What Is Sun Damaged Skin? How To Deal With It?
A guide to eliminating the signs of sun damage with effective skin care ingredients.
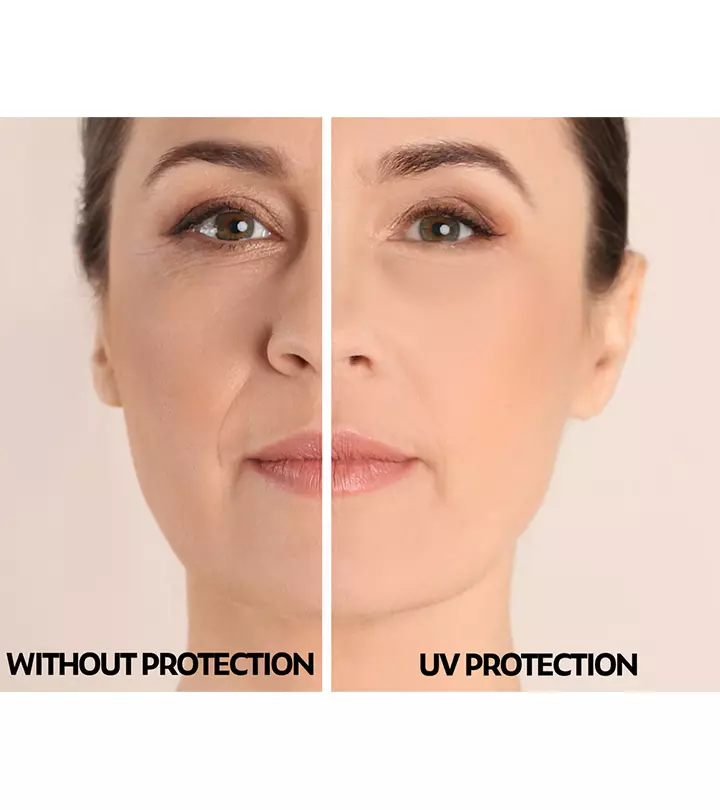

Image: Shutterstock
There is an inexplicable joy in being outdoors on a nice sunny day! Lying on the beach, soaking up the sun, sipping on an ice-cold drink, feels just perfect. But, all that sun exposure may be harmful to your skin as you age and may cause a phenomenon called sun-damaged skin. What exactly is it? Is there a way to prevent it? Keep reading this article and you will find out.
In This Article
What Is Sun-damaged Skin?
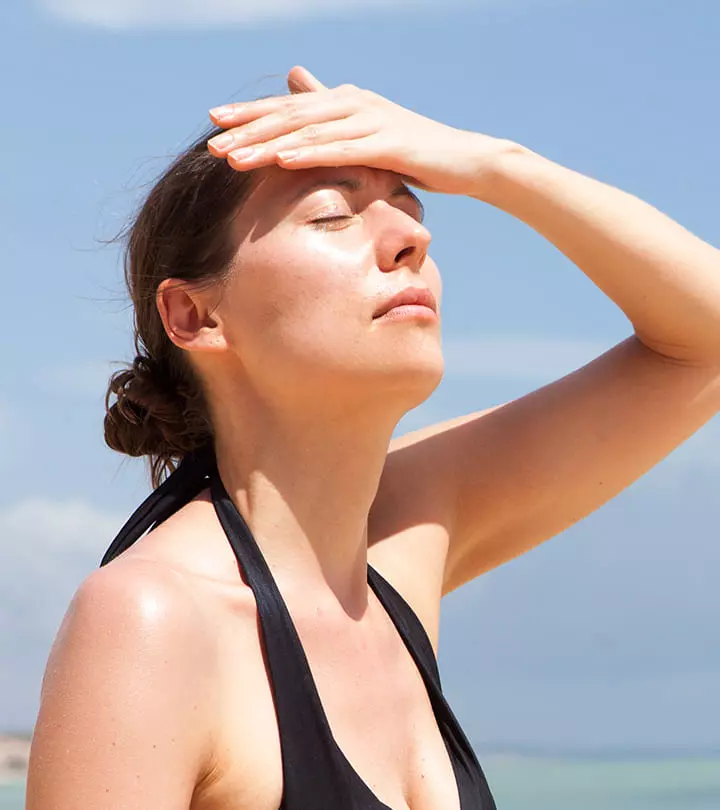
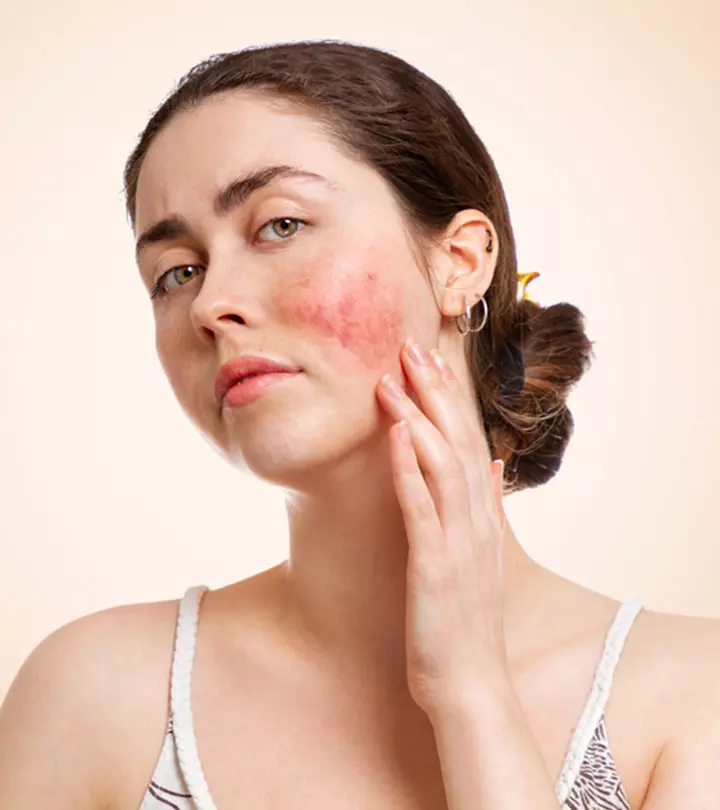
Sun-damaged skin or photoaging is caused due to prolonged exposure of your skin to the harmful UV radiation emitted by the sun. Areas of your body such as the face, arms, legs, and neck are most likely to be affected as they are exposed the most (1).
In most cases, 90% of photoaging is due to UV exposure. However, some studies suggest, UV exposure combined with visible light (VL) emitted from LED devices and other electronic devices might also contribute to photoaging (2).
So, how do you find out if your skin is sun-damaged? Are there any symptoms to look out for? Read the next section to know.
Key Takeaways
- Excess sun exposure and lack of proper sun protection may lead to signs of sun-damaged skin like wrinkles, freckles, hyperpigmentation, or loss of skin elasticity.
- The face, arms, neck, and legs are commonly affected by photoaging.
- Niacinamide, azelaic acid, vitamin C, and retinoids based skin care products can help reduce the effects of sun damage, but it needs some time and constant effort before you can see any visible changes.
- Keeping your skin protected from the harmful UV rays with appropriate sunscreen and clothing can help prevent further sun damage.
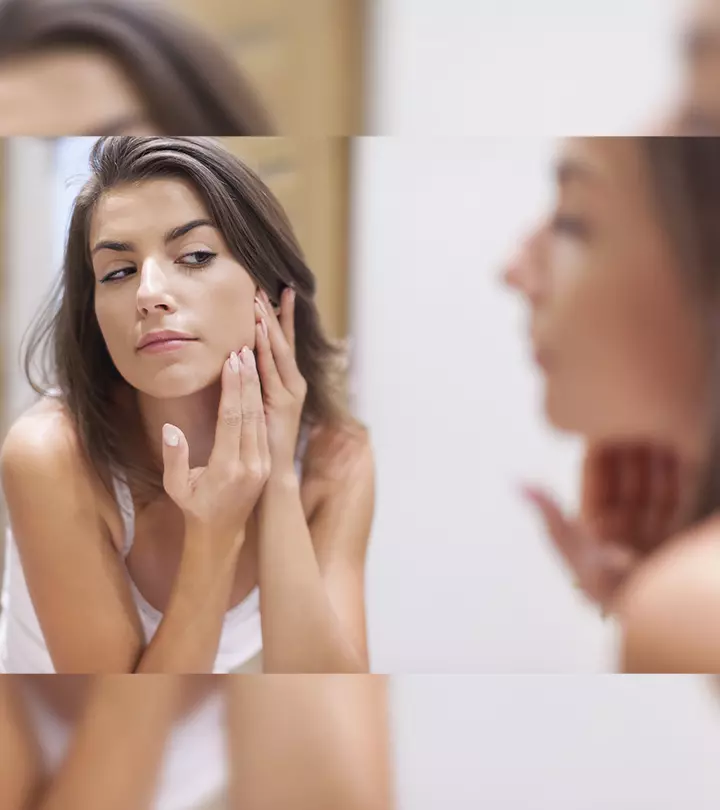
Symptoms Of Sun-damaged Skin
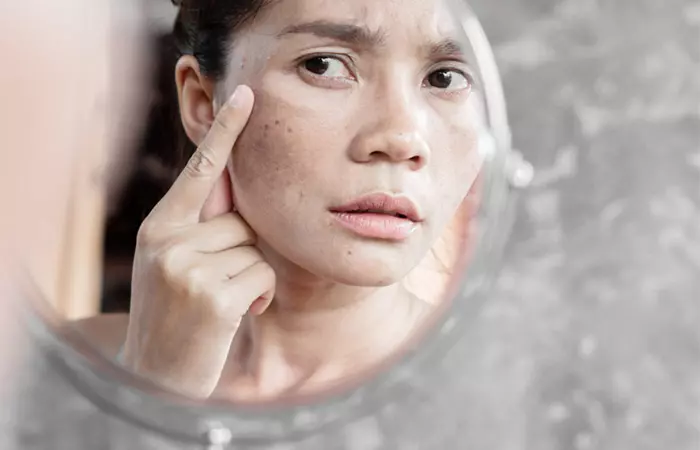

Unlike the chronological aging of your skin that is caused by old age and genetic conditions, photoaging is caused by the severity of UV exposure. Some of the most common symptoms of sun-damaged skin are (1):
- Wrinkling of skin
- Pigmentation of the skin that causes sunspots and liver spots to appear
- Freckling of skin
- Sun rashes on skin
- Dryness and roughness of the skin
- Loss of skin elasticity
If you notice any of these symptoms, there is a probability that your skin is sun-damaged.
Carole Rosner, a blogger, shares how she noticed a freckle on her lip at the end of the day that was not there in the morning. She recalled that she didn’t apply SPF, and it was due to sun damage. She notes, “And hopefully, in time, I’ll come to acknowledge that this new mark is maybe a blessing in disguise because I will NEVER leave the house un-SPF’d ever again (i).”
So if you often wonder “Why is sunscreen important?”, the various symptoms of sun damage listed above are your answer.
But who is more prone to sunburn or sun-damaged skin? Find out in the next section.
Who Is Prone To Photoaging?

Research suggests that anyone who is exposed to the sun is prone to photoaging (3). However, a study aimed at exploring if any particular demographic is more prone to sun damage found something interesting. It revealed that people with fair skin, especially fair-skinned men are more likely to experience severe photoaging of the skin (4).
 Quick Tip
Quick TipHaving said that, if your skin is sun-damaged, what can you do to reverse it? Or is it even reversible? Let’s find out.
How To Reverse Sun Damaged Skin

When UV rays damage the skin, they can alter your DNA and cause melanoma (a type of skin cancer) which is irreversible (5). Reversing UV damage on the skin is not easy, it requires a lot of time, patience, and use of specific skincare products. It might or might not work for most people. Here are a few products that you can try and use to reverse sun-damaged skin.
- Niacinamide
Research suggests that topical application of niacinamide may help in reversing the effects of sun damage on the skin. It may help remove fine lines and wrinkles that are caused by photoaging (6). Niacin, a type of niacinamide, is readily available as an ingredient in certain serums and creams that can be easily incorporated into your skincare routine.
- Azelaic Acid
Though azelaic acid is commonly used to treat acne, some research suggests that it may also help reverse photoaging of the skin (7). Studies on mice suggest that azelaic acid in concentrated form might be able to inhibit melanoma cells and reduce pigmentation caused by them (8).
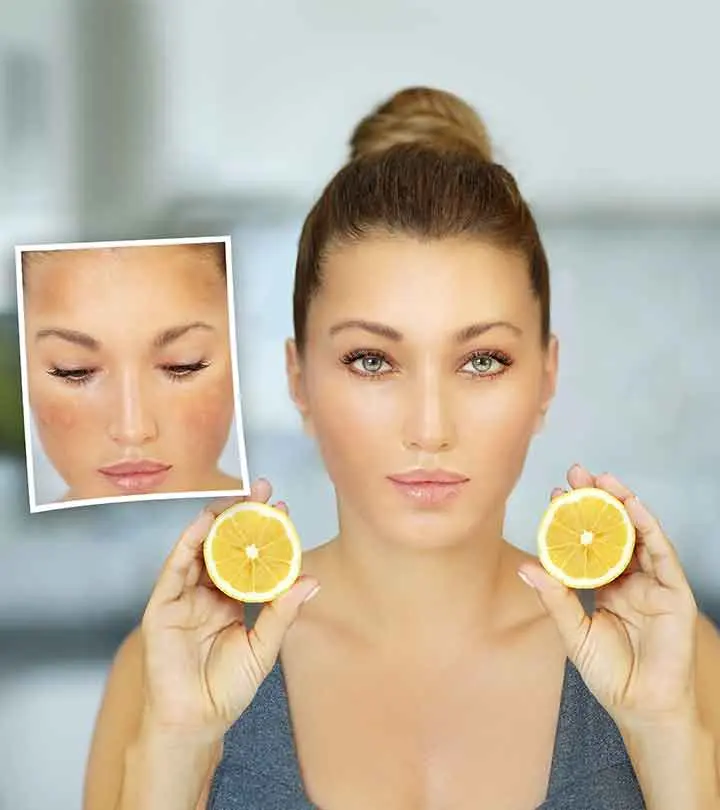
- Vitamin C
Studies suggest that the topical application of vitamin C-based skincare products might be able to reduce and prevent your skin from photoaging. Vitamin C is also known for its photoprotective, antioxidative, and anti-aging properties. It can also help improve collagen production and make your skin look younger (9).
- Alpha Hydroxy Acids (AHAs)
Research indicates that AHAs might help increase the thickness of your epidermis and make it less susceptible to photoaging and potentially reverse its effects (10). Using sunscreens and creams that contain AHAs or glycolic acid can be added to your skincare routine to help reverse the effects of photoaging.
- Retinoids
Skincare products that contain retinoids may help reverse photoaging of the skin. Research suggests that they may be able to reduce pigmentation that causes dark spots and age spots. Among the various retinoids, tretinoin is considered to be most potent in reversing the symptoms of photoaging (11).
If these topical solutions do not work, you can try some professional treatments. Learn more about them in the next section.
Professional Treatment Options For Sun-Damaged Skin
Here are some medical treatments that your dermatologist may recommend to treat the symptoms of sun-damaged skin:
- Laser Therapy: It uses light of different wavelengths to target deeper layers of the skin. This helps improve texture, reduce wrinkles, and lighten sunspots (12).
- Microneedling: It uses a device with multiple tiny needles to create controlled micro-injuries in the skin. This helps promote collagen and elastin production to improve the appearance of symptoms like fine lines, wrinkles, and pigmentation (13).
- Chemical Peels: These are chemical solutions that are applied directly to the skin to exfoliate the outer layers. They may help improve uneven skin texture that may occur due to sun exposure (14).
Reversing sun-damaged skin must be your last resort, preventing sun damage or photoaging should be your primary focus. After all, prevention is better than cure and is cost-effective as well. Let us find out how you can prevent your skin from being sun-damaged.
How To Protect Your Skin From Sun Damage

Protecting your skin from sun damage is easy. Follow these simple tips and you should be good to go.
1. Using sunscreen every day, regardless of the weather outside is crucial in protecting your skin from sun damage (15). Apply it 15-30 minutes before you head outside.
2. Choose a sunscreen that provides protection against both UVA and UVB rays and is at least SPF-30.
3. If you have an infant at home, it’s best to keep them away from harsh sunlight as they have very sensitive skin.
4. Try and reduce the amount of time you spend out in the sun. If possible, avoid sun exposure between 10 a.m. to 4 p.m, as UV radiations are the most intense during this time.
5. Wearing long-sleeved shirts and trousers minimizes the amount of skin exposure to the sun. Also wearing dark-colored clothes may help in blocking the harmful rays of the sun. Research suggests that colors like navy blue, black, and dark red absorb more UV rays and offer better protection (16). If possible try and use UV protective clothes for better effect.
6. For the head and neck areas, you could use scarves, or hats to block the sunlight. You could also use photochromic sunglasses or ones with UV protective lenses.
7. You should regularly inspect your skin for any unusual spots or changes. Visit a dermatologist for them, as early detection of skin damage is key for successful treatment.
Try these simple tips and you might be safe from the harmful UV rays that damage your skin. However, following these tips every time may not be feasible for all. Certain professions that require you to be out in the sun for long hours, inevitably increase the risk of sun-damaged skin.
 Quick Tip
Quick TipIn the next section, let us find out when you require medical assistance for sun-damaged skin.
When To See A Doctor
Minor symptoms of photoaging like dryness of skin, fine lines, and wrinkles would not require medical assistance. However, in some of the following cases, you will need to see a doctor or a dermatologist.
- Actinic Keratosis
This is a common skin condition that is caused by prolonged exposure to UV rays, which may develop into squamous cell carcinoma (a type of skin cancer) and other skin issues. These appear as rough, scaly, and bumpy patches near your arms, hands, ears, and neck (17). The treatment for this condition will vary from person to person.
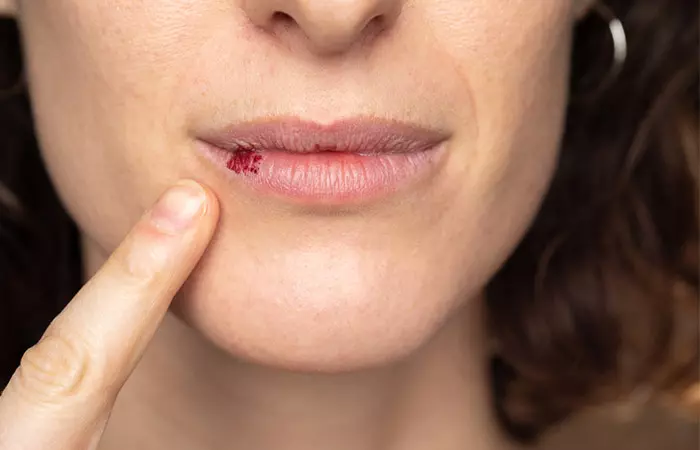
- Actinic Cheilitis
Similar to actinic keratosis, this skin condition is also caused by exposure to UV rays. It is also known as “sailor’s lip” and commonly occurs on the lower lip. This is considered to be a high-risk form of skin cancer and should be diagnosed at the earliest to manage and treat it better (18).
- Poikiloderma Of Civatte
This is another skin condition that is caused by prolonged UV exposure that causes lesions to appear on the skin around the neck area. The affected area feels itchy and may also cause a burning sensation (19). This condition can be treated with a pulse dye laser.
In conclusion, sun-damaged skin or photoaging is caused due to prolonged exposure to UV rays. As a result of photoaging, the appearance of sunspots on the skin, along with freckles, fine lines is common. Sun-damaged skin is unavoidable and inevitable as anyone who is exposed to sunlight is prone to photoaging of the skin. However, you can reduce the signs of photoaging by applying sunscreen, wearing long-sleeved clothes, and avoiding the sun between 10 a.m. to 4 p.m. Excessive sun exposure may cause skin issues like actinic keratosis and actinic cheilitis which might further develop into skin cancer. It is essential to get yourself examined by a doctor or dermatologist in the event of such skin conditions.
Frequently Asked Questions
How long does it take for skin to heal from sun damage?
Mild sun damage can last for 3-5 days. Severe sun damage can last for longer than a week, and it must be medically treated.
Will a chemical peel remove sun damage?
Yes. A chemical peel can help in treating sun damaged skin by gently removing the outer damaged layer of skin to reveal the smoother, new skin underneath.
Is apple cider vinegar good for sun damaged skin?
No. ACV has many anti-inflammatory properties and is an amazing exfoliator, but it can cause chemical burns when not used properly. Moreover, good exfoliators have to irritate the skin to an extent to help remove dead skin cells. Sun damaged skin is delicate and can do without the mistreatment. ACV can potentially make the process worse and more painful.
Unlock the secrets to repairing sun-damaged skin and reversing the signs of aging in this insightful video. Check it out to explore effective strategies and skincare tips to restore youthfulness and achieve a radiant complexion.
Personal Experience: Source
StyleCraze's articles are interwoven with authentic personal narratives that provide depth and resonance to our content. Below are the sources of the personal accounts referenced in this article.
i. The Frecklehttps://medium.com/heart-soul-pen/the-freckle-896879f0f2b7
References
Articles on StyleCraze are backed by verified information from peer-reviewed and academic research papers, reputed organizations, research institutions, and medical associations to ensure accuracy and relevance. Read our editorial policy to learn more.
- Chronic Sun Damage And The Perception Of Age Health And Attractiveness
https://www.researchgate.net/publication/42768812_Chronic_sun_damage_and_the_perception_of_age_health_and_attractiveness - Effects Of Visible Light On Mechanisms Of Skin Photoaging
https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/pdf/10.1111/phpp.12736 - UV Radiation And The Skin
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3709783/ - Effect Of The Sun On Visible Clinical Signs Of Aging In Caucasian Skin
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/labs/pmc/articles/PMC3790843/ - Niacinamide: A B Vitamin That Improves Aging Facial Skin Appearance
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16029679/ - How Much Do We Really Know About Our Favorite Cosmeceutical Ingredients?
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/labs/pmc/articles/PMC2921764/ - Azelaic Acid Reduced Senescence-Like Phenotype In Photo-Irradiated Human Dermal Fibroblasts: Possible Implication Of PPARγ
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23278893/ - An Evaluation Of The Effectiveness Of Azelaic Acid As A Depigmenting And Chemotherapeutic Agent
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/4031538/ - Topical Vitamin C and the Skin: Mechanisms of Action and Clinical Applications
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5605218/ - Effects Of Alpha-Hydroxy Acids On Photoaged Skin: A Pilot Clinical Histologic And Ultrastructural Study
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/8642081/ - Retinoids In The Treatment Of Skin Aging: An Overview Of Clinical Efficacy And Safety
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/labs/pmc/articles/PMC2699641/ - Lasers & Light Therapies for Skin Rejuvenation
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC6188454/ - Microneedling
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK459344/ - Chemical Peels for Skin Resurfacing
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK547752/ - Awareness To Sun Exposure And Use Of Sunscreen By The General Population
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/labs/pmc/articles/PMC5489041/ - UV clothing and skin cancer
https://www.researchgate.net/publication/49818831_UV_clothing_and_skin_cancer - How To Treat Actinic Keratosis? An Update
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/labs/pmc/articles/PMC4517799/ - Actinic Cheilitis
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK551553/ - Treatment Of Poikiloderma Of Civatte Using A Redesigned Pulsed Dye Laser With A 15 Mm Diameter Treatment Spot: PDL TREATMENT OF POC
https://www.researchgate.net/publication/329216589_Treatment_of_poikiloderma_of_Civatte_using_a_redesigned_pulsed_dye_laser_with_a_15_mm_diameter_treatment_spot_PDL_TREATMENT_OF_POC
Read full bio of Dr. Priya Gill
Read full bio of Eshna Das
Read full bio of Anjali Sayee
Read full bio of Swathi E























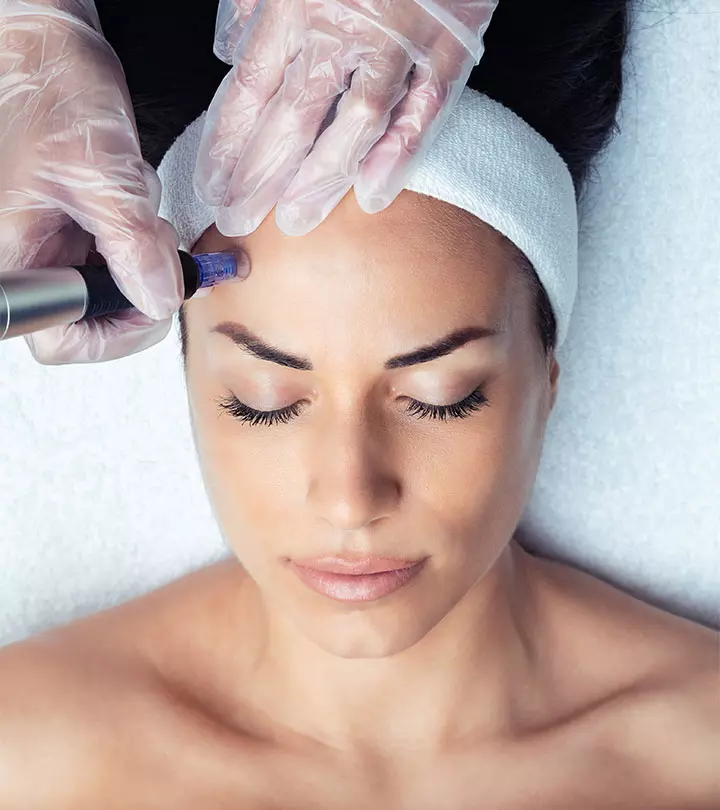
Community Experiences
Join the conversation and become a part of our empowering community! Share your stories, experiences, and insights to connect with other beauty, lifestyle, and health enthusiasts.