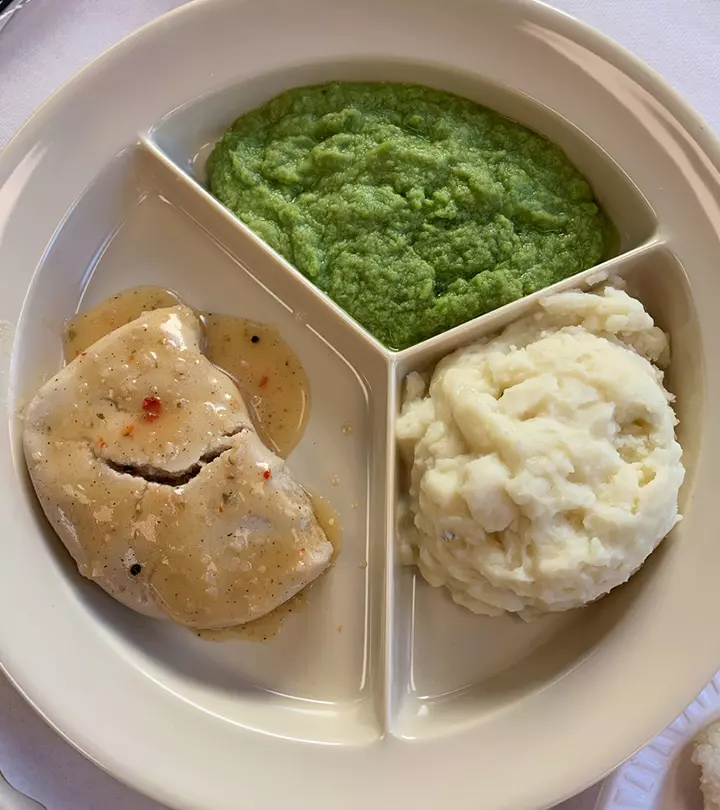

Image: Shutterstock
Dysphagia, or difficulty swallowing foods and liquids, can disrupt your daily life (1). Whether caused by neurological conditions, structural issues, or aging, dysphagia requires a tailored approach to food and liquid consumption. The dysphagia diet helps people with swallowing difficulties enjoy their meals safely.
This diet can be followed at various levels, each with specific modifications to food texture and consistency. This reduces the risk of choking, making eating and drinking a more comfortable experience. In this article, we will explore the different levels of the diet, guidelines for modifying food textures, dietary recommendations, and practical tips to ensure adequate nutrition. Read on!
 At A Glance: The Dysphagia Diet
At A Glance: The Dysphagia Diet- Principle: Consumption of soft and pureed foods as well as thickened liquids for safe swallowing.
- Purpose: To manage dysphagia and reduce the risk of choking.
- Who It Is For: Individuals diagnosed with dysphagia
- Duration: Long-term
- Cons: Limited food choices
In This Article
What Is The Dysphagia Diet?

The dysphagia diet is a dietary strategy for individuals having trouble swallowing their food and liquids. This diet ensures that individuals with dysphagia can consume food and liquids safely and with minimal discomfort. It involves meticulous adjustments to the texture and consistency of solids and liquids to reduce the risk of choking or aspirationi Accidental entry of substances or foods into the airway that can increase the risk of choking. . Customizing the food and drinks for people with dysphagia helps in improving their nutritional well-being.
Apart from improving nutritional well-being, the dysphagia mechanical soft diet is needed for other reasons too. Scroll down to the next section to know more.
Key Takeaways
- The dysphagia diet promotes the consumption of soft and pureed foods and thickened liquids for safe swallowing and consumption.
- Ripe fruits, starch, cereals, and thickened liquids are allowed while alcohol, hard foods, and spicy foods are avoided on this diet.
- Consume small frequent meals and puree or mince your food to avoid choking or aspiration.
Why The Dysphagia Mechanical Soft Diet Is Needed
- Swallowing Safety: Dysphagia elevates the risk of choking and aspiration as the food or liquids may enter the airway. The mechanical soft diet modifies the texture and consistency of foods for safe swallowing.
- Nutritional Adequacy: Dysphagia can impede an individual’s ability to follow a regular diet, which can result in inadequate nutrition. This diet provides food options while ensuring proper nutrition.
- Improved Quality Of Life: Eating and drinking difficulties can lead to frustration and a diminished dining experience. This diet focuses on a wide variety of foods that are easier to consume, which helps one enjoy their meals and improve one’s quality of life.
- Medical Management: Healthcare professionals frequently prescribe this diet along with swallowing rehabilitation to manage dysphagia (2).
- Customization: The dysphagia mechanical soft diet can be tailored to suit the unique needs and preferences of the individual to ensure that it helps manage their dysphagia and overall health requirements.
The dysphagia diet is divided into various levels to ensure that all the above requirements are met. Take a look in the next section.
Dysphagia Diet Levels
The levels of the dysphagia diet focus on matching the food and liquid texture to the individual’s swallowing ability. It aims to minimize the risk of choking and aspiration to ensure that the individual receives proper nutrition and enjoys a satisfying dining experience (3). Healthcare professionals such as speech-language pathologists and dietitians assess the individual’s condition and recommend the appropriate diet level based on their needs. The flexibility of these levels allows for personalized dietary plans that prioritize safety and nutrition.
Level 1: Pureed Diet
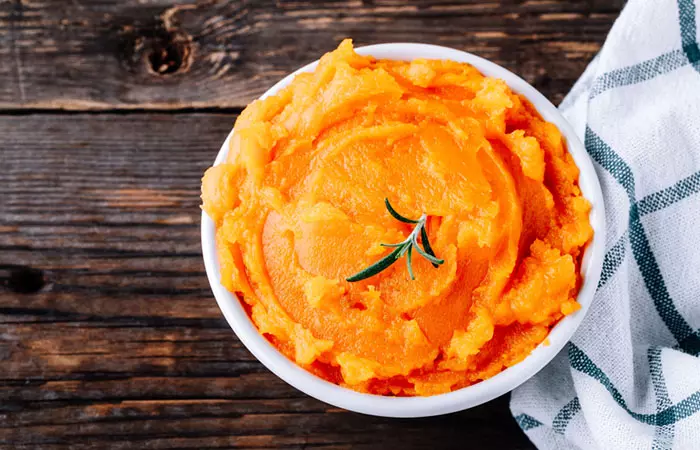

This level involves transforming foods into a smooth, uniform puree. It is primarily recommended for individuals with severe dysphagia where swallowing is extremely challenging. The pureed diet with its softer texture, minimizes the need for extensive chewing, making it safer and convenient to swallow.
Pureed vegetables, fruits, meats, and desserts are recommended at this level.
Level 2: Mechanical Soft Diet
This caters to individuals with moderate dysphagia. It focuses on soft, moist, and easy-to-chew foods, eliminating the need for strong biting or grinding. While this diet ensures safe swallowing while expanding food choices, it is important to maintain food moistness and adjust portion sizes for comfortable consumption. Overall, the mechanical soft diet strikes a balance between safety and palatability for people with dysphagia.
Soft-cooked vegetables, tender meats, scrambled eggs, and mashed potatoes are recommended at this level.
Level 3: Dysphagia Diet
The dysphagia diet focuses on meticulously chopping or mincing food into small, bite-sized pieces. This level is for individuals with mild to moderate swallowing difficulties. It introduces greater diversity in food texture and allows for smaller, manageable bites for safe and easy swallowing.
Finely diced fruits, cooked grains, small pieces of tender meat, and foods with manageable textures are recommended at this level.
Apart from the levels mentioned above, there are some additional guidelines that one needs to follow when preparing this diet. Scroll down to the next section to know more.
Diet Texture Modification Guidelines For Dysphagia Pureed Diet
Speech-language pathologists (SLPs) conduct a comprehensive assessment and consider the patient’s health and needs before recommending a pureed diet. The American Speech-Language-Hearing Association (ASHA) does not provide specific guidelines for diet levels or terminology. Your doctor will consider factors like dysphagia severity, nutritional requirements, and preferences before recommending a diet.
- IDDSI Framework
The International Dysphagia Diet Standardisation Initiative (IDDSI) provides guidelines for labeling texture-modified foods and thickened liquids. SLPs are encouraged to use IDDSI as a guideline for pureed diets to ensure consistency and safety in diet modifications.
- Facility-Established Protocols
Healthcare facilities may have their own unique dysphagia diet protocols. SLPs should coordinate and communicate with them to ensure consistency in care.
- State-Specific Regulations
Some state health departments may provide guidelines on dysphagia diets. SLPs should adhere to state-specific regulations for the proper management of pureed diets.
- Ordering Pureed Diets
The process of ordering pureed diets varies based on state laws and facility regulations. SLPs should follow specific guidelines and collaborate with other healthcare professionals when addressing nutritional restrictions outside their scope of practice.
The levels and guidelines mentioned above can help create a sustainable dysphagia diet plan. But if you need some inspiration, scroll down to the next section for a sample diet menu.
Level 1: Dysphagia Pureed Diet
| Meals | Foods |
| Breakfast |
|
| Morning Snack |
|
| Lunch |
|
| Evening Snack |
|
| Dinner |
|
Level 2: Dysphagia Minced And Moist Diet
| Meals | Foods |
| Breakfast |
|
| Morning Snack |
|
| Lunch |
|
| Evening Snack |
|
| Dinner |
|
Level 3: Dysphagia Mechanical Soft Diet
| Meals | Foods |
| Breakfast |
|
| Morning Snack |
|
| Lunch |
|
| Evening Snack |
|
| Dinner |
|
Note:
While preparing these meals ensure that meat and vegetables are softened in a broth or gravy before serving and fibers from vegetables, such as sweet potatoes, are removed to avoid swallowing issues.
In addition to curating a healthy and nutritious food menu, one needs to follow a few tips to ensure that the individuals’ nutritional requirements are being met. Take a look in the next section.
Tips For Getting Adequate Nutrition
- Consult With Healthcare Experts: Consult specialized healthcare professionals like speech-language pathologists (SLPs) and physicians to evaluate the severity of dysphagia to determine the most suitable diet.
- Follow Dietary Guidance: Adhere closely to the dietary recommendations provided by the healthcare team for safe swallowing.
- Adjust Food Texture: Modify solid foods as needed to match the recommended texture. This might involve using processes like blending, mincing, or finely chopping the ingredients to ensure safe swallowing.
- Manage Liquid Consistency: If the individual requires thickened liquids, use approved thickeners by a registered dietitian for the desired consistency for liquids like water, juice, and soup.
- Diverse Nutrition: Ensure the individual receives a well-rounded diet that covers various food groups and meets the nutritional requirements.
- Smaller, More Frequent Meals: Consume small meals throughout the day to help reduce the risk of choking.
- Mealtime Supervision: Take smaller bites and chew your food slowly and thoroughly to prevent swallowing issues.
- Appropriate Tableware: Choose utensils and dishes that match the recommended dietary texture. For instance, opt for soft and flexible utensils for those on a pureed diet.
- Proper Seating And Positioning: Ensure the individual sits upright with their head and neck properly aligned to promote safe swallowing.
- Hydration Management: Maintain adequate fluid intake to avoid dehydration. If thin liquids are a challenge, provide thickened liquids.
 Quick Tip
Quick TipNow that you know the different tips to ensure safe swallowing eating, move on to the next section to know the foods you can eat with dysphagia. Scroll down.
Foods To Eat With Dysphagia
Beverages/Liquids
- Thickened water, juice, and soup
- Smoothies made with yogurt or pureed fruits
- Milkshakes
- Thickened herbal teas
Starches, Breads, And Cereals
- Cooked oatmeal
- Cream of wheat
- Mashed potatoes
- Pureed sweet potatoes
- Moistened, soft bread without crusts
- Soft rice or pasta
- Porridge or congee
Meat And Meat Substitutes
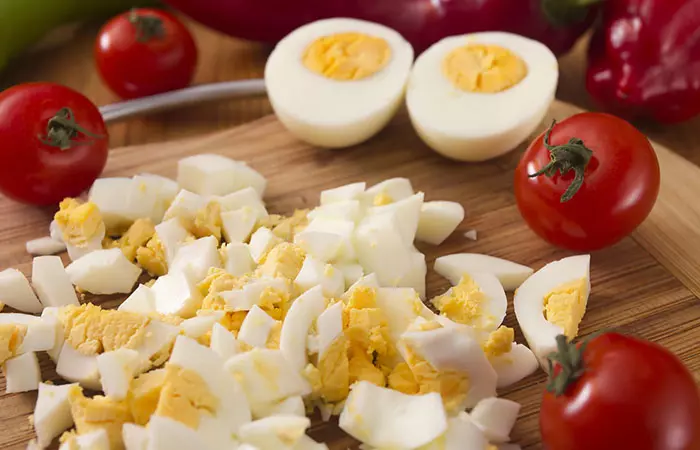

- Moist, tender, finely minced or shredded meat, poultry, or fish
- Soft meatloaf or meatballs
- Pureed tofu or well-cooked beans
- Scrambled or soft-boiled eggs
Fruits And Vegetables
- Canned or cooked fruits without skin
- Ripe bananas
- Mashed avocado
- Cooked and mashed vegetables
- Smooth fruit or vegetable puree
Desserts

- Puddings
- Gelatin desserts
- Soft cakes and muffins without nuts or dried fruits
- Pureed fruit sorbets
- Smooth ice creams and frozen yogurt
While the foods mentioned above provide you with the required nutrients, it is also important to learn about the foods one should avoid with dysphagia. Take a look in the next section.
Dysphagia Foods To Avoid
- Hard, Crunchy Foods – Nuts, seeds, hard candies, chips, and pretzels.
- Dry, Crumbly Foods – Dry bread or crackers, dry cereals, and biscuits.
- Tough Meats – Rare or undercooked meat, tough steak, and jerky.
- Sticky Foods – Peanut butter (unless thinned), sticky candies, and caramel
- Large Chunks Or Whole Foods – Whole grapes, cherry tomatoes, and large chunks of raw vegetables.
- Foods With Thin, Slippery Consistency – Overly greasy or slippery food as they can be challenging to control in the mouth.
- Carbonated Beverages – Soda and sparkling water as they can increase the risk of aspiration.
- Alcohol – Alcoholic beverages since they may impair swallowing reflexes.
- Spicy Foods – Very spicy foods or foods with hot seasonings as they may cause discomfort or irritation.
- Foods With Small, Hard Parts – Bones in fish or poultry and fruit pits. They should be carefully prepared and removed before consumption.
Consult a healthcare professional or speech-language pathologist (SLP)i A health professional that specializes in the diagnosis and treatment of communication and swallowing disorders. to determine a personalized diet plan that suits your specific needs.
While many foods need to be avoided on this diet, you do not need to compromise on taste. Check out the next section for some delicious recipes you can experiment with at home.
Dysphagia Diet Recipes
1. Creamy Broccoli Soup
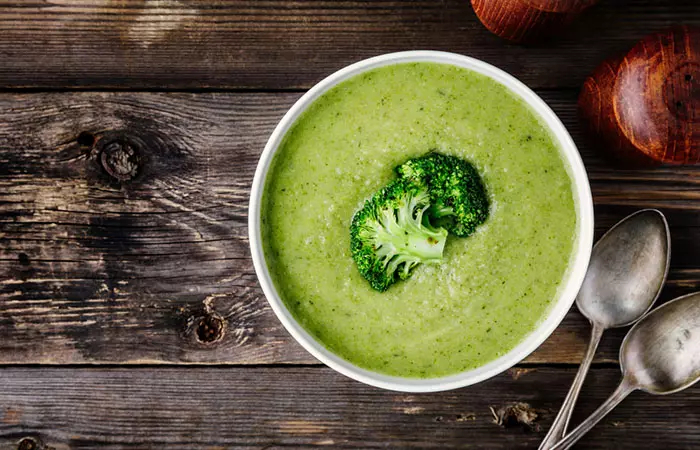

Ingredients
- 1 cup of cooked and pureed broccoli
- 1 cup of low-sodium chicken or vegetable broth
- 1/2 cup of dairy or almond milk
- 1 tablespoon of butter or margarine
- Salt and pepper to taste
How To Prepare
- Melt the butter over low heat in a saucepan.
- Add the pureed broccoli and sauté for a few minutes.
- Pour the chicken or vegetable broth and bring the mixture to a simmer.
- Add the milk and continue to simmer for about 5-7 minutes, stirring occasionally.
- Season with salt and pepper.
- Let the soup cool slightly before serving.
2. Mashed Sweet Potatoes
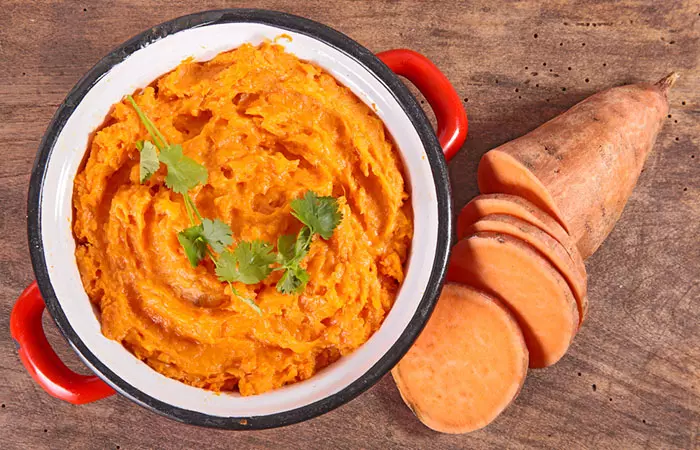

Ingredients
- 1 medium sweet potato, peeled, cooked, and mashed
- 2 tablespoons of butter or margarine
- 2-3 tablespoons of milk or almond milk
- Cinnamon or nutmeg for flavor
- Salt and pepper to taste
How To Prepare
- Place the cooked sweet potato in a bowl.
- Add butter and milk and mash the sweet potato with a fork or potato masher until smooth and creamy. Add more milk for the desired consistency.
- Add a pinch of cinnamon or nutmeg.
- Season with salt and pepper.
- Mix well and serve.
3. Creamy Butternut Squash Puree
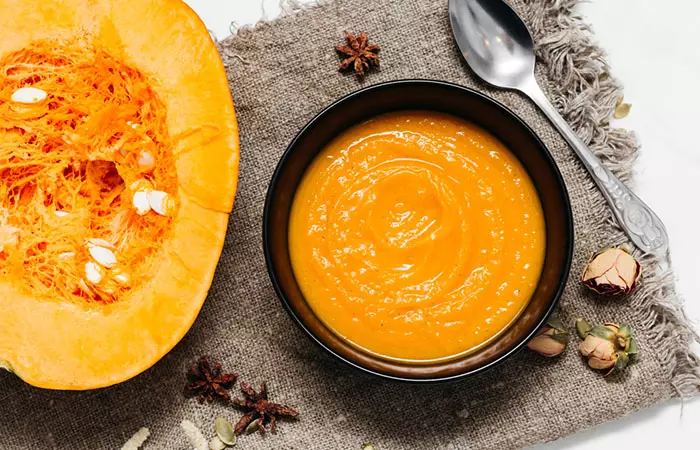

Ingredients
- 1 cup of cooked and pureed butternut squash
- 1/2 cup of low-sodium chicken or vegetable broth
- 2 tablespoons of Greek yogurt or sour cream
- 1 tablespoon of butter or margarine
- Ground nutmeg for flavor
- Salt and pepper to taste
How To Prepare
- Add the pureed butternut squash and chicken or vegetable broth in a saucepan.
- Stir over low heat until mixed well.
- Stir in the Greek yogurt or sour cream.
- Add the butter and stir until the mixture is creamy and heated through.
- Season with ground nutmeg, salt, and pepper.
- Let it cool slightly before serving.
4. Soft Scrambled Eggs With Spinach
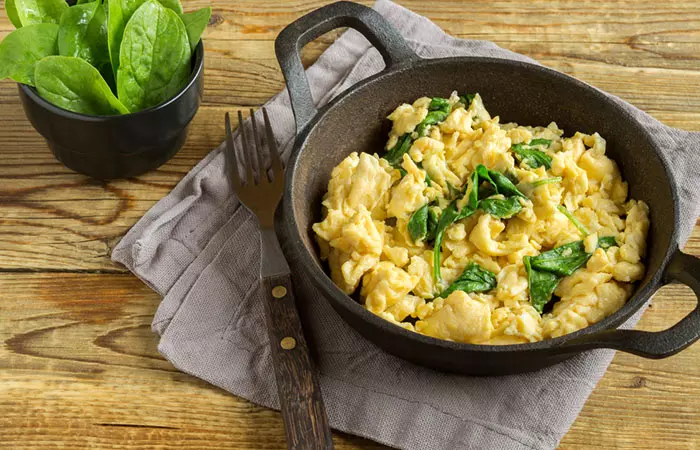

Ingredients
- 2 large eggs
- 2 tablespoons of dairy or almond milk
- 1/4 cup of finely chopped cooked spinach
- 1 tablespoon of butter or margarine
- Salt and pepper to taste
How To Prepare
- Whisk the eggs and milk together in a bowl until well combined.
- Melt the butter over low heat in a non-stick skillet.
- Add the chopped spinach and sauté briefly.
- Pour the egg mixture into the skillet and cook over low heat, stirring gently, until the eggs are soft and fully cooked.
- Season with salt and pepper.
- Let it cool a bit before serving.
5. Applesauce With Cinnamon
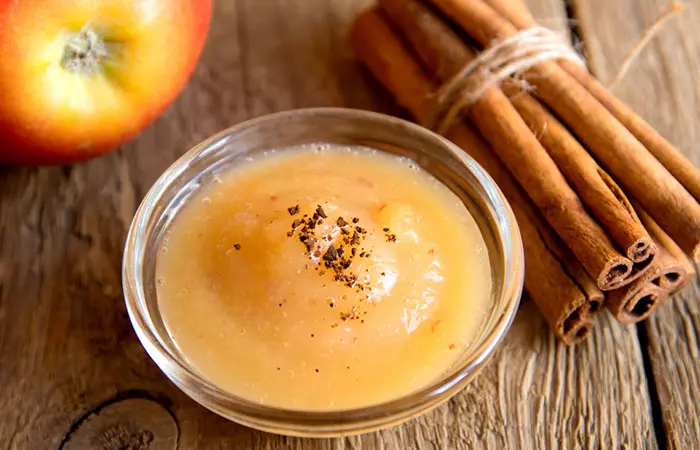

Ingredients
- 1 cup of unsweetened applesauce
- 1/4 teaspoon of ground cinnamon
How To Prepare
- Mix the unsweetened applesauce with ground cinnamon in a bowl.
- Stir until well combined.
- Serve at room temperature.
 Quick Tip
Quick TipWhile a wide variety of dishes can be included in this diet, are regular liquids allowed on the dysphagia pureed diet? Find out in the next section.
Are Regular Liquids Allowed On The Dysphagia Pureed Diet?
Regular liquids are typically not allowed on the dysphagia-puréed diet as all foods and liquids must be pureed to reduce the risk of choking and aspiration.
Liquids are often thickened to a specific consistency to provide the required hydration as they are less likely to penetrate the airway and cause aspiration. Follow the recommended guidelines given by your healthcare provider to avoid these issues.
Apart from following the listed recommendations and guidelines, you can follow a few tips for preparing foods to ensure safety. Take a look in the section below.
Tips For Preparing Dysphagia Foods
- Adjust Food Texture: Puree or finely mince solid foods to match the recommended texture level.
- Thicken Liquids Properly: Follow the recommended guidelines given by your dietitian to achieve the prescribed liquid thickness using commercial thickeners.
- Serve Food At Safe Temperatures: Ensure that foods and liquids are served at safe and comfortable temperatures and avoid extremes of hot or cold.
- Enhance Flavor Thoughtfully: Add herbs, spices, and low-sodium seasonings to infuse flavor into puréed or minced dishes.
- Optimize Moisture Levels: Include liquids like broth or gravy to retain appropriate moisture in pureed or minced meals.
- Adhere To Food Safety: Follow standard food safety practices during preparation to prevent potential foodborne issues.
Dysphagia is characterized by difficulty in swallowing food and liquid. It requires a tailored dietary approach to ensure safe swallowing. The dysphagia diet has 3 different levels that signify different food textures and is recommended as per the individual’s needs. Ripe fruits, starches, and thickened liquids are allowed on this diet while tough meat, spicy foods, and alcohol are avoided to prevent choking or aspiration. Ensure that you follow proper food safety standards and consume food at the right temperatures to avoid any issues while swallowing. Consult your healthcare professional for a customized diet to ensure your nutritional needs are met while keeping your safety in mind.
Frequently Asked Questions
What fruits are good for dysphagia?
Soft and ripe fruits such as bananas, apples, and pears are recommended for dysphagia. You can puree or mash them for easier swallowing.
Is milk good for dysphagia?
Yes, you can consume milk if you have dysphagia. However, you may use thickeners to adjust the consistency if you have trouble swallowing thin liquids.
Can dysphagia be cured?
No, there is currently no cure for dysphagia. However, proper medical treatment can help improve swallowing and manage the condition.
Are eggs good for dysphagia?
Yes, scrambled or soft-boiled eggs are recommended for people with dysphagia as they are easier to swallow.
Is water good for dysphagia?
You can consume water. However, it must be thickened with a thickener to reduce the risk of choking. However, consult your doctor or speech-language pathologist to determine if you can tolerate thin liquids
Is ice cream good for dysphagia?
Yes, soft ice cream may be suitable for some individuals with dysphagia. It is recommended that you consult a healthcare professional for a personalized dietary plan.
Illustration: Dysphagia Diet: How Does It Work Diet Plan & Recipes

Image: Dall·E/StyleCraze Design Team
Dysphagia can increase the risk of choking and disrupt your daily eating. Check out this video to learn how to puree and thicken your foods for safe and easy swallowing.
References
Articles on StyleCraze are backed by verified information from peer-reviewed and academic research papers, reputed organizations, research institutions, and medical associations to ensure accuracy and relevance. Read our editorial policy to learn more.
- Dysphagia
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK559174/ - Nutritional Management Enhances the Recovery of Swallowing Ability in Older Patients with Sarcopenic Dysphagia
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7917588/# - The Effectiveness of International Dysphagia Diet Standardization Initiative–Tailored Interventions on Staff Knowledge and Texture-Modified Diet Compliance in Aged Care Facilities: A Pre-Post Study
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8994209/
Read full bio of Staci Gulbin
Read full bio of Aparna Mallampalli
Read full bio of Arshiya Syeda
Read full bio of Sindhu Koganti






















Community Experiences
Join the conversation and become a part of our empowering community! Share your stories, experiences, and insights to connect with other beauty, lifestyle, and health enthusiasts.