7 Impressive Hawthorn Berry Benefits, Dosage, & Side Effects
Boost your heart health and rejuvenate your mind with this delicious and vibrant fruit.

Image: Shutterstock
The tiny red hawthorn berries are commonly found in North America, Asia, and Europe. The health benefits of hawthorn berries could be associated with their anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and gastro-protective properties. These tangy fruits may help improve heart health, enhance digestion, lower blood pressure, and ease anxiety. The hawthorn plant’s stems, leaves, and bark also possess important medicinal properties. In this article, we will discuss the various health benefits of hawthorn berries, their nutrition profile, dosage, and any potential side effects. Keep reading.
 Know Your Ingredient: Hawthorn Berry
Know Your Ingredient: Hawthorn BerryWhat Is It?
Red, tangy, edible berry-like fruit produced from the Hawthorn tree.
What Are Its Benefits?
It may lower blood pressure, treat heart failure, improve digestion and bowel movement, and reduce stress and anxiety.
Who Can Use It?
It is safe for consumption for all except for those who are on medication to improve their heartbeat, or taking beta-blockers, calcium channel blockers, and nitrates.
How Often?
You can consume it thrice daily in moderation.
Caution
They may cause nausea, dizziness, headache, and cardiac and gastrointestinal symptoms in some people. It is not recommended for children and pregnant/breastfeeding women.
In This Article
7 Impressive Health Benefits Of Hawthorn Berry
1. May Help Treat Heart Failure
Studies show that hawthorn berry is used as a combination drug to treat heart failure (a condition where the heart can’t pump as much blood as it should) (1). The narrowed arteries in the heart gradually leave your heart too weak to pump blood efficiently, leading to heart failure. Trials conducted on 855 patients with chronic heart failure showed that hawthorn improved heart function and blood circulation when used in combination with conventional treatments (2).
A study conducted on patients with chronic heart failure stage NYHA II (people with symptoms of fatigue, palpitation, and dyspneai Medical term for shortness of breath caused by an infection in the respiratory system or an external factor such as high altitude. even with ordinary physical activity) found that those who took hawthorn berry extract had fewer symptoms (3). Hawthorn berry was also found to reduce the risk of sudden death due to heart-related issues (4). However, more studies are needed to understand this benefit of the hawthorn berry.
2. May Improve Cardiovascular Function
Hawthorn berry contains flavonoids, polyphenols, and procyanidinsi A subclass of major flavonoids that is widely distributed in multiple parts of a plant. They are antioxidants and protect healthy cells. . Its extract has been found to work well for patients with angina (chest pain caused by reduced blood flow). It improves the blood flow and oxygen supply of the heart and also enhances cardiac energy metabolism (5). Hawthorn berry is said to possess anti-atherosclerosis properties and may prevent the accumulation of cholesterol, fats, and plaque on the artery walls (6) and may improve the immune system as well. Research shows that the flavonoids in hawthorn berries interact with enzymes that help enhance myocardial contractility (the ability of the heart muscle to contract) (5).
3. May Lower Blood Pressure
Hawthorn berry has been used for treating high blood pressure (5). A study conducted by the University of Reading found that hawthorn extract can have a hypotensivei A patient whose blood flow is lower than normal. Common symptoms include blurred vision and dizziness. effect (7). Hawthorn relaxes blood vessels and allows blood to flow more easily. Its active components were found to cause vasorelaxation (reduction in tension of the blood vessel walls) in rat studies (8), (9).
In another small-scale study conducted on 79 individuals with type 2 diabetes, a daily intake of 1200 grams of hawthorn extract for sixteen weeks along with prescription drugs was found to lower blood pressure (10). No herb-drug interactions were recorded during this controlled trial. However, more human studies are warranted to further understand this benefit of the hawthorn berry.
4. May Improve Digestion
Hawthorn berries and extracts have been used in traditional medicine for treating digestive problems. In a study, the phenolic and flavonoid compounds in hawthorn berry extracts showed anti-inflammatory, gastroprotective, anti-microbial, and free radical-scavenging properties (11). Its gastroprotective effect was tested in rats with ulcers. It was found to exhibit bactericidal activity against gram-positive bacteria such as Micrococcus flavus, Bacillus subtilis, and Lysteria monocytogenes. Dried hawthorn fruit contains antioxidants and digestion-improving agents that were found to accelerate gastrointestinal transit in mice (12).
This graph from a 2021 study published in Frontiers in Genetics explains the prebiotic potential of 11 immunomodulatory herbs, including hawthorn berry. The study attempted to test the herbs with the use of 16S rDNA sequence analysis and understand the change in their metabolism and prebiotic potential. As suggested in the graph, the therapeutic benefits of the tested herbs may be due in part to their ability to change the community metabolism of gut microbiota, which affects proper functioning of the digestive system.

Immunomodulatory Effects Of Hawthorn Berry
Source: Community Metabolic Interactions, Vitamin Production and Prebiotic Potential of Medicinal Herbs Used for Immunomodulation5. May Reduce Anxiety

Hawthorn berries can reduce anxiety (13). In a study, hawthorn extract, with a combination of five other extracts, showed a mild sedative effect and helped lower anxiety in patients with anxiety disorders (14). Another study conducted by the University of Reading found that hawthorn exhibited hypotensive and anti-anxiety effects (7). The extracts of hawthorn proved safer and more effective when compared with placebo (medical treatment) for treating anxiety disorders (15). You can take two cups of hawthorn tea every day post your meals to help reduce anxiety.
6. May Lower Cholesterol Levels

The polyphenols in hawthorn berries help lower serum cholesterol levels (5). In an animal study, the ethanol extract of hawthorn could suppress the stimulation effect of a high-fat diet (16). This resulted in lower levels of total serum cholesterol, triglycerides, and low-density lipoprotein.
Another study conducted on hamsters found that the triterpenic acid in hawthorn extracts can lower plasma cholesterol levels (17). It works by inhibiting acyltransferase, an enzyme that promotes cholesterol absorption.
Another study conducted by the Victoria University on mice with high cholesterol levels found that hawthorn fruit could lower the levels of LDL cholesterol and triglycerides as good as cholesterol-lowering medication (18). However, more studies are needed to understand this benefit of hawthorn berries in humans.
7. May Improve Skin Health
Hawthorn berries are rich in antioxidants and vitamins that may protect the skin from oxidative stress. They also may help manage skin damage caused by UV radiation (19). Further, their antibacterial properties may help combat various skin infections (20). Their ability to inhibit melanin production may also help combat issues associated with skin pigmentation (20).
Hawthorn berry extracts are often used in skin care products due to their ability to enhance blood circulation and potentially boost skin glow. Whether consumed or applied topically, hawthorn berries may play a vital role in maintaining skin vitality and radiance.
Apart from all these benefits, hawthorn berries also help prevent early aging signs and symptoms as they are rich in antioxidants and have anti-inflammatory properties. They also help prevent hyperpigmentation by blocking melanin production in skin cells. Anecdotal evidence suggests that hawthorne berries may boost immunity and help manage insomnia. However, more studies are warranted to support these claims.
 Fun Fact
Fun FactFrom eating raw hawthorn berries to making tea, jellies, and tinctures, you can consume these fruits in various ways. In the following section, we discuss how you can add hawthorn berries to your diet.
Key Takeaways
- Hawthorn berries are commonly grown across North America, Europe, and Asia and are rich in vitamin C, iron, and antioxidants.
- Hawthorn berry tea may lower blood pressure, improve bowel movement, and reduce stress and anxiety.
- However, consult a doctor before consuming hawthorn berries as they may cause side effects such as nausea, dizziness, and rashes.
How To Add Hawthorn Berry To Your Diet?
- Hawthorn Berry Tea
What Do You Need
- Dried hawthorn berries – 1 tablespoon
- Dried organic rose petals – 1 to 2 tablespoons
- Crushed cinnamon – ¼ teaspoon
Process
- Soak dried hawthorn berries overnight.
- Boil 2 cups of water and place the hawthorn berries into a pot.
- Lower the heat and simmer the mix for about half an hour.
- Make sure to keep the lid on.
- Add rose petals and cinnamon to the pot and cover it with a lid.
- Steep for 10 minutes and strain.
- Hawthorn Berry Jelly
What Do You Need
- Hawthorn berries – 2 pounds
- White sugar – 2 cups
- Juice of one lemon
Process
- Take four cups of water in a large saucepan and simmer over medium heat for 40 minutes.
- Break the fruits using a potato masher and strain them through a jelly bat to get clear jelly.
- Add white sugar and lemon juice to the fruit juice.
- Stir the mixture constantly and boil it until it sets.
- Pour the mixture into clean jars and let it cool to room temperature. Store in the refrigerator.
Lucinda, a blogger, shares how she makes decoctions and tinctures using hawthorn berries. She writes, “I like to prepare my berries in alcohol or vinegar as well as drying a good number for use in decoctions (i).” She continues, “This year I made a simple hawthorn tincture in vodka and another in which I combined the berries with rosehip and ginger in a mixture of port and brandy, yum.”
Apart from Hawthorn tea and jelly, you may also add it to your diet in the following ways:
- Hawthorn berries have a tart, slightly sweet taste and can be eaten as a snack.
- Add fresh or powdered hawthorn berries to your smoothies, yogurt, or oatmeal for a nutritional twist in your diet.
- Ferment them to prepare vinegar or alcoholic beverages.
- Add dried hawthorn berries to your trail mixes or energy bars.
- You may also have them in the form of supplements or tinctures. Hawthorn tinctures are made by steeping hawthorn leaves, flowers, and fruits in alcohol.
 Trivia
TriviaAround 7000 BC, the ancient Chinese used beverage made of hawthorn berries for medicinal and religious use because of its therapeutic properties.
Hawthorn berries can also be used in winemaking. They are even available as hawthorn berry supplements. But what is their ideal dosage?
What Is The Recommended Dosage Of Hawthorn Berry?
A minimum dose of 300 mg of hawthorn extract daily is recommended for treating heart failure (21). A dose of 160 to 900 mg of hawthorn extract per day is recommended for the treatment of congestive heart failure (22). These dosages are highly dependent on the forms of hawthorn. Also, hawthorn supplements are not regulated by any authorized organizations. Hence, procure them from a reputed brand after consulting your doctor.
Hawthorn berries have an impressive nutritive profile. Read on to know the key nutrients in these berries.
Nutrition Profile Of Hawthorn Berry
Hawthorn berries are rich in several vitamins and plant nutrients (5).
- Phenols
- Saponins
- Catechins
- Procyanidins
- Flavonoid rutin
- Vitexin
- Vitamin C
- Folic acid
- Iron
These nutrients are high in anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and antiseptic properties. They help improve blood flow, metabolism, cardiovascular health, and nutrient absorption.
You should store these berries carefully to avoid damage. We tell you how in the following section.
How To Store Hawthorn Berries?
Hawthorn berries can look fresh for two weeks if stored in a cool, dry place. You can also freeze these fruits in the refrigerator. Died hawthorn berries can be used in the preparation of tea, extracts, and infusions.
In general, hawthorn berries are considered safe for consumption for many people. But they may cause side effects in some individuals. We will explore more in the next section.
Side Effects And Precautions
Intake of hawthorn berry is generally considered safe for many individuals. However, some people have complained about the following symptoms (22):
- Nausea
- Dizziness
- Headache
- Mild rashes
- Sweating
- Cardiac symptoms
- Gastrointestinal symptoms
Also, it is not recommended for children and pregnant/breastfeeding women as there is little information about its safety. Consult your doctor before you start using any hawthorn berry supplements.
Hawthorn can interact with drugs such as digoxin (that helps improve heartbeat). Avoid taking hawthorn with digoxin (23). As per studies, hawthorn can also interact with beta-blockers, calcium channel blockers, and nitrates (24), (25).
It also reacts with anticoagulant medication, which might increase the chances of bleeding.
Infographic: 5 Ways Hawthorn Berry May Improve Your Health
Hawthorn berries are rich in vitamin C, folic acid, iron, and other nutrients that are essential for vital bodily processes. From improving your heart health to boosting digestion, these delicious red berries provide numerous health benefits. Check out the following infographic to know more!
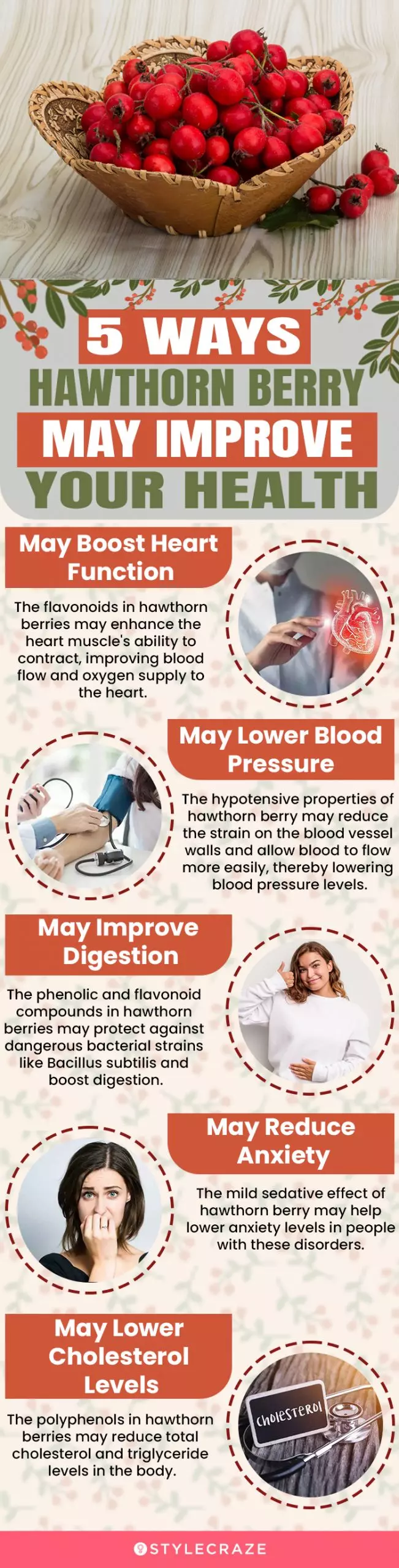
Illustration: StyleCraze Design Team
The benefits of hawthorn berries can be attributed to their rich nutrients profile. When included as a part of your regular diet, they help treat heart failure, improve cardiovascular health, lower blood pressure, improve digestion, and reduce anxiety. In addition, the polyphenols in hawthorn berries help in lowering cholesterol levels. Although the consumption of hawthorn berries is generally safe, there have been reports of these berries causing headaches, nausea, dizziness, sweating, and gastrointestinal discomfort. Therefore, caution is advised when consuming them. Include hawthorn berries in moderation in your diet to reap their benefits.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can hawthorn berries be used in combination with other herbs?
Yes, you may use hawthorn berries in combination with other herbs like California poppy. Research suggests that the two herbs together may reduce mild anxiety (26). However, it is best to consult a healthcare professional before combining hawthorn with any herb to avoid potential interactions that may lead to adverse effects.
Is hawthorn good for weight loss?
Yes. In one rat study, the group that received hawthorn berry drinks showed significantly lowered body weights after the 10th week of treatment (27).
Does hawthorn slow heart rate?
Maybe. Anecdotal studies suggest that hawthorn berry extract induces a slight but significant decrease in heart rate. However, limited studies are available to prove this claim.
What is better, hawthorn berries or leaves?
The berries and leaves of hawthorn are very similar in terms of their nutritional profile. But they differ in the ratio of specific flavonoids and procyanidins concentrations (24). However, more studies are warranted to understand which of the two is the better option.
How many hawthorn berries can I eat?
There is no recorded recommended dosage of hawthorn berries. However, having 250-500 mg of hawthorn berries, 3 times daily, in a supplement form is considered safe.
Illustration: Impressive Hawthorn Berry Benefits Dosage & Side Effects

Image: Stable Diffusion/StyleCraze Design Team
Hawthorn berry is a superfood with amazing health benefits! Learn how it can help improve heart health, reduce inflammation, and more!
Personal Experience: Source
StyleCraze's articles are interwoven with authentic personal narratives that provide depth and resonance to our content. Below are the sources of the personal accounts referenced in this article.
i. Hawthorn, My Heroinehttps://whisperingearth.co.uk/2010/10/02/hawthorn-my-heroine/
References
Articles on StyleCraze are backed by verified information from peer-reviewed and academic research papers, reputed organizations, research institutions, and medical associations to ensure accuracy and relevance. Read our editorial policy to learn more.
- Herbs and Dietary Supplements in the Prevention and Treatment of Cardiovascular Disease
https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1111/j.1520-037X.2000.80355.x - Hawthorn extract for treating chronic heart failure
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/18254076/ - Prospective, comparative cohort studies and their contribution to the benefit assessments of therapeutic options: heart failure treatment with and without Hawthorn special extract WS 1442
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15353901/ - The efficacy and safety of Crataegus extract WS 1442 in patients with heart failure: the SPICE trial
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19019730/ - Crataegus Extract
https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/medicine-and-dentistry/crataegus-extract - Hawthorn Extract Alleviates Atherosclerosis through Regulating Inflammation and Apoptosis Related Factors: An Experimental Study
https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s11655-018-3020-4 - Promising hypotensive effect of hawthorn extract: a randomized double-blind pilot study of mild, essential hypertension
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/11807965/ - Procyanidins in crataegus extract evoke endothelium-dependent vasorelaxation in rat aorta
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/10901280/ - Endothelium-dependent relaxation induced by hawthorn extract in rat mesenteric artery
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/9839542/ - Hypotensive effects of hawthorn for patients with diabetes taking prescription drugs: a randomised controlled trial
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16762125/ - Anti-inflammatory, gastroprotective, free-radical-scavenging, and antimicrobial activities of hawthorn berries ethanol extract
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/18698794/ - Chemical constituents, antioxidant and gastrointestinal transit accelerating activities of dried fruit of Crataegus dahurica
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29291866/ - Hawthorn (Crataegus spp.): An Updated Overview on Its Beneficial Properties
https://www.researchgate.net/publication/341469316_Hawthorn_Crataegus_spp_An_Updated_Overview_on_Its_Beneficial_Properties - A combination of plant extracts in the treatment of outpatients with adjustment disorder with anxious mood: controlled study versus placebo
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/9107558/ - Double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled study to evaluate the efficacy and safety of a fixed combination containing two plant extracts (Crataegus oxyacantha and Eschscholtzia californica) and magnesium in mild-to-moderate anxiety disorders
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/14741074/ - Ethanol extract of Zhongtian hawthorn lowers serum cholesterol in mice by inhibiting transcription of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-CoA reductase via nuclear factor-kappa B signal pathway
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26825354/ - Triterpenic Acids Present in Hawthorn Lower Plasma Cholesterol by Inhibiting Intestinal ACAT Activity in Hamsters
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19228775/ - A study of the comparative effects of hawthorn fruit compound and simvastatin on lowering blood lipid levels
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19885950/ - Botanical, Phytochemical, Anti-Microbial and Pharmaceutical Characteristics of Hawthorn (Crataegus monogyna Jacq.), Rosaceae
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8659235/ - Application of dry hawthorn (crataegus oxyacantha l.) extract in natural topical formulations
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29648721/ - Integrating Complementary Medicine Into Cardiovascular Medicine
https://www.jacc.org/doi/pdf/10.1016/j.jacc.2005.05.031 - Hawthorn: pharmacology and therapeutic uses
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/11887407/ - Interference of hawthorn on serum digoxin measurements by immunoassays and pharmacodynamic interaction with digoxin
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/20670141/ - Hawthorn (Crataegus spp.) in the treatment of cardiovascular disease
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3249900/ - Use of Herbal Products and Potential Interactions in Patients With Cardiovascular Diseases
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2831618/ - The effects of magnesium supplementation on subjective anxiety and stress—A systematic review
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC5452159/ - The effects of Crataegus pinnatifida (Chinese hawthorn) on metabolic syndrome: A review
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6556496/
Read full bio of Silky Mahajan
Read full bio of Sindhu Koganti
Read full bio of Ravi Teja Tadimalla
Read full bio of Moksha Gandhi


























Community Experiences
Join the conversation and become a part of our empowering community! Share your stories, experiences, and insights to connect with other beauty, lifestyle, and health enthusiasts.