Fungal Acne: Symptoms, Causes, And Treatment Options
Combat this stubborn type of acne with some safe and effective remedies.
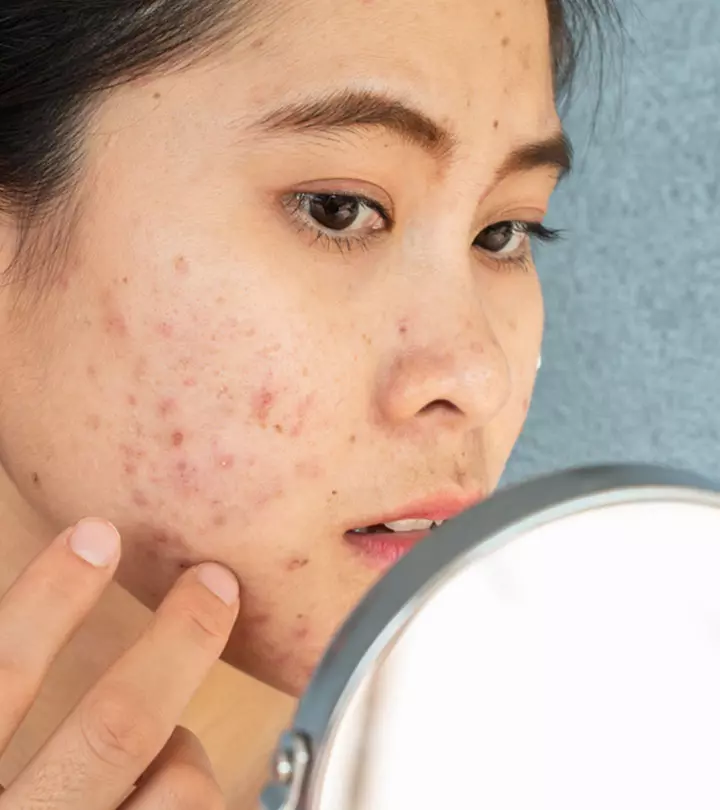

Image: Shutterstock
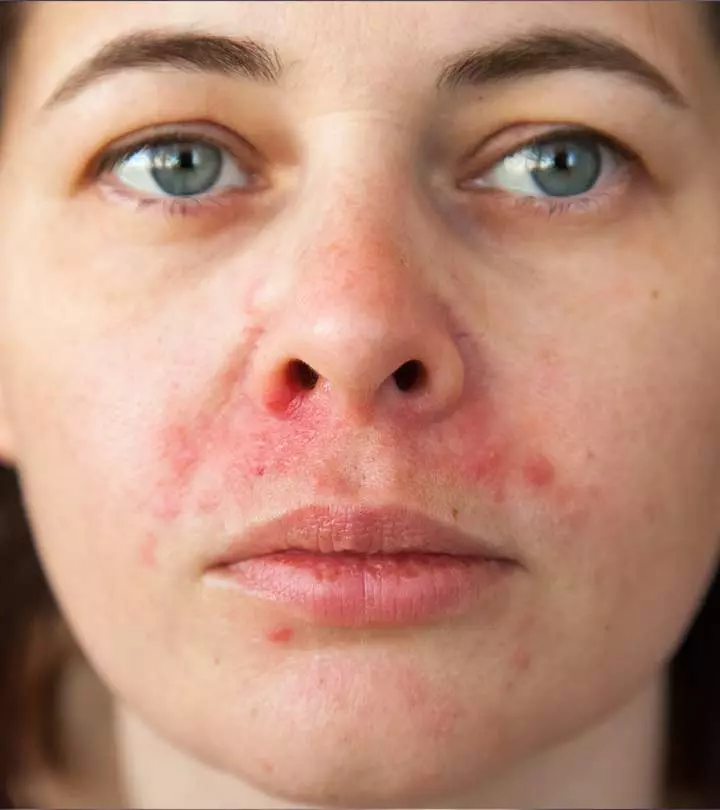
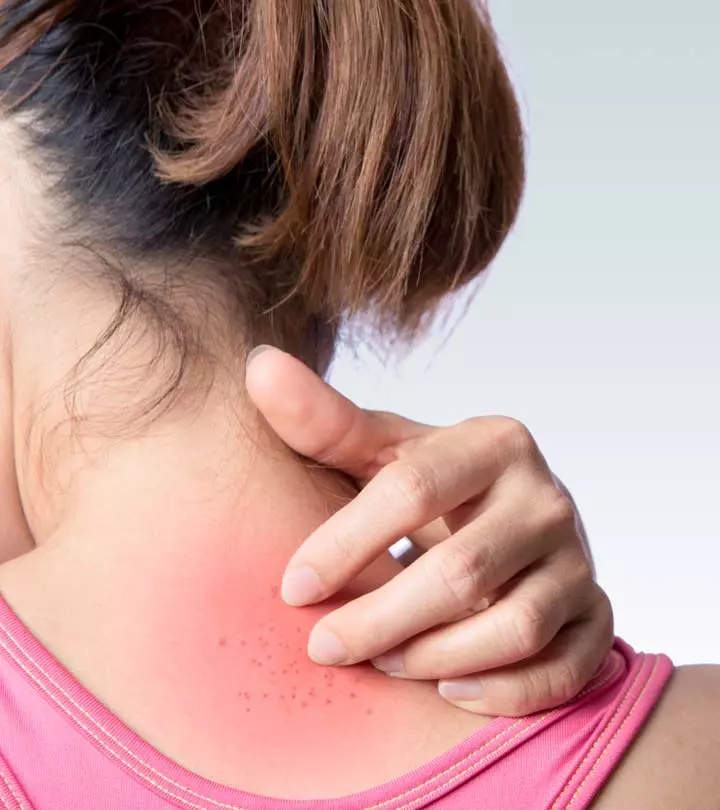
Not all acne clears easily. Some might be so stubborn that the usual treatments are not enough for them. These could be fungal acne and may cause irritation and breakouts on your back, chest, and arms.
Though it is not easy to get rid of fungal acne, there are some ways to soothe the inflammation and eliminate the fungus. This article discusses the signs and symptoms of fungal acne, its causes, treatment options available, and prevention tips for managing this condition. Keep reading.
 Did You Know?
Did You Know?In This Article
What Is Fungal Acne (Malassezia Folliculitis)?
Fungal acne is also referred to as pityrosporum folliculitis or Malassezia folliculitis (1). It is non-contagious and non-infective.
Malassezia furfur is a type of yeast naturally found on your skin. During fungal acne, the yeast can grow excessively in the hair follicles. The sebaceous glands over-secrete the oily sebum and clog the pores and the hair follicles in your skin. They trap the yeast and bacteria within and lead to inflammation in your hair follicles.
Fungal acne (Malassezia folliculitis) and regular or bacterial acne (acne vulgaris) are often confused with each other. As fungal acne has a different cause, it does not respond to the usual acne treatment. In fact, using a regular treatment approach can even worsen the symptoms.
It is important to note that fungal acne is primarily caused by an overgrowth of Malassezia yeast, a fungi commonly found on the skin. This makes it distinct from bacterial acne, which arises from different pathogens. Because of this difference, fungal acne has unique characteristics and requires specific treatments, unlike the typical approaches used for bacterial acne.
 Did You Know?
Did You Know?Do you suspect you may have this condition? Keep reading to know the symptoms of fungal acne.
Key Takeaways
- Fungal acne is caused due to the over secretion of sebum and overgrowth of yeast within the hair follicles.
- You can observe pus-filled bumps on the skin and acne-like breakouts on the arms, chest, and back.
- Trapped moisture, tight clothes, and chronic medical conditions are common causes of fungal acne.
- Using multifunctional serums, oil-free moisturizers, and topical medications may help manage it.
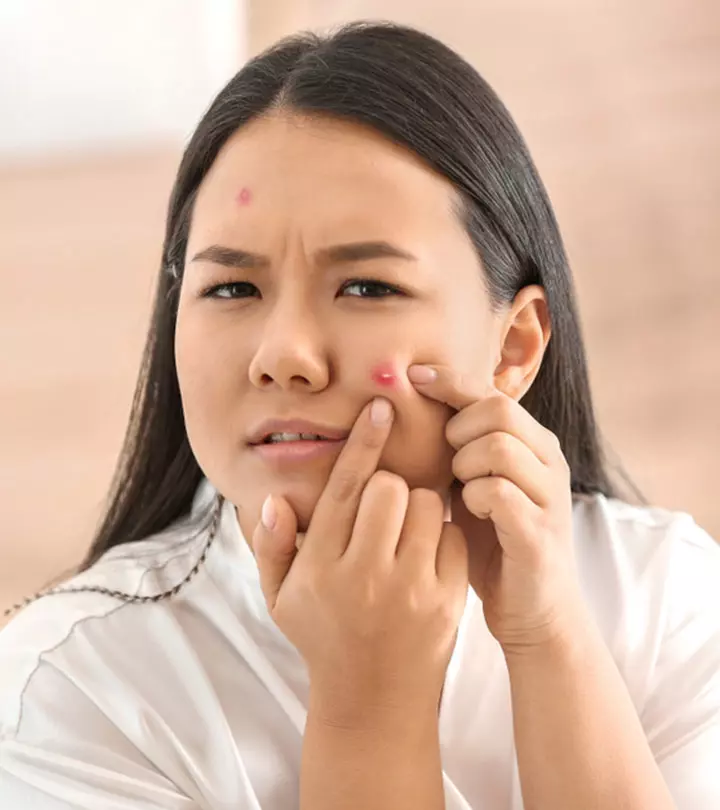
What Are The Symptoms Of Fungal Acne?
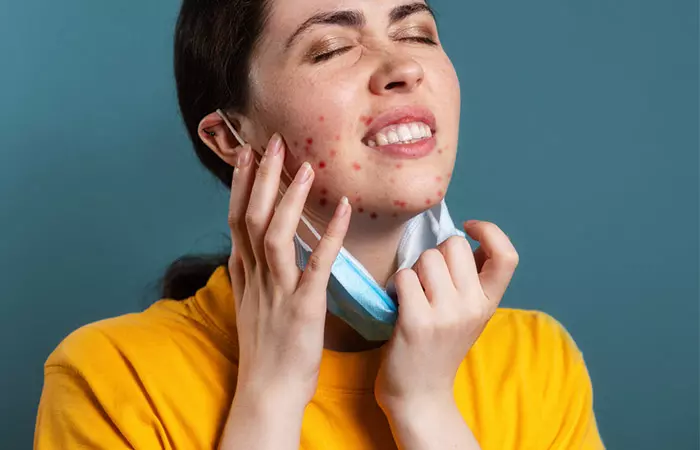

The following symptoms of fungal acne can help you recognize the condition and seek proper treatment:
- Equal-sized, pus-filled bumps on the skin
- Acne-like breakouts, especially on the chest, arms, and back
- Itchiness of the skin around breakouts
- Occasional stinging sensation
- Clustered whitehead appearance
Consult a dermatologist if you have these symptoms. But what causes them?
What Causes Fungal Acne?
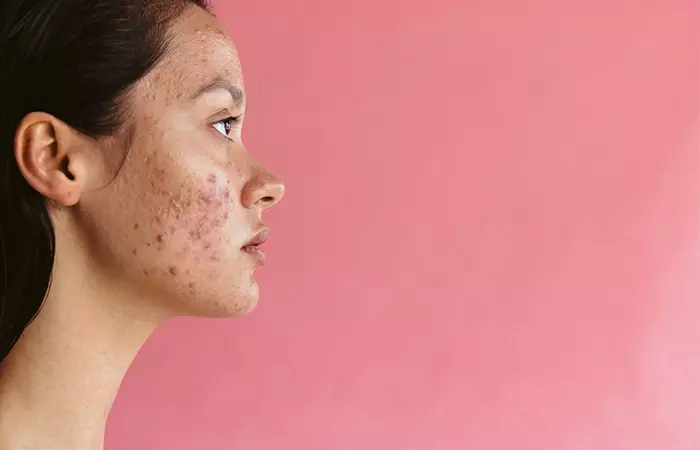

The overgrowth of Malassezia furfur (the fungus responsible for fungal acne) is caused by a disturbance in the natural balance between yeast and bacteria. The following factors can create the imbalance:
- Trapped Moisture
Re-wearing your sweaty workout clothes can cause the moisture to get trapped.
This moisture further exposes your skin to both bacterial and fungal overgrowth.
- Tight And Synthetic Clothes
Tight and synthetic clothes prevent breathability and can encourage additional sweating and moisture trapping. Synthetic fabrics further create an environment for yeast and fungal growth.
- Medications
Prescription antibiotics may disrupt the natural skin microbiome (2). This way, they may lead to the overgrowth of opportunistic microorganisms such as fungi. Also, prolonged use of topical steroids may reduce the defensive mechanism of your skin and allow microbial growth (3).
- Chronic Medical Conditions
Individuals dealing with chronic conditions with a compromised immune system may develop secondary infections such as Malassezia folliculitis. More research is warranted to further understand this phenomenon.
- Comedogenic Skin Products
Fungal infections on the skin feed on the sebum (a type of oily secretion). Using comedogenic skincare products, such as sunscreens and lotions, may clog the skin pores and trap the sebum. Such products could increase the risk of acne, both bacterial and fungal.
Saj, a YouTuber, shared how she got fungal acne after applying chemical sunscreen to protect her skin from sun exposure. She said, ???My face was just a mess it was a mess. I had tiny bumps covering from where my hands are like right here all the way down to my neck (i).”
- Excess Sebum Production
Excess sebum production can also increase your risk of developing fungal acne. Adolescents are more likely to experience excess sebum production and develop fungal acne due to hormonal changes during their puberty.
- Diet Changes
and excess sweets in your diet may exacerbate fungal growth. Balancing your diet may check fungal growth.
- Climatic Conditions
Yeast (being fungi) multiplies rapidly in hot and humid climates. People living in such climatic conditions are more prone to fungal acne.
As discussed, fungal acne can be mistaken for regular acne. It is best to talk to a healthcare professional to determine what acne you have. Read on to know how your doctor can diagnose the condition.
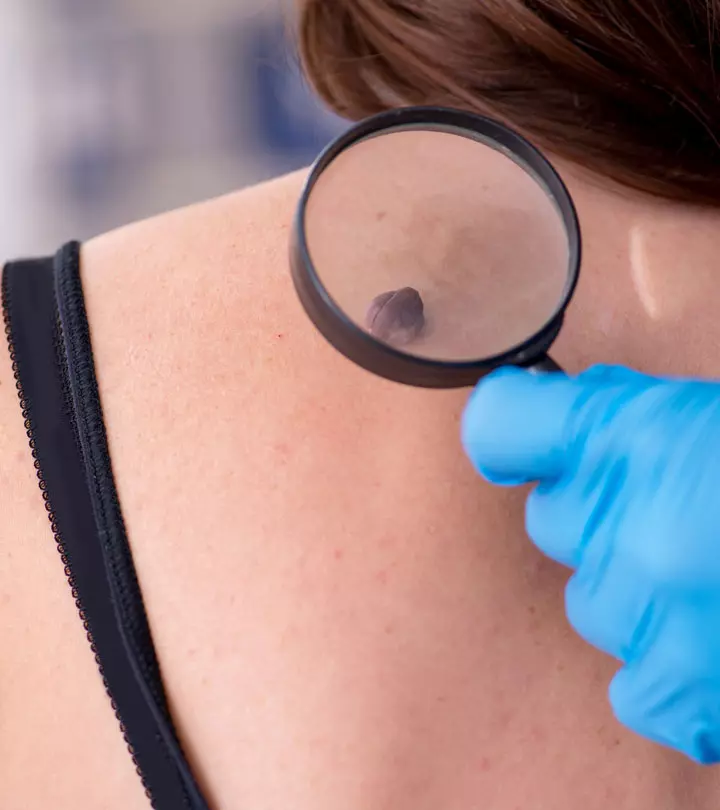
How Is Fungal Acne Diagnosed?
Your doctor will diagnose fungal acne by taking a detailed medical history and asking you about your symptoms. The characteristics of your symptoms, such as their onset, duration, severity, and treatment methods you may have tried previously, will help your doctor reach a diagnosis.
Specific diagnostic procedures such as skin samples and biopsy can help confirm your diagnosis (4). Your doctor may recommend these procedures, if necessary.
As stated before, the usual acne treatment is ineffective against fungal acne. In the next section, we look at some effective treatment methods for fungal acne.
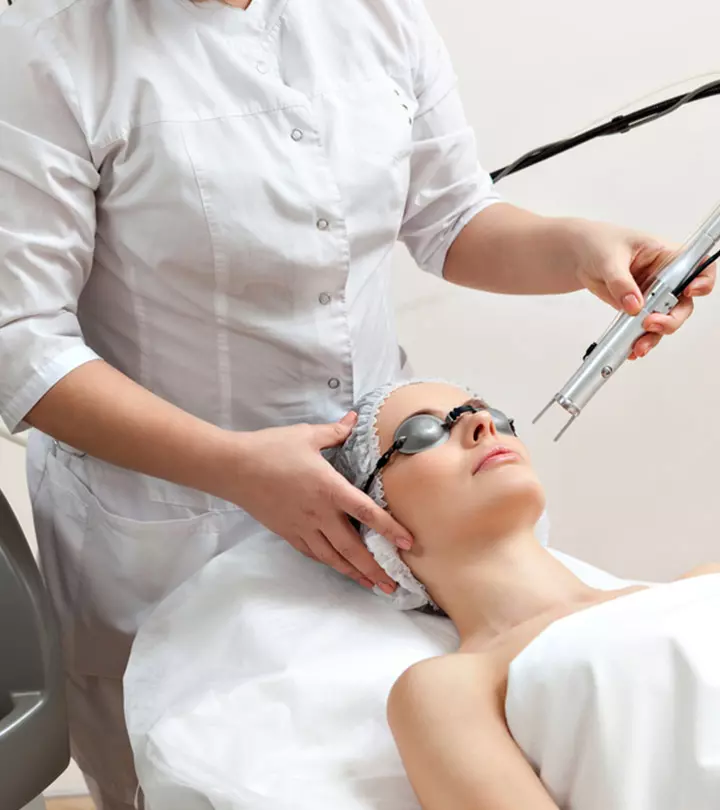
How Is Fungal Acne Treated?
While curing Malassezia folliculitis could be very difficult, you can manage its symptoms. Here are some common treatments for fungal acne:
Take The Right Medications
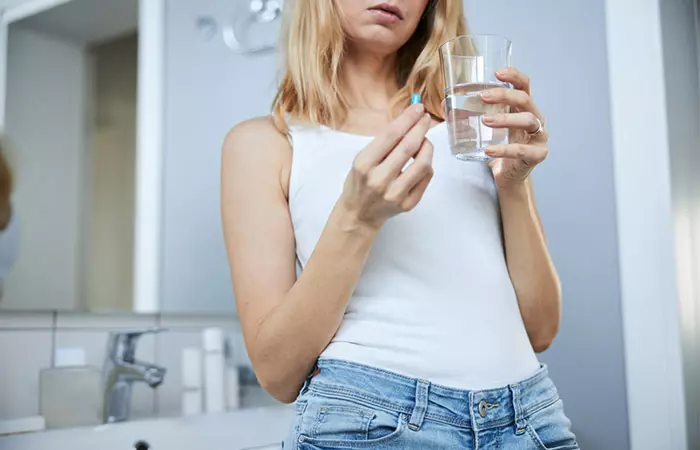

Medications help control fungal overgrowth and restore the bacterial flora balance on your skin. Addressing these two concerns may keep the acne from recurring (1), (4). There are two classes of medications used to treat Malassezia folliculitis:
- Oral Medications
The treatment length of antifungal oral medications depends on the extent of your condition. You can reduce or stop the medications once the itchiness and inflammation subside. You can then switch to topical medications.
- Topical Medications
These medications help prevent a recurrence of acne. They are available in body wash or shampoo form. You will have to wash the affected area regularly with the product when you have an active breakout. Once the irritation is relieved, you can use the product once a week.
Use Oil-Free Moisturizers
Using oily, comedogenic skin products will invite fungal infections. These products can clog the pores and allow the fungus to breed, further worsening your acne.
Your skin may also develop bouts of irritation and dryness during the course of the treatment. Hence, going for an oil-free gel or water-based moisturizer would be ideal.
Use Multifunctional Serums
Less is more when it comes to taking care of acne-prone skin. Instead of using too many products, switch to a multifunctional serum that can target your breakouts and help fade the dark spots.
Exfoliate Your Skin

Exfoliation clears away dead skin cells, excess sebum, and dirt from your skin. These factors may otherwise promote the growth of bacteria and fungi within the pores of your skin. Regular use of a body exfoliator can reduce the chances of developing fungal acne.
Apply Tea Tree Oil
Tea tree oil is a natural antifungal ingredient with antiseptic properties (5). The oil may help treat fungal acne. Before incorporating the oil into your skincare routine, do a patch test by applying the oil mixture to a small area of your skin and check for any allergic reactions. Tea tree oil is quite potent; hence, dilute it with a carrier oil before use.
Pityrosporum folliculitis (PF) is often misdiagnosed as acne vulgaris. This review analyzed data from 15 studies on PF in immunocompetent patients. The average age of onset was 24.26 years, predominantly affecting males (64%). Lesions commonly appeared on the chest (70%) and back/shoulders (69.2%). Pruritus was a common symptom (71.7%), and 40.5% had previously unsuccessful treatments. Oral antifungals (92%) and topical antifungals (81.6%) demonstrated high treatment success rates. Proper diagnosis is important, distinguishing PF from acne based on pruritus and emergence after antibiotic or immunosuppressive therapy. Antifungal treatments yield positive outcomes for most PF cases.
Are you wondering how long the symptoms of fungal acne can take to subside? Keep reading.
How Long Does It Take To Reduce Fungal Acne?
While some people claim to notice results in 2 to 3 days, fungal acne may also take months to improve (even with the right treatment). The exact duration depends on the extent and severity of your acne. In some cases, it may not resolve and keep recurring.
As we saw, the total cure of fungal acne is extremely difficult. However, you can reduce the risk of re-infection with some handy tips.
Preventing Fungal Acne: Dos And Don’ts
Dos:

- Use antifungal body wash and shampoo at least once each week.
- Wear breathable clothes made of natural fabrics to let your skin breathe.
- Wipe your body with wipes after every workout if you are unable to shower immediately.
- If you live in an area with a very humid climate, consider showering or rinsing frequently.
- To get rid of fungal acne on the forehead and other areas of the face, avoid wearing make-up. Wash your face frequently.
- Add probiotics to your diet to support a healthy skin microbiome and prevent fungal overgrowth.
Don’ts:
- Avoid wearing very tight clothing. It may block sweat and trap the fungi.
- Change your workout clothes and wash them before wearing them for your next session.
- Do not use comedogenic products containing coconut or olive oils on your scalp and skin. These may clog your pores and worsen the condition.
Fungal acne often appears similar to acne vulgaris. How are the two different?
How Does Fungal Acne Differ From Regular Acne?
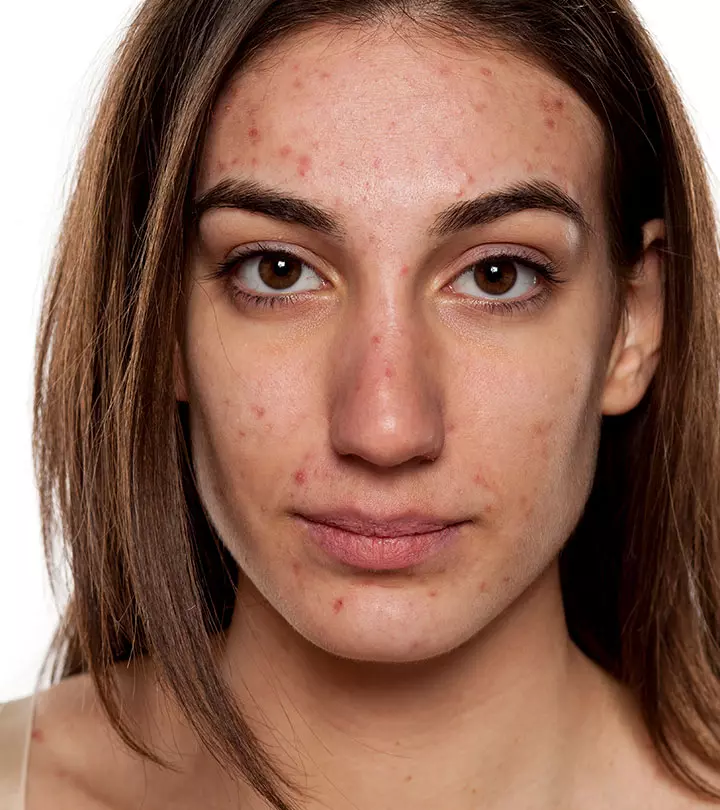
Regular acne usually is scattered on the face and occasionally over the neck, chest, and back. The breakouts may have different lesions involving whiteheads, blackheads, nodules, pustules, papules, etc. These acne breakouts are of varying sizes. Although regular acne begins in adolescents, it can persist and pass into adulthood (6).
Malassezia folliculitis differs in appearance. These breakouts are usually smaller (1 to 2 mm) and are of similar size and shape. The skin condition accompanies itchiness (absent in acne vulgaris).
Unlike regular acne, fungal acne is present over the shoulders, back, chest, and hair roots in clusters (7). Moreover, it typically affects young adults.
When Should I See A Doctor?
If your acne persists for more than 3 weeks, you should consult your dermatologist. Your doctor can prescribe you medications and topical applications for treating the fungal infection. These treatments can be more efficient at reducing infection.
You should also consult your doctor for treating recurring and chronic fungal acne infections.
Infographic: Fungal Acne Home Remedies That Work
Effective treatment for fungal acne may require both oral medications and topical ointments. You can also speed up your recovery by incorporating a few simple home remedies using natural ingredients.
Look at the infographic below to learn which combination of kitchen ingredients would work best to clear your stubborn acne scars and pimples. Illustration: StyleCraze Design Team
Fungal acne is a skin infection that develops anywhere on the body and may also appear as acne between eyebrows due to inflammation of your hair follicles. The symptoms of fungal acne you should look out for include pus-filled bumps, itchiness, and a burning sensation. It may also be like dandruff, an itchy scalp, or seborrheic dermatitis. Factors such as clogged pores, medications, excess oil, and poor diet may contribute to the development of fungal acne. Your doctor will prescribe oral medications and topical creams like ketoconazole-based products to reduce infection and inflammation. You can easily prevent fungal acne by wearing breathable clothes, limited makeup, and maintaining personal hygiene. If the acne persists for more than three weeks, consult a doctor for proper treatment.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is aloe vera good for fungal acne?
Aloe vera has antimicrobial properties and may help soothe fungal acne.
What foods are good for fungal acne?
Fungal growth is encouraged by sugary carbohydrates, so it is best to avoid them and eat a diet rich in citrus fruits and a variety of vegetables.
Can you squeeze fungal acne?
No. You should never squeeze any kind of acne.
Can apple cider vinegar cure fungal acne?
No, diluted apple cider vinegar is not a strong antifungal agent, and undiluted apple cider vinegar can damage the skin. Therefore, apple cider vinegar is not considered to be a remedy for fungal acne.
Does toner help fungal acne?
Using a toner regularly may reduce the amount of oil that gets trapped under the skin. Therefore, it may indirectly help fungal acne.
Does Accutane help fungal acne?
Yes, Accutane may help with fungal acne, but it is recommended to avoid using Accutane unless under the supervision of a dermatologist.
Illustration: Fungal Acne: Symptoms Causes And Treatment Options

Image: Stable Diffusion/StyleCraze Design Team
Is fungal acne bothering you? Understand more about it as a dermatologist sheds light on its causes and effective treatment methods. Gain valuable insights and expert advice in this enlightening video created just for you.
Personal Experience: Source
StyleCraze's articles are interwoven with authentic personal narratives that provide depth and resonance to our content. Below are the sources of the personal accounts referenced in this article.
i. My Fungal Acne Nightmare! | Fungal Acne journey and How I got rid of it | Skincare with SAJhttps://www.youtube.com/watch?v=pHaj7PNayBE
References
Articles on StyleCraze are backed by verified information from peer-reviewed and academic research papers, reputed organizations, research institutions, and medical associations to ensure accuracy and relevance. Read our editorial policy to learn more.
- Malassezia (pityrosporum) folliculitis,
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24688625/ - Acne, the Skin Microbiome, and Antibiotic Treatment,
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6534434/ - Side-effects of topical steroids: A long overdue revisit,
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4228634/ - Malassezia-Associated Skin Diseases, the Use of Diagnostics and Treatment,
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32266163/ - Antifungal activity of the essential oil of Melaleuca alternifolia (tea tree oil) against pathogenic fungi in vitro,
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/9055360/ - Acne,
https://www.niams.nih.gov/health-topics/acne - Special types of folliculitis which should be differentiated from acne,
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5821164/ - Malassezia (Pityrosporum) Folliculitis
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3970831/
Read full bio of Dr. Suchana Marahatta
Read full bio of Annie Jangam
Read full bio of Ramona Sinha
Read full bio of Swathi E























Community Experiences
Join the conversation and become a part of our empowering community! Share your stories, experiences, and insights to connect with other beauty, lifestyle, and health enthusiasts.