Malaria: Causes, Symptoms, Natural Remedies, And Prevention Tips
Be aware and employ home remedies to prevent infection and aid in faster recovery.

Image: shutterstock
Malaria is a devastating disease that primarily affects people in tropical and subtropical areas of the globe. For treatment, doctors prescribe quininei First-line medication for falciparum malaria, belonging to a class of drugs called antimalarials. or artemisinin based drugsi Medication for uncomplicated falciparum malaria comprising artemisinin derivatives combined with a drug from a different class. . However, you can also assist your body to recover more quickly and effectively by turning to Ayurveda and homeopathy as complementary, supportive therapy or combining a few home remedies for malaria with the prescription medications you are taking.
You are more likely to get this infectious disease if you happen to be in a humid climate or have a weakened immune system. Read on to learn more about malaria, including why and how it develops, its symptoms, how to prevent it, and the excellent natural therapies that can help you recover from it. Keep scrolling for all the information you need on malaria!
In This Article
What Is Malaria?
The word ‘malaria’ has been derived from the Italian word ‘mala aria’, which means bad air, as it was once believed to be caused by bad air. But medically, malaria is an infectious disease caused by a protozoani Protozoa are a group of single-celled microorganisms that are either free-living or parasitic in nature and feed on organic matter. parasite. The female Anopheles mosquito acts a carrier for this parasite.
The female Anopheles mosquitoes are found breeding in stagnant waters, from where they can contract the parasite and spread it to humans. When this mosquito bites a person, the parasite enters his/her body and initially grows in the liver for a few days. It then enters the bloodstream and attacks the red blood cells. This is when the various symptoms of malaria start to present themselves. A warm climate is a convenient breeding environment for the parasite and the mosquito. Hence, people living in the tropical regions are more susceptible to this disease (1) (2).
Here are some fast facts about malaria.

Key Takeaways
- Malaria treatment involves conventional plants like neem, tulsi, and ginger.
- Using organic supplements such as papaya, garlic, and vitamin C can improve malaria conditions.
- Adopting lifestyle modifications such as drinking enough water, avoiding insect bites, and eating healthily can also work wonders.
- Use essential oils in massage therapy and aromatherapy to treat malaria.
Malaria Facts
- People living in 106 countries and territories across the world i.e. more than three billion people are at a risk of malaria.
- In the United States, malaria was eliminated in the 1950s. However, almost 2000 cases are reported every year, mostly by people who have recently traveled to a tropical country.
- Three different species of the Anopheles mosquito have been found to be responsible for spreading the infection.
- When a pregnant woman contracts the infection, it can result in a decreased birth weight of the baby, reducing the chance of its survival.
- Multiple diagnostic tools used by an experienced laboratory technician or pathologist can help differentiate the type of parasite causing the infection so that the appropriate treatment can be planned by the doctor.
 Trivia
TriviaLet us now look at the root cause of this disease.
What Causes Malaria?
Malaria is caused by the protozoan parasite called Plasmodium. Five species of this parasite have been recognized so far that infect humans. These are:
- Plasmodium falciparum – predominant in Africa
- Plasmodium vivax – predominant in Asia, Latin America, and a few regions in Africa
- Plasmodium ovale – predominant in West Africa and western Pacific
- Plasmodium malariae – predominant worldwide
- Plasmodium knowlesi – predominant in Southeast Asia (3)
Find below the different types of malaria and its symptoms.
Types Of Malaria And Its Symptoms

Based on the severity of the infection, there are two types of malaria – uncomplicated and severe (or complicated).
(a) Uncomplicated Malaria – The malarial fever attack consists of the cold stage (shivering and chills), the hot stage (fever), and the sweating stage (sweating and tiredness). Typically, an attack lasts for 6-10 hours and repeats on the second day when the infection is caused by these parasites – P.falciparum, P.vivax, and P.ovale. These are referred to as ‘tertian’ parasites. The P.malariae is called as a ‘quartan’ parasite, and the malarial attack repeats every third day during this type of infection.
Symptoms of this type of malaria include:
- Fever
- Chills
- Sweats
- Headache
- Nausea and vomiting
- Tiredness
- Body pains
- Joint pain
- Loss of appetite
- Confusion
- Diarrhea (3)
(b) Severe Malaria –
This is when the infection has spread to various organs and is causing organ failure and more serious symptoms. These manifestations are:
- Cerebral malaria – seizures, coma, and other neurological abnormalities
- Severe anemia
- Hemoglobinuriai A condition where a rise in hemoglobin in the blood leads to the appearance of hemoglobin in the urine.
- Abnormalities in the blood coagulation process
- Respiratory conditions, such as ARDS
- Kidney failure
- Hypoglycemiai A condition characterized by lowered blood sugar levels in the body. Symptoms include heart palpitations, anxiety, and confusion.
- Low blood pressure
- Metabolic acidosis
Immediate treatment is essential for severe malaria (4).
Diagnosis Of Malaria
Malaria can be diagnosed via the following tests (5):
- Blood Smear
This is the most common and reliable method for diagnosing malaria. It involves taking a small blood sample, staining it with a special dye, and examining it under a microscope. - Rapid Diagnostic Tests (RDTs)
These provide results within 15-20 minutes. They help detect specific malaria antigens or proteins in a drop of blood. RDTs are useful in places where laboratory facilities are limited. - Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR)
It is a highly sensitive test that can distinguish between different parasite species and strains. PCR is particularly useful for high-end research purposes.
The sight of a malaria patient makes most of us panic. However, it is possible to treat this disease with the right combination of prescribed or herbal medicine and home remedies. Given below are the best home remedies for malaria treatment.
Home Remedies To Treat Malaria Naturally
- Apple Cider Vinegar
- Ginger
- Cinnamon
- Fever Nut
- Orange Juice
- Grapefruit
- Citrus Limetta Fruit
- Holy Basil
- Alum
- Herbal Teas
- Chirayta
- Datura
- Fenugreek Seeds
- Mustard Seed Oil
- Turmeric
1. Apple Cider Vinegar For Malaria
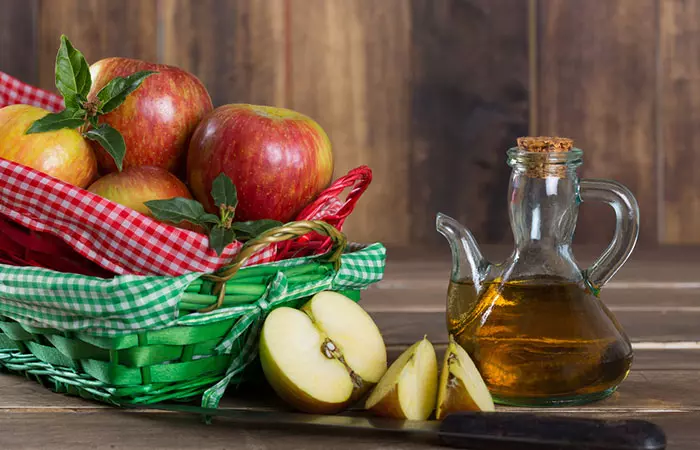

You Will Need
- 1/2 cup apple cider vinegar
- 2-3 glasses water
- 2 soft cloths or tea towels
What You Have To Do
- Dilute the ACV with water and soak the cloth pieces in it.
- Place these on the calves for 10-12 minutes.
How Often You Should Do This
Do this during the fever stage of the malaria attack.
Why This Works
This a folk remedy that is known to reduce fever (6).
2. Ginger
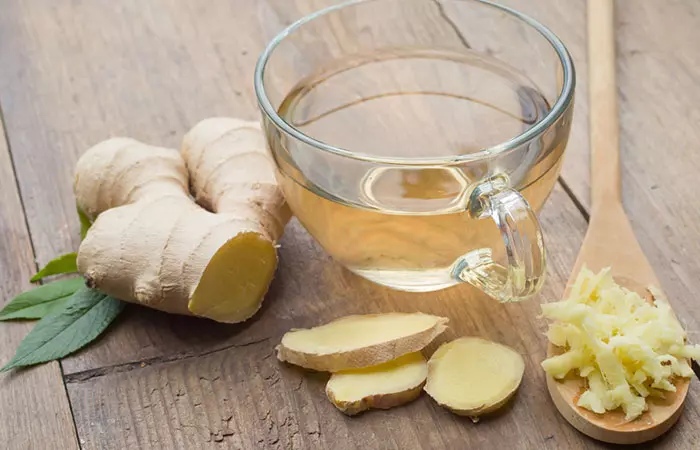

You Will Need
- 1-inch piece of ginger
- 1-1 1/2 cups of water
What You Have To Do
- Chop the ginger and boil the pieces in water for a few minutes.
- Strain and drink this decoction once it cools down a little. You can add some honey for taste.
How Often You Should Do This
Drink 1-2 cups of this every day.
Why This Works
The active constituents of ginger, like gingerol, possess antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory properties. This remedy can give you relief from the pains as well as nausea as ginger aids digestion (7).
3. Cinnamon

You Will Need
- 1 teaspoon coarse cinnamon powder
- A pinch of pepper powder
- 1 teaspoon honey
- A glass of water
What You Have To Do
- Boil the cinnamon powder and pepper powder in water for a few minutes.
- Strain and add honey to it.
- Mix well and drink this.
How Often You Should Do This
Consume this once or twice a day.
Why This Works
Cinnamon is also an effective natural treatment for malaria symptoms. The cinnamaldehyde, procyanidins, and catechins present in cinnamon have antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and antimicrobial properties (8).
4. Fever Nut

You Will Need
- 3 gms fever nut seeds
- A cup of water
What You Have To Do
These seeds should be ingested with water two hours before the expected onset of fever and one hour after it.
How Often You Should Do This
Repeat this before and after every malarial attack.
Why This Works
The seeds of the fever nut plant are considered an effective remedy for malaria. This is a rare plant, but it can be obtained from any herbal store and preserved for use. This will prevent the paroxysm of fever, but if it occurs, the same procedure can be repeated to cut short the duration of fever. It has antimalarial and anti-inflammatory properties (9).
5. Orange Juice

You Will Need
Orange juice
What You Have To Do
Drink orange juice in between meals.
How Often You Should Do This
Have 2-3 glasses of fresh juice every day.
Why This Works
With its roots in naturopathyi A form of alternative medicine that focuses on the body’s self-healing capacity through natural therapies. medicine, this alternative medicine might be effective in reducing the fever because of the high vitamin C content of oranges (10). Vitamin C boosts the immune system (11).
6. Grapefruit

You Will Need
- 1/4 grapefruit
- Water
What You Have To Do
- Boil the grapefruit.
- Strain the pulp and drink it.
How Often You Should Do This
Have this every day.
Why This Works
Raw grapefruit or grapefruit juice is quite effective in controlling the intensity of malarial infection. It contains a natural quinine-like substance that can alleviate malarial symptoms (12).
Caution
If quinidine is a part of the prescribed medicines you are taking, do not drink grapefruit juice. This fruit alters certain enzymes in your stomach, reducing the absorption capacity of quinidine.
7. Citrus Limetta Fruit

You Will Need
Citrus limetta (Sweet lime)
What You Have To Do
Extract fresh juice from the fruit and drink it.
How Often You Should Do This
Drink two glasses of sweet lime juice every day.
Why This Works
Known as mosambi in the Indian subcontinent, sweet lime is part of the citrus fruits family. Apart from the obvious vitamin C content, it can inhibit the growth of the malarial parasite (13).
8. Holy Basil

You Will Need
- 12-15 holy basil leaves
- 1/2 teaspoon black pepper powder
What You Have To Do
- Crush the leaves and press them on a sieve to separate the juice.
- To this juice, add the black pepper and mix well.
- Ingest this concoction.
How Often You Should Do This
Drink this juice thrice a day, especially during the initial stages of the disease.
Why This Works
Holy basil leaves are regarded as a herbal remedy for various diseases, and malaria is one of them. This plant is known as the ‘queen of herbs’. Its leaves promote healthy functioning of the body. It has antimalarial effects when ingested regularly during the infection. It also gives relief from other symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and fever (14).
9. Alum

You Will Need
An inch-sized piece of alum
What You Have To Do
- Roast the alum on a hot plate and powder it.
- Take half a teaspoon of this before the expected attack.
- Take half a teaspoon every two hours after the attack.
How Often You Should Do This
Do this before and after every malarial attack for immediate relief from the symptoms.
Why This Works
Alum is also quite useful in treating malaria as it is antimicrobial in nature (15).
10. Herbal Teas

You Will Need
- 1 green tea bag
- A small piece of tamarind
- A cup of hot water
What You Have To Do
- Soak the green tea bag and the tamarind in hot water for a few minutes.
- Remove the tea bag. Strain the herbal tea prepared and drink it.
How Often You Should Do This
Have two cups of this herbal tea every day.
Why This Works
The antioxidants in green tea strengthen your immune system while the tamarind helps reduce the fever (16) (17).
11. Chirayta

You Will Need
- 15 gms chirayta herb (or chirata)
- 250 ml hot water
- 2 cloves
- 1 teaspoon cinnamon powder
What You Have To Do
- Prepare an infusion by steeping the herb in hot water along with the cloves and cinnamon powder. Let it sit for 2-3 minutes.
- Strain the liquid and drink three tablespoons of this.
How Often You Should Do This
Repeat this 4-5 times in a day.
Why This Works
Chirayta, botanically known as Swertia andrographis paniculata, is another herb that is known for its health benefits. It is quite effective in treating intermittent malarial fevers. This will significantly lower the body temperature (18).
12. Datura

You Will Need
- 2-3 freshly sprouted Datura leaves
- 1/2 teaspoon jaggery
What You Have To Do
- Take the leaves and make them into a pill by rubbing them with jaggery.
- This should be taken two hours before the onset of the malarial attack.
How Often You Should Do This
Ingest this on a daily basis.
Why This Works
Datura is an Indian herb that is beneficial in treating malaria. The leaves of this plant are useful in the treatment of tertian type of malaria fever (19).
13. Fenugreek Seeds

You Will Need
- 5 gms fenugreek seeds
- A glass of water
What You Have To Do
Soak the seeds in water overnight and drink this water in the morning on an empty stomach.
How Often You Should Do This
Do this every day until the malarial infection goes away completely.
Why This Works
Malaria patients often feel weak due to intermittent fever. Fenugreek seeds are the best natural remedy to combat this weakness. They help in quick recovery from malaria by boosting your immune system and fighting the parasites (20). Thus, it is recommended that malarial patients increase their consumption of fenugreek seeds.
14. Mustard Seed Oil

Mustard oil, especially from the black mustard seeds, has been shown to possess antimalarial activity in lab experiments (21). Incorporating it in your daily diet by using it as a cooking oil or adding a teaspoon of it to a smoothie can help your body fight the infection better. This oil can act as a wonderful supplement to the traditional medicine that has been prescribed by your doctor.
15. Turmeric

You Will Need
- 1 teaspoon turmeric powder
- A glass of warm milk
What You Have To Do
- Add the turmeric to the milk and mix well.
- Have this before going to bed.
How Often You Should Do This
Drink this every night.
Why This Works
Turmeric is a powerful antioxidant and antimicrobial agent. It cleanses the body of the toxins that are building up because of the Plasmodium infection and also helps to kill the parasite. Turmeric also has anti-inflammatory properties that can alleviate malaria symptoms like muscle aches and joint pain (22).
It is very important to understand that none of these remedies will eliminate the parasite from your body. The medicines prescribed by your doctor are necessary to do that. However, these remedies can alleviate the symptoms, giving relief from the fever, pains, and aches, and aid the parasite-killing process of the medicines.
An official vaccine for malaria has been not released into the market by WHO. There is a very good candidate in the making. Read on to know about this.
Malaria Vaccination
RTS, S/AS01 is the most progress scientists have made when it comes to a vaccine for malaria. It is effective against malaria caused by P. falciparum. Pilot distributions of this vaccine are ongoing in a few African countries. Apart from this, more than 20 other vaccines are currently undergoing tests for their efficacy against the various Plasmodium parasites (23).
Prevention is always better than cure. Unhygienic surroundings and unhealthy feeding habits act as trigger factors for this disease and so, the following steps should be taken to prevent malaria.
 Trivia
TriviaMalaria Prevention Tips

- Do not allow water to stagnate as this serves as the breeding ground for Anopheles mosquitoes, which reproduce and multiply, thus spreading the fever wherever they go.
- Water bodies should be sprayed with mosquito repellent or other effective chemicals to keep the mosquito population under control.
- Keep your surroundings clean by keeping your home clean, dry, and hygienic. Use disinfectants like Dettol, phenyl, etc. for cleaning your house and toilets.
- Use mosquito repellents while sleeping. And if you are allergic to commercial ones, you can try using homemade mosquito repellents or a mosquito net to avoid getting bitten by mosquitoes.
- Wear long-sleeved clothing and full-length pants while stepping out of the house.
- Drink clean water only, especially when traveling.
Let us now look at the answers to some doubts you may have regarding malaria.
Discover effective home remedies for treating malaria and gain valuable insights into its symptoms, causes, and self-care methods. Explore the top 10 natural remedies that can aid in alleviating malaria symptoms at home. Watch now to empower yourself with knowledge!
Infographic: 5 Most Effective Natural Remedies To Treat Malaria
Malaria is a life-threatening disease caused by the Plasmodium parasite. It can cause fever, headache, and flu. But there are specific measures you can take at home to alleviate the symptoms. The infographic below lists the 5 most effective home remedies you may try to deal with the symptoms of malaria. Take a look.

Illustration: StyleCraze Design Team
Malaria is caused by a protozoan parasite that is carried by female Anopheles mosquitoes and can be of two primary types, uncomplicated and severe. Uncomplicated malaria is characterized by periods of attacks resulting in fever, sweating, shivers, and chills that repeat in a specific frequency. Severe malaria is a condition where various organs in the body get infected, and immediate medical assistance is needed. The different home remedies for malaria help manage the different symptoms of uncomplicated malaria and can be used along with prescribed medications for accelerated healing and symptomatic relief.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can home remedies replace traditional medicine for malaria?
No, home remedies cannot replace over-the-counter medications for malaria. While they may help alleviate some symptoms, it’s important to remember that malaria is a serious disease that requires professional treatment. Home remedies, no matter how well-intentioned, are not a substitute for prescription antimalarial drugs.
Is malaria a virus?
Malaria is a disease caused by a parasite called Plasmodium. It is a single-celled organism, which is not a type of virus.
What is the incubation period of malaria?
The incubation period is slightly different, depending on the type of parasite that is causing malaria. For P. falciparum, the incubation period is 9-14 days. For P.ovale and P. Vivax, it is 12-18 days, and for P. malariae, it is 1840 days.
Which organs are affected by malaria?
During the initial stages, the parasite affects the red blood cells only, but as the disease progresses, it starts to affect the liver and the spleen. In extreme cases, it can affect the brain and cause cerebral malaria.
How does malaria affect the human body?
The parasite initially lies dormant in the red blood cells of the blood. After this dormant stage, it starts to multiply and feed on the contents of the red blood cells. Every 48-72 hours, the cell bursts to release more parasites into the bloodstream. This is the time that is referred to as a malarial attack when a person experiences the symptoms. Fever, chills, nausea, vomiting, headache, tiredness, and body pain are commonly experienced.
Can malaria cause joint pain?
Yes, it can cause joint pain.
Can malaria cause miscarriage in pregnant women?
Malaria and its symptoms can be more pronounced in a pregnant woman. Miscarriage is very rarely caused during the initial stages as treatment options are available that are safe to be used during pregnancy. As the malaria progresses, the chances of it causing miscarriage increase.
Is malaria contagious?
Malaria does not spread from person to person. If the Anopheles mosquito bites an infected person, the parasite can be transferred to a healthy person by that mosquito’s bite.
How long does it take to recover from malaria?
Generally, for malaria, recovery takes about two weeks.
How long does it take to die from malaria?
Death due to malaria is highly subjective. It depends on the current condition of the patient, which type of Plasmodium is responsible for the infection, and if any treatment is being taken or not. There is no specific timeline. However, if left untreated, malaria can easily progress to anemia, hypoglycemia, and cerebral malaria. This can eventually lead to coma and death.
How long is a malaria vaccine good for?
The vaccine is still under testing. Hence, there is no information about the duration it will be effective for.
Malaria diet: What to eat and avoid?
Diet plays a crucial role in the speedy treatment of malaria.
After the malarial fever has subsided, it is advisable to maintain an exclusive fresh fruit diet along with milk for the first few days. Thereafter, the patient should follow a balanced diet consisting of fresh fruits and raw vegetables.
- Develop the habit of having a light diet without using much oil or butter.
- Oily, spicy, and junk foods can only make the situation worse.
- Fruits like apples, bananas, grapes, and guava help in quick recovery from malaria.
- You can also try juice made from papaya leaves as it is said to have antimalarial properties (24).
- In case of high fever, extract some fresh lemon juice and add it to a cup of lukewarm water. The patient should slowly sip this lemon water. This will prevent the rise in temperature during the initial period of fever.
Though it is a serious disease, malaria can be cured if diagnosed at the right time and with the right medication. If you suspect malaria, immediately consult a doctor. Use the remedies given in this article to get relief from the symptoms of this disease while the medicines do their work.
Preventive measures work best when you do not want to face the consequences of this infection. So, keep those in mind for sure, especially if you are in a high risk area.
Wishing you (or the patient) a quick recovery! Take care!
Illustration: Effective Natural Remedies To Treat Malaria At Home

Image: Stable Diffusion/StyleCraze Design Team
References
Articles on StyleCraze are backed by verified information from peer-reviewed and academic research papers, reputed organizations, research institutions, and medical associations to ensure accuracy and relevance. Read our editorial policy to learn more.
- Malaria
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2928834/ - Malaria Disease Basics
https://www.cdc.gov/malaria/about/index.html - Malaria Pathogenesis
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5749143/ - Clinical review: Severe malaria
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC270697/ - Malaria diagnosis: a brief review
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2688806/ - The Effectiveness of Warm Vinegar Compress in Lowering Children Body Temperature with Acute Febrile Illness
https://www.semanticscholar.org/paper/The-Effectiveness-of-Warm-Vinegar-Compress-in-Body-Antono/fee0744cd825a274ae47a46e89dce865bf4d6ab4 - The Amazing and Mighty Ginger
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK92775/ - Cinnamon: a multifaceted medicinal plant
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4003790/ - Antibacterial antidiarrhoeal and cytotoxic activities of methanol extract and its fractions of caesalpinia bonducella (l.) roxb leaves
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3661353/ - Efficacy and safety of vitamin C in the management of acute respiratory infection and disease: a rapid review
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7393036/ - [Vitamin C and immune function]
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19263912/ - Prophylactic Effect of Grapefruit Juice Against Plasmodium berghei berghei Infection in Mice
https://scialert.net/fulltext/?doi=ijp.2008.60.63 - Ascorbic acid co-administration with artemisinin based combination therapies in falciparum malaria
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4989825/ - Tulsi – Ocimum sanctum: A herb for all reasons
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4296439/ - In vitro antimicrobial activity of potash alum
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/8783521/ - Beneficial effects of green tea: A literature review
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2855614/ - Tamarindus indica: Extent of explored potential
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3210002/ - A review of swertia chirayita (gentianaceae) as a traditional medicinal plant
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4709473/ - Isolation purification and characterization of homogenous novel bioactive protein from datura stramonium stem exhibited larvicidal activity against anopheles stephensi
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC9744620/ - Investigating therapeutic potential of trigonella foenum-graecum l. As our defense mechanism against several human diseases
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4739449/ - Antimalarial activity of 80 % methanolic extract of brassica nigra (l.) koch. (brassicaceae) seeds against plasmodium berghei infection in mice
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26471058/ - Herbal Medicine: Biomolecular and Clinical Aspects. 2nd edition.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK92752/ - RTSS: the first malaria vaccine
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8718142/ - Antimalarial activity of Carica papaya (Family: Caricaceae) leaf extract against Plasmodium falciparum
https://www.researchgate.net/publication/233778301
Read full bio of Dr. Saba
Read full bio of Kushneet Kukreja
Read full bio of Arshiya Syeda
Read full bio of Dipti Sharma






















Community Experiences
Join the conversation and become a part of our empowering community! Share your stories, experiences, and insights to connect with other beauty, lifestyle, and health enthusiasts.