Healthy Food Vs. Junk Food: All You Need To Know
Because what's on your plate decides your overall health and well-being.
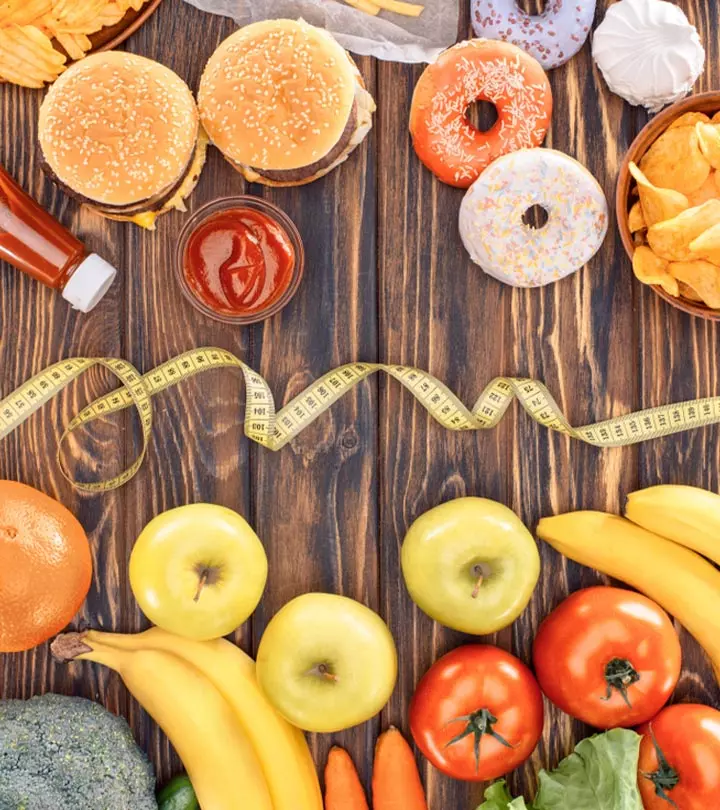

Image: Shutterstock
We all are aware of the negative effects junk food poses on our health, and yet we tend to grab bites of junk very often because of their tempting taste. But, have you ever wondered why the junk food vs. healthy food debate is discussed so heatedly?
Learn about how the empty calories in junk food negatively affect your overall health and how eating clean can improve your wellbeing by reading this article. Also, have a look at the foods that have many detrimental effects on your health if you consume them regularly. Keep reading to know more!
In This Article
The Difference Between Healthy And Unhealthy Foods
Before diving deeper into the differences between healthy and unhealthy food, let’s be clear about a few aspects. on a few things. What exactly do junk food and healthy food refer to? Healthy food contains good fats and nutrients that are vital for your body. Healthy food items offer your body the strength and the capacity to fight against various diseases. Junk food is a highly processed food and contains a high amount of calories. These foods are harmful to your health. Most of the junk foods are available as packaged items.
To get a deeper understanding of the difference between healthy and unhealthy foods, let us first delve into junk foods in the next section.
Key Takeaways
- Junk food is high in calories and is mostly available as packaged items.
- These are loaded with sugars, high fats, and simple carbohydrates that increase the risk of obesity and other diseases.
- Soft drinks, pizzas, French fries, pastries, burgers, sandwiches, and processed meat are certain food items that are not good for your health.
What Is Junk Food?
Junk food refers to highly processed, nutritionally poor foods that are often laden with excessive sugars, salt, and unhealthy fats. These include popular fast foods such as pizzas and burgers, sugary beverages such as cola, and different kinds of candies.
Frequent consumption of junk food can take a toll on your overall health and cause nutritional imbalance as well as deficiencies in the absence of a balanced diet containing essential nutrients. It may also lead to unwanted weight gain, spike your blood sugar levels, and even mental health disorders (1).
While the occasional indulgence is considered fine, a balanced diet, which majorly comprises fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins, is essential for long-term health and vitality.
The difference between healthy food and junk food often depends on their calorie and fat content. So, it is always better to know how to distinguish healthy foods from their unhealthier counterparts. Following is a list of factors that you can check to keep yourself away from unhealthy/junk food.
1. Type Of Oil Used In Food: Makes A Big Difference
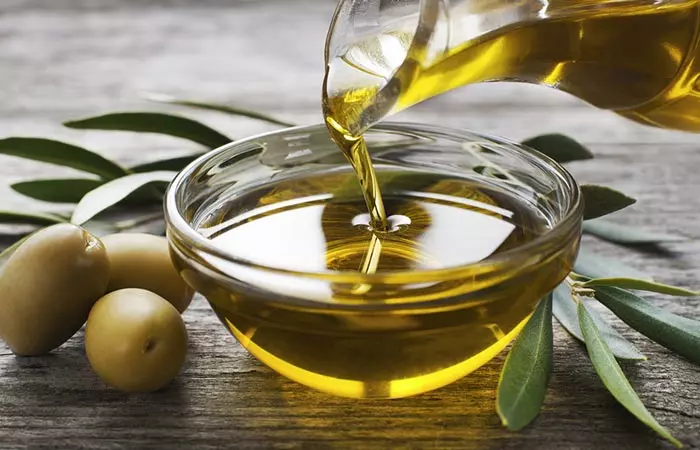

There are many varieties of cooking oils on the market. But do you know which is the best among those? The key difference between unhealthy and healthy oils is the amount of saturated and unsaturated fats they contain. The oils with a high percentage of unsaturated fats are considered a healthier option (2). Olive oil and sunflower oil are low on saturated fats and are considered healthy. Whereas oils with high saturated fats like palm oil, butter, and lard are considered unhealthy. Generally, junk foods are loaded with a high amount of saturated fats and are unhealthy to eat.
2. Nutrient Value Of The Foods: Shows Its Impact On Your Health
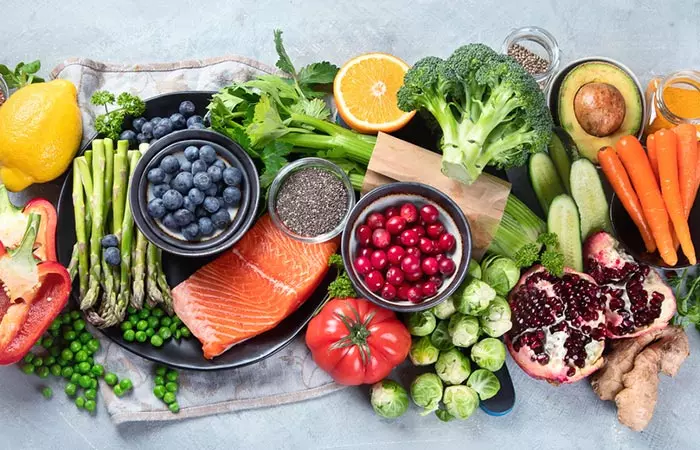

Healthy foods are rich in nutrients that are essential for your body. Nutrients like calcium, fiber, potassium, and vitamin D are available in leafy vegetables, dairy products, nuts, fruits, eggs, fish, whole grains, and legumes. Junk foods are rich in calories, but they don’t provide you with the vital nutrients. Also, People who frequently consume junk food with low nutrient values may have nutritional deficiencies (1).
3. Refined Or Unrefined Foods: Choose The Best One!
During refining, lots of enzymes, vitamins, and fibers are lost from the oils. The refined food becomes unhealthy to some extent (1). The vegetable oils are originally good for health if consumed reasonably. Usually, the oils are partially hydrogenated to increase their shelf life. It makes them into less healthy trans-fats, which are unhealthy. The processed oil has disastrous long-term effects on the body. So, always try to use unrefined, unprocessed, and natural ingredients for maintaining better health.
4. Are You Consuming Your Daily Quota Of Vital Nutrients?
Do you know how many people around the people have nutrient deficiencies? According to the World Health Organization (WHO), more than 2 billion people worldwide are estimated to be deficient in key vitamins and minerals (3). Intake of foods rich in vital nutrients provides good health and also lowers the risk of developing health issues. At the same time, junk food has the opposite impact on your health. Fast food consumption increases the risk of metabolic syndromei A group of conditions like high blood pressure, blood sugar, and abdominal fat that increase the risk of heart disorders and diabetes. by increasing triglyceridei A type of stored fat in the body cells that forms when you consume extra calories from butter, oils, and fast food. levels. Fast food also triggers blood sugar and blood pressure spikes. Such food also increases the risk of obesity leading to cardiovascular problems and type 2 diabetes (1), (4).
5. Which Type Of Food Has More Antioxidants?
Antioxidants are essential to defend the body from free radicals, which can cause cancer
(5). Healthy foods such as vegetables, fruits, and beans are rich sources of antioxidants. In contrast, junk food does not contain enough quantities of antioxidants essential for your body.
6. Are You Eating Healthy Snack Items?
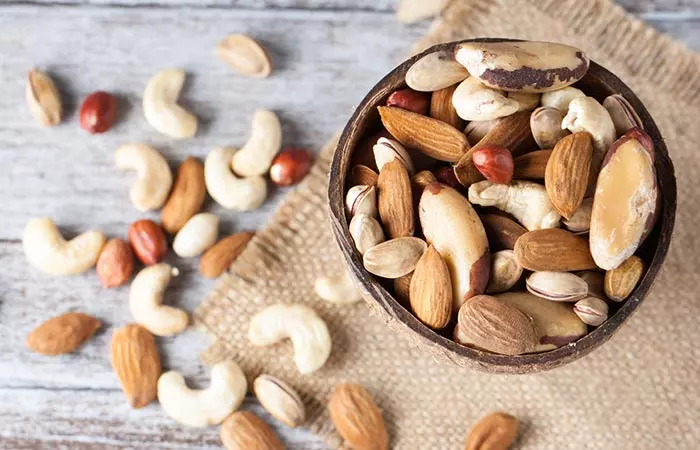

Most of us tend to hog on snacks. Hence, it is important to choose healthy snacks. It is healthier to have crunchy, nutritious vegetables, such as celery and carrots with a low-fat dip instead of potato chips or French fries with an onion dip. Nuts and air popcorn are healthier than processed snacks like chips.
7. Problems Associated With Junk Food
Junk food rich in fat and sugar can be addictive. The blend of sugar and fat is mostly linked with addictive symptoms, including loss of self-control over food. Regular consumption of junk foods can further increase your cravings. Also, the added sugars, high fats, and simple carbohydrates in junk food can increase the risk of obesity and other diseases.
A 2018 survey conducted on 2537 adults found that 49% of them are ‘health-oriented eaters’ i.e., prefer wholesome and nutritious foods. The other 51% select healthy food half the time or less. Furthermore, health-oriented eaters limited their intake of artificial sweeteners (53% vs. 36%), sugar (51% vs. 26%), and artificial preservatives (47% vs. 20%) compared to less health-conscious eaters (51%).
 Fun Fact
Fun FactThese are the differences between healthy and unhealthy foods. In the following section, we will further explore the benefits of eating healthy.
What Are The Benefits Of Eating Healthy?
Convenience often takes precedence over health in our fast-paced lives, especially when it comes to food choices. However, knowing the numerous benefits of healthy foods should reassure us that making healthier choices is the right path to follow.
- Healthy foods like fruits and vegetables are high in fiber. Fiber releases energy slowly and keeps our stomach full for a longer time. It keeps you from overeating (6). High-fiber foods also keep your gastrointestinal tract healthy, thus controlling your cholesterol and blood sugar levels (7).
- The protein from lean meat and nuts improves your brain function. The antioxidants and nutrients in fruits and fresh veggies can influence the hormones responsible for mental health (8). Try to take foods rich in omega-3 fats that can influence your brain health and mental well-being (9). They hold all the nutrients intact, unlike fried foods which drain the essential nutrients.
- Healthy and organic food is not processed. Hence, it is low in calories and rich in essential nutrients. It provides your body with exactly what it needs to maintain good health. Having fruits, veggies, nut milk, seeds, beans, sprouts, pulses, and millets will give you good nutrition.
- Healthy food is the one which gives you balance along with satiety, and can help control your weight. If you are overweight or obese, consult a doctor or a nutritionist at the earliest and strictly follow a high fiber diet.
- A daily diet of healthy and nutritional food will also promote your heart health. It helps regulate your cholesterol, blood sugar, and blood pressure levels.
- Foods high in fat and sugar can cause dry skin and dull hair (10). Nutrient-rich foods can give you a youthful appearance (11).
Brandon William, a health and fitness vlogger, stopped eating sugar, dairy, and gluten for 60 days and achieved clear skin. His acne scars and eczema flares reduced with healthy diet habits. He says, “My skin has almost completely cleared up with only faint red remnants of the previous acne healing. Also, the red and itchy eczema that I had in the inside of my arm at the beginning of the challenge is now completely gone now (i).”
 Trivia
TriviaEating healthy is a key to being healthy. But what are some healthy eating practices? Keep reading to learn about those.
Healthy Eating Tips
Here are a few tips that can help you keep up the healthy eating plan.
- Plan your grocery shopping to avoid impulsive purchases.
- Similarly, plan your meals so that you don’t go hungry and eat something directly off the shelf or from a packet.
- Have wholesome snacks on hand may also help reduce cravings for junk food.
- Try new recipes that incorporate a range of fruits and vegetables.
- Eat mindfully. Chew thoroughly. Do not indulge in a screen as you eat. This will help you feel more satiated.
- Do not eat in order to push aside emotions. Adopt different coping mechanisms like taking a walk or listening to music.
- If you are trying a new diet, don’t shift overnight; ease into it gradually.
- Avoid overly restrictive diets. It may lead to binge eating if your patience wears out.
Now, let’s look at some foods that are bad for your health in the following section.
Foods That Are Bad For Your Health
- Soft drinks: Consumption of soft drinks with high sugar content could cause type 2 diabetes, obesity, and dental erosion (12), (13). Sugary drinks are harmful to your health. There is a rising prevalence of obesity, mainly in children, with soft drink consumption (14). Also, when you drink soft drinks, your brain doesn’t register them as food. Hence, you could end up consuming more calories.
The high fructose concentration in sugary beverages leads to nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (15). Added sugar is associated with cardiovascular disease (16). A decrease in sugary beverage consumption will reduce the prevalence of obesity and its related diseases (17).
- French fries:
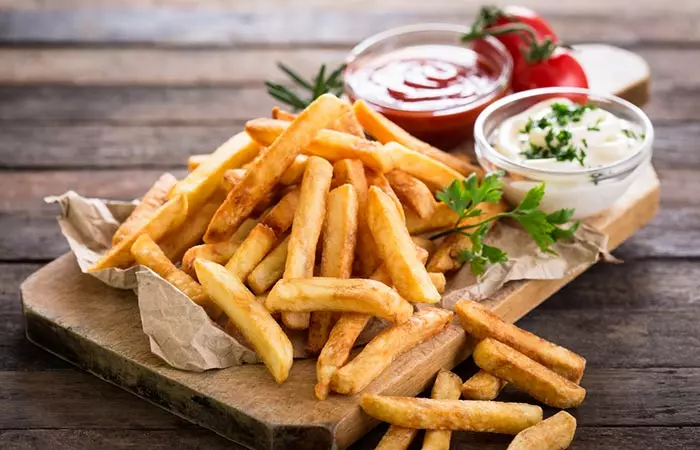

French fries and potato chips have more trans-fat and salt and are associated with larger weight gain (18). These fried foods are high in calories too. Deep-fried potato foods contain large amounts of acrylamides. Acrylamide is a proven carcinogen in rodents and has a positive association with human cancer (19).
- Pizzas: Pizza is the favorite junk food for many around the globe. It is processed food with more unhealthy ingredients and calories. The highly refined grain products in pizza have been linked with weight gain. Regular consumption of these types of foods is linked with heart problems and obesity (20).
- Pastries: Pastries are one of the favorite baked items for many. These are made from hydrogenated fats that are unhealthy (21). These are sweet and tasty but contain many preservatives and no essential nutrients.
- Sandwiches: Sandwiches are high-fat breakfast items that have a negative impact on your heart. The high fat in warm bread slices, cheese, and processed meat can slow down blood flow in the arteries (22). These foods can impact blood vessel function and increase the risk of cardiovascular disease.
- Burgers:
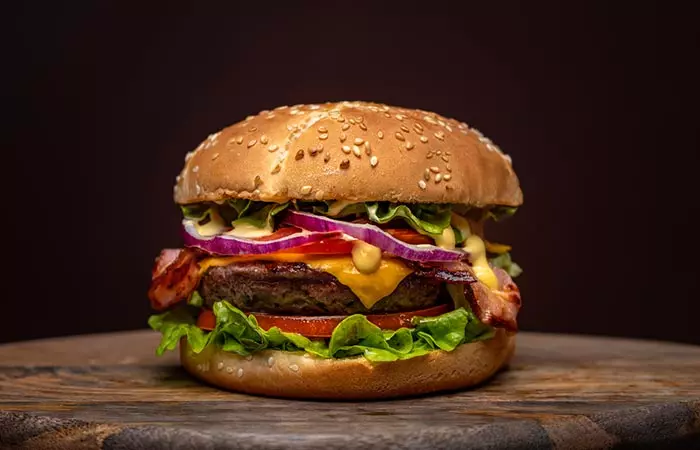

Burgers are high in cholesterol, saturated fat, and salts. The high sodium content in burgers can elevate blood pressure (23), (24). This condition may also lead to stroke and kidney diseases.
- Processed Meat: Processed meat intake is linked with colon cancer (25). It can also be linked to coronary heart disease, diabetes, and stroke (26).
White bread, low-fat yogurt, high-calorie coffee, ice creams, most fruit juices, and full cream cheese could also negatively impact your health. Consuming these unhealthy foods on a regular basis may result in chronic health problems, such as metabolic syndrome, a group of disorders that increase the risk of diabetes, heart disease, and stroke. Making healthy food choices might be encouraged by being aware of these hazards.
Infographic: Easy Ways To Stop Eating Junk Food
There is a never-ending battle between healthy and junk food. While junk food is not healthy, resisting it seems like a difficult task. But, some practical ways may help you stop your cravings for junk food. Check out the infographic below to learn some easy ways to move junk food away from your focus. Illustration: StyleCraze Design Team
The secret to a healthy body is a balanced diet. So it comes as no surprise that the verdict of the junk food vs. healthy food debate heavily favors the latter. While junk food can trick you with its taste, its ingredients can contribute to a variety of health issues. Healthy food contains a higher concentration of nutrients, antioxidants, and beneficial minerals that are good for your health. Reduce the risk of long-term health issues by replacing junk food with fresh produce. Also, sleep well and exercise regularly to reap the benefits of eating healthy in the long run.
Frequently Asked Questions
Why being healthy is important?
Good physical and mental health is crucial for a fulfilling life. It empowers you to handle challenges and make the most of opportunities, both in personal and professional aspects. Your good health also benefits those around you, promoting well-being and progress in your community. Embrace healthy habits and reap the rewards for a better present and future.
What are the 5 healthiest foods?
Nourish your body with these five superfoods for optimal wellness: nuts, berries, kale, spinach, and broccoli. They are packed with nutrients, easy to incorporate into meals, and provide numerous health benefits. Embrace their goodness and boost your health and wellbeing.
How much junk food is OK?
It is not recommended to have junk food to lead a healthy lifestyle. However, there is no harm in having it once in a while. You can consume junk food once or twice a week if you are physically active. Also, it is important to have it in moderation.
Is junk food bad for the brain?
Junk foods like cookies, burgers, chips, and other packaged foods may contain trans fat. These have an adverse effect on the brain and nervous system as they can alter the ability of neurons to communicate and reduce mental performance (27).
Can I eat junk once a day?
No. Eating junk food once a day may not be good for the health and may gain more weight.
Is white rice junk food?
No. white rice is not junk food. It is a staple food source with a healthy nutrient profile.
Does junk food affect IQ?
Junk food consumption may affect the brain, as discussed above. However, there is no scientific evidence that suggests it affects the IQ of a person.
Illustration: Healthy Food Vs. Junk Food: All You Need To Know

Image: Dall·E/StyleCraze Design Team
While you may know what foods are healthy and what are not, making the right choices is hard. But understanding the deeper differences between nutritious and unhealthy foods can help. Check out the following video and help yourself make healthier decisions for a better lifestyle.
Personal Experience: Source
StyleCraze's articles are interwoven with authentic personal narratives that provide depth and resonance to our content. Below are the sources of the personal accounts referenced in this article.
i. No Sugar, Dairy, and Gluten for 60 Days. Heres What Happenedhttps://www.youtube.com/watch?v=6BlPfnp85S8
References
Articles on StyleCraze are backed by verified information from peer-reviewed and academic research papers, reputed organizations, research institutions, and medical associations to ensure accuracy and relevance. Read our editorial policy to learn more.
- The Hidden Dangers of Fast and Processed Food
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6146358/ - Unsaturated Fatty Acids and Their Immunomodulatory Properties
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC9953405/ - Preventing and controlling micronutrient deficiencies in populations affected by an emergency
https://www.who.int/docs/default-source/nutritionlibrary/preventing-and-controlling-micronutrient-deficiencies-in-populations-affected-by-an-emergency.pdf?sfvrsn=e17f6dff_2 - Fast Food Pattern and Cardiometabolic Disorders: A Review of Current Studies
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4772793/ - Free radicals, antioxidants and functional foods: Impact on human health
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3249911/ - Dietary fiber and obesity
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/707393/ - High Fiber Diet
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK559033/ - Fruit, Vegetable and Antioxidant Intakes are Lower in Older Adults with Depression
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3520090/ - Brain Health across the Lifespan: A Systematic Review on the Role of Omega-3 Fatty Acid Supplements
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6116096/ - Diet and Skin Aging—From the Perspective of Food Nutrition
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7146365/ - Discovering the link between nutrition and skin aging
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3583891/ - Impact of soft drinks to health and economy: a critical review
https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s40368-019-00458-0 - Dietary sugar and body weight: have we reached a crisis in the epidemic of obesity and diabetes?: health be damned! Pour on the sugar
Url - Effects of Soft Drink Consumption on Nutrition and Health: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1829363/ - Dietary fructose in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23390127/ - Added sugar intake and cardiovascular diseases mortality among US adults
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24493081/ - Resolved: there is sufficient scientific evidence that decreasing sugar‐sweetened beverage consumption will reduce the prevalence of obesity and obesity‐related diseases.
https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1111/obr.12040 - Dietary Patterns and Changes in Body Weight in Women
https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1038/oby.2006.164 - Acrylamide formation in fried potato products – Present and future, a critical review on mitigation strategies
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S030881461101096X - Fat, Sugar, Whole Grains and Heart Disease: 50 Years of Confusion
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5793267/ - Pastries
https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/agricultural-and-biological-sciences/pastries - Functional Foods as Modifiers of Cardiovascular Disease
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2847297/ - The variability of reported salt levels in fast foods across six countries: opportunities for salt reduction
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3381762/ - Sodium Intake and Hypertension
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6770596/ - Processed Meat and Colorectal Cancer: A Review of Epidemiologic and Experimental Evidence
https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/abs/10.1080/01635580701684872#.VS5zDvmsVA1 - Red and processed meat consumption and risk of incident coronary heart disease, stroke, and diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2885952/ - New data on harmful effects of trans-fatty acids
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27215959/
Read full bio of Karishma Shah
Read full bio of Sindhu Koganti
Read full bio of Ravi Teja Tadimalla
Read full bio of Himanshi Mahajan


























Community Experiences
Join the conversation and become a part of our empowering community! Share your stories, experiences, and insights to connect with other beauty, lifestyle, and health enthusiasts.