Medlar Fruit Benefits: Everything You Need To Know
Backed with antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and immune-boosting properties, this fruit has a lot to offer.
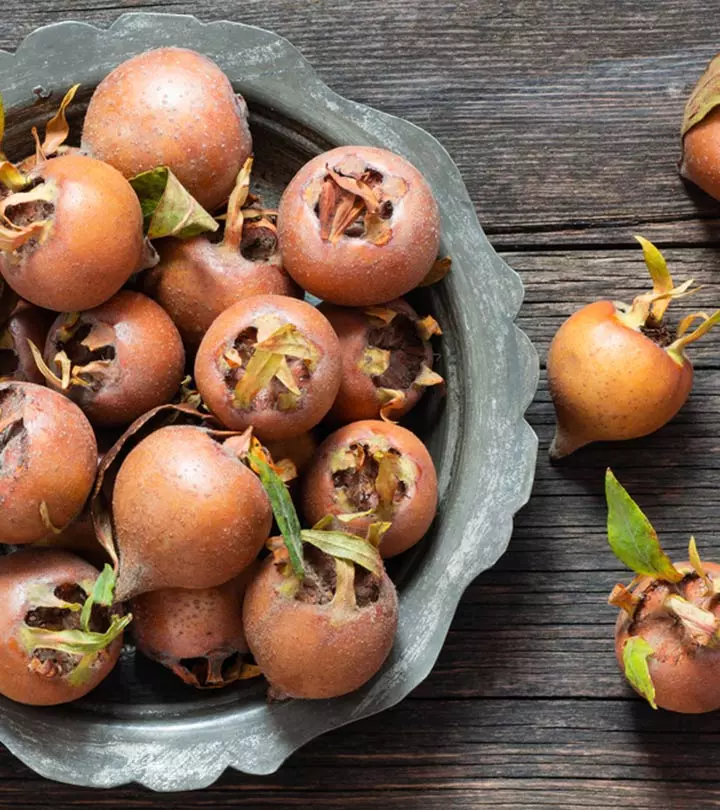

Image: Shutterstock
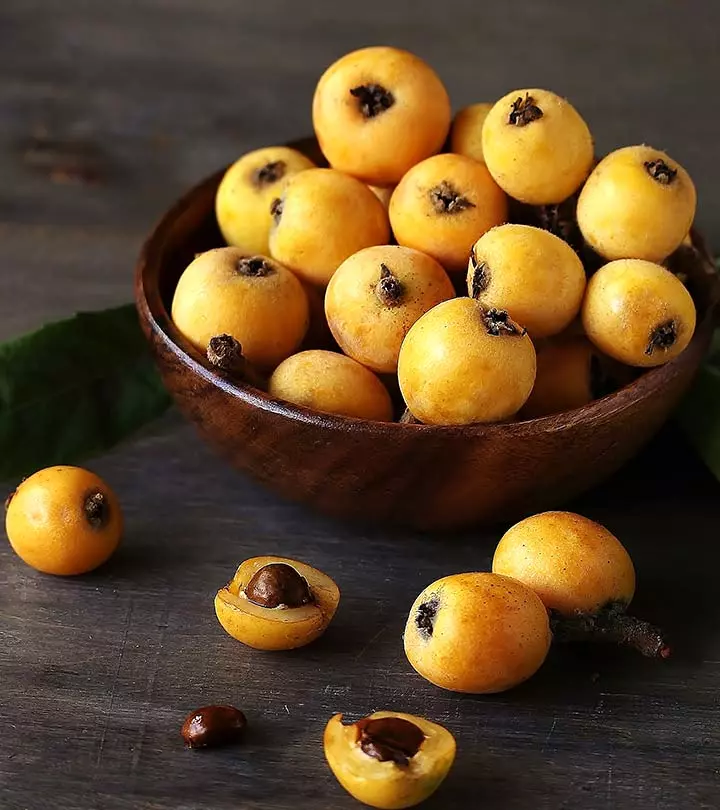
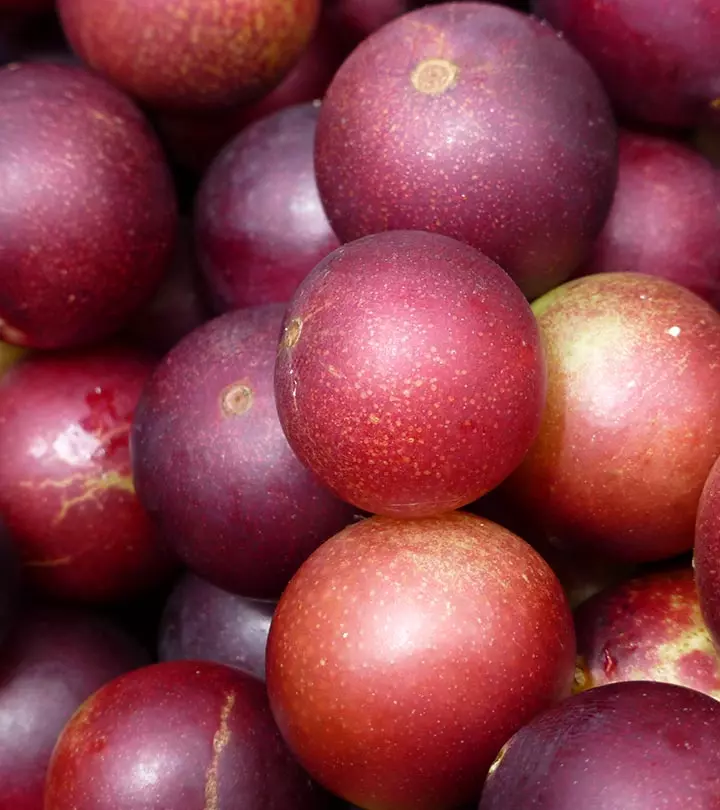
Fruits taste best when consumed fresh and help you get all the benefits they offer. But there is a fruit that tastes best when it is rotten. It is the medlar fruit. The benefits of medlar fruit are gaining attention slowly. This edible fruit belongs to the Rosaceae family and is grown in autumn. It is harvested raw and rotten, and fermented before consumption. Continue reading to know more about medlar fruit, its nutrition, recipes you can try with it, and how can you include this fruit in your diet.
 Know Your Ingredient: Medlar
Know Your Ingredient: MedlarWhat Is It?
It is a small, round fruit picked in the autumn and left to rot until it becomes soft and mushy.
What Are Its Benefits?
It treats digestive issues, reduces the risk of diabetes, boosts immunity, and might help maintain brain health.
Who Can Use It?
Consuming medlar fruit as a part of the diet can benefit all due to its immunity-boosting properties.
How Often?
You can consume 2-3 medlar fruits daily.
Caution
Do not consume the seeds of the medlar food as they are poisonous.
In This Article
What is Medlar Fruit? History And Origin
The medlar is a pome, ornamental fruit from the Rosaceae family, closely related to quinces, pears, and apples. Originally from southwestern Asia, it was brought initially to Greece and Italy and later on, to the whole of Europe. Interestingly, this fruit has been mentioned in Shakespeare’s Romeo and Juliet.
The fruit is unusual for two reasons.
- They are harvested in late autumn, mostly in November and December, making them an important source of sugar in the cold winters.
- They can be eaten only when they’re rotten.
Medlar fruits are picked raw in late autumn and are allowed to rot beyond ripening, a process called “bletting”. They are usually stored in a cool dry place until they become soft and mushy and darker brown in color. It then takes on a sweet and slightly acidic flavor. These can then be eaten directly scooped out of the fruit or can be baked, roasted, or made into jelly, tarts, cider, wine, or brandy.
Jonathan Kent, a writer and blogger, shares his experience of having medlar liquor: “It’s one of the most delicious things I have ever tasted, it’s dead simple to make, and it uses up all that rotten cheap brandy you can buy in Lidl that would only otherwise mess up your liver without you having much fun in the process (i).”
 Fun Fact
Fun FactMedlars, though not as known and widely found as apples and pears, are regaining their use and popularity because of their abundance in nutrition.
Key Takeaways
- The medlar fruit is rich in amino acids, tannins, sugars, pectins, and organic acids that combine to give it its distinctive sweet yet tart flavor.
- This fruit can be used to treat intestinal infections, menstruation irregularities, diarrhea, bloating, Alzheimer’s disease.
- Do not consume medlar seeds as they can be poisonous.
Nutritional Information Of Medlar Fruit
The medlar fruit is rich in nutrition and healthy components. It contains significant amounts of amino acids, tannins, sugars, pectins, and organic acids (1). These add up to give it the characteristic sweet yet tart flavor.
Medlar contains nutrients such as carotene, vitamin C, and vitamin B complex. It is also a rich source of calcium, potassium, iron, magnesium, sodium, and phosphorus that are found in smaller yet significant concentrations (2), (3).
Medlar fruit, with its phenolic compounds, flavonols, and ascorbic acid can also be an important source of natural antioxidants (4).
With the above important nutrients, medlar can provide you with a host of health benefits as discussed below.
Potential Health Benefits Of Medlar Fruit

The medlar fruit helps in treating intestinal infections and inflammations, menstrual irregularities, diarrhea, stomach bloating, internal bleeding, and strengthens the nerves as well (5). It offers the following benefits as well:
- Rich In Antioxidants
Common medlar is a natural source of polyphenolic compounds, particularly phenolic acids that show strong antioxidant properties.
The medlar fruit, bark, and leaves all contain significant amounts of plant flavonoids and polyphenols (6). The consumption of food rich in polyphenols has been associated with a reduced risk of several diseases such as atherosclerosisi A cardiovascular disease that causes a buildup of cholesterol plaque and fats on the artery walls, leading to blockage of proper blood flow. and diabetes (7), (8).
- Anti-inflammatory And Antibacterial Properties
Gallic acid is a polyphenol found in the highest proportion in medlar extracts (6). Gallic acid, with its anti-inflammatory properties, might be instrumental in reducing fat storage in obese people (9). Simultaneously, it might have potential antibacterial activity against food-related Pseudomonas strains (10). This means a possible application of medlar extracts in the food preservation industry as well.
- Rich In Immunity-boosting Minerals

Calcium, potassium, magnesium, iron, and other minerals found in medlar fruit help boost overall immunity. With its rich content of vitamin C, medlars also hold the potential to help treat scurvy (2), (11).
- Rich In Health-promoting Pectin
Pectin is a good source of dietary fiber derived from the cell walls of plants. Medlar fruit with its rich pectin content may help reduce cholesterol levels, prevent constipation, and stimulate bowel activity along with its other anti-inflammatory effects (12), (13).
- Might Help Treat Diabetes
Polyphenols found in medlar, especially phenolic acids, and flavonoids are known to inhibit α-glucosidase and α-amylase in carbohydrate metabolismi A biochemical process that supports metabolic formation and is responsible for the conversion of carbohydrates to energy. . This can be useful in the formulation of medicines and nutraceuticals significant for diabetes treatment (14), (15).
- Might Help Prevent Alzheimer’s Disease
As per a study on rats, high levels of flavonoids in the medlar fruit might be effective in the prevention of memory loss and neural injury. This could be further investigated for potential treatment options of similar neurodegenerative diseasesi A range of disorders that arise due to constant damage to neurons and cells, affecting cognition, mobility, and coordination. in humans (16).
With knowledge of the medlar health benefits above, let’s explore the many ways you can include them in your diet.
Apart from its health benefits, medlar trees serve as valuable assets in eco-friendly landscaping. Scroll down to know more.
Ecological Impact
Medlar trees provide several ecological benefits. They promote sustainable landscaping and improve local ecosystems. They use less water and fertilizer because they are drought-tolerant and hardy plants, which reduces the need for resource-intensive maintenance. Medlar trees are an excellent addition to eco-friendly landscapes because they enhance biodiversity by serving as habitat for a variety of insects, birds, and pollinators. They are also an excellent option for sustainable gardening, lowering the need for pesticides and promoting soil health due to their pest resistance and soil-type adaptability.
These trees are undoubtedly a valuable resource for the ecosystem. Its fruits can also be a delicious addition to your diet. Scroll down to know more.
How To Use Medlar Fruit In Your Diet
Now that you know what is medlar and what its benefits are, let’s take a look into how they can be used. When ripe, the medlars can burst open easily at the slightest touch, so you need to be careful while taking the pulp out. Gently peel off the stalk and squeeze out the pulp holding at the crown. Remove the seeds before eating.
Once ripe, medlars can either be eaten raw or can be used for culinary purposes in a number of ways as follows:
- It can be easily made into jams, jellies, marmalade, or syrups.
- Medlar can also be consumed as candied fruit or with cheese as a dessert.
- The fruit pulp with eggs and butter can be made into medlar cheese.
- Unripe fruit can be pickled with vinegar and sugar.
- Medlar can also be used as a condiment in making fruit wine (17).
- Can be made into a thick sauce that enhances many meat dishes.
 Trivia
TriviaLet us help you with some popular medlar recipes in case you happen to come across this hidden gem of fruit.
Popular Recipes Of Medlar
1. Compote Of Ripe Medlars
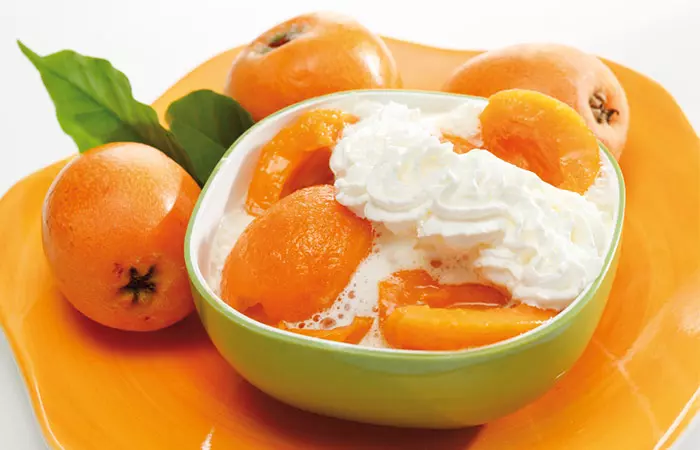

Ingredients
- medlars (half-ripe) – 1kg
- brown sugar – 800 g or honey – 50 g
- water – 0.5 litres
Instructions
- Wash, clean, and dice the half-ripe medlars into small pieces.
- Dissolve the honey or sugar in water.
- Pour the liquid mixture over the cut medlars.
- Cook on low heat for an hour.
- Cool it down slightly.
- When lukewarm, pour into jars.
- Seal and keep aside.
2. Medlar Jelly

Ingredients
- medlars – 2kg
- water
- sugar – 375 g per 500ml of strained juice
- lemon (juiced) – 2
Instructions
- Let the medlars ferment and soften.
- Place them in a preserving pan and cover them with sufficient water.
- Bring it to a boil and let it simmer for about 90 minutes to 3 hours (depending on the amount of bletting).
- Strain the mixture through a muslin cloth or jelly bag.
- Do not push the fruit through to avoid a cloudy jelly.
- Measure and add 375g of sugar per 500ml of the strained liquid.
- Add in the lemon juice.
- Bring to a boil and simmer for about 10 minutes until the setting point is reached.
- Pour hot into sterilized jars and seal.
To know if it has set well, place a plate with a spoonful of jelly in your freezer. Let it cool and then run your finger through it. If it parts through and crinkles at the edges, it’s ready. If not, you need to cook the jelly for another 5 minutes.
Now that you know how to include medlar in your diet and its popular recipes, let’s also be aware of its potential side effects.
Possible Side Effects Medlar Fruit
Like other members of the Rosaceae family, the seeds of medlar contain hydro-cyanic acid (prussic acid) and might be poisonous if eaten (5).
Even though the medlar fruit is rich in nutrients and health benefits, the use and intake of medlar seeds should be avoided.
Infographic: Top 5 Ways Medlar Fruit Can Improve Your Overall Health
Medlar fruit is hailed for its various health benefits. It is rich in polyphenols and various essential vitamins and minerals, which is why adding it to your diet can help lower cholesterol, aid weight management, and prevent various inflammatory health conditions. Check out the infographic below to learn more about how it is good for your health.

Illustration: StyleCraze Design Team
Medlar fruit’s benefits can be attributed to its rich nutrients. When included as a part of your regular diet, this fruit can reduce the risk of diabetes and atherosclerosisi A cardiovascular disease that causes a buildup of cholesterol plaque and fats on the artery walls, leading to blockage of proper blood flow. as it is rich in antioxidants. In addition, it has antibacterial and anti-inflammatory properties. Medlar fruit can boost immunity and help in managing constipation, cholesterol levels, and diabetes. It may also preventAlzheimer's diseasei A type of neurodegenerative disease that affects brain cells, causes brain shrinkage and dementia (memory loss). . You can add medlar fruit to your diet in the form of jam and jelly, and you can make medlar cheese as well. However, the seeds of medlar fruit are poisonous. Hence, caution is advised.
Frequently Asked Questions
What does medlar wine taste like?
Medlar wine has hints of applesauce and cinnamon. It might remind you of toffee and applesauce with notes of alcohol mixed in.
Can you grow medlars from seeds?
Yes. In order to germinate, the medlar seeds require a cold stimulus and a moist soil environment.
Is medlar tree self pollinating?
Yes. Medlar trees are self-fertile deciduous trees so you do not need another tree for fruiting.
Some thing wrong with illustration image shortcode. please verify shortcode syntax_illustration.jpg” alt_txt=”medlar fruit” image_title=”Medlar Fruit – Benefits, Nutrition Facts, Recipes [Important Winter Fruit]” image_credit=”Stable Diffusion/StyleCraze Design Team”]
Learn how to eat a medlar fruit with this easy video tutorial! Discover the best way to enjoy this unique fruit. Check it out now!
Personal Experience: Source
StyleCraze's articles are interwoven with authentic personal narratives that provide depth and resonance to our content. Below are the sources of the personal accounts referenced in this article.
i. Medlarshttps://jonathankent.wordpress.com/2011/11/25/medlars/
References
Articles on StyleCraze are backed by verified information from peer-reviewed and academic research papers, reputed organizations, research institutions, and medical associations to ensure accuracy and relevance. Read our editorial policy to learn more.
- Changes in sugars organic acids and amino acids in medlar (Mespilus germanica L.) during fruit development and maturation
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0308814603000979?via%3Dihub - Effect of Five Different Stages of Ripening on Chemical Compounds in Medlar (Mespilus germanica L.)
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/labs/pmc/articles/PMC6259355/ - Mineral composition of medlar (Mespilus germanica) fruit at different stages of maturity
https://www.researchgate.net/publication/230165739_Mineral_composition_of_medlar_Mespilus_germanica_fruit_at_different_stages_of_maturity - Phytochemical and antioxidant characteristics of medlar fruits (Mespilus germanica L.)
https://www.researchgate.net/publication/232259484_Phytochemical_and_antioxidant_characteristics_of_medlar_fruits_Mespilus_germanica_L - Medicinal benefits and usage of medlar (Mespilus germanica) in Gilan Province (Roudsar District) Iran
https://academicjournals.org/journal/JMPR/article-abstract/6669A2526228 - Functional Properties of Fruits of Common Medlar (Mespilus germanica L.) Extract
https://www.mdpi.com/2076-3417/11/16/7528 - Flavonoids as antioxidants
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/10924197/ - Antidiabetic Effects of Simple Phenolic Acids: A Comprehensive Review
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26634804/ - Inflammation and Oxidative Stress in an Obese State and the Protective Effects of Gallic Acid
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30577684/ - Antimicrobial activity of gallic acid against food-related Pseudomonas strains and its use as biocontrol tool to improve the shelf life of fresh black truffles
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29227905/ - Scurvy
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/labs/pmc/articles/PMC2567249/ - Characterization of chemical molecular thermal and rheological properties of medlar pectin extracted at optimum conditions as determined by Box-Behnken and ANFIS models
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0308814618313712 - Health-promoting properties of pectin
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24864109/ - Dietary polyphenols as potential nutraceuticals in management of diabetes: a review
https://link.springer.com/article/10.1186/2251-6581-12-43 - Polyphenol Contents and Antioxidant Properties of Medlar (Mespilus germanica L.)
https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Fevzi-Topal-2/publication/267361786_Polyphenol_Contents_and_Antioxidant_Properties_of_Medlar_Mespilus_germanica_L/links/5591134708ae1e1f9bae4a68/Polyphenol-Contents-and-Antioxidant-Properties-of-Medlar-Mespilus-germanica-L.pdf - Effect of Medlar (Mespilus germanica L) fruit and seed flavonoids on learning and memory and also hippocampal CA3 neurons in Alzheimer′s rats
https://www.omicsonline.org/proceedings/effect-of-medlar-mespilus-germanica-l-fruit-and-seed-flavonoids-on-learning-and-memory-and-also-hippocampal-ca3-neurons–57447.html - Chapter 7 – Specific Features of Table Wine Production Technology
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/B9780128008508000077
Read full bio of Anastasia Kirilchik
Read full bio of Varsha Patnaik
Read full bio of Ravi Teja Tadimalla
Read full bio of Payal Karnik




















Community Experiences
Join the conversation and become a part of our empowering community! Share your stories, experiences, and insights to connect with other beauty, lifestyle, and health enthusiasts.