Red Spots On The Skin: Causes, Treatments & How To Get Rid Of Them
Unmask the red marks on your skin, from cause to treatment.
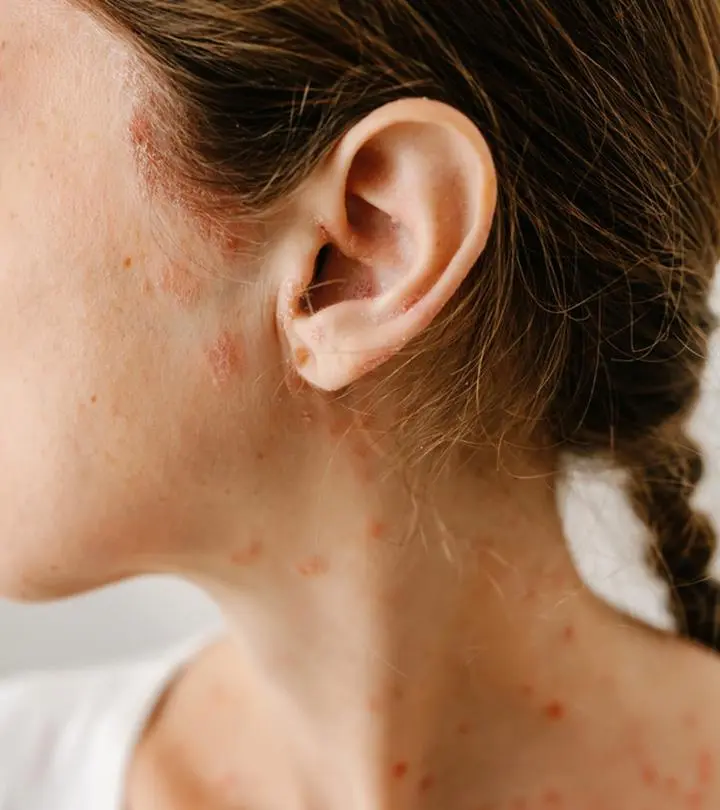
Image: StyleCraze Design Team
Waking up to find random red spots on your skin, that sprouted overnight with no apparent cause, can be troubling indeed. Sometimes, they are simply tiny red dots or discolored patches and other times, they may be swollen little bumps, filled with pus, causing a lot of pain, itching, or general discomfort.
The causes for these red spots range from subconscious scratching and insect bites to chronic skin conditions like psoriasis or an undiagnosed underlying condition. If these red spots persist for a prolonged period, consulting a medical expert is the ideal course of action to ensure appropriate and prompt treatment. However, these spots are only temporary in most cases, causing slight irritation, but can be managed with over-the-counter medication, home remedies, and some basic precautions.
Explore some common plausible causes of red spots on the skin, discuss rare possibilities, correct treatment methods, and helpful home care tips to expedite the healing process in this article. Keep reading to learn more.
In This Article
What Are Red Spots On The Skin?
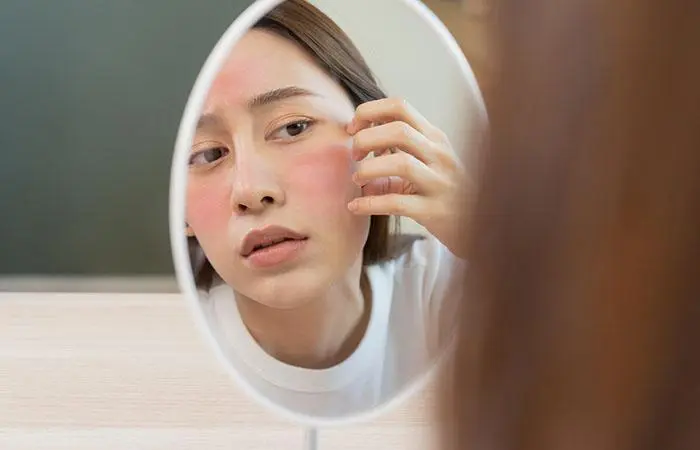

The most common misconception is that red spots are, more often than not, caused by acne. In some cases, you may experience tiny red spots with a burning sensation, itching, and scaly skin. These spots can have multiple causes ranging from acute skin infections to serious conditions. They may appear as tiny red bumps with scaly skin or even flat patches. Sometimes, these spots can be accompanied by swollen skin and pus-like discharge.
However, the symptoms and appearance vary according to the underlying condition. Therefore, it is necessary to learn the causes of these spots. Keep reading to learn more about it.
Key Takeaways
- Red spots on the skin may result from various conditions, ranging from mild irritations to serious diseases.
- Some of the conditions causing red spots include eczema, cherry angiomas, heat rash, keratosis pilaris, contact dermatitis, and meningitis.
- Home remedies such as oatmeal baths, cold compresses, aloe vera gel, and coconut oil can help soothe and reduce red spots.
- However, it is important to seek medical attention if red spots worsen, persist, or show signs of infection.
What Causes Red Spots On Skin
There are several conditions that may cause red color spots on the skin. Some are harmless and will disappear in a few days, while others may require treatment with home remedies or a consultation with a healthcare professional.
Note: It is best recommended to consult a dermatologist if you notice any red spots or patches (or any discoloration on the skin) to properly diagnose the cause and treatment.
- Leukemia
Leukemias are serious cancers that affect the blood and bone marrow. When leukemia affects the skin, you notice small bumps and spots on the skin called leukemia cutis (1). These bumps or spots appear as red or purplish-red dots or patches, sometimes darker in color. It affects the layers of the skin and tissue beneath it.
In acute myeloid leukemiai A fast-growing cancer of the blood and bone marrow characterized by the rapid accumulation of abnormal white blood cells. (AML), low platelet levels can lead to the development of small purple, red, or dark spots known as petechiae (2). These are tiny, non-blanchingi Refers to skin lesions or spots that do not turn pale when pressed, indicating bleeding beneath the skin. spots smaller than 2 mm that appear on the skin and mucous membranesi Specialized linings in areas of the body exposed to external environments, such as the mouth, nose, throat, and genitalia. (3).
Symptoms of leukemia include:
- Small red spots
- Mouth sores and swollen gums
- Easy bruising and bleeding
- Skin color changes
- Skin infections
Treatment
In this case, seeking medical care is important. Treatment for red spots due to leukemia typically involves chemotherapyi Treatment using drugs to kill or shrink tumors, prevent cancer from spreading, or alleviate symptoms. tailored to the specific type of cancer. This treatment not only addresses blood issues but may also help improve skin problems simultaneously. In some instances, radiation therapy may be used for more challenging cases or to alleviate symptoms (1).
- Cherry Angioma
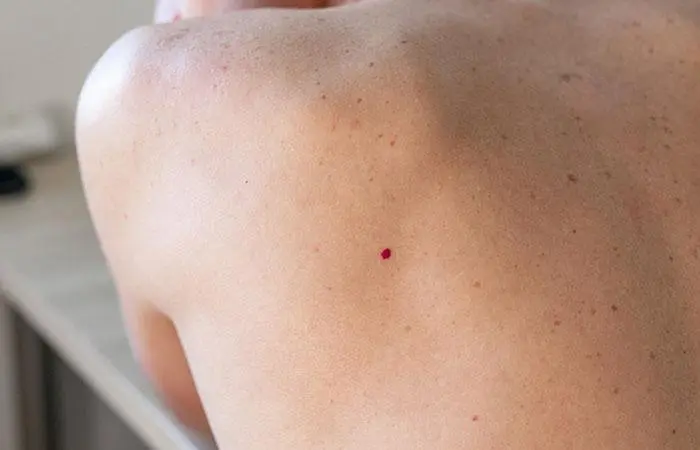
Cherry angiomas are the most common type of skin growth caused by blood vessels. They look like small, bright red bumps with a pale ring around them (4). They usually appear as multiple spots on the trunk or upper arms and legs and are rarely found on the face, hands, or feet.
Symptoms of cherry angioma include:
- Red, flat spots and grow into 1 to 5 mm red bumps
- May bleed if injured
- May turn blue in some cases
Treatment
These spots are usually asymptomatic but may bleed if injured. Some people may choose to remove them for cosmetic reasons or to prevent bleeding. The treatment to remove small spots involves local anesthesia followed by electrocauterizationi Surgical technique where a high-frequency electric current is applied to tissue to freeze, cut, or destroy it. . Larger spots are typically treated with shave excisioni Surgical procedure performed under local anesthesia to remove skin lesions or growths by shaving them off with a blade. combined with electrocauterization.
 Trivia
Trivia- Heat Rash
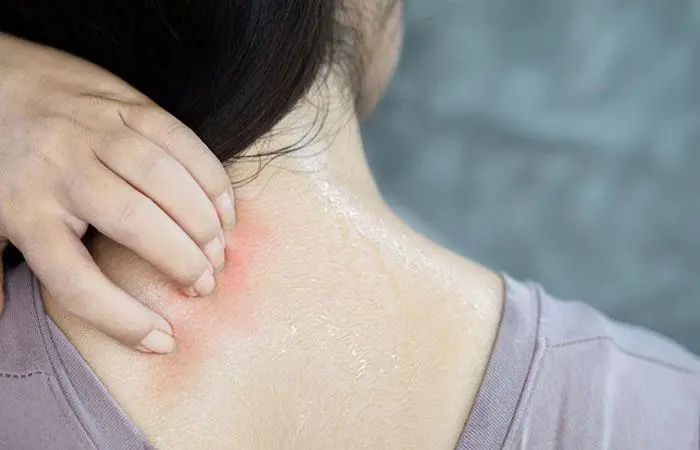
A heat rash may result in small, red, itchy, and prickly spots on the skin. It typically appears in areas where sweat collects, such as the groin, chest, back, arms, and armpits (5).The spots appear as tiny blisters, about 1 to 2 mm in size, and affect adults and newborns typically under 2 weeks old.
Symptoms of heat rash include:
- Groups of small, firm, and flesh-colored bumps
- Feeling itchy or prickly
- Decreased or no sweating in the affected area
- Feeling dizzy
- Experiencing nausea
Treatment
Treatment for heat rash involves managing sweating and blocked sweat ducts, which are usually the main causes. This includes staying in cooler environments, wearing breathable clothing, exfoliating the skin, and removing any items that cover the skin like bandages or patches. However, it may vary based on the type of heat rash you have. Certain types of heat rash may resolve within a day, while others may require antibiotics for treatment. It is best recommended to consult a dermatologist to check which type of heat rash you have and what is the best course of action.
- Keratosis Pilaris
This condition typically manifests as small bumps around the hair follicles with redness. People with keratosis pilaris have red, bumpy skin that isn’t painful or itchy (6). These small bumps often occur on the upper arms, thighs, and buttocks, but may also appear on the face, trunk, and lower legs.
Symptoms of keratosis pilaris include:
- Dry skin
- Painless small red spots
- Red and swollen bumps if squeezed.
- Appearance of bumps may cause emotional distress.
Treatment
The red spots caused by keratosis pilaris may be managed by maintaining good hygiene, using gentle soaps, and avoiding picking at the bumps. Using creams like salicylic acid (6%) or urea (20%) may make the skin smoother. Sometimes, treatments like retinoids or vitamin D creams and chemical peels with glycolic acid may also help improve the condition.
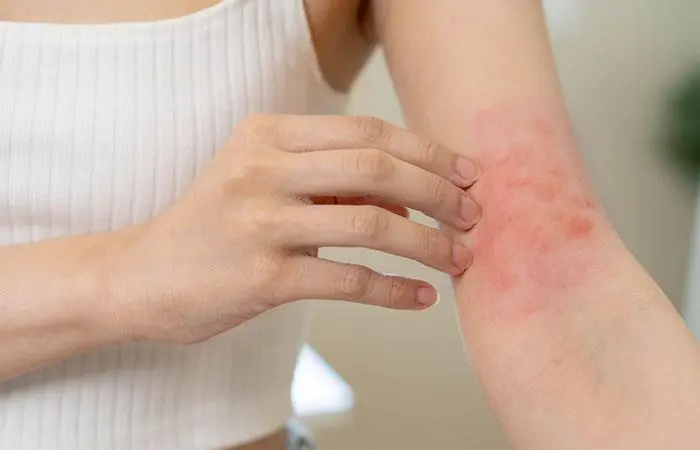
- Contact Dermatitis
This is a common skin allergy triggered by contact with an allergen or irritant, resulting in an itchy, red rash (7). Symptoms typically appear 1 to 3 days after exposure to the trigger and peak around 3 to 4 days later.
Symptoms of contact dermatitis include:
- Burning
- Itching
- Stinging
- Soreness
- Pain
- Dry, flaking skin
- Bright, flushed rash
- Clusters of small dots on the skin
- Fluid-filled blisters that crust over
- Dark, thickened skin
- Sunlight sensitivity
Treatment
Treating contact dermatitis depends on its main cause and how bad the symptoms are. Mild to moderate cases of dermatitis usually get better if you avoid whatever caused the irritation. This means you may have to avoid harsh chemicals in skin products, nickel or gold jewelry, certain foods, or medicines that may trigger allergic reactions. You can also use over-the-counter 1% hydrocortisone cream if the symptoms are mild. If that does not help, consult a doctor who can prescribe stronger steroid creams if needed.
- Atopic Dermatitis
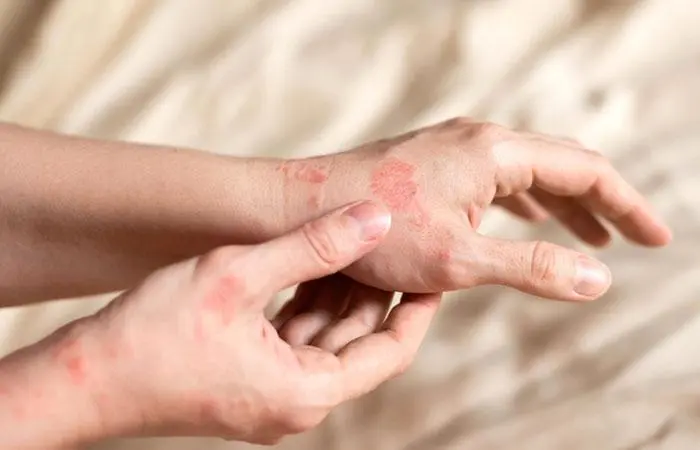
Atopic dermatitis is the most common chronic inflammatory skin disease and a type of eczema. The condition’s symptoms vary by age. Infants develop swollen bumps and plaques, sometimes with blisters or crusts, on the scalp, face, and arms or legs while adults often have thickened skin patches, mainly on the hands (7).
According to the 2021 National Health Interview Survey (NHIS) conducted by the National Center for Health Statistics (NCHS), the prevalence of eczema was higher among women (8.9%) compared to men (5.7%). The percentage of adults with eczema shows a decreasing trend with age, dropping from 8.4% in the 18–44 age group to 6.5% in those aged 45–64, 6.8% in individuals aged 65–74, and further down to 5.5% in adults aged 75 and older.
Symptoms of atopic dermatitis include:
- Swollen, red bumps
- Plaques with blisters or crusting
- Redness
- Flakiness
- Thick, scaly plaques
Treatment
Taking prescription medications, such as steroids and antihistaminesi Medications that block the action of histamine to reduce allergic reactions such as itching, swelling, and redness. , may help manage atopic dermatitis. There are also light therapy treatments that may provide effective relief. However, you need to take proper care of your skin to improve the condition. Regular application of a moisturizer is essential to treat dry, cracking skin. Also, it is best to avoid triggers like dry air, stress, wool products, and allergens.
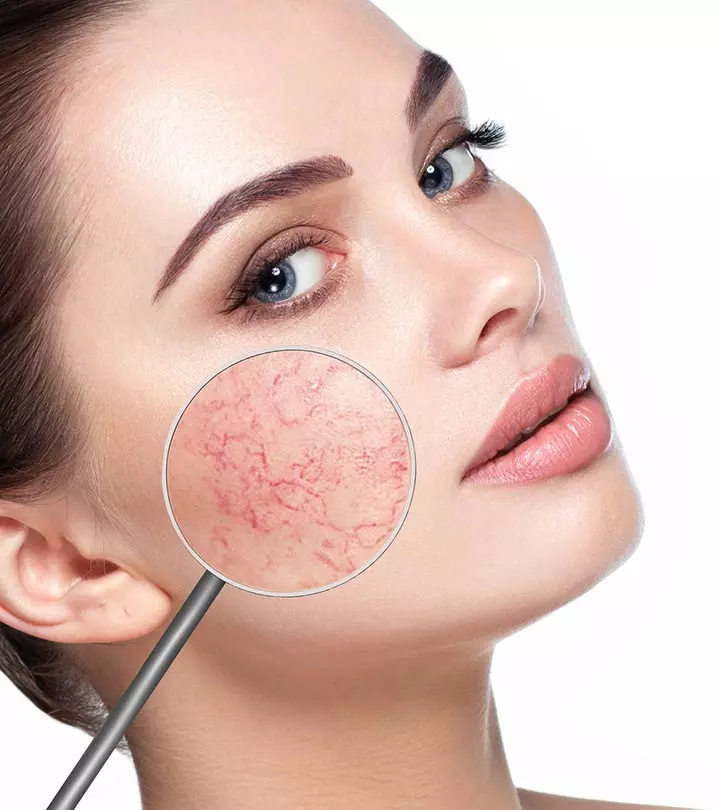
- Rosacea
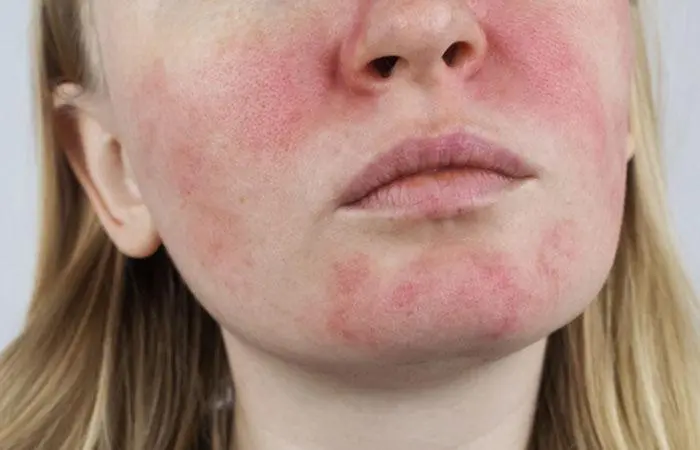
Rosacea is a common chronic inflammatory disease that manifests as recurrent flushing, redness, visible blood vessels, bumps, or pimples on the nose, chin, cheeks, and forehead (8). Though it usually only affects the skin, it has been linked to other health issues like neurological diseases, inflammatory bowel disease, and heart diseases.
Symptoms of rosacea include:
- Skin irritation
- Visible blood vessels beneath the skin
- Clusters of small red bumps
- Thickened skin on the face
- Inflammation of the eyelids
- Blurred vision
- Dryness, redness, tearing in the eye
- Tingling or burning sensation in the eye
- A feeling of a foreign object in the eye
- Sensitivity to light
Treatment
There are many ways you can manage rosacea symptoms. Avoiding triggers like sunlight, alcohol, and harsh chemicals is important. Also, you should wash your face with mild cleansers regularly and use moisturizers frequently. Always apply a broad-spectrum sunscreen with SPF 30 or higher. Medical treatments for rosacea include oral and topical medications, as well as therapies like laser or light treatments.
- Ringworm
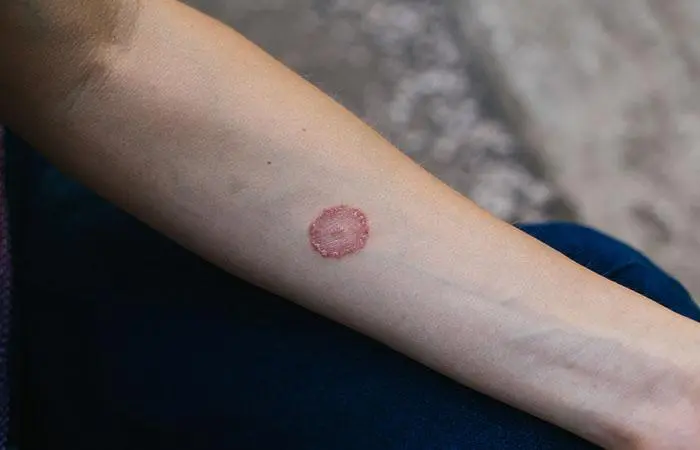
Tinea corporis, commonly known as ‘ringworm,’ appears as a defined oval or circular patch on the skin. It is a contagious fungal infection caused by common mold-like parasites. It affects most areas of the skin except for the hands, feet, scalp, beard, face, groin, and nails (9).
Symptoms of ringworm include:
- Oval or circular patch on the skin
- Mild itching
- Mildly red and scaly bumps
- Skin inflammation
Treatment
Topical treatments are often effective, for mild cases of ringworm infection, when applied once or twice daily for about two to three weeks. However, if these treatments do not work and there is no sign of improvement, you may have to start oral medication. Since fungi prefer warm, moist conditions, you may have to wear loose, lightweight clothing to avoid sweating. It is important to keep the skin clean and dry.
- Drug Rash
A drug rash refers to a skin reaction caused by medication that often shows up as a skin reaction. These reactions can vary from mild in most cases to severe or life-threatening in others (10).
Symptoms of a drug rash include:
- Redness spreading and merging together
- Facial swelling
- Pain or tenderness in the area
- Small, palpable red or purple spots
- Blisters or peeling of the skin
- Erosion of mucous membranes
- Hives
- Swelling of the tongue
Treatment
Treating a drug rash involves stopping the medication causing the rash, if possible. You may use cool compresses and moisturizers to soothe the skin. Also, there are a few over-the-counter antihistamines that may help soothe the itching. However, severe cases may need prescription creams or oral medications from a doctor.
- Psoriasis
Psoriasis is a chronic inflammatory skin condition marked by red patches covered with silver-colored scales. These patches often appear on the elbows, knees, scalp, and lower back. Though this skin condition can start at any age, there are two main age groups it is typically common in, 15 to 20 years old and another peak between 55 to 60 years old (11).
Symptoms of psoriasis include:
- Raised patches with scales
- Small, drop-shaped lesions
- Thick scales resembling oyster shells
- Widespread redness
- Shedding of skin
- Pus-filled bumps
- Rash in skin folds
- Thickened skin on palms and soles
- Joint inflammation
Treatment
For mild to moderate psoriasis, you may start with topical treatments as your first line of defense. Using emollients and moisturizers may strengthen your skin barrier and keep it hydrated. Your doctor may prescribe specific topical medications to reduce inflammation and scaling. These treatments help control symptoms and improve the appearance of affected areas. If your condition is more severe, combining topical therapies with phototherapy may be the best course of action.
- Meningitis
Meningitis is an infection that affects the fluid and membranes around the brain and spinal cord. It can be caused by bacteria, viruses, or fungi (12). People with meningitis often experience skin rashes and changes in skin color.
Symptoms of meningitis include (13):
- Red tiny flat spots on the skin
- Large purple patches
- Rash spreading quickly
- Severe headache
- Stiff neck
- Fever
- Drowsiness or confusion
- Nausea and vomiting
- Sensitivity to bright lights
Treatment
You need proper medical care to treat red spots caused by meningitis. The treatment usually includes antibiotics and supportive care that help manage the airway, ensure proper oxygen levels, give enough IV fluids and control fever. The choice of antibiotic depends on the bacteria causing the infection, and doctors consider the patient’s background and medical history to choose the best treatment (14).
These are some of the major causes of red spots on the skin. It is important to note that there can be other reasons for red spots such as skin inflammation. Viral infections like rubella, measles, chickenpox, and shingles may also cause red spots on the skin. These spots typically resolve once the infection is treated or the body recovers. While these conditions are generally easily resolved, some may require good aftercare and remedies for complete recovery. Keep reading to know more about it.
How To Get Rid Of Red Spots On Skin

In order to ensure the right treatment for your specific red spot affliction, it is important to know the root cause behind it, as it will determine the type of treatment you need to reduce redness on the face or anywhere else and minimize the intensity of the spots. Once you have properly diagnosed the reason behind your sports, there are a few home remedies you can try to ease the discomfort, expedite the healing process.
1. Oatmeal Bath
The topical application of colloidal oatmeal to soothe irritated skin conditions like eczema, fire burns, sunburns, rashes, and itching is a trusted age-old home remedy. Oatmeal has strong anti-inflammatory, and antioxidant properties that may be responsible for reducing skin irritation and redness (15).
- Prepare an oatmeal bath by grinding one cup of oats into fine powder, then mix into a full bathtub of lukewarm water.
- Soak in the bath for 10-15 minutes to relieve dry skin and itchiness and reduce red spots.
- After the bath, apply a good moisturizer to prevent your skin from drying out.
You can enjoy an oatmeal bath every day to alleviate your skin condition; just make sure the water is lukewarm, as hot water can further irritate your skin.
 Did You Know?
Did You Know?2. Cold Compress
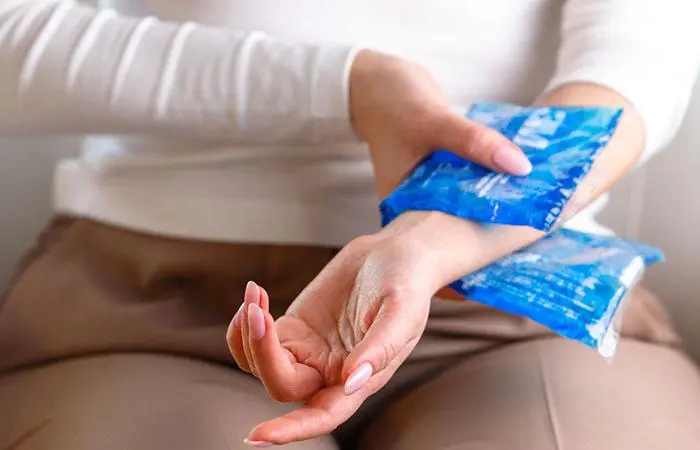

Studies show that keeping the irritated skin cool with the help of cold compresses, ice packs, gel packs, or cold water, may temporarily reduce itching, swelling, irritation, and resultant redness in cases of skin conditions like psoriasis and atopic dermatitis (16).
- Make your own cold compress by putting ice cubes or frozen vegetable cuts in a plastic ziplock bag or a clean cotton cloth.
- Apply it on the affected area for 15-20 minutes.
- Do not exceed 20 minutes per session to avoid skin sensitivity or escalated irritation.
- You can use cold compresses for 20-minute sessions several times a day to soothe irritation and redness of the skin.
- After the session, pat your skin dry and apply a good-quality moisturizer.
3. Aloe Vera
Aloe vera gel is known to soothe mild or moderate skin irritation conditions. Research shows that topical application of an aloe-based gel product may help alleviate skin conditions like acne and psoriasis (17). It has also been observed to reduce pain and speed up healing in case of skin burns.
- Wash the affected area.
- Gently pat dry with a clean towel.
- Then apply a liberal amount of aloe vera gel to the affected area.
The gel may take some time to dry and then you can continue on with your day. Make sure to use natural aloe vera or a product that uses pure hundred percent aloe vera to avoid contact with potential allergens.
A blogger and skincare enthusiast shares her experience using aloe vera to treat her eczema, highlighting the benefits of the gel. Though she felt itchy on the first day of applying aloe vera, she started seeing results by the second week. She writes, “The eczema area improved greatly, thanks to the medication and the aloe vera gel. The color around the area is almost back to normal and there’s no itchiness nor discomfort (i).” Using aloe vera helped her heal from eczema in three weeks.
4. Coconut Oil
Coconut oil is another remedy used to moisturize the skin and keep dryness-induced irritation at bay. Studies have shown that coconut oil has strong emollient properties that successfully hydrate the skin and soothe irritation in conditions like atopic dermatitis and xerosis (18). Topical application of coconut oil may help reduce the appearance of resultant red spots on the skin.
- Wash the affected area thoroughly.
- Gently pat the area dry.
- Use coconut oil as a moisturizer or lotion.
- Apply it twice a day, or as often as necessary to soothe any flare-ups or itching sensation on the skin.
Note:
When using commercial aloe vera, coconut, or oatmeal products, make sure to check the ingredients. Avoid any known allergens. The safest way to go about these home remedies is to go for pure, natural ingredients that keep the risk of further irritation minimal.
Ideally, these home remedies should be helpful in mild or moderate cases of skin irritation and red spots. However, if the spots persist even after using these remedies for 24-48 hours, it is time to see a doctor. The following section discusses a few indications of escalated skin conditions that require immediate medical attention.
When To See A Doctor
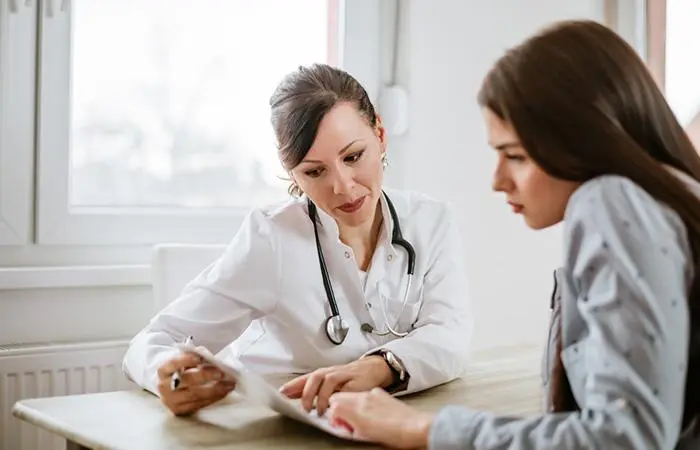

If at-home remedies or over-the-counter ointments do not help with your skin condition or, in some cases, worsen them, then you need to see the doctor immediately. Here are a few symptoms indicating the need for immediate medical intervention:
- Stubborn red spots that show no improvement despite diligent use of home remedies.
- Escalated itching, swelling, and pain in the affected area.
- Spreading of redness and irritation to the surrounding areas.
- Formation of blisters or pus oozing from the spots.
- Bleeding of the spots.
If red spots come with symptoms like fever, a bad headache, or a stiff neck, it’s important to seek medical help right away. These could be signs of serious conditions like meningitis (13). If left untreated, these worsened red spots may potentially impact your health and lifestyle. However, it may vary depending on the cause. Some of the complications include:
- Infections that may require antibiotics or even surgery (4) (9).
- Permanent discoloration or scarring on the affected skin area (19).
- Psychological strain due to being conscious about the spots may lead to depression or social anxiety (20).
The red spots on your skin can be either a cause for concern or a benign condition that resolves on its own. These spots range from harmless conditions like heat rash and cherry angiomas to more serious issues like meningitis or leukemia. While some spots may fade on their own or with simple home remedies, others need medical attention. Home remedies like oatmeal baths, cold compresses, aloe vera, and coconut oil may help soothe mild skin irritations that cause red spots. However, for persistent or severe symptoms, seeking medical attention is important to address underlying conditions or infections that may require specific treatments or medications. Timely care can help manage symptoms effectively and prevent any potential complications.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the warning signs that red spots may be serious?
Watch out for warning signs like spots spreading quickly, the development of blisters, or symptoms like fever, fatigue, or joint pain. These could mean something serious and require immediate medical attention.
Can stress cause tiny red spots or rashes?
Stress may exacerbate certain skin conditions like eczema or psoriasis, leading to red spots or rashes (21). However, stress is not known to cause skin rashes.
Are petechiae serious?
Petechiae can indicate serious conditions like infections or blood disorders (3). If you notice unexplained petechiae, it is important to seek medical advice promptly.
Are red spots signs of skin cancer?
Red spots can be benign, like cherry angiomas, but some types of skin cancer may present as red or pink spots. Therefore, it is best to have any new or changing spots evaluated by a dermatologist as soon as you notice them.
Are red spots on the skin contagious?
Generally, red spots like cherry angiomas or heat rash are not contagious. However, infections like chickenpox can cause contagious red spots.
Can sun exposure cause red spots on the skin?
Sun exposure can cause sunburn, leading to redness and sometimes red spots. Prolonged exposure without protection can also cause conditions like polymorphous light eruption that causes itchy red spots and small bumps on sun-exposed skin (22).
Can red spots on the skin be related to an underlying autoimmune condition?
Yes, autoimmune conditions like psoriasis and eczema may cause red spots or rashes as a result of inflammation affecting the skin.
Can a vitamin D deficiency cause red spots?
Vitamin D deficiency is not directly linked to red spots. However, it may affect skin health, potentially contributing to certain skin conditions indirectly (23).
Can a vitamin C deficiency cause red spots?
A vitamin C deficiency can lead to scurvy, causing bleeding under the skin that appears as red spots or petechiae in severe cases (24).
Can lemon remove red spots?
Lemon juice is sometimes used in home remedies to lighten dark spots, but it may irritate sensitive skin. Therefore, it is best to not use lemon on the red spots. Consult a dermatologist and seek medical advice to help treat the spots.
Can a B12 deficiency cause red spots on the skin?
A B12 deficiency can lead to various skin changes, but red spots specifically are less common (25).
Red spots on the skin can result from conditions treatable at home or requiring medical attention. While various causes exist, some are particularly common. What are those? Watch this video to learn more.
Personal Experience: Source
StyleCraze's articles are interwoven with authentic personal narratives that provide depth and resonance to our content. Below are the sources of the personal accounts referenced in this article.
(i) My eczema treatment ( part 3 ): pure aloe vera sap
https://myorganicjourney11.blogspot.com/2012/09/my-eczema-treatment-part-3-pure-aloe.html
References
Articles on StyleCraze are backed by verified information from peer-reviewed and academic research papers, reputed organizations, research institutions, and medical associations to ensure accuracy and relevance. Read our editorial policy to learn more.
- Leukemia cutis
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK541136/ - Acute myeloid leukemia
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK507875/ - Petechiae
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK482331/ - Cherry hemangioma
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK563207/ - Miliaria
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK537176/ - Keratosis pilaris
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK546708/ - Contact dermatitis
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK459230/ - Rosacea
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK557574/ - Tinea corporis: an updated review
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7375854/ - Cutaneous adverse drug reaction
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK533000/ - Psoriasis
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK448194/ - Meningitis
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2804524/ - Skin rash in meningitis and meningoencephalitis
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3719428/ - Meningitis
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK459360/ - Anti-inflammatory activities of colloidal oatmeal (Avena sativa) contribute to the effectiveness of oats in treatment of itch associated with dry, irritated skin
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25607907/ - Cooling the Itch via TRPM8
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6301073/ - Aloe Vera
https://www.nccih.nih.gov/health/aloe-vera - In vitro anti-inflammatory and skin protective properties of Virgin coconut oil
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6335493/# - Postinflammatory hyperpigmentation
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK559150/ - Psychosocial aspects of rosacea with a focus on anxiety and depression
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5844253/ - Psychological stress and atopic dermatitis: a focus group study
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC10579569/ - Polymorphic light eruption
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK430886/ - Comparison of vitamin D levels in patients with and without acne: a case-control study combined with a randomized controlled trial
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27560161/ - Vitamin C deficiency as a mimicker of a coagulation disorder
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/38417944/ - Cutaneous lesions and vitamin B12 deficiency
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2294086/
Read full bio of Terri L Watts
Read full bio of Swathi E
Read full bio of Anjali Sayee
Read full bio of Monomita Chakraborty





















Community Experiences
Join the conversation and become a part of our empowering community! Share your stories, experiences, and insights to connect with other beauty, lifestyle, and health enthusiasts.