Flexitarian Diet: Benefits, Meal Plan, & How Does it Work
Meatless when possible, but delicious always – flex your diet for health and sustainability!

Image: Shutterstock
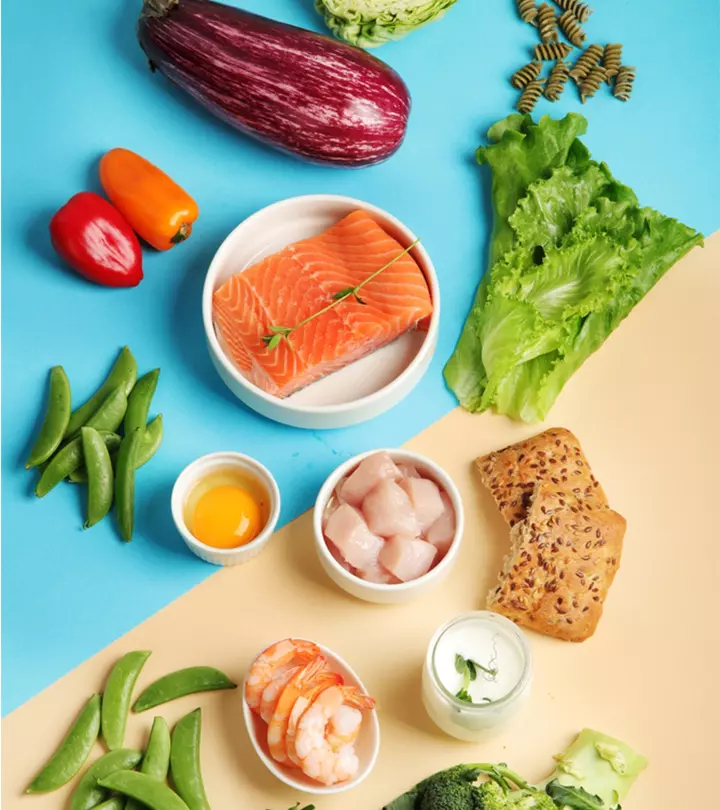
A flexitarian diet strikes the ideal balance between sustainability and health. This flexible way of eating is all about incorporating more plants into your meals while still allowing for the occasional inclusion of meat, fish, and dairy products. This dietary approach not only improves your health but also reduces the adverse environmental effects of eating meat. With the flexitarian diet, you can simply enjoy your favorite foods in a more sustainable and balanced way, rather than having to give them up entirely. Due to the smooth shift to vegetarianism, veganism, or ethical eating it offers without the stress of strict dietary adherence, this diet may also be therapeutic for some people. Join the flexitarian movement now to explore a world of delicious, environmentally friendly, and nutritious eating. Keep reading to learn more!
 At A Glance: Flexitarian Diet
At A Glance: Flexitarian Diet- Principle: A transitional plant-based diet with occasional consumption of meat and fish.
- Purpose: To develop sustainable yet healthy eating habits.
- Who Is It For: People who want to eat ethically without completely converting to vegetarianism or veganism.
- Duration: Long-term
- Who Should Avoid: People with diabetes, celiac disease, or nutrient deficiencies, pregnant or lactating individuals, and people who are underweight.
- Cons: Limited options for those making a transition, may lack essential nutrients, and may result in overconsumption of meat due to deprivation.
In This Article
What Is A Flexitarian Diet?
Flexitarianism is the new buzzword in the world of plant-based diets. The term “flexitarian” is a combination of the words ‘flexible’ and ‘vegetarian,’ which means it is a more moderate and balanced approach to eating.
It is primarily a plant-based diet that allows for the occasional consumption of meat, fish, and dairy products for a healthy lifestyle. Basically, it emphasizes eating mostly fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, and nuts. This type of diet is considered a more balanced approach to eating as it promotes the health benefits of a plant-based diet while also allowing for the inclusion of animal products for those who choose to consume them (1).
In recent years, the popularity of vegetarian diets has been on the rise. There are several reasons for this trend, including increasing awareness of the health benefits of plant-based diets, concerns about the environmental impact of meat production, and ethical concerns about the treatment of animals.
The diet also allows for a more gradual shift toward a plant-based and meatless diet for those who may not be ready to commit to an entirely vegetarian or vegan lifestyle. So, if you are an Omnivore, Carnitarian, or Pescatarian looking for a fish or meat reduction plan, this balanced diet might be suitable for you.
Overall, the flexitarian diet is a healthy and sustainable way of eating that can support overall health and well-being. The following section will explain how this diet works and how it can help you stay healthier.
Key Takeaways
- The flexitarian diet is a plant-based eating regimen that permits the occasional inclusion of meat.
- This diet’s objective is to lower overall meat consumption for environmental and health reasons.
- Compared to rigorous vegetarian or vegan diets, it is regarded as a more flexible and easy way of eating.
How Does A Flexitarian Diet Work?
A flexitarian diet is a more pragmatic approach to vegetarianism or veganism. It allows you to adjust the frequency of meat consumption according to your dietary needs and preferences. For instance, some people may eat meat 2-3 times a week, while others may consume meat only once a week.
It is crucial to understand that the flexitarian diet does not necessarily involve eating minimal meat, but rather it emphasizes plant-based foods while still allowing for the odd consumption of animal products. Due to this, it helps in reducing meat consumption and may help you move towards a meat-free lifestyle. Here are some tips to follow the diet effectively:
- Start by incorporating more plant-based and meat-alternative foods into your meals. Try to make these items the star of your meals, and use animal products as more of a side dish or a condiment.
- Make an effort to eat at least one vegetarian or vegan meal daily. This can be for lunch, dinner, or both. This is a fantastic method to increase your intake of plant-based foods without feeling too restricted.
- Pay attention to portion sizes. If you do decide to consume animal products, strive to limit your intake and make sure your diet is well-balanced with plant-based meals.
- Plan ahead. Making healthy decisions when traveling can be facilitated by planning your meals and snacks. This can be accomplished by carrying your own lunch, keeping nutritious snacks on hand, or cooking meals in advance.
- Be adaptive and open-minded. Don’t be too hard on yourself if you slip up or end up eating out something that is not 100% plant-based. After all, the flexitarian diet is all about flexibility.
 Quick Tip
Quick TipFind a balance that suits you and enables you to take advantage of various delicious and healthy foods while being conscientious of the environment and your general health. The following section has more information on these benefits.
Flexitarian Diet: Pros And Cons
As always, there are several pros and cons of the flexitarian diet:
Pros
- May Increase Nutrient Intake
The flexitarian diet is rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, and nuts, which are all nutrient-dense foods that provide essential vitamins and minerals. Studies have shown that vegetarians and vegans consume more folate, vitamin E, and magnesium compared to meat eaters. Vegans also consume more vitamins B1, B6, and C (2).

- May Help Manage Weight
Plant-based foods are generally lower in calories and fat than animal-based products, which can help with weight management. According to studies, people assigned to vegetarian diet groups in clinical trials lost noticeably more weight than people assigned to the non-vegetarian diet groups (3), (4).
 Quick Tip
Quick Tip
- May Reduce The Risk Of Cardiovascular Disorders
According to studies, adopting a vegetarian diet lowers the risk of coronary heart diseasei Key blood vessels of the heart may incur damage from plaque buildup, which narrows them and reduces the blood supply to the heart. (CHD) and mortality related to cardiovascular disorders by 40%.
It is the only dietary pattern that has demonstrated CHD reversal. Furthermore, research points to the advantages of vegetarian eating habits in the treatment and prevention of heart failure and cerebrovascular illness (5).
Compared to non-vegetarian diets, plant-based diets have been linked to lower blood pressure, blood lipids level, and platelet aggregation, thereby helping promote heart health (5).
- May Reduce The Risk Of Diabetes
According to studies, adopting a vegetarian diet has proven to be more effective in reducing the symptoms of diabetes than conventional treatments. In comparison to a diet that included weekly meat eating, lifelong adherence to a vegetarian diet in a study was found related to a 74% lower risk of acquiring diabetes (6).
A lifelong commitment to a vegetarian diet has been linked to a 35% decreased chance of developing diabetes, according to research on non-smoking, non-drinking Buddhists. More importantly, compared to non-vegetarians, those who switched to a vegetarian diet after previously not doing so had a 53% decreased chance of developing diabetes (6).
- May Reduce The Risk Of Cancer
A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains has been linked to a reduced risk of certain cancers. According to studies, plant-based diets exert anti-inflammatory and antioxidative actions against the onset of cancer. It has also been shown to protect against digestive tract cancers (7), (8).
- May Benefit The Environment
Eating a diet that is mostly plant-based can positively impact the environment by reducing the demand for meat and dairy products. Studies have demonstrated that compared to the majority of modern omnivorous diets, ovolactovegetarian, and vegan diets produce greenhouse gas emissions that are 50% and 35% lower, respectively, and consume correspondingly fewer natural resources (9).
- May Aid In Weight Loss
Can you lose weight on a flexitarian diet? Research suggests, yes (1). The diet encourages a higher intake of plant-based foods like fruits, vegetables, and whole grains that are low in calories and rich in fiber. A high intake of fiber is associated with an increased feeling of fullness. This can prevent overeating and may help you manage obesity (10). Further, the diet also allows you to choose your meals according to your preferences. This way, you will be able to stick to it for a long time and achieve sustainable weight loss.
Cons
- Offers Limited Options
Flexitarians may find it difficult to find suitable options when eating out, especially when traveling and in areas where meat-centric meals are the norm. This can make it more challenging to stick to the diet, especially if you eat out frequently.
Additionally, some social situations may involve peer pressure to eat meat or other animal products, which could make it difficult to stick to the diet. It requires you to explain your dietary choices to others, which can be time-consuming or uncomfortable.
A social stigma may be associated with being a “flexitarian” or “semi-vegetarian” in some circles. It could also be challenging for people to follow a flexitarian diet in cultures where meat consumption is a traditional and important part of the society.
- May Lack Essential Nutrients
It may be challenging to get the right balance of nutrients for some people, especially if you are not used to planning your meals and find it difficult to keep track of your nutrient intake. A flexitarian diet may not provide enough of certain nutrients, such as iron, calcium, and vitamin B12, that are typically found in animal products. Studies have shown that vegetarians, and particularly vegans, consume less protein, iodine, EPAi Eicosapentaenoic acid; a type of omega-3 fatty acid obtained from fish oil that may help reduce cellular inflammation. , and DHAi Docosahexaenoic acid; a type of omega-3 fatty acid obtained from fish oil that aids in boosting brain health. on average than meat eaters (2).
 Quick Tip
Quick Tip- May Promote Overindulge In Animal-Based Products
Since this diet is not strict, there is a potential for some individuals to consume more meat, fish, and dairy products than is recommended for optimal health.
It is important to note that these challenges can vary depending on your location and social circle, but with planning and communication, they can be manageable. This pressure can be greatly reduced by clearly understanding what you can and cannot eat when following this diet.
What Can You Eat On A Flexitarian Diet?
Focus on including healthy eating options like fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, and nuts in your diet. This can include leafy greens, berries, whole wheat bread, lentils, and almonds. Additionally, you should restrict your consumption of meat, fish, and dairy products. When you do choose to consume them, pick lean, grass-fed, or sustainably produced options.
| What To Eat | What To Eat (Occasionally) | What To Avoid |
| Whole grains (quinoa, brown rice, oatmeal) | Meat and fish (grass-fed beef, wild-caught fish) | Processed meats (bacon, sausages, deli meats) |
| Legumes (beans, lentils, chickpeas) | Dairy and eggs (Greek yogurt, cottage cheese) | Processed foods (pre-packaged meals, frozen dinners) |
| Fruits and vegetables (leafy greens, berries, avocados) | Refined grains (white bread, pasta) | |
| Nuts and seeds (almonds, chia seeds, flax seeds) | Added sugars (candy, soda, syrups) | |
| High-fat dairy (whole milk, cream, cheese) | ||
| Trans fats (margarine, shortening, fried foods) |
 Quick Tip
Quick TipA diet recipe that follows the principles of a flexitarian diet may include a dish that features a plant-based protein source, such as lentils or tofu, along with a variety of colorful fruits and vegetables and a small portion of lean meat or dairy. Discover our meal plan in the following section for simple meal planning and preparation.
Flexitarian Diet Meal Plan
Here is a sample 7-day flexitarian meal plan that you can follow:
Day 1
| Meal | What To Eat |
| Breakfast | Oatmeal with berries and nuts |
| Lunch | Black bean and sweet potato tacos |
| Dinner | Grilled vegetable and quinoa stir-fry |
Day 2
| Meal | What To Eat |
| Breakfast | Greek yogurt with granola and fruit |
| Lunch | Grilled portobello mushroom burger with avocado and tomatoes |
| Dinner | Spaghetti with marinara sauce and sautéed vegetables |
Day 3
| Meal | What To Eat |
| Breakfast | Scrambled eggs with spinach and mushrooms |
| Lunch | Chickpea and vegetable curry |
| Dinner | Lentil and vegetable soup |
Day 4
| Meal | What To Eat |
| Breakfast | Avocado toast with poached egg |
| Lunch | Vegetable and bean burrito |
| Dinner | Steamed fish with quinoa and vegetables |
Day 5
| Meal | What To Eat |
| Breakfast | Smoothie bowl with spinach, banana, and almond milk |
| Lunch | Vegetable and bean chili |
| Dinner | Grilled salmon with mixed greens salad |
Day 6
| Meal | What To Eat |
| Breakfast | Chia seed pudding with almond milk and fruit |
| Lunch | Vegetable and tofu stir-fry |
| Dinner | Grilled vegetable and lentil burgers |
Day 7
| Meal | What To Eat |
| Breakfast | Tofu scramble with peppers and onions |
| Lunch | Lentil and vegetable salad |
| Dinner | Baked chicken breast with roasted vegetables |
 Quick Tip
Quick TipThis meal plan is merely a recommendation. You may always make changes per your dietary choices and limitations. The most crucial thing is to focus on wholesome, nutrient-dense meals and maintain a balance of plant-based and animal-based foods. Scroll down to learn some simple and delectable dishes you can make while following this plan.
Flexitarian Diet Recipes
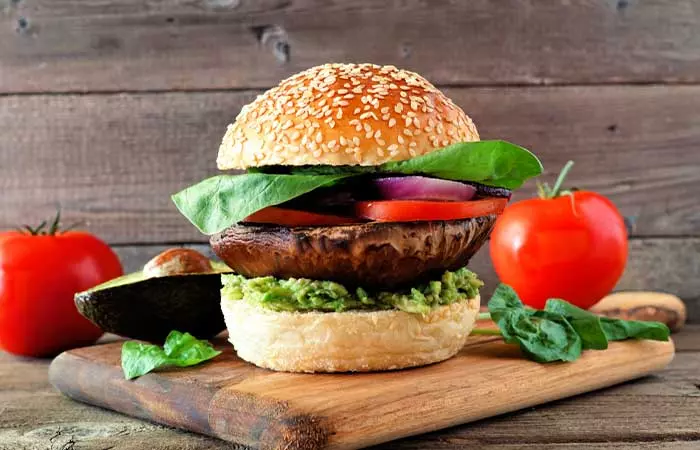

1. Portobello Mushroom And Avocado Burger

What You Need
- 4 portobello mushrooms
- 1 avocado
- 1 onion
- 2 tablespoons low-fat yogurt
- ½ teaspoon garlic
- 4 hamburger buns
- 3 tablespoons olive oil
- ¾ teaspoon salt
- ½ teaspoon black pepper
Instructions
- Remove the stems of the portobello mushrooms and slice the onion.
- Drizzle olive oil over them and season with a pinch each of salt and pepper.
- Cook the mushrooms over medium heat in a skillet for 10 mins. Set them aside.
- Saute the onions until golden brown and set them aside.
- Mince the garlic and mash the avocado to combine them.
- Add yogurt and the leftover salt and pepper to this mixture.
- Lightly toast the hamburger buns and assemble the burger.
- You can add tomato, lettuce, and other seasonings as per your taste.
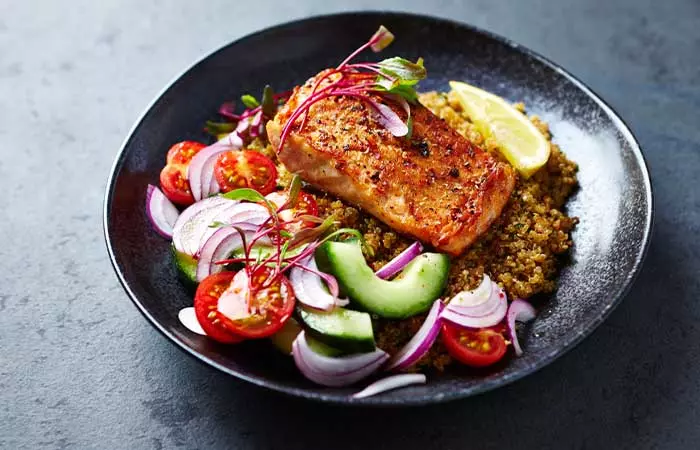
2. Salmon And Vegetable Quinoa
What You Need
- 1 cup quinoa
- 20 ounces salmon filet
- ¾ cup cucumbers
- 1 cup cherry tomatoes
- ¼ cup red onion
- 4 basil leaves
- ¼ cup parsley
- 1 teaspoon kosher salt
- ¼ teaspoon black pepper
- 1 teaspoon cumin
- ½ teaspoon paprika
Instructions
- Cook the quinoa with 2 cups of water and ½ teaspoon salt over medium heat in a saucepan.
- Bring it to a boil, then simmer for around 20 minutes with the lid on. Set it aside.
- Dice and deseed the cucumbers, halve the tomatoes, dice the onions, and thinly slice the basil leaves.
- Once the quinoa has cooled down, add the above ingredients to it.
- Lightly grease a sheet pan with olive oil and place the salmon filet on it.
- Mix the seasonings and coat the salmon with about ½ teaspoon of this spice mix.
- Broil on high heat for about 10 minutes.
- Garnish with parsley and serve over the quinoa.
Although many people may find this recipe for a filling flexitarian dinner choice to be tempting, it is important to highlight that people with certain dietary requirements or allergies should exercise caution before trying it.
Who Should Not Follow A Flexitarian Diet Plan?
Some individuals who should avoid a flexitarian diet include:
- People with allergies or intolerances to certain plant-based foods.
- People with certain medical conditions that require a strict diet, such as celiac disease or diabetes.
- Pregnant or breastfeeding women who may need to consume more animal-based products for proper nutrition.
- People who are underweight or have a hard time gaining weight, who may need to consume more animal-based products for calorie and nutrient needs.
It is always important to consult with a healthcare professional or registered dietitian before making any significant changes to your diet.
Infographic: Flexitarian Diet: What To Eat And What To Avoid
A flexitarian diet is the perfect balance of health and sustainability. This infographic provides a guide to help you make smart choices on this meat-reduction diet. It lists the foods you should eat regularly, foods you can eat occasionally, and foods that should be avoided. By following this guide, you can enjoy a delicious and nutritious diet while also reducing your environmental impact.

Illustration: StyleCraze Design Team
The Final Word
A flexitarian diet finds the ideal harmony between a vegetarian and a meat-inclusive diet. This low-carbon diet strongly emphasizes eating whole foods that are nutrient-dense and abundant in fiber, vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants to lower the risk of chronic diseases and support sustainability. It gives you the freedom to choose from a range of delectable and healthy meals without feeling constrained. You can follow this diet easily if you consume more plant-based foods, try different animal meat substitutes, watch your portion sizes, prepare meals ahead of time, and have an open mind. The flexitarian diet should, however, be followed with the advice of a healthcare provider or a qualified dietitian, especially if you have any dietary restrictions or medical issues.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is flexitarian better than vegan?
There is a lack of scientific evidence that compares the benefits of vegan and flexitarian diets. While the former significantly lower greenhouse gas emissions (that cause global warming and climate change) than the latter, a flexitarian diet may support better dietary balance because animal-based meals are a good source of some essential minerals like vitamin B12 and iron.
Is the flexitarian diet successful?
Yes. The flexitarian diet allows people to gradually change their dietary preferences without restricting them at their own pace. Several studies have shown that it has beneficial effects on your weight, blood sugar levels, and heart health (1).
How popular is the flexitarian diet?
The flexitarian diet is slowly gaining popularity across the world. According to a study conducted on the Swiss population of 10,797 individuals, 15.6% claimed to follow the flexitarian diet (11).
Do flexitarians live longer?
Possibly. A study found that those who consumed meat less than weekly may increase their life expectancy by 3.6 years (12).
Is a flexitarian diet affordable?
Yes. A study showed that sustainable and healthy diets like the flexitarian diet are significantly cheaper than a regular diet (13).
Illustration: Flexitarian Diet: Benefits, Meal Plan, & How Does it Work
Image: Stable Diffusion/StyleCraze Design Team
References
Articles on StyleCraze are backed by verified information from peer-reviewed and academic research papers, reputed organizations, research institutions, and medical associations to ensure accuracy and relevance. Read our editorial policy to learn more.
- Flexitarian Diets and Health: A Review of the Evidence-Based Literature
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5216044/ - Nutrient Intake and Status in Adults Consuming Plant-Based Diets Compared to Meat-Eaters: A Systematic Review
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8746448/ - Vegetarian Diets and Weight Reduction: a Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4699995/ - Plant-Based Diet as a Strategy for Weight Control
https://www.mdpi.com/2304-8158/10/12/3052 - Vegetarian Dietary Patterns and Cardiovascular Disease
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29800598/ - Vegetarian Diets and the Risk of Diabetes
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6153574/ - The Impact of Plant-Based Dietary Patterns on Cancer-Related Outcomes: A Rapid Review and Meta-Analysis
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7400843/ - The Relationship Between Plant-Based Diet and Risk of Digestive System Cancers: A Meta-Analysis Based on 3059009 Subjects
https://www.frontiersin.org/journals/public-health/articles/10.3389/fpubh.2022.892153/full - Vegetarian Diets: Planetary Health and Its Alignment with Human Health
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6855976/ - Effect of Fibre Supplementation on Body Weight and Composition, Frequency of Eating and Dietary Choice in Overweight Individuals
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7525113/ - Vegetarian, pescatarian and flexitarian diets: sociodemographic determinants and association with cardiovascular risk factors in a Swiss urban population
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7525113/ - Does low meat consumption increase life expectancy in humans?
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12936945/ - The global and regional costs of healthy and sustainable dietary patterns: a modelling study
https://www.thelancet.com/journals/lanplh/article/PIIS2542-5196(21)00251-5/fulltext
Read full bio of Olesya Wilson
Read full bio of Payal Karnik
Read full bio of Ravi Teja Tadimalla
Read full bio of Himanshi Mahajan


























Community Experiences
Join the conversation and become a part of our empowering community! Share your stories, experiences, and insights to connect with other beauty, lifestyle, and health enthusiasts.