How To Increase Melanin In Skin Naturally
Learn the importance of melanin and what impacts its production, like age.

Image: Shutterstock
Melanin is the pigment that imparts color to your skin, hair, and eyes (1). In addition, according to the American Cancer Society, melanin protects the skin from UV damage and skin cancer (2). Thus, this is the exact reason why many people seek to boost their melanin levels and give their skin some much-needed sun protection. But, do you know how to increase melanin and protect your skin naturally? Is that even possible? Understanding melanin is key to improving skin health and appearance. So, we are here to answer all your questions related to it. In this article, we cover natural methods and dietary tips to effectively boost melanin for healthier skin. Keep reading to know more!
In This Article
Why Is Melanin Important For Your Skin?
Melanin-producing cells (melanocytes) are present in the basal layer of the skin. Structural proteins of melanosomes (organelle where melanin is produced and stored), enzymes that help in melanin synthesis, and proteins that help transport and distribute melanosomes contribute to melanin production (3). Genetic influence, hormonal changes, age, inflammation, and UV exposure also affect the production of melanin (4).
Melanin production can reduce if any of these factors is affected – and this can lead to hypopigmentation disorders such as vitiligo, albinismi A group of hereditary disorders caused by gene mutations where there is little or no melanin production. , phenylketonuriai An inherited condition that causes amino acid buildup in the body that may lead to brain damage and intellectual disabilities. , Chediak–Higashi syndromei A rare, inherited immune disorder characterized by less pigment in the skin and eyes and a tendency to bleed and bruise easily. , Griscelli syndromei A hereditary disorder characterized by light-colored skin and a silvery-gray sheen of hair, which starts in infancy. , Waardenburg syndromei A group of genetic issues characterized by hearing loss and color change in the hair, eyes, and skin. , and microangiopathy (3), (5).
 Quick Tip
Quick TipMoreover, research shows that melanin is UV-absorbent and has antioxidant properties. Also, people with lighter skin color are at a higher risk of skin cancer due to repeated exposure to UV rays as compared to people with darker skin color (6). Thankfully, there are natural ways you can increase melanin content in your skin. Scroll down to the next section to find out how to increase melanin naturally.
Key Takeaways
- Genetics, hormonal changes, and UV exposure reduce melanin production, leading to hypopigmentation disorders.
- Since melanin is UV-absorbent, people with dark skin are at a lower risk of getting skin cancer compared to individuals with lighter skin.
- You can increase your melanin level by consuming more vitamins B9, B12, C, D, and E, amino acids, and antioxidants.
- Tanning beds, sunbathing, and melanin tablets are alternative ways to increase melanin.
How To Increase Melanin In Skin Naturally?
Dietary changes can help increase melanogenesis or melanin production naturally. Here’s what you need to consume.
- Vitamin D
Low levels of vitamin D cause vitiligo, a skin condition triggered due to the low production of melanin (7). Hence, it is important to consume vitamin D-rich foods on a regular basis. To include vitamin D in your diet, consume whole eggs (not exceeding 5 per week), sardines, mackerel, red meat, organ meat, and vitamin D-fortified milk, cereals, or juices. However, it is also recommended to have 10 minutes of sun exposure in the morning before 8 AM every day. The sun’s UV-B rays convert inactive vitamin D3 to active vitamin D3, increasing melanin production (8). There are also various other health benefits of sunlight such as losing weight and reducing the risk of diabetes.
- Vitamin E
Vitamin E, an antioxidant, helps improve skin pigmentation without UV exposure (9). Consuming vitamin E-rich foods or taking vitamin E supplements may also help to a great extent. Consume avocados, sunflower seeds, pumpkin seeds, flax seeds, almonds, peanuts, peanut butter, olive oil, and avocado oil.
- Vitamin B12
Vitamin B12 is an essential nutrient that helps keep the cells, DNA, and nerves healthy (10). To increase vitamin B12, consume fish, red meat, milk, eggs, liver, and other foods fortified with vitamin B12. You can also take vitamin B12 supplements after talking to your doctor.
- Vitamin C
A study with vitamin C supplementation found a significant increase in melanin production (9). Vitamin C is a potent antioxidant found in most citrus fruits and a few vegetables. Consume orange, sweet lime, tangerine, lime, lemon, grapefruit, berries, kiwi, guava, papaya, broccoli, kale, and tomatoes to keep your skin protected and to naturally induce melanin production.
- Folate
Folate or folic acid (vitamin B9) is essential for good reproductive health. People with low melanin may have lower levels of folate. Folate also protects the skin from UV-A radiation and skin cancer (11). Increase your folate intake by consuming leafy green vegetables, broccoli, liver, kidney beans, garbanzo beans, and foods fortified with folic acid.
- Amino Acids
Tyrosine and phenylalanine are two amino acids required for melanin production (12), (13). Deficiency in these two amino acids can lead to hypopigmentation disorders. A study conducted on animals showed that different concentrations of tyrosine and phenylalanine helped increase melanin levels (14). However, a separate study showed that phenylalanine may not be a precursor for melanin synthesis in mammals (15). Therefore, it is safe to suggest that consuming foods rich in tyrosinase, like yogurt, milk, cheese, cottage cheese, pumpkin seeds, sesame seeds, banana, avocado, fish, chicken, and turkey, may help in the natural production of melanin.
- Antioxidants
Antioxidants like carotenoids help protect the skin and improve melanin synthesis. Two such carotenoids are beta carotene and lycopene. In a study, supplementation with beta carotene and lycopene increased melanin concentration in the skin (9). Consume foods like tomato, carrot, sweet potato, kale, spinach, guava, watermelon, apricot, cantaloupe, and grapefruit to increase beta carotene and lycopene levels in your body.
 Quick Tip
Quick TipThese are the nutrients that can help you naturally increase melanin in the skin. But, apart from these natural remedies, there are a few other ways that can help. Swipe up to find out.
Other Ways To Increase Melanin In Skin
- Tanning Bed
You can use a horizontal or vertical tanning bed to expose your body to UV rays that will help increase melanin in your skin. This artificial tanning method requires you to wear protective eyewear. Also, it is best to talk to your doctor first before option for this method – especially if you have an existing medical or skin condition.
Morgen Raeh, a YouTuber, shared her experience of using a tanning bed for a week. She said, “I definitely have noticed results. It’s a super even tan from head to toe, and as long as you take it really slow, you’ll be fine (i).”
- Sunbathing
Sunbathing is quite popular and practiced by people who want to get a tan. However, sunbathing post 10 AM can be dangerous as the sun’s harmful UV-A rays can lead to severe health issues and even skin cancer. It is ideal to sunbathe early in the morning or late in the afternoon when the sun’s rays are not as harsh. However, cases of sunburn have been reported even during these times. So, do not forget to apply generous amounts of sunscreen with a minimum SPF 30 to keep your skin protected from the UV-A rays.
- Melanin Pills And Hormones
There are melanin pills and hormones available to help induce hyperpigmentation or increase melanin levels in your skin. You need a prescription to use these – it is best to talk to a licensed dermatologist.
These are the other ways you can increase melanin levels in your skin. However, if you have medically diagnosed hypopigmentation disorder, these may not work for you. You must seek a dermatologist’s expert opinion to increase melanin levels in your skin.
 Quick Tip
Quick TipYour doctor may also suggest professional treatments for melanin deficiency. Check out the next section to learn more about it.
Clinical Treatment For Melanin Deficiency
Your doctor may recommend photochemotherapy for the treatment of melanin deficiency. It induces repigmentation by using ultraviolet light and a chemical called psoralen that makes the skin temporarily sensitive to ultraviolet light. It is also known as PUVA or ultraviolet radiation therapy and is used alone or with immunosuppressants like azathioprine (17). Studies suggest that this treatment option delivers moderately good results. However, another UV treatment called the narrow-band ultraviolet B therapy, uses shortwave UV radiation and may be slightly better as it causes fewer side effects (17). Consult your doctor to determine if you require any of these procedures.
Note: All of the information given in this article is based on scientific research, anecdotal evidence, and expert opinion from nutritionists and dermatologists. If you have any skin conditions, health issues, or known allergies, it is recommended that you speak to a doctor before trying any of the above suggestions. The suggestions listed in the article should not be taken as medical advice.
Infographic: What Are The Types Of Melanin?
Melanin is a pigment-producing substance produced by melanocytes on the skin’s surface. Each person’s skin contains a varied quantity of melanin. The number of melanocytes and the ratio of different types of melanin in your skin determine your skin color. The amount of melanin in the skin can be reduced or increased by certain circumstances and environmental factors. To learn more about the three types of melanin, check out the infographic below. Illustration: StyleCraze Design Team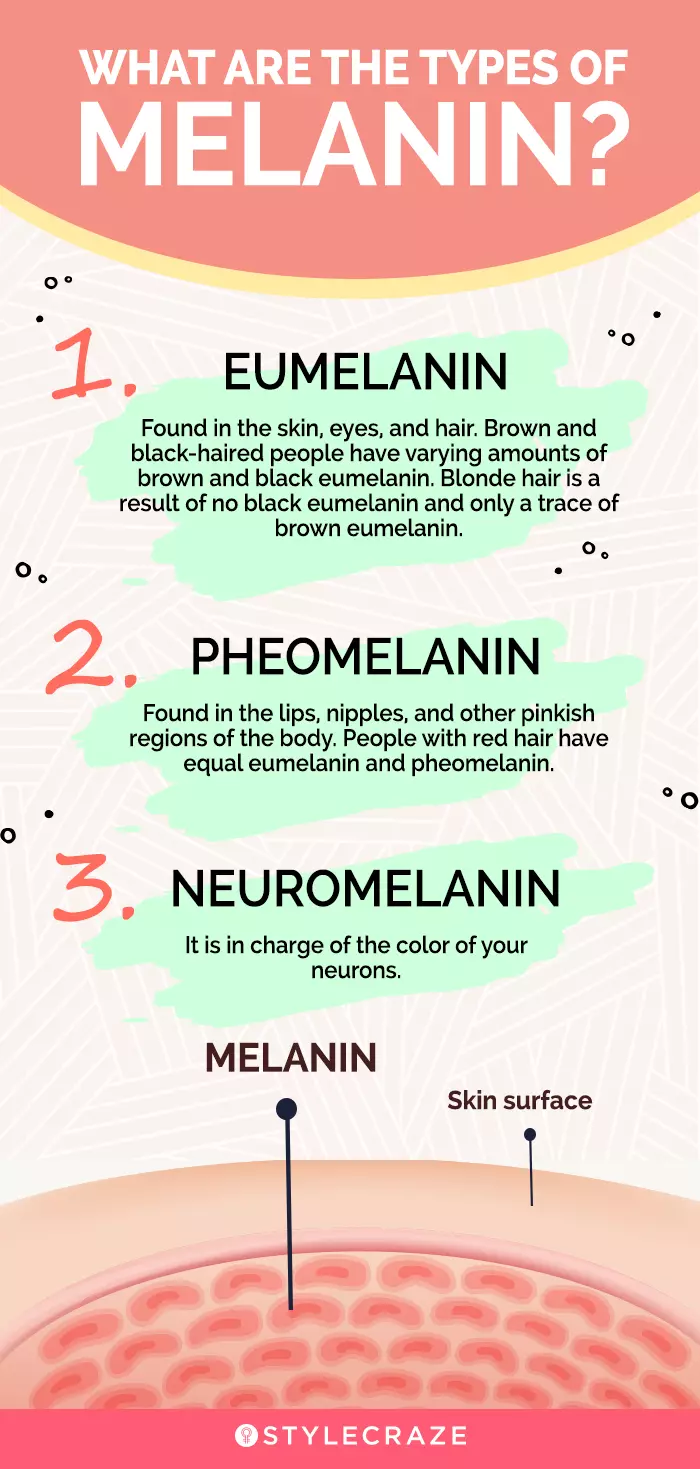
Melanin is a pigment that imparts color to the hair, skin, and eyes. Besides, it also protects the skin from harmful UV rays and helps minimize the risk of skin cancer. Several factors such as genetics, age, hormones, ethnicity, and UV exposure play a part in determining the melanin content of your skin. So, to protect your skin naturally, you can increase your melanin levels by consuming foods rich in vitamins, folates, amino acids, and antioxidants. Consult your dermatologist and plan your diet and skin care accordingly to increase the melanin levels. You can also try other options like a tanning bed, sunbathing, and melanin pills to help increase melanin. Remember, while there are many natural remedies on how to increase melanin, you should consult a health care provider for personalized advice to support your skin’s natural defense.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can amla increase melanin?
No, amla helps to reduce melanin production in the body (18).
Does melanin make the skin dark?
Yes, the more melanin your body produces, the darker your skin becomes.
How long does it take to see results when trying to increase melanin?
Skin cells produce melanin every 48 hours. An immediate response of skin darkening can be observed within 1-2 hours in the sun, and this may fade in due time. UV radiation is the best promoter of melanin synthesis, and it may require several sessions to get the desired pigmentation.
Can melanin production be increased in specific body areas, such as the face or hands?
Cosmetic procedures such as a chemical peel and UV or laser treatment can regulate melanin production in specific areas in the body.
Does aging affect melanin production?
Yes, the amount of melanin in hair reduces over the years, causing your locks to turn gray as you age (18).
Can I reverse or decrease melanin production if I want lighter skin?
The genetic constitution determines melanin formation by the skin. It is not possible to reduce overall melanin production, but chemical peels and laser therapy can help lighten hyperpigmented skin.
Are there any specific vitamins or minerals that support melanin production?
Vitamin D, B9, and B12 are major contributors to the skin’s melanin production capacity (19). Tyrosine, copper, and vitamin C also play a major role in melanin production, while minerals such as calcium, zinc, and iron may increase melanin pigmentation in animals (20).
Can regular exercise or physical activity boost melanin production?
Physical activity can increase the heat level of the skin and thus cause increased melanin production. Sun spots can also be caused due to increased body heat (21).
Is it possible to maintain a balanced and healthy level of melanin production?
It can be maintained by using a sun protection SPF sunscreen, following a balanced diet, staying hydrated, getting proper sleep, and managing stress.
Are there any specific precautions or guidelines to follow when trying to increase melanin?
Sun exposure, tanning beds, and supplements can help increase melanin. However, avoid excessive sun exposure as it can cause sunburns. Consult with a healthcare professional for guidance.
Illustration: How To Increase Melanin In Skin Naturally

Image: Stable Diffusion/StyleCraze Design Team
Take a look at this informative video that teaches you how to enhance the melanin content of your skin naturally. Discover valuable tips and tricks to stimulate your body’s melanin production. Check it out now!
Personal Experience: Source
StyleCraze's articles are interwoven with authentic personal narratives that provide depth and resonance to our content. Below are the sources of the personal accounts referenced in this article.
i. my tanning bed experience || + weekly updateshttps://www.youtube.com/watch?v=-oic3zyeKeE
References
Articles on StyleCraze are backed by verified information from peer-reviewed and academic research papers, reputed organizations, research institutions, and medical associations to ensure accuracy and relevance. Read our editorial policy to learn more.
- Biochemistry Melanin
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK459156/ - Are Some People More Likely to Get Skin Damage from the Sun?
https://www.cancer.org/cancer/risk-prevention/sun-and-uv/sun-damage.html - Melanocytes and Their Diseases
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3996377/ - Signaling Pathways in Melanogenesis
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4964517/ - Lower melanin content in the skin of type 1 diabetic patients and the risk of microangiopathy
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24623500/ - The Protective Role of Melanin Against UV Damage in Human Skin
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2671032/ - The role of vitamin D in melanogenesis with an emphasis on vitiligo
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24177606/ - Sunlight and Vitamin D
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3897598/ - Evidence for antioxidant nutrients-induced pigmentation in skin: results of a clinical trial
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/9285071/ - Vitamin B12
https://ods.od.nih.gov/factsheets/VitaminB12-Consumer/
- Folate in Skin Cancer Prevention
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3795437/ - Skin Under the Sun: When Melanin Pigment Meets Vitamin D
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4272394/ - Aminoacids–precursors of melanin synthesis in hamster melanoma
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/6511810/ - Increased dietary intake of tyrosine upregulates melanin deposition in the hair of adult black-coated dogs
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30564763/ - Mammalian melanocytes do not use phenylalanine for melanin synthesis
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/556959/ - Phyllanthus emblica L. (amla) branch: A safe and effective ingredient against skin aging
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8427479/ - Photochemotherapy (PUVA) in psoriasis and vitiligo
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25382505/ - Melanin and lipofuscin as hallmarks of skin aging
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5420599 - “Skin Color” in: The Wiley Blackwell Encyclopedia of Race Ethnicity and Nationalism Online
https://sites.hampshire.edu/agoodman/files/2017/04/Skin_Color.pdf - Dietary mineral content influences the expression of melanin-based ornamental coloration
https://academic.oup.com/beheco/article/18/1/137/208981 - Skin Color Cues to Human Health: Carotenoids Aerobic Fitness and Body Fat
ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7078114/
Read full bio of Dr. Sravya Tipirneni
Read full bio of Arshiya Syeda
Read full bio of Ramona Sinha
Read full bio of Monomita Chakraborty


























Community Experiences
Join the conversation and become a part of our empowering community! Share your stories, experiences, and insights to connect with other beauty, lifestyle, and health enthusiasts.