Lupus Diet: How Does It Work And Foods To Eat & Avoid
Explore the potential of lupus-friendly dietary choices and regain control over the symptoms.

Image: Shutterstock
The lupus diet plays a crucial role in managing the symptoms of lupus, a common autoimmune condition that even celebrities like Selena Gomez and Lady Gaga contend with. You can gain better control over its symptoms like inflammation, fatigue, and joint pain by maintaining a well-balanced diet with abundant fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, antioxidants, and omega-3 fats. In this article, we talk about how proper nutrition may help you take charge of your health and ease lupus symptoms. Keep reading to learn more!
 At A Glance: Lupus Diet
At A Glance: Lupus Diet- Principle: Prioritizes the intake of anti-inflammatory and antioxidant-rich foods to reduce potential inflammation triggers.
- Purpose: To effectively manage the symptoms of lupus by minimizing inflammation in the body.
- Who It Is For: Individuals with lupus.
- Duration: Long-term.
- Who Should Avoid: Individuals with gastrointestinal disorders like Crohn’s diseasei An autoimmune chronic inflammatory condition that primarily affects the digestive tract, causing pain, diarrhea, and weight loss. and irritable bowel disorderi A functional gastrointestinal disorder causing abdominal pain and bloating without any signs of inflammation in the digestive tract. , and pregnant or breastfeeding individuals.
- Cons: It is restrictive and tough to sustain and may lead to nutritional deficiencies.
In This Article
What Is Lupus Diet?

The lupus diet involves consuming certain foods that may help manage the symptoms of lupus. While there is no established diet for lupus, healthcare professionals prioritize proper nutrition as a part of the treatment plan. The idea is to formulate a well-balanced diet that includes foods from all major food groups, especially foods rich in antioxidants and anti-inflammatory compounds, to help reduce inflammation in the body.
Lupus is a chronic autoimmune disease that leads to inflammation and other symptoms like fatigue, joint pain, muscle aches, and skin rashes. It occurs when the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks the healthy tissues. This condition can affect anyone but is more common in women. They are at ten times more risk of developing it than men (1).
Lupus is categorized into four types (2):
- Neonatal lupus: It is a rare form of the disease affecting newborns caused when the mother’s antibodies pass through the placenta.
- Discoid lupus erythematosus: This is thought to be genetic and is prevalent in women.
- Drug-induced lupus: It is caused by exposure to drugs, which trigger an autoimmune response.
- Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE): This is the most common type of lupus and affects multiple organs in the body.
 Did You Know?
Did You Know?Lupus can’t be cured. However, several approaches may help manage its symptoms (1). One of these approaches involves adopting a lupus diet.
Certain foods can either worsen inflammation or help reduce it (3). That’s why identifying and eliminating the trigger foods is crucial. Incorporating an anti-inflammatory diet, which includes whole grains, lean protein, fruits, etc., into your lupus diet can help reduce flare-ups and ease inflammation-related symptoms. Learn more about it in the next section.
Key Takeaways
- The lupus diet emphasizes the intake of anti-inflammatory and nutrient-rich foods to manage symptoms effectively.
- A diet rich in antioxidants, omega-3 fatty acids, and whole grains can help reduce inflammation.
- It is important to avoid consuming processed foods high in calories and fat, as they may worsen lupus symptoms, and increase the risk of heart issues, common in people with lupus.
- However, consult a registered dietitian for tailored advice, as lupus affects individuals differently. This will ensure proper lupus management per the health needs and lifestyle of the individual.
How Does Lupus Diet Work?
Some of the preferred foods in a diet for lupus include those rich in antioxidants, such as colorful fruits and vegetables. Antioxidants, like vitamin C and beta-carotene, may help neutralize the harmful molecules called free radicals, which can trigger inflammation (4).
Omega-3 fatty acids in fatty fish like salmon and flaxseeds are another key component of the lupus diet. These fats have anti-inflammatory properties, and incorporating them into your diet may help reduce inflammation and relieve symptoms to a great extent (5).
 Pro Tip
Pro TipThe diet also encourages the intake of whole grains, like brown rice and quinoa. They provide essential nutrients and fiber, contribute to overall health, and may help regulate inflammation (7).
Additionally, medications used to treat lupus, such as corticosteroidsi A class of medications used to reduce signs of inflammation like pain and swelling and suppress the immune system's response. (like prednisone) and immunosuppressants, may have adverse effects on the bones. Prolonged use of corticosteroids, for instance, may lead to bone loss, making bones more susceptible to fractures (8). Thus, consume foods rich in calcium and vitamin D to boost bone health (9).
Conversely, several foods may exacerbate inflammation and these need to be eliminated from your diet. For instance, processed foods are high in trans fats and refined sugars, which may trigger inflammation (3). Additionally, excessive red meat consumption has been associated with inflammation in some individuals, so it is advisable to have it moderately (10).
The diet also recommends avoiding the intake of sodium-rich foods. They include heavily salted snacks or processed meals, which may contribute to water retention and worsen swelling, a common lupus symptom (11).
Apart from a balanced diet rich in antioxidants and anti-inflammatory foods, portion control and meal timing can also significantly impact lupus patients’ energy levels and inflammation responses. By paying attention to these factors, individuals with lupus can better manage their condition and improve their overall well-being.
However, maintaining a balanced diet for lupus management requires a systematic approach. Therefore, it is recommended to consult a healthcare provider or registered dietitian to tailor your diet to ensure it complements any prescribed treatments. They will also take your dietary preferences and restrictions in mind and organize an appropriate meal plan for you.
Thus, the choices individuals with lupus make in the kitchen can impact their overall well-being.
While the lupus diet can be restrictive, it does include a wide range of natural foods that can help you create nutritious balanced meals. Discover what foods are allowed on this diet in the following section.
Food To Eat If You Have Lupus
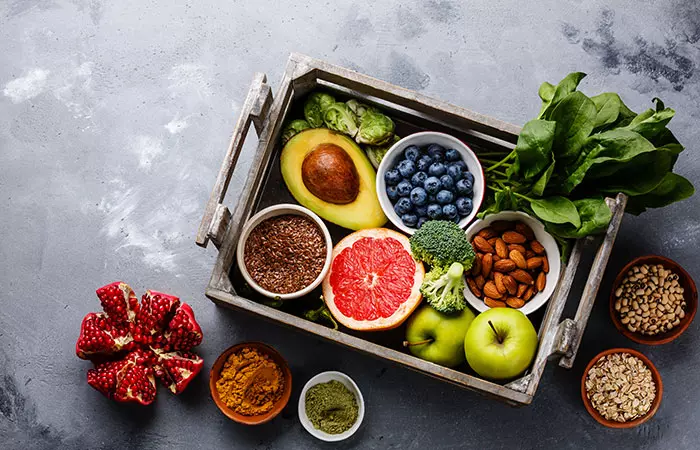

Any diet where you increase the intake of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins, including fatty fish, seeds, and nuts, is beneficial, especially for managing lupus. Such a diet, rich in antioxidants, omega-3 fatty acids, and fiber, can help reduce inflammation, boost the immune system, and maintain overall health. Here are some of the foods you can have on the lupus diet:
1. Fruits And Vegetables
- Berries
- Spinach
- Sweet potatoes
- Bell peppers
2. Fatty Fish
- Salmon
- Mackerel
- Sardines
- Trout
3. Whole Grains
- Brown rice
- Quinoa
- Whole wheat bread
- Oats
4. Lean Proteins
- Poultry
- Tofu
- Beans
- Lentils
5. Nuts And Seeds
- Almonds
- Walnuts
- Flaxseeds
- Chia seeds
Aside from these foods, consume foods like probiotics to maintain your gut health and boost your bone health with calcium and vitamin D-rich foods. Now, let’s look at the foods you should avoid when on a lupus diet. Keep scrolling through to learn more about them.
Foods To Avoid If You Have Lupus
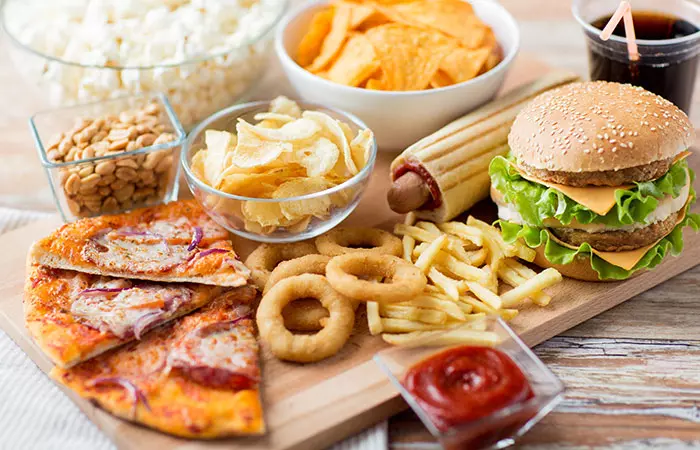

It is important to limit the intake of processed foods, sugars, and saturated fats, which can exacerbate inflammation and contribute to health complications. Here are some of the foods you must limit or avoid on a lupus diet:
1. Processed Foods
- Fast food
- Sugary cereals, foods, and drinks
- Packaged snacks
2. High-Sodium Foods
- Chips
- Canned soups
- Processed deli meats
3. Red Meat4. Alcohol
Also, some individuals with lupus are sensitive to dairy. In such cases, consider dairy alternatives or lactose-free options if needed.
Alongside a lupus diet, exploring natural remedies for lupus, such as massaging with essential oils, soaking in Epsom salt, having a cup of holy basil, etc., can provide additional relief and help manage symptoms holistically.
The foods you include in your diet can not only nourish your body but also ease your symptoms. However, like any dietary plan, a lupus diet has its own set of advantages and disadvantages. Learn more about them in the next section.
Pros And Cons Of The Lupus Diet
Pros
1. May Help Reduce Inflammation
A well-planned lupus diet can help reduce inflammation, a common issue for people with lupus. Foods rich in antioxidants, omega-3 fatty acids, and anti-inflammatory compounds may help alleviate symptoms like rashes, headaches, and breathing issues (3), (4), (5), (7).
2. May Help Manage Weight
Lupus diet typically includes nutrient-dense foods like fruits, vegetables, and lean proteins. These foods are often lower in calories while providing essential nutrients, helping individuals feel satisfied, which may help reduce food intake and cravings (12). The diet also recommends reducing sodium intake, which may help prevent water retention and bloating, contributing to a healthier weight (11).
3. May Reduce The Risk Of Heart Issues
Some dietary choices, such as a low-sodium, heart-healthy diet, may help prevent cardiovascular issues, which people with lupus may be at higher risk for (13), (14).
Cons
1. May Not Work For Everyone
Lupus affects people differently, and there is no one-size-fits-all diet. It may require individual variation, as what works for one person may not work for another. It can be challenging to find the right dietary approach.
2. May Lead To Nutrient Deficiency
Some lupus diets may require you to restrict or eliminate certain foods or food groups. A poorly planned, restrictive lupus diet could lead to nutrient deficiencies. For instance, eliminating dairy can reduce calcium intake, which may affect your bone health.
3. May Be Difficult To Sustain
Sticking to a specific diet can be challenging, especially during social events and when dining out. This may lead to feelings of frustration or deprivation.
Even though it is a restrictive diet, you can still make it flavorful by preparing delicious recipes with compliant foods. You can create your meal plans and try different variations, keeping your preferences in mind. Keep scrolling through to discover some of our lupus diet-friendly recipes that you can include in your meals.
Lupus Diet Recipes
1. Spinach And Berry Salad With Balsamic Vinaigrette
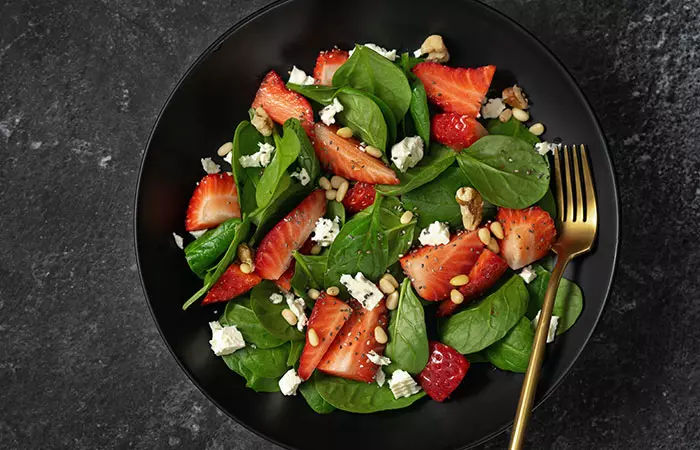

Ingredients
- 2 cups of fresh spinach leaves
- 1/2 cup of mixed berries
- 1/4 cup of chopped walnuts
- 2 tablespoons of crumbled feta cheese
- 2 tablespoons of balsamic vinegar
- 1 tablespoon of olive oil
- 1 teaspoon of honey
- Salt and pepper to taste
How To Prepare
- Wash and dry spinach leaves and place them in a salad bowl.
- Add the mixed berries, chopped walnuts, and feta cheese to the spinach.
- Whisk balsamic vinegar, olive oil, honey, salt, and pepper In a separate bowl to prepare the vinaigrette dressing.
- Drizzle the vinaigrette over the salad and toss gently to coat.
2. Baked Salmon With Lemon And Herbs
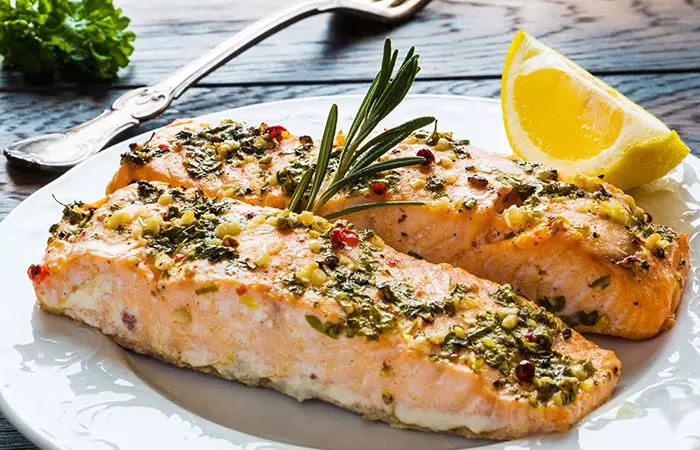

Ingredients
- 2 salmon fillets
- 1 lemon
- 2 cloves of garlic
- 1 tablespoon of fresh dill
- 1 tablespoon of fresh parsley
- 1 tablespoon of olive oil
- Salt and pepper to taste
How To Prepare
- Preheat your oven to 375°F (190°C).
- Place salmon fillets on a baking sheet lined with parchment paper.
- Chop dill and parsley and mince the garlic cloves.
- Mix garlic, dill, and parsley with olive oil in a small bowl.
- Season salmon fillets with salt and pepper, then brush the herb mixture evenly on top of them.
- Lay thinly sliced lemon slices over the salmon fillets.
- Bake in the oven for 15-20 minutes or until salmon flakes easily with a fork.
- Serve hot with your choice of side vegetables.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is curd good for lupus?
Yes, it may have some positive impact on your condition. A study indicated that a particular beneficial bacteria in yogurt could potentially alleviate symptoms in certain individuals with lupus (15).
How to avoid lupus?
Unfortunately, you cannot avoid lupus. It is an autoimmune disease with no known prevention or cure. Managing it involves early diagnosis, medical treatment, and a healthy lifestyle to minimize symptoms.
What is the best exercise for lupus patients?
Low-impact exercises like swimming, walking, or gentle yoga are often well-tolerated by lupus patients. It is recommended to consult with your healthcare provider or a certified trainer for a personalized exercise plan.
How to live your best life with lupus?
Living well with lupus involves following the prescribed treatment, taking medicines, managing stress, getting enough rest, and adopting a balanced diet. You can join a support network or group and seek guidance from doctors to help you improve your quality of life.
Illustration: Lupus Diet: How Does It Work Foods To Eat And Avoid

Image: Stable Diffusion/StyleCraze Design Team
Watch the following video and learn the importance of maintaining a nutritious diet while managing lupus symptoms effectively. It offers valuable insights: strategies, and dietary guidance for better health.
References
Articles on StyleCraze are backed by verified information from peer-reviewed and academic research papers, reputed organizations, research institutions, and medical associations to ensure accuracy and relevance. Read our editorial policy to learn more.
- Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK535405/ - Lupus: An Overview of the Disease And Management Options
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3351863/ - Stress, Food, and Inflammation: Psychoneuroimmunology and Nutrition at the Cutting Edge
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2868080/ - Role of Antioxidants and Natural Products in Inflammation
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5075620/ - Omega-3 fatty acids in inflammation and autoimmune diseases
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12480795/ - Predictors of stress in patients with Lupus
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC9556948/ - Whole Grain Consumption and Inflammatory Markers: A Systematic Literature Review of Randomized Control Trials
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8778110/ - Osteoporosis in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus – Correlations with Disease Activity and Organ Damage
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6201199/ - Diet and Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE): From Supplementation to Intervention
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC9565311/ - Higher Meat Intake Is Associated with Higher Inflammatory Markers, Mostly Due to Adiposity: Results from UK Biobank
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8754571/ - Effects of the DASH Diet and Sodium Intake on Bloating: Results From the DASH–Sodium Trial
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7122060/ - Consumption of fruits, vegetables, and legumes are associated with overweight/obesity in the middle- and old-aged Chongqing residents: A case-control study
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC9259125/ - Sodium Intake and Heart Failure
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7763082/ - Systemic lupus erythematosus and cardiovascular disease: prediction and potential for therapeutic intervention
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3718673/ - Control of lupus nephritis by changes of gut microbiota
https://microbiomejournal.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s40168-017-0300-8
Read full bio of Karin Littleton
Read full bio of Payal Karnik
Read full bio of Ravi Teja Tadimalla
Read full bio of Aparna Mallampalli


























Community Experiences
Join the conversation and become a part of our empowering community! Share your stories, experiences, and insights to connect with other beauty, lifestyle, and health enthusiasts.