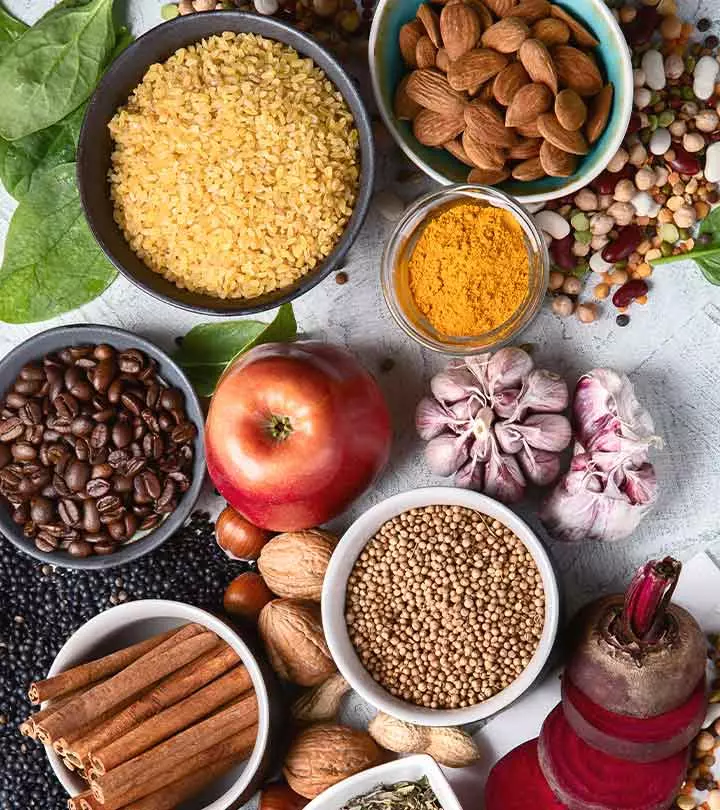
Best Foods For Digestion: 16 Foods To Relieve Upset Stomach
Satiate your hunger pangs and soothe your gut with nutritious fruits, grains, and more.

Image: shutter stock
Indigestion, bloating, and constipation are signs that your digestive system is not functioning to its full potential. If you experience any of these issues, it’s time to switch to the best foods for digestion. These will help prevent acid burps, bloating, gurgling stomachs, and heartburns. They also help in improving digestion, bowel movement, and nutrient absorption. As a result, you will get relief from improper digestion and other gut problems. A healthy gut will also boost immunity, improve mood, and heal skin and liver problems. Continue reading to learn about the foods good for digestion and those that may aggravate gut problems.
In This Article
16 Best Easy-To-Digest Foods For Upset Stomach Relief
1. Yogurt

Yogurt is a simple and easily digestible food that provides the gut with good bacteria that help in digestion. Several studies have shown that yogurt consumption can inhibit diarrhea, inflammatory bowel disease, improve bowel movement, and reduce the risk of colon cancer (1). You can have a small bowl of yogurt after lunch or dinner to help digest the food. But in case you are lactose intolerant, consider a yogurt alternative made from almond or goat milk, or even coconut milk.
 Quick Tip
Quick Tip2. Papaya

Papayas are rich in the proteolytic enzymes, chymopapain, and papain that have antimicrobial properties and aid digestion by breaking down food. Moreover, papayas are also a rich source of vitamins A, B. and C, which helps to flush out toxins (2). Austrian scientists carried out an experiment on individuals with digestion problems. One group was given papaya extract and the other was on placebo. The group that got the papaya extract, showed a considerable reduction in bloating, constipation, and heartburn (3). Have papaya after 1 hour of having lunch. You can also have papaya smoothie in the morning or add papaya to your fruit bowl.

3. Whole Grains

Whole grains are a great source of soluble and insoluble fiber. Soluble fiber acts by forming a gel-like substance in the large intestine thereby trapping the foods and increasing satiety while slowing glucose absorption. Insoluble fiber helps to promote bowel movement by adding bulk to the stool. Fiber also provides nutrition to the gut good bacteria. According to the American Dietary Guideline (2005), you should consume at least 3 ounces of whole grains per day (4). Consume wheat, broken wheat, sorghum, brown rice, oats, quinoa, etc. to get the recommended amount of fiber. If you are gluten intolerant, please stick with brown rice, buckwheat, sorghum, millet, and quinoa. These don’t cause digestive irritation.
4. Banana

Bananas are rich in fiber (a medium banana contains about 3 gm fiber) and pectini Pectin is a type of polysaccharide found in ripe fruits. It works as a setting agent in jellies and jams. , which helps to improve bowel movement and aid carbohydrate digestion (5). Bananas are also low GI food (they help keep blood sugar low) that are easy to chew and palatable too. Add one tender banana every day either in your breakfast cereal, smoothie, or pancakes. You can also have a banana with frozen yogurt or vanilla ice cream for dessert.
Lilja, a blogger, documented the experiment of eating bananas exclusively for five days, referring to it as her “Banana Island”. She notes, “My digestion gets so much better after completing Banana Island because I have given my digestive system the time to heal because it was only digesting one food those whole 5 days. Even just eating one mono meal per day can slowly and gradually help you get better digestion since you’re only digesting one food (i).”
5. Fish

Cold water fish are an excellent source of omega-3-fatty acids that help to reduce inflammation in the stomach or colon wall. This, in turn, can contribute to improving your digestion and bowel movement. In fact, scientists have found evidence that consuming fatty fish that contain a good amount of omega-3-fatty acid can help reduce the symptoms of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). It acts by decreasing oxidative stress and proinflammatory biomolecules (6). Consume small, wild-caught salmon, herring, cod, tuna, and carp to get the adequate amount of omega-3-fatty acid.
6. Ginger

Ginger root is commonly used in foods, but it also has many health benefits. For thousands of years, ginger has been used as a herbal medicine to treat cold, cough, inflammation, and nausea. It is also used as a home remedy for digestive problems like improper digestion. It is believed that ginger has a positive effect on enzymes that help break down fats and proteins (7). A group of scientists from Taiwan confirmed that ginger speeds up gastric emptying and boosts antral contractions (8). You can have a small piece of ginger with a little salt and chew it in the morning or add ginger to your fruit juice or cooked food.
7. Cumin

Cumin is extensively used in many cuisines as a flavoring agent. But cumin also possesses antioxidant, antimicrobial, antidiabetic, anticancer, and antiepileptic properties. Cumin acts as an appetite stimulant and helps relieve dysentery and diarrhea. Thymol, a phytochemical present in cumin stimulates the secretion of enzymes, acids, and bile to promote proper digestion. The essential oils, sodium, and magnesium present in cumin help relieve stomach ache (9).
 Quick Tip
Quick Tip8. Fennel
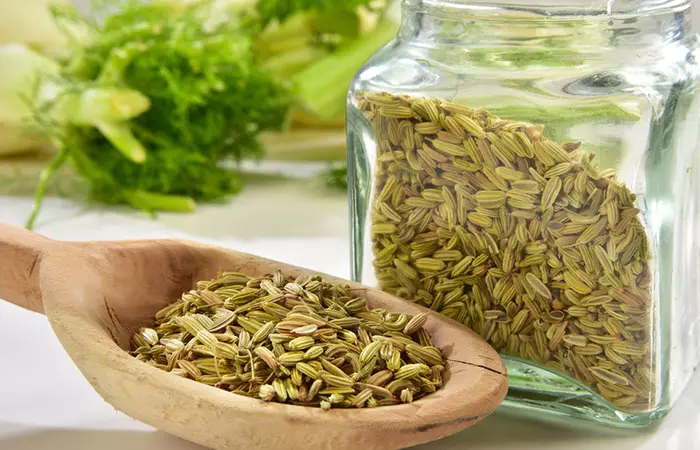

If you are looking for home remedies for gas and other symptoms that accompany an upset stomach, do not miss out on the fennel seeds. Fennel is a carminative (a formulation that helps reduce gas) herb and helps prevent bloating, indigestion, flatulencei It refers to the accumulation of gas in the stomach and its release through the anus, often caused by food intolerance or indigestion. , stomach ache, etc. Fenchone, a bioactive compound found in fennel seeds relaxes the lining of the digestive tract, which in turn, helps cleanse the colon. Fennel seeds are also responsible for stimulating the secretion of digestive juices and improve nutrient absorption (10). Toss in sliced fennel in your favorite salad, sandwich or stew. You can add fennel seeds to enhance the flavor of grilled chicken or fish, salads, and even in desserts.
9. Beetroot
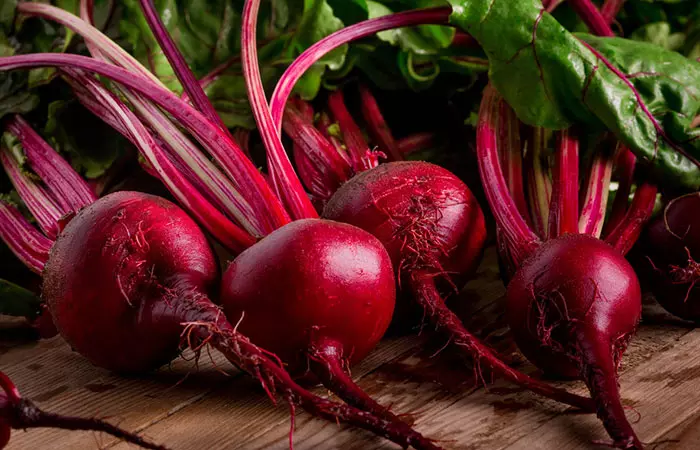

This plum red sweet vegetable has anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties that help prevent inflammatory disorders of the digestive system and also flush out toxins. Beetroots also stimulate the production of bile, which promotes digestion, and even the digestion of fats (11) (12). Toss beetroots into your salad, stew or bake beetroot chips.
10. Sweet Potato
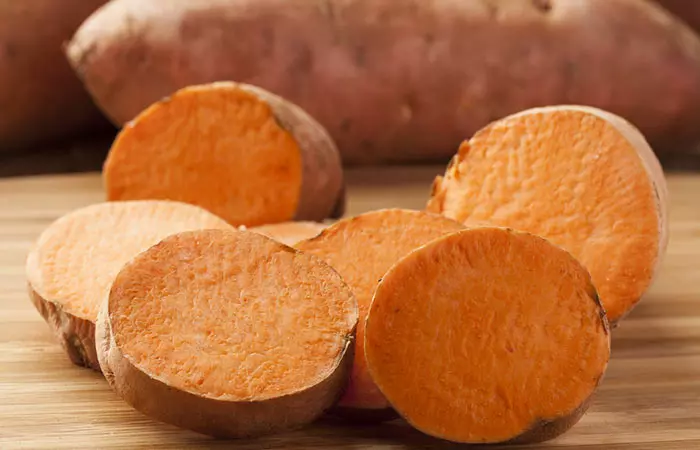

Sweet potatoes are rich in dietary fiber that aid proper bowel movement and nutrient absorption. They also stimulate the synthesis of cells in the gut that promote the activities of digestive enzymes in the colon (12). You can have mashed, baked or grilled sweet potato with olive oil, salt, and pepper. You can also substitute potatoes with sweet potato in curries.
11. Apple
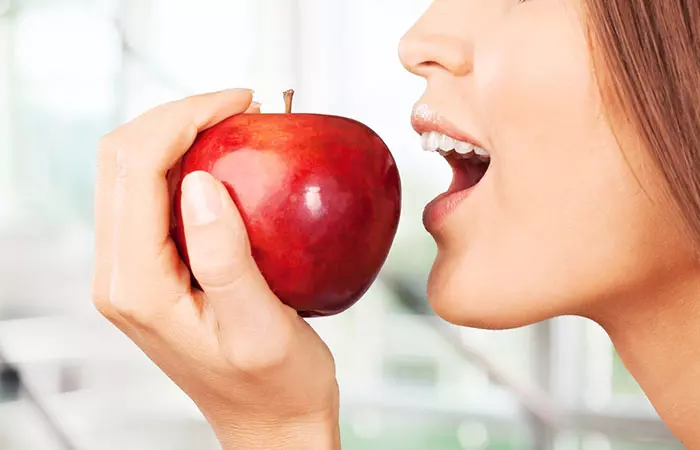

Apples are packed with vitamins, minerals, and dietary fiber. They also have an antioxidant property that helps reduce oxidative damage and inflammation in the digestive organs. The pectin present in apples is also believed to promote the growth of good gut bacteria, which also helps improve digestion (13) . Have apples as a snack, with breakfast cereal, in smoothies, as juice, etc. However, if you are suffering from IBS or IBD, ulcer, etc. peel the apple (and even cook) before eating.
12. Cucumber

Cucumbers are loaded with vitamins, minerals, antioxidants, and have anti-inflammatory properties. Due to the high fiber and water content, cucumbers help prevent constipation by softening the stool and aiding smooth bowel movements. Antioxidants also help prevent toxic buildup that can lead to indigestion and stomach infections (14). So, the next time you wonder how to get rid of indigestion and an upset stomach, have cucumbers for a snack or add them to your smoothies, juices, or salads.
13. Avocado

Avocado is one great food to consume if you are suffering from stomach inflammation. It helps to soothe the inflamed stomach and duodenum wall. Avocado also helps to change the microorganisms present in the gut and thereby helps treat colitis, autointoxication, and biliousness (15). Include avocado in your breakfast, in smoothies, and in salads to help heal your gut and improve digestion.
In case you have stomach issues, please consult your doctor first. As the latex in avocados can make some individuals to vomit.
14. Kimchi

Kimchi is a Korean fermented food, made of spiced cabbage or carrots. It is a great source of dietary fiber, iron, calcium, and vitamins A, B, and C. Since it is fermented, like yogurt, it also is rich in good beneficial bacteria . Good gut bacteria help in digestion by secreting enzymes that aid digestion (16). Have kimchi as a condiment with your grilled or baked chicken/fish, or add kimchi to your food to spice it up and bolster your gut health.
15. Prune

Prunes are rich in soluble and insoluble fiber. It acts as a laxative, which stimulates the peristaltic movement of the digestive tract and colon. Prunes also help reduce inflammation and boosts immunity (17). Have prune juice in the morning before breakfast or after lunch, it will be gentle on the stomach.
16. Broccoli

The high fiber in broccoli may help promote the feeling of fullness and contribute to a healthy digestive system. It may also increase the number of healthy gut bacteria and ease bowel movements (18). Additionally, it is rich in vitamins A, C, and K, potassium, calcium, and iron. Adding this vegetable to your diet may not only improve digestion but also benefit your bone health, improve cardiovascular function, regulate cholesterol, and boost the immune system (18). Add steamed or sauteed broccoli to your salads, soups, and quinoa dishes. You may even include it in your smoothies and pasta sauce.
So, these were the 16 foods to alleviate your digestive issues. But you should also know the foods that you need to avoid in order to have a better digestion. Here’s a list of those foods, take a look.
So, these were the 16 foods to alleviate your digestive issues. But you should also know the foods that you need to avoid in order to have a better digestion. Here’s a list of those foods, take a look.
Key Takeaways
- Yogurt is beneficial for the digestive system and may improve bowel movement.
- Papayas exhibit antimicrobial properties that can tackle constipation and bloating.
- Consuming ginger can help treat common stomach conditions, such as indigestion and nausea.
- Fishes like salmon and tuna are rich in omega-3-fatty acids that can tackle inflammation and support bowel movement.
11 Foods To Avoid Digestion Problems

1. Oily/Fatty Food
Completely avoid oily and spicy food when you are battling problems of the gut. These are also a big no if you are following a bland diet to relieve your diarrhea. Oily or fatty foods can either slow down the stomach emptying, leading to constipation and bloating or hasten the stomach emptying leading to diarrhea. Deep fried foods can lead to acidity and bloat.
2. Spicy Food
Spicy foods can irritate your digestive organs leading to stomach ache and discomfort while passing stool.
3. Processed food

Processed foods are a big no-no for you if you have digestive issues. Processed foods lack fiber and contain artificial sugar, artificial color, and too much of salt and preservatives. All these ingredients can cause inflammation and aggravate your digestion problems. Plus, without fiber, your digestive tract has to work extra hard to move the food through the tract – and this can lead to constipation.
4. Some Legumes
This is especially true with larger beans like kidney, garbanzo, lima, edamame, and soybeans – as they contain more starch and are difficult to digest. You can go with small legumes like lentils, mung beans, and split beans.
5. Adulterated Dairy

Yogurt is undoubtedly the most natural prebiotic food in its purest form. Unfortunately, we hear of cows being injected with antibiotics, hormones and fed GM corn. Moreover, pasteurization and processing remove all the healthy fats and beneficial vitamins in the milk. Plus, if you are lactose intolerant you should avoid dairy altogether. You can have organic dairy products, but I suggest you stay away from inorganic milk, cheese, butter, ghee, etc. for a while when you are battling digestive issues.
6. Alcohol
Stay away from the irresistible parties and free alcohol for a while to get your digestion back to normal. Alcohol causes dehydration that can lead to constipation and bloat. It is also toxic to the stomach and digestive tract and can change liver metabolism. Also, when your gut problems seem to have improved do not jump right into drinking too much alcohol. Avoid for a while, as alcohol is quite acidic and can again irritate your stomach lining. It can even aggravate GERD.
7. Caffeine

Caffeine is present in coffee, tea, chocolate, soft drinks, energy drinks, baked foods, and even ice cream. Caffeine stimulates the bowel movement, speeding up the stomach emptying. This can lead to diarrhea and stomach ache. So stay away from caffeine-containing foods till you get better.
8. Sugar
Consuming too much sugar or sugary foods can aggravate your digestive problems. That’s because sugar encourages the growth of bad bacteria in your gut. The bad bacteria can cause inflammation and weaken your immunity. So, avoid consuming sugar in beverages or packaged fruit and vegetable juices, doughnuts, pastries, cakes, etc. if you are fighting indigestion.
9. Aerated/Carbonated Drinks
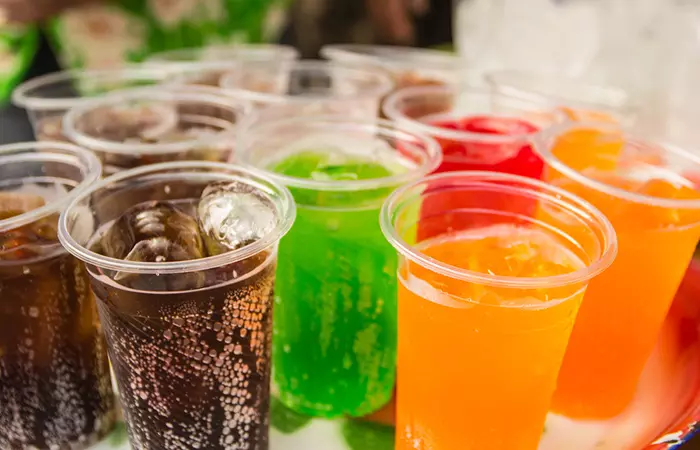

The gas bubbles in aerated or fizzy drinks can cause bloating and also irritate the stomach and digestive tract lining. Plus, these drinks contain a humongous amount of sugar that can also worsen your digestion problems. Also, the carbonationi The chemical reaction of carbon dioxide to produce carbonic acid, carbonates, and bicarbonates is called carbonation. causes electrolyte imbalance – and this can dehydrate the body and interfere with the healing process. So, avoid consuming soda or any fizzy drinks for a while till your digestive organs heal and start functioning normally.
10. Berries
Berries are nutritious but avoid them if you are suffering from diverticulitisi A gastrointestinal disease. Some of its symptoms include abdominal pain, nausea, fever, diarrhea, and constipation. , ulcer, or IBS and IBD. The fiber and the small seeds (such as in strawberries) can scrape the lining of the stomach and colon thereby causing inflammation, irritation, and bleeding. Therefore, avoid consuming berries or foods that may contain berries like cakes, pastries, jams, etc. for a while.
11. Nuts & Seeds
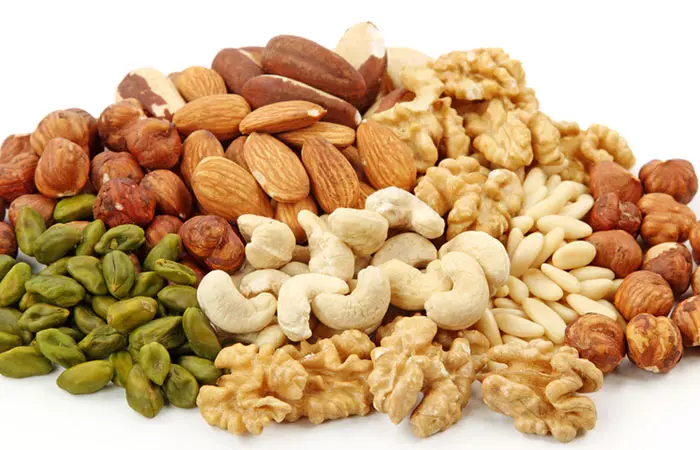

Nuts and seeds are not an ideal option if you have an upset stomach or have any other digestion problems. Roughage in nuts can aggravate your digestion problems by irritating the walls of the stomach.
According to this statistic, gastrointestinal issues are more common among women than men. The graph below shows the distribution of gastrointestinal conditions by gender across select countries. 61 percent of the adult population diagnosed with gastrointestinal issues in the US were women.

Gastrointestinal Conditions In Selected Countries
Source: StatistaSo stay away from the otherwise healthy nuts till you get better. You could eventually reintroduce nuts into your diet.
Infographic: Digestive Problems: Symptoms And Causes
The number of people experiencing digestive issues is constantly on the rise, courtesy unhealthy food habits and faulty lifestyle practices. Unfortunately, not many individuals are aware of the underlying causes that could turn severe if ignored. The following infographic sheds light on some of the common causes of your digestive woes and the precautions to take. Keep scrolling.
Some thing wrong with infographic shortcode. please verify shortcode syntax
When you consume too much food or don’t follow a balanced diet, you’re likely to suffer from gastrointestinal issues like indigestion, gas, bloating, or heartburn. But these issues can be easily corrected by consuming foods that promote gut function. Some of the best foods for digestion are whole grains, yogurt, ginger, and sweet potatoes. These are rich in nutrients like dietary fiber and help stimulate bowel movements. They also have beneficial bioactive compounds that relieve common gastrointestinal problems. In addition, you should also avoid foods high in sugar and other spicy and oily foods as they also may aggravate gastrointestinal problems.
Frequently Asked Questions
Are easy-to-digest foods suitable for everyone?
Yes, easy-to-digest foods are generally suitable for most people, especially those with digestive issues. However, individual needs vary, and it is important to consult a healthcare provider for personalized advice based on specific health conditions.
How can I incorporate easy-to-digest foods into my diet?
You can start by including options like bananas, white rice, and oatmeal in your meals. Cook foods well, avoid heavy seasonings, and eat smaller, more frequent meals to help with digestion. Adjust your diet gradually based on how your body responds.
What causes poor digestion?
An unhealthy and sedentary lifestyle, poor nutrition, food allergies, an underlying medical condition, and stress are the major triggers of poor digestion.
Are eggs good for digestion?
Yes, eggs are good for digestion. They are packed with many nutrients and are easier to digest compared to other high-protein foods like soy, legumes, and meat.
What food digests fastest?
Foods high in fiber, like vegetables and fruits, are digested faster compared to meat, fish, and other protein-rich foods.
Discover the 10 best foods that are gentle on your digestive system. From soothing soups to nourishing fruits, this video highlights easy-to-digest options for optimal digestive health.
Personal Experience: Source
StyleCraze's articles are interwoven with authentic personal narratives that provide depth and resonance to our content. Below are the sources of the personal accounts referenced in this article.
i. MY EXPERIENCE ON BANANA ISLAND FOR 5 DAYS!https://2joyfulfruitlovers.wordpress.com/2015/03/16/my-experience-on-banana-island-for-5-days/
References
Articles on StyleCraze are backed by verified information from peer-reviewed and academic research papers, reputed organizations, research institutions, and medical associations to ensure accuracy and relevance. Read our editorial policy to learn more.
- Yogurt and gut function
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15277142/ - Traditional and Medicinal Uses of Carica papaya
https://www.plantsjournal.com/archives/?year=2013&vol=1&issue=1&part=A&ArticleId=5 - Papaya preparation (Caricol®) in digestive disorders
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23524622/ - Putting the Whole Grain Puzzle Together: Health Benefits Associated with Whole Grains—Summary of American Society for Nutrition 2010 Satellite Symposium
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3078018/ - Banana Resistant Starch and Its Effects on Constipation Model Mice
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4126267/ - Inflammatory bowel disease: can omega-3 fatty acids really help?
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4700845/ - The Amazing and Mighty Ginger
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK92775/ - Effects of ginger on gastric emptying and motility in healthy humans
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/18403946/ - Cumin Extract for Symptom Control in Patients with Irritable Bowel Syndrome: A Case Series
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3990147/ - Effects of dietary fennel (Foeniculum vulgare Mill.) seed powder supplementation on growth performance, nutrient digestibility, small intestinal morphology, and carcass traits of broilers
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7847707/ - The Potential Benefits of Red Beetroot Supplementation in Health and Disease
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4425174/ - Positive effects of dietary fiber from sweet potato [Ipomoea batatas (L.) Lam.] peels by different extraction methods on human fecal microbiota in vitro fermentation
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC9490365/ - Apple-Derived Pectin Modulates Gut Microbiota, Improves Gut Barrier Function, and Attenuates Metabolic Endotoxemia in Rats with Diet-Induced Obesity
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4808856/ - Antioxidant Supplements and Gastrointestinal Diseases: A Critical Appraisal
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5588418/ - Avocado Consumption Alters Gastrointestinal Bacteria Abundance and Microbial Metabolite Concentrations among Adults with Overweight or Obesity: A Randomized Controlled Trial
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8030699/ - Gut Microbiome: Profound Implications for Diet and Disease
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6682904/ - Rationale and study design of Randomized Controlled Trial of Dietary Supplementation with prune (dried plums) on bone density, geometry, and estimated bone strength in postmenopausal women: The Prune study
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC9163423/ - Broccoli: A Multi-Faceted Vegetable for Health: An In-Depth Review of Its Nutritional Attributes, Antimicrobial Abilities, and Anti-inflammatory Properties
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC10376324/
Read full bio of Dr. Millie Lytle
Read full bio of Ravi Teja Tadimalla
Read full bio of Aparna Mallampalli


























Community Experiences
Join the conversation and become a part of our empowering community! Share your stories, experiences, and insights to connect with other beauty, lifestyle, and health enthusiasts.