16 Herbs For Diabetes That May Control Your Sugar Levels
Manage your blood glucose levels with some of the effective herbal teas and supplements.

Image: Source:Shutterstock
High sugar levels can lead to diabetes. Thankfully, natural remedies also work great for keeping your sugar levels under control. Using herbs for diabetes is one such remedy you can use. Of course, you also must reduce consuming foods high in sugar or with a high glycemic index. You must also start exercising 4-5 times a week. While diabetes type 1 may require you to take insulin injections along with these herbal remedies, diabetes type 2 can be reversed by changing your lifestyle and taking these herbs. These natural remedies may help regulate blood sugar levels and boost overall health. In this article, we will look at 16 effective herbs that can aid in diabetes management, supported by scientific studies and traditional uses. Fixing your lifestyle and your daily diet can go a long way in improving your health. Read on to learn about how to procure and consume these helpful herbs.
In This Article
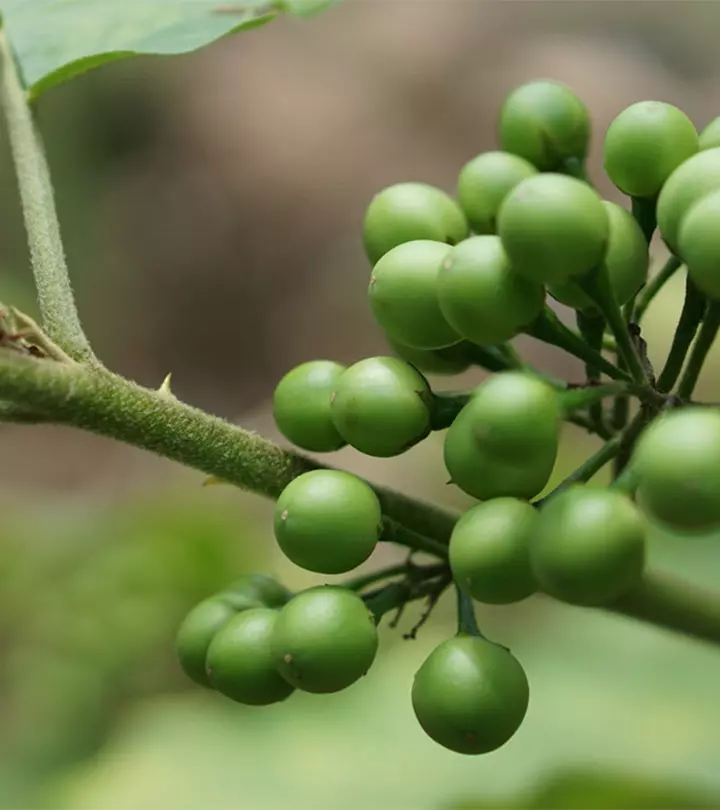
1. Gymnema Sylvestre

This plant is literally called ‘sugar destroyer’ in Hindi, so you can well imagine its diabetes-busting properties. The herb is loaded with glycosides known as gymnemic acids. These essentially reduce your taste bud’s sensitivity to sweet things, thereby lowering sugar cravings in prediabeticsi A health condition in which blood sugar levels are higher than normal but not high enough to be categorized as type 2 diabetes. . Even those who are already affected by type 2 diabetes can control their sugar levels with the help of this herb. It increases the enzyme activity in the cells, which results in utlization of excess glucose in the body. It can also positively affect insulin production (1).
How To Consume Gymnema Sylvestre & The Dosage
You can consume it in the powdered form, make tea with its leaves or have capsules. You can make tea by steeping the leaves in boiled water for 10 minutes. You can also add the powder to a cup of lukewarm water and consume it. The dosage is as follows.
- Capsule: 100mg
- Powder: ½-1 teaspoon
- Leaves: 1 teaspoon
When To Consume Gymnema Sylvestre
The best time to consume Gymnema Sylvestre is in the morning or 20 minutes before meals.
Where To Buy Gymnema Sylvestre
You can buy it online and at Ayurvedic stores or pharmacies.
Key Takeaways
- Bitter gourd, fenugreek, cinnamon, and aloe vera may help naturally control blood glucose levels.
- Cinnamon consumption may improve insulin sensitivity.
- Turmeric and neem are enriched with antibacterial and anti-glycemic properties.
- Chromium and alpha lipoic protein may help mobilize fat and lower cholesterol levels.

2. Ginseng

Ginseng has been known as an immunity boosting and disease-fighting herb for ages, but researchers have recently found that it also contains anti-diabetic properties. When you take ginseng, the absorption of carbohydrates slows down, and the cells take up and use more glucose. Apart from that, insulin production in the pancreas also increases. All these contribute to a healthier body that is less prone to diabetes (2). If you already have diabetes, this can help lower the blood glucose levels by 15 to 20%, better than placeboi A substance or treatment with no therapeutic value that is given to trick the brain into functioning as if it were real treatment. , as shown by the research team from the University of Toronto .
How To Consume Ginseng & The Dosage
You can have ginseng root or powder. Chop the root and add it to boiled water. Let it steep for 5-6 minutes. You can also mix powdered ginseng in warm water and have it. The dosage is as given below.
- Powder: 1 teaspoon
- Root: 2-3 g or 7-8 slices
When To Consume Ginseng
Consume ginseng early in the morning and before dinner.
Where To Buy Ginseng
You can buy it online or at Chinese medicine shops and Ayurvedic pharmacies.
3. Sage

Consuming sage on an empty stomach can help reduce the blood glucose levels significantly. It boosts insulin secretion and activity, which helps to curb blood sugar in prediabetics and manage it in type 2 diabetics (3). Apart from that, it also affects liver function positively, thus improving immunity. Although favored as an addition to meat dishes, this herb is at its medicinal best when it is consumed as tea .
How To Consume Sage & The Dosage
The best way to consume sage is in the form of tea. You can also include chew sage leaves or add them to your food or take sage supplements. To prepare sage tea, pour boiling water in a cup containing 1-2 sage leaves. Let it steep for 5 minutes. The dosage is as follows.
- Leaves: 4-6 g/day
- Dried leaves: ⅙-½ teaspoon
- Tea: 2-3 cups/day
When To Consume Sage
Consume sage tea or chew sage leaves early in the morning on an empty stomach. You can include sage leaves in your food for lunch and dinner.
Where To Buy Sage
You can buy sage at grocery stores or online.
4. Bilberry

This is another effective herb for diabetes treatment that has shown immense medicinal potential. Not only does it help type 2 diabetics, who suffer from high blood sugar levels, but it is also quite effective in treating diabetes mellitus. Bilberry contains a compound called glucoquinine, which is chiefly responsible for lowering the blood sugar levels. Bilberry infusions can also help people whose eyesight has been compromised due to this disease. However, you should be careful if you are taking bilberry infusion along with diabetes medication as it might cause your blood sugar to drop to dangerous levels. So, monitor your blood sugar levels regularly (4).
The following graph was taken from a study published in the Journal of Functional Foods that noted the effect of bilberry and wild freeze dried bilberry extract on salivary α-amylase activity. The extracts showed better inhibitory activity than the commercial standard acarbose (control). Human salivary α-amylase was inhibited by bilberry extract and wild freeze-dried bilberry extract in a dose-dependent manner. Bilberry extract inhibited human salivary – amylase by 61%, 57%, and 55% at doses of 66, 6.6, and 0.66 g/ml, respectively, but freeze dried wild bilberries inhibited the enzyme by 78%, 73%, and 68% at the corresponding concentrations.

Effect Of Bilberry Extract On Salivary Alpha-Amylase Activity
Source: Anthocyanin-enriched bilberry extract attenuates glycaemic response in overweight volunteers without changes in insulinHow To Consume Bilberry & The Dosage
Bilberry extract is widely available and is the safest way to control your blood sugar levels. Here’s the dosage.
- Bilberry extract: 10-100 mg with 25% anthocyanosidesi Water-soluble pigments that appear red, purple, or any color depending on their pH and control pigmentation in plants.
When To Consume Bilberry
You can consume the extract once in the morning and once in the evening an hour before dinner.
Where To Buy Bilberry
You can buy bilberry extract at a pharmacy, Ayurvedic stores, or online.
5. Oregano

Also known as marjoram, this exotic herb of Spanish and Mediterranean origin is known to contain glycosides that lower the blood sugar levels in the body. The water extracts of oregano exhibit a glycosidase inhibitory activity in vitro. The Rosmarinic acid separated from the extract has been shown to increase the pancreatic amylase activity. It also boosts the immune system. It helps in increasing insulin activity and mobilizes glucose in the cells, thus reducing the rate of carbohydrate formation (5).
How To Consume Oregano & The Dosage
Oregano is regularly used in different cuisines. You can use fresh or dried oregano in your food, chew the leaves, make oregano tea, consume diluted oregano oil or capsules. Make oregano tea by adding a teaspoon of dried or fresh oregano to a cup of boiled water. Let it steep for 5 minutes. Scroll down for the dosage.
- Oregano capsule: 600 mg per day
- Oregano oil: 4-6 drops per day (diluted)
- Dried oregano leaves: 1 teaspoon, twice a day
- Fresh oregano leaves: 4-5 leaves, twice a day
When To Consume Oregano
It is best to drink oregano tea early in the morning. You can also chew fresh leaves in the morning. Use dried oregano for lunch and dinner.
Where To Buy Oregano
You can buy oregano at any supermarket or online.
6. Aloe Vera

This fleshy leaf plant grows widely in India, South Africa, Mexico, Australia, and China. It is mostly used in cosmetic and pharmaceutical industries. Aloe vera has been used for ages to treat inflammation, improve digestion, prevent acne, and reduce hair fall. Recent scientific studies have found that aloe vera gel contains lipid-lowering and blood sugar lowering properties (6).
How To Consume Aloe Vera & The Dosage
Aloe vera juice and extract are available in the market. You can consume them as per the instructions on the bottle. You can also prepare aloe vera juice at home. Take a 3-inch aloe vera leaf, extract the gel and blend it. Add water and lemon juice to dilute it. You can also consume aloe vera capsules. Here’s the dosage.
- Aloe vera capsule: 300 mg per day
- Aloe vera juice or extract: as per instructions on the bottle
- Homemade aloe vera juice: 100 gm aloe vera gel
When To Consume Aloe vera
Consume aloe vera juice or extract early in the morning. You can have a capsule before lunch.
Where To Buy Aloe vera
You can buy aloe vera juice, extract, or capsule at any Ayurvedic store or online.
7. Ginger

The mighty ginger is widely used in Asian cuisines and is grown in China, India, Australia, Africa, and Jamaica. Like aloe vera, ginger has also been used in herbal medicines since ancient times. This aromatic spice can also help lower the blood glucose levels. Many scientific studies have confirmed that ginger helps to control the blood sugar levels by increasing insulin secretion and insulin sensitivity (7).
How To Consume Ginger & The Dosage
You can chew raw ginger, use it in your food, drink ginger tea, consume ginger powder, use its oil, and add it as one of the ingredients in a glass of juice. Here’s how much much ginger you should consume per day.
- Ginger root: 1-2 inches
- Ginger oil: 3-4 drops
- Ginger in juice: 1 inch
- Ginger powder: ½-1 teaspoon
When To Consume Ginger
Ginger tea is great to start your day with. Try to avoid consuming ginger after 6 pm. Have a fruit juice along with a little ginger juice before lunch.
Where To Buy Ginger
You can buy it at any supermarket or online.
 Quick Tip
Quick Tip8. Fenugreek

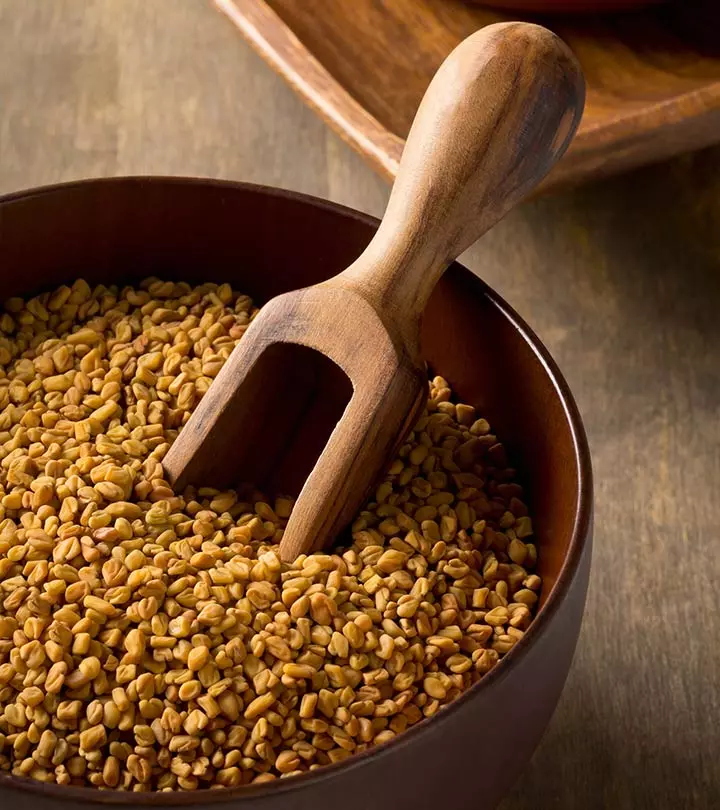
Fenugreek seeds and leaves are extremely useful to treat metabolic disorders and digestive problems. This plant is native to Spain, India, Pakistan, Bangladesh, Turkey, France, Egypt, Argentina, and Morocco. It has been used since ages to treat hair fall, skin issues, and slow metabolism. This spice is also widely used in various cuisines. A study confirmed that fenugreek seeds have blood glucose-lowering effects and can be used to treat type 2 diabetes (8).
How To Consume Fenugreek &The Dosage
The best way to consume fenugreek for diabetes is to soak the seeds overnight and consume the water the next day. You can also include the seeds and leaves in food preparations. Here is how much fenugreek you should consume per day.
- Fenugreek seeds: 2 teaspoons
- Fenugreek powder: 1 teaspoon
- Fenugreek leaves: 200 g
When To Consume Fenugreek
Drink fenugreek soaked water first thing in the morning. You can have fenugreek seeds or leaves during lunch or dinner.
Where To Buy Fenugreek
You can buy fenugreek seeds and leaves at any supermarket or online.
9. Cinnamon

This strong-smelling spice, derived from the bark of cinnamon trees, is regularly used in South Asian cuisines and desserts. It is an amazing herbal supplement for diabetes and treat obesity, muscle spasms, diarrhea, and common cold. Many studies have confirmed that consuming cinnamon regularly can help to control high blood sugar and hence, it can be used as an alternative medicine to treat diabetes (9).
How To Consume Cinnamon & The Dosage
You can consume cinnamon bark, powder, or capsules. The dosage is as stated below.
- Cinnamon stick: 2 inches
- Cinnamon powder: ½ teaspoon
- Cinnamon capsule: 500 mg per day
When To Consume Cinnamon
You can have cinnamon tea in the morning and evening. Add cinnamon powder to your smoothie or juice for breakfast. Have the capsule once in two days.
Where To Buy Cinnamon
You can buy cinnamon at any grocery store or online.
10. Clove

Clove is a flower bud that is popularly used in Indian, Pakistani, Bangladeshi, Sri Lankan, and Tanzanian cuisines. This aromatic spice has anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and digestive properties. Research has confirmed that clove helps to improve insulin sensitivity and lowers the levels of bad cholesterol and triglycerides (10).
How To Consume & The Dosage
You can consume clove by chewing it raw. You can also use whole or powdered cloves in food preparations or consume clove capsules. Here is how many cloves you should consume.
- Clove: 2 for chewing, 5-6 in food preparation
- Clove powder: ½ teaspoon
- Clove capsule: 500 mg per day
When To Consume
Soak 3-4 cloves in a cup of water overnight and drink it in the morning. Use whole or powdered cloves in your food for lunch or dinner. Take 2-3 clove capsules in a week before dinner.
Where To Buy
You can buy clove atany grocery store and clove capsules at an Ayurvedic store or online.
11. Turmeric

Turmeric is commonly used in Indian, Bangladeshi, Pakistani, and Iranian cuisines. This ginger-like spice adds color and a distinct flavor to food. Turmeric is also an Ayurvedic medicine that is used to treat bacterial infections, wounds, skin issues, and digestive problems. Research has found that a phytochemicali A chemical substance present in plants that helps them resist bacterial and fungal infections and prevent damage. called curcumin is responsible for turmeric’s yellow color and medicinal properties. Curcumin is also responsible for having a blood glucose-lowering effect. In fact, one study confirmed that patients with type 2 diabetes could lower their blood glucose levels by consuming turmeric (11).
How To Consume Turmeric & The Dosage
You can chew a small bit of raw turmeric, take capsules, or consume it in the powder form. Here is how much turmeric you should consume per day.
- Raw turmeric root: ½ inch
- Turmeric root paste: 1-2 teaspoons
- Turmeric powder: 1-2 teaspoons
- Turmeric capsule: 500 mg, twice a day
When To Consume Turmeric
You can chew turmeric on an empty stomach and use its paste or powder in cooking or smoothies/juices. Take the capsules before lunch or dinner.
Where To Buy Turmeric
You can buy turmeric at any Indian or Pakistani grocery store or order it online.
12. Neem
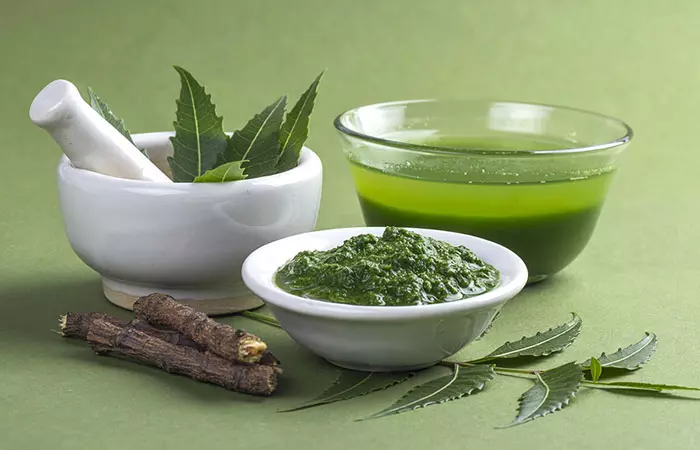

Neem or Azadirachta indica is native to India. It also grows in the neighboring countries like Bangladesh, Nepal, Sri Lanka, and Pakistan. Neem trees have bright to dark green leaves that possess many medicinal properties. Taking neem leaves is one of the best ways to lower blood sugar naturally. In fact, its bark and fruit are also used in traditional medicines. Ayurveda says that neem has antidiabetic, antifungal, antibacterial, antiviral, antioxidant, and anti-inflammatory properties. A few studies show that it possesses blood glucose-lowering properties. This confirms neem’s antidiabetic property as mentioned in Ayurveda (12).
How To Consume Neem & The Dosage
You can chew thoroughly washed leaves of neem or take neem paste or neem capsules. Here is how much neem you should consume.
- Neem leaves: 4-5
- Neem paste: 1 teaspoon
- Neem capsule: As per instructions on the bottle
When To Consume Neem
You should consume neem paste diluted in a glass of water early in the morning. Chewing neem leaves in the morning is also effective. Take neem supplements before breakfast once a day.
Where To Buy Neem
You can buy neem supplements/capsules online or at any Ayurvedic store. You can also buy neem leaves at the local market or Indian supermarkets.
13. Shilajit
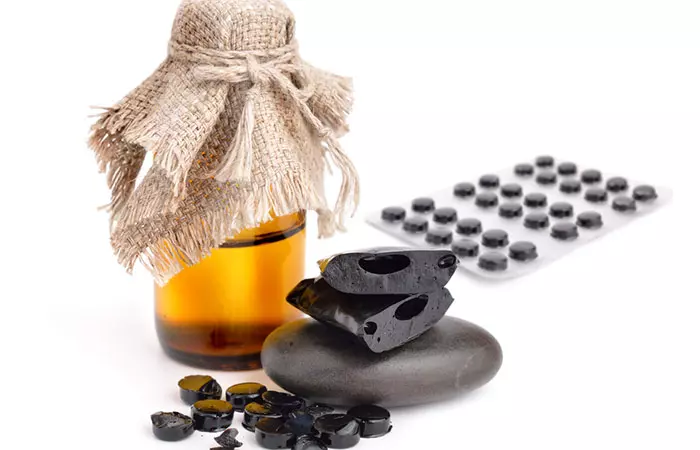

Shilajit is found in the Himalayas, Altai Mountains, Caucasus Mountains, and Gilgit-Baltistan Mountains. It is a tar-like mineral oil that oozes out of these mountains. Its color can range from light brown to dark brown. It has antioxidant properties and has been used to improve muscle power, reduce the risk of heart disease, slow down aging, and boost fertility. It has also been found that Shilajit can help stabilize the blood sugar levels (13).
How To Consume Shilajit & The Dosage
You can consume good quality shilajit supplements with milk, honey or sesame oil. Here is the dosage.
- Shilajit capsule: 100-300 mg per day
When To Consume Shilajit
You can consume it in the morning and before lunch/dinner.
Where To Buy Shilajit
You can buy Shilajit online or at any Ayurvedic store.
14. Chromium

When it comes to lowering blood sugar, chromium is one of the best supplements. It has recently gained popularity as a dietary supplement. Chromium helps to keep your carb cravings at bay, lowers bad cholesterol levels, mobilizes fat, and improves insulin sensitivity (14).
How To Consume Chromium & The Dosage
Chromium supplements, such as chromium picolinate, chromium polynicotinate, and chromium chloride, are available in the market. Here is the recommended dosage.
- 100-200 mcg, twice a day
- When To Consume Chromium
- You can take chromium supplements before lunch and dinner.
Where To Buy Chromium
You can buy the supplements at any pharmacy.
 Quick Tip
Quick Tip15. Alpha Lipoic Acid
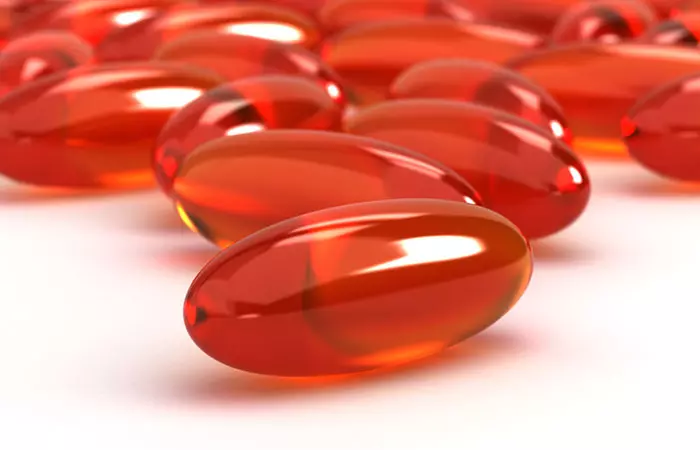

Alpha Lipoic Acid (ALA) is an antioxidant mainly found in potato, spinach, broccoli, liver, yeast, and kidney. It is usually used to treat fatigue, memory loss, kidney disease, liver disease, neuropathyi Damage to the peripheral nerves that causes weakness, pain, and fatigue in hands and feet due to nerve damage. , and Lyme diseasei A tick-borne illness caused by bacteria and characterized by rash, fever, fatigue, weakness, and joint pain. . It has been found that alpha lipoic acid supplements can help lower the blood glucose levels and hence, it is a potent supplement for treating diabetes type 2 (15).
How To Consume Alpha Lipoic Acid & The Dosage
ALA supplement capsules are the best way to provide your body with an extra amount of ALA. Dosage is as follows.
- ALA capsule: 600 mg per day for three weeks
When To Consume
Before lunch.
Where To Buy
You can buy it online or at any pharmacy.
16. Rosemary
Research indicates that rosemary exhibits anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties that may aid in managing diabetes (16). Moreover, rosemary has been linked to lowering bad cholesterol and triglyceride levels, which are risk factors for diabetes-related complications (17).
How To Consume Rosemary & The Dosage
You can use fresh or dried rosemary leaves for cooking. Here is a recommended dosage of its extracts:
- Fresh or dried rosemary leaves: About 1-2 g daily.
- Rosemary capsules: 500 mg to 750 mg
- Rosemary extracts: 2 – 4 ml
- Follow the dosage guidelines on the product label or consult a healthcare professional for guidance.
When To Consume Rosemary
Enjoy rosemary in your meals throughout the day.
Where To Buy Rosemary
You can easily purchase fresh or dried rosemary leaves from your local grocery store, while rosemary supplements are available at health food stores or online.
In addition to these 16 herbs, you could also try incorporating stevia, licorice root, milk thistle, mint, and holy basil into your diabetes diet due to their therapeutic effects ins managing the condition (18) (19) (20) (21).
Joel Stein, a columnist and an author, spoke about how mint helped him cut down his sugar craving. He said, “Any mint is oddly satisfying after a meal, and knowing that desserts are going to taste worse is a big disincentive to eat them (i)”.
Infographic: 7 Herbs To Manage Blood Sugar Levels
Did you know there are natural ways to keep your sugar levels in check and promote your overall health? Yes, there are several herbs and spices that may help regulate blood sugar levels, which makes them extremely helpful for people with diabetes. Check out the infographic below to know the different herbs you can include in your lifestyle. Illustration: StyleCraze Design Team
People with diabetes or those keeping a close watch on their blood sugar levels understand the importance of consuming the right foods. On that note, the use of herbs for diabetes treatment has been gaining popularity in recent times in blood sugar regulation. These may help reduce or control blood sugar levels. These herbs include ginseng, sage, and oregano, among others. These natural ingredients are effective as they contain antioxidants, nutrients, and beneficial bioactive compounds that may control sugar levels or improve insulin function and reduce insulin resistance. Besides these herbs, avoiding foods with high sugar content, following a balanced diet, and exercising regularly can help you achieve the best results.
Frequently Asked Questions
How can I incorporate herbs into my diabetes management plan?
To incorporate herbs into your diabetes management plan, start by consulting with your healthcare provider for personalized advice. You can sprinkle herbs like cinnamon or fenugreek into your meals. You can also prepare herbal teas with ginger or sage. Make sure you make ease into the process and not do anything drastic while monitoring your blood sugar levels to see how they affect you.
Can herbs be used as a sole treatment for diabetes or are they best used in conjunction with conventional medications?
Herbs cannot be a standalone treatment for diabetes. Consult your doctor and understand the best conventional medications you can combine with these herbs to reduce the risk of diabetes and help manage its symptoms.
Are there any potential side effects or risks associated with using herbs to treat diabetes?
Yes, using herbs to treat diabetes may cause an allergic reaction. Herbs that contain adulterants like dust, microbes, or pesticides may also lead to stomach irritation, mercury poisoning, or cerebral edema (22).
Are there any interactions between herbs and conventional diabetes medications that people with diabetes should be aware of?
Yes, herbs and conventional diabetes medications may interact with each other, leading to a significant and sudden drop in blood sugar levels (23). Always consult your doctor before combining herbs with conventional medications to control your blood sugar levels.
Illustration: Herbs For Diabetes That Keep Your Sugar Levels In Control

Image: Dall·E/StyleCraze Design Team
Unlock the secrets of powerful herbs that can help individuals with diabetes. Click on the video below and learn how to use these herbs to improve your overall health and well-being.
Personal Experience: Source
StyleCraze's articles are interwoven with authentic personal narratives that provide depth and resonance to our content. Below are the sources of the personal accounts referenced in this article.
(i). Could a Tiny Mint Kick My Sugar Cravings?https://elemental.medium.com/could-a-tiny-mint-kick-my-sugar-cravings-4f7a08bd82e5
References
Articles on StyleCraze are backed by verified information from peer-reviewed and academic research papers, reputed organizations, research institutions, and medical associations to ensure accuracy and relevance. Read our editorial policy to learn more.
- Gymnema sylvestre: A Memoir
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2170951/ - The Efficacy of Ginseng-Related Therapies in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4753873/ - Preventive effects of Salvia officinalis leaf extract on insulin resistance and inflammation in a model of high fat diet-induced obesity in mice that responds to rosiglitazone
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5765810/ - Bilberry (Vaccinium myrtillus L.)
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK92770/ - Anti-hyperglycaemic activity of the aqueous extract of Origanum vulgare growing wild in Tafilalet region
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15138008/ - Effect of Aloe vera leaves on blood glucose level in type I and type II diabetic rat models
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/11268118/ - Effects of Ginger (Zingiber officinale Roscoe) on Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Components of the Metabolic Syndrome: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5818945/ - Effect of fenugreek seeds on blood glucose and lipid profiles in type 2 diabetic patients
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19839001/ - Cinnamon Use in Type 2 Diabetes: An Updated Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3767714/ - Syzygium aromaticum L. (Clove) extract regulates energy metabolism in myocytes
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24999964/ - Effect of curcumin supplementation on blood glucose
plasma insulin - Antidiabetic Properties of Azardiracta indica and Bougainvillea spectabilis: In Vivo Studies in Murine Diabetes Model
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3136679/ - Effect of shilajit on blood glucose and lipid profile in alloxan-induced diabetic rats
https://journals.lww.com/iphr/pages/default.aspx - Effect of chromium supplementation on blood glucose and lipid levels in type 2 diabetes mellitus elderly patients
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15296075/ - Effect of alpha-lipoic acid on blood glucose
insulin resistance and glutathione peroxidase of type 2 diabetic patients - Antidiabetic Effects and Mechanisms of Rosemary ( Rosmarinus officinalis L.) and its Phenolic Components
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33016104/ - Rosemary Extract as a Potential Anti-Hyperglycemic Agent: Current Evidence and Future Perspectives
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5622728/ - Effects of stevia on glycemic and lipid profile of type 2 diabetic patients: A randomized controlled trial
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7103435/ - Effect of licorice extract on the complications of diabetes nephropathy in rats
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21314459/ - The Therapeutic Potential of Milk Thistle in Diabetes
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4310066/ - The Clinical Efficacy and Safety of Tulsi in Humans: A Systematic Review of the Literature
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5376420/ - Contamination and adulteration of herbal medicinal products (HMPs): an overview of systematic reviews
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22843016/ - Interactions between antidiabetic drugs and herbs: an overview of mechanisms of action and clinical implications
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5527439/
Read full bio of Heather M. Duquette-Wolf
Read full bio of Ravi Teja Tadimalla
Read full bio of Sindhu Koganti

























Community Experiences
Join the conversation and become a part of our empowering community! Share your stories, experiences, and insights to connect with other beauty, lifestyle, and health enthusiasts.