Oat Milk: 5 Health Benefits, Nutrition Facts, And DIY Recipe
Dairy-free and nutritious, discover why this milk is featured in everyone's coffee order.

Image: Shutterstock
Plant-based diets are being popularized for many reasons. Dairy specifically is being replaced by many plant-based products, and oat milk is preferred by many among the plant-based milk options available. Oat milk is chosen primarily for its simple preparation process and easy storage.
Oat milk is one of the most sustainable options for milk. It is also easier to prepare and store. The graph below shows how low-impact the preparation process of oat milk is compared to other types of milk that involve more water consumption and leave a higher carbon footprint.
 Know Your Ingredient: Oat Milk
Know Your Ingredient: Oat MilkWhat Is It?
A non-dairy, creamy liquid extracted from whole oat grains that’s used as a vegan alternative to cow milk.
What Are Its Benefits?
Lowers cholesterol levels, promotes bone health, manages blood sugar levels, and helps ease constipation.
Who Can Use It?
Anyone looking for a lactose-free, low-calorie, and vegan alternative to cow milk.
How Often?
You can consume oat milk daily.
Caution
Avoid consuming commercial oat milk filled with additives and preservatives as it may lead to gastrointestinal discomfort.

Sustainability Of Oat Milk As Compared To Other Milk Types
Source: Statista
More importantly, it also offers many health benefits. Continue reading to know more about the benefits of oat milk, its nutrition, how to make it, and its possible side effects.
In This Article
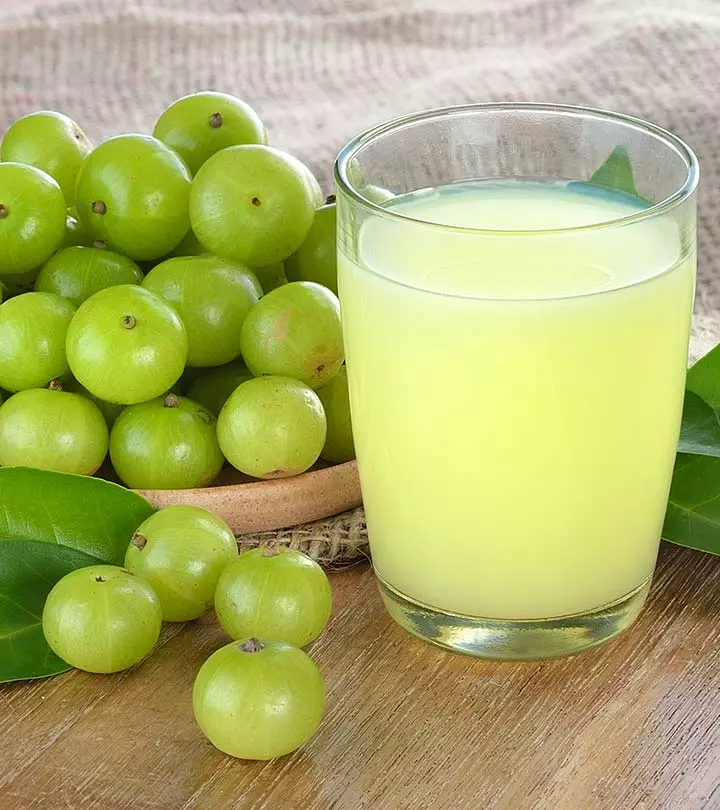
What Is Oat Milk?
Oat milk is a non-dairy, lactose-free, and vegan-friendly alternative to cow milk. It’s made from oats that have been soaked in water, blended, and strained. The resultant milk can be consumed as is or you can also add natural sweeteners like vanilla, dates, or cinnamon for extra flavor. Oat milk is majorly used in many vegan diets and is being popularized for its low-calorie content.
Oat milk replaces dairy in many recipes and tastes delicious. Its lactose-free nature also makes it a perfect choice for those with lactose intolerance. It is also nut-free and ideal for individuals with nut allergies. In short, it is a great alternative milk option, especially for those just starting to dabble with plant-based food options.
Despite all these benefits, it is important to learn what it tastes like in order to really appreciate it. The next section gives you an idea.
Key Takeaways
- Oat milk may help reduce cholesterol levels with its soluble fiber content. The high fiber content in oat milk can also promote good digestion and help prevent constipation.
- Oat milk may be suitable for individuals who are lactose intolerant or have a dairy allergy.
- To prepare oat milk, simply blend the oats and water and strain the mixture to remove any solids; it is easily made at home.
- We recommend you check the ingredients label and choose a brand that contains no additives to get the best quality oat milk.
What Does Oat Milk Taste Like?
Oat milk has a mild and slightly sweet flavor with a smooth, creamy texture. It’s often described as having a naturally neutral taste with a hint of sweetness, which comes from the natural sugars present in oats. Unlike some plant-based milks, oat milk doesn’t have a pronounced nutty or beany flavor, which makes it a viable alternative to dairy milk.
Oat milk pairs well with coffee, tea, and cereals. Its texture is one of its strengths as it froths nicely for lattes and adds creaminess to smoothies. It can also be used as a substitute for dairy milk in various recipes without significantly altering the flavor.
 Trivia
TriviaOat milk is a healthy, dairy-free alternative that is rich in calcium and other essential nutrients. Know more in the next section.
Oat Milk Nutrition
100 ml of oat milk contains the following nutrients (1):
| Energy | 50 Kcal |
|---|---|
| Fiber | 0.8 g |
| Protein | 1.25 g |
| Calcium | 146 g |
| Carbohydrates | 6.67 g |
| Sugars | 2.92 g |
| Fatty acids | 0.21 g |
| Sodium | 42 mg |
| Vitamin B12 | 0.0005 mg |
| Riboflavin | 0.25 mg |
| Phosphorus | 112 mg |
| Iron | 0.12 mg |
| Potassium | 162 mg |
| Cholesterol | 0 mg |
Thanks to these nutrients, oat milk offers important health benefits. Read on to learn more about them.
Health Benefits Of Oat Milk
1. May Lower LDL Cholesterol
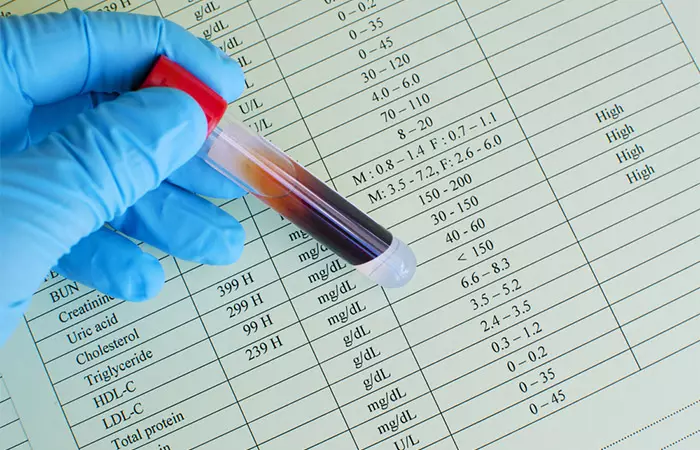
Oat milk has dietary fiber (especially β-glucan). In studies, intake of oat milk had resulted in significantly lower serum total cholesterol and LDL cholesterol levels (2).
Consumption of sufficient quantities of oat products has been shown to reduce cholesterol and decrease the risk of cardiovascular disease. These effects could be attributed to the gel-forming properties of β-glucan. This fiber plays a role in cholesterol metabolism and removes intestinal cholesterol for excretion.
β-glucan in oats also modulates the gut microbiota, particularly those bacterial species that influence body bile acid metabolism and production of short-chain fatty acids. These factors play a role in cholesterol reduction too (3).
2. May Promote Bone Health
Antioxidants such as vitamin E are known to protect against the damaging free radicals. They also help reduce the risk of arthritis (4). Oat milk contains a decent amount of calcium, iron, potassium, magnesium, phosphorus, zinc, vitamin D, and various other minerals. These play a vital role in maintaining bone mineral density.
Commercial oat milk is also a good source of vitamin B12, which has been linked to healthy bones and a lower risk of osteoporosis (hollow and porous bones). However, more research is warranted in this regard.
3. May Help Manage Constipation

Intermediate soluble and fermentable fibers are abundant in oats (5). These fibers may help reduce constipation by increasing stool bulk and accelerating colon transit.
Fermenting fiber produces short-chain fatty acids, like butyrate or acetate, which accelerate colon transit. These fatty acids also may improve stool consistency and aid in easing constipation.
4. May Regulate Blood Sugar Levels
Dietary fiber helps regulate blood glucose and blood lipid levels due to its non-digestibility in the small intestine and fermentation in the colon. Oats and oat products (like oat milk) are a good source of soluble dietary fiber rich in β-glucan, which may help reduce postprandiali In medical terms, it refers to anything carried out after a meal, such as a test. It is the opposite of preprandial. glucose and insulin responses.
β-glucan may also improve insulin sensitivity and maintain glycemic control. In studies, oats intake had significantly reduced the concentrations of glycosylated hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c), fasting blood glucose (FBG), total cholesterol, and low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) (6).
5. May Accelerate Weight Loss

Diets rich in fiber may contribute positively to long-term weight management. The beneficial role of β-glucan in insulin resistancei The inability of cells to accept the hormone insulin, which is responsible for controlling glucose in the blood. and obesity is being continuously documented. This fiber forms highly viscous solutions in the human gut and improve satietyi A feeling or state of being satisfied with regards to food consumption, acquired at the end of a meal. .
β-glucan also helps in the generation of short-chain fatty acids. These short-chain fatty acids also promote satiety by modulating various appetite-regulating hormones like PYY, GLP-1, and ghrelin (7). However, research in this area is limited, and further investigation is warranted.
Mike Pridgen, a blogger, shares his experience of switching to oat milk most hilariously: “Back up, peasants! Make way for the king! Let it be known that I, Michael A. Pridgen, have switched to oat milk and am now perfect as a result (i).” He continues, “Due to my correct and infallible lactose-free lifestyle, I can do anything and go anywhere and will never be sick or injured in any way.”
Oat milk is being popularized for its proven health benefits and many are including it in their diet as a healthy alternative to regular milk. But it may cause some side effects in a few. Learn more in the next section.
Potential Side Effects Of Oat Milk
- Processed Varieties May Have High Sugar And Preservatives
Commercial oat milk is filled with additives, preservatives, and artificial flavorings. So, it can affect your digestive system and intestinal flora. Oat milk also contains added sugars, especially when sweetened. It can be unhealthy and cause diarrhea when combined with the high fiber content. Hence, always try opting for sugar-free varieties of oat milk.
- May Cause Gastrointestinal Discomfort

Oat milk may cause stomach upset in a few due to its high fiber content. One may also experience intestinal gas, bloating, flatulence, burping, and stomach pain. The soluble fiber in oat milk may absorb excess water, turn it into a gel-like substance, and possibly slow down the digestion process. If you are intolerant or allergic to oats, you may also experience vomiting or nausea.
Heather Hanks, a nutritionist, says oats and oat milk contain a compound called phytic acid that acts as an anti-nutrient and blocks the proper absorption of certain minerals. It may also cause digestive inflammation.
You can eliminate most of the phytic acid content by soaking your oats overnight before making oat milk.
However, these side effects are rare and are observed with the excess intake of commercial oat milk containing high sugar or preservatives. You can reduce the risk of these side effects by preparing oat milk at home.
How To Make Your Own Oat Milk
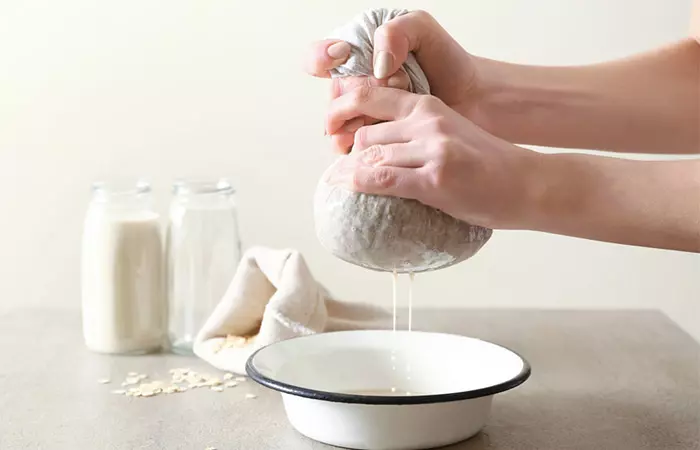

- Soak a cup of oats in water for about 15 minutes. After soaking, your oats will blend better and strain out more easily.
- Rinse and drain the oats. This ensures your oat milk has a nice, clean flavor and creamy (not slimy) texture.
- Add some freshwater, maple syrup, and vanilla. Add the water in two equal batches for smooth blending. Add a pinch of salt to enhance the milk’s flavor.
- Blend until smooth.
- Strain and chill.
- Pour the mixture over a fine-mesh sieve into a pitcher. The sieve will catch any stubborn oat bits that refuse to blend. For the best flavor, chill your oat milk for at least 30 minutes before serving.
 Trivia
TriviaYou can use this oat milk as a substitute for regular milk in your delicacies for a unique flavor. However, the protein content in oat milk is a point of concern when you are replacing regular dairy with it. How much protein does oat milk contain? Let us understand in the next section.
How Much Protein Does Oat Milk Contain?
100 ml of oat milk contains 1.25 grams of protein. It is comparatively less than regular milk. Hence, if you are substituting regular milk with oat milk, ensure you also include other protein-rich foods in your diet regularly.
Oat milk is one of the popular choices for substituting dairy. It contains important nutrients that are associated with several health benefits. From improving heart health and boosting skin health to supporting the immune system, this dairy-free milk can be a great addition to your regular diet. However, commercially available oat milk may cause some undesirable side effects. Hence, caution is advised. Oat milk is easy to prepare at home. It also has a low calorific value with a unique taste. Try including it in your diet regularly.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is oat milk good for you every day?
Yes, daily consumption of oat milk may reduce cholesterol levels and the risk of arthritis (2), (4).
Which is better: almond or oat milk?
Both almond milk and oat milk are beneficial for your health. Oat milk is low-fat and is rich in protein, iron and sodium (1). While almond milk benefits are attributed to its low calories and carbohydrates, and rich calcium content (8). You can choose as per your preference.
Is oat milk good for your skin?
Yes, oat milk is rich in calcium which may help in wound healing and skin barrier formation (1), (9).
Illustration: Oat Milk: Nutrition, Benefits, And How To Make It

Image: Stable Diffusion/StyleCraze Design Team
Oat milk is a tasty and nutritious substitute for dairy milk. Watch this video to find out about the surprising health advantages of oat milk!
Personal Experience: Source
StyleCraze's articles are interwoven with authentic personal narratives that provide depth and resonance to our content. Below are the sources of the personal accounts referenced in this article.
i. I Switched To Oat Milk And Now I’m Perfecthttps://medium.com/slackjaw/i-switched-to-oat-milk-and-now-im-perfect-d2f6731fac73
References
Articles on StyleCraze are backed by verified information from peer-reviewed and academic research papers, reputed organizations, research institutions, and medical associations to ensure accuracy and relevance. Read our editorial policy to learn more.
- Oat Milk
https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/719016/nutrients - Consumption of oat milk for 5 weeks lowers serum cholesterol and LDL cholesterol in free-living men with moderate hypercholesterolemia
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/10749030 - The Cholesterol-Lowering Effect of Oats and Oat Beta Glucan: Modes of Action and Potential Role of Bile Acids and the Microbiome
https://www.frontiersin.org/journals/nutrition/articles/10.3389/fnut.2019.00171/full - Nutritional advantages of oats and opportunities for its processing as value-added foods – a review
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4325078 - Diets for Constipation
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4291444/ - The Metabolic Effects of Oats Intake in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4690088/ - Beta Glucan: Health Benefits in Obesity and Metabolic Syndrome
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3236515/ - PLAIN ALMOND MILK, PLAIN
https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/2150252/nutrients - Skin Barrier and Calcium
https://www.researchgate.net/publication/324776853_Skin_Barrier_and_Calcium
Read full bio of Dr. Pallavi Srivastava
Read full bio of Aparna Mallampalli
Read full bio of Ravi Teja Tadimalla
Read full bio of Himanshi Mahajan




























Community Experiences
Join the conversation and become a part of our empowering community! Share your stories, experiences, and insights to connect with other beauty, lifestyle, and health enthusiasts.