Seitan Nutrition: Benefits, Side Effects, And How To Make It
Relish your taste buds and refresh your health with this protein-rich wheat meat.

Image: Shutterstock
From mimicking the taste of meat to being one of the best alternatives to animal-based protein sources, seitan’s nutritional value is commendable. You can never go wrong with adding seitan to your diet or substituting meat with it. Seitan’s resemblance to meat in terms of taste and texture can even make a pure “non-vegetarian” doubt their taste buds.
But why is it more popular than other meat alternatives? How is seitan prepared? And is it easily available? We have all the answers for you. In this article, you will learn all about seitan, its nutrition profile, health benefits, and preparation. Read on!
In This Article
What Is Seitan?
Seitan is a dense and chewy plant-based meat substitute made of wheat gluteni A structural protein found in certain grains like wheat and barley. It helps bind the food together and make it stretchy. flour.
It is commonly prepared using vital wheat gluten or whole-wheat flour. Prepared wheat dough is rinsed to remove the starch, resulting in a sticky mass of protein known as seitan. It can be cooked, flavored, and used as an ingredient in burgers, deli slices, and hot dogs. Since it is prepared from wheat, this ingredient is also known as “wheat meat.”
This popular meat substitute has a distinguishable texture. Sarah, a blogger who tried seitan for the first time said, “I can’t really describe seitan, other than to say I find it just as delicious and versatile as tofu and tempeh (i).” It has a savory meat-like taste, making it easy to combine with several different ingredients and modify it to fit various cuisines. The versatility of this ingredient has contributed to its rise in popularity over the years. Though the Chinese have been using this ingredient as a meat replacement for vegans and vegetarians for centuries, it gained popularity when Buddhists started using it. Soon, this vegan protein became popular in the US and picked up the Japanese-derived name “seitan” in the 1960s.
 Quick Tip
Quick TipApart from being known as a substitute for meat, it contains nutrients that help improve your overall health. Learn more about its nutritional value in the next section.
Key Takeaways
- Seitan is a plant-based alternative to meat derived from animals.
- It is high in protein and low in fat and carbohydrates.
- You can prepare it at home or buy pre-packed seitan and use it as a substitute for burgers, sausages, or burritos.
- People with gluten and wheat allergies should not consume seitan.
Seitan – Nutrition Facts
Seitan is low in fat, calories, and carbohydrates but
high in protein.
Additionally, it contains considerable amounts of minerals like iron, calcium, and sodium. While the nutrition content may differ based on brands and preparations, below is the nutritional data for the average seitan available in stores (1).
| Nutrients | Amount (in 100 gm) |
|---|---|
| Energy ProteinTotal lipid (fat) Carbohydrate Fiber Sugars Calcium Iron Sodium Polyunsaturated fatty acids | 141 kcal 24.7 g 2.35 g 5.88 g 1.2 g 2.35 g 24 mg 1.69 mg 447 mg 1.18 g |
Like all plant-based protein foods, seitan also contains some amounts of essential amino acids (2). However, they may be in limited amounts only.
 Quick Tip
Quick TipIf you are looking for other plant-based sources of protein, consider nuts, beans, tofu, and broccoli.
A study involving 808 participants outlines the dietary habits of Norwegian adults adhering to a plant-based diet. Seitan, tofu, or tempeh were consumed by 1% of participants daily and 7% of participants weekly. The highest incidence was among vegans (29%), lacto-ovo vegetarians (13%), pescatarians (10%), and flexitarians (1%). The self-perceived health condition of the participants was rated as good or very good.
Wondering whether this plant-based protein is healthy for you? Read on to know if you can include it in your daily diet.
Is Seitan Healthy?
Seitan is a
vegan ingredient and is usually considered healthy.
Since it is low in calories, carbs, and fat, many people prefer to include it in their vegan diet. However, consuming seitan alone for your protein requirement may not be a good idea as it contains only limited amounts of essential amino acids. Therefore, it is healthy when consumed as part of a well-rounded diet including varied foods like beans, quinoa, and lentils to fill the other nutritional gaps. However, if you are sensitive to gluten, Seitan is something you should stay away from.
But how does the nutritious seitan help your health? Let us find out.
Benefits Of Seitan
Seitan is famous as a meat substitute and for being low in calories and carbohydrates. Its high amount of protein and presence of essential minerals like calcium and iron make it a healthy addition to your diet. Though there are not many scientific studies on seitan, there are a few purported advantages of adding it to your meal.
1. May Aid Weight Loss

The high amount of protein and low levels of carbohydrates in seitan may help in weight loss. A study examining a vegan diet, which also included seitan, proved that a low carbohydrate diet can help reduce weight. It has been found that there was an additional 2% advantage in body weight reduction when compared to a high carbohydrate diet (3).
2. May Prevent Cardiovascular Diseases

The increased intake of protein through gluten may help decrease the risk of cardiovascular diseases. A study conducted on a plant-based protein diet that included seitan showed an improvement in LDL cholesterol levels, which is a known risk factor for cardiovascular diseases (3).
3. May Treat Diabetes
Although there are no studies to back this claim about seitan, there is some research about plant-based diets aiding in diabetes treatment. According to a study, a plant-based low-carbohydrate diet helped lower the risk of diabetes by 22%. Such a diet may help reduce visceral fati Fat that develops over time and wraps around the internal organs and inside the abdominal cavity. and improve oxidative stressi A bodily condition that occurs when the antioxidant levels are low and affects the body’s ability to prevent diseases. markers more than a conventional diet in individuals with type 2 diabetes (4).
It is important to note that there are very limited scientific studies that draw a direct link between seitan and its supposed health benefits.
Now that you know of the benefits of seitan, it is time to learn more about the flip side.
Side Effects Of Seitan
As healthy as seitan is claimed to be, it also has some potential adverse effects.
1. Allergic Reactions

Since seitan is made from wheat gluten, it may cause allergic reactions in people who are allergic to gluten. So, people with a wheat allergy, gluten intolerance, or celiac diseasei An autoimmune disorder triggered due to the consumption of gluten, causing fatigue, bloating, and diarrhea. should avoid seitan as it may cause symptoms like bloating, abdominal pain, fatigue, indigestion, or diarrhea (5).
2. Affects Gut Health
Though there is not enough scientific evidence to prove seitan affects gut health, there is some anecdotal evidence that it may cause a leaky gut syndromei A digestive condition where the digestive lining is damaged and allows bacteria and toxins into the bloodstream. that allows larger particles to pass through into the bloodstream. This is called increased intestinal permeability (6).
3. High In Sodium
Since most people consume pre-made seitan from restaurants and stores, it may contain high quantities of sodium. When we eat too much salt, our body tries to balance it by holding onto water, which increases blood volume. This makes it harder for blood to flow through the blood vessels, thus raising blood pressure. Therefore, this ultra-processed product can contribute to high blood pressure (7). Further, people with kidney disease may also have a harder time excreting excess sodium, as their kidneys may not function properly to filter extra salt from the bloodstream. This can lead to additional strain on the kidneys and worsen their health over time (7). Moreover, it may also contain preservatives and additives that may cause more harm than good for your health.
Therefore, it is best to prepare seitan at home instead of buying it pre-made. Read on to learn how to prepare seitan.
How To Make Your Own Seitan

Ingredients
For The Dough
- 6 cups whole wheat flour
- 2 cups cold water
For The Broth
- 4 cups water
- 1/4 cup soy sauce
- 1/2 onion chopped
- 1 tablespoon miso paste
- 1 medium tomato cut in quarters
- 2 cloves garlic
Method
- Mix water and flour to make stiff-but-cohesive dough.
- Place the dough in a bowl.
- Pour the water into the bowl, cover it, and leave it for 4-8 hours.
- Knead the dough and rinse it until the water runs clear.
- Squeeze the dough to remove water and air.
- Cut the gluten (dough) into small pieces.
- Mix all the ingredients for the broth.
- Bring the broth to a boil.
- Add the gluten pieces to the boiling broth.
- Turn the heat down to a simmer.
- Cook and stir the gluten pieces for about 30 minutes.
- Discard the vegetable pieces.
- Drain and saute the seitan in a little oil to use it right away.
 Quick Tip
Quick TipYou can use seitan as a substitute for a burger patty, breakfast sausage, or even as a filling in burritos. Check out the interesting recipes given below that you can add to your vegetarian cuisine.
Seitan Recipes You Can Try At Home
1. Seitan Twizzlers
Ingredients
- Seitan cut into sausage shapes
- 150 g plain flour
- 1 teaspoon sugar
- 1 teaspoon garlic powder
- 1 teaspoon smoked paprika
- 1 teaspoon onion powder
- 120 ml soya milk
- Oil for frying
Method
- Roll up the seitan pieces tightly in tin foil.
- Place the sausages into a steamer for 45 minutes.
- Allow them to cool for 10 minutes.
- Combine the flour, paprika, sugar, onion powder, and garlic powder.
- Place the seitan sausages onto skewers.
- Cut the seitan into a spiral.
- Roll the seitan into the soya milk mixture.
- Roll it in the flour and spice mixture for an even coating.
- Heat oil in a frying pan over medium-high heat.
- Fry each twizzler for 3 to 4 minutes on each side.
- Remove the skewers and serve with a dip of your choice.
2. Seitan Saag
Ingredients
- 1 tablespoon peanut oil
- 1 large onion
- 1 peeled and finely chopped ginger
- ½ teaspoon salt
- 300 g shredded seitan
- 1 teaspoon sugar
- 2 teaspoon curry powder
- ½ teaspoon turmeric
- ½ teaspoon cumin
- 1 dash cinnamon
- 1 teaspoon minced chili
- 1 tablespoon tomato paste
- 200 g diced fresh tomatoes
- 235 ml water
- 2 handfuls spinach
Method
- Saute the onion in peanut oil with the ginger and some salt.
- Add the seitan when the onion becomes translucent.
- Fry until the onion is slightly browned.
- Add sugar, chili, salt, sugar, curry powder, turmeric, cumin, cinnamon, and tomato paste.
- Stir till it gets a brown color.
- Add diced fresh tomatoes.
- Stir and cook the tomatoes for about 5 minutes.
- Pour water and bring the heat up and cook until you have half the amount of liquid left in the pan.
- Once cooked, reduce the heat and add the spinach.
3. Seitan Mole

Ingredients
- 3 tablespoons of smoked paprika
- 1 tablespoon sesame seeds
- 3 tablespoons of raisins
- 3 tablespoons of maple syrup
- 1 tablespoon cider vinegar
- 2 tablespoons of olive oil
- 1 tablespoon dried chili flakes
- 3 tablespoons of chopped almonds
- 1 teaspoon dried oregano
- 2 chopped onions
- 1 tablespoon cacao powder
- 1 tablespoon water
- 600 ml vegetable stock
- 450 g seitan pieces
Method
- Toast the paprika, chili flakes, sesame seeds, almonds, cinnamon and oregano over medium heat.
- Blend these with raisins, onion, maple syrup, cacao powder, cider vinegar, and water until a smooth paste is formed.
- Warm 1 tablespoon olive oil over medium heat.
- Add the paste and cook for 3 to 4 minutes until the paste thickens.
- Slowly add the stock whilst whisking
- Bring it to a boil and cook for 10 to 15 minutes.
- Add the remaining tablespoon of olive oil and seitan to a frying pan
- Fry the seitan for 3 to 4 minutes on medium heat until crispy
- Add this to the mole sauce before serving.
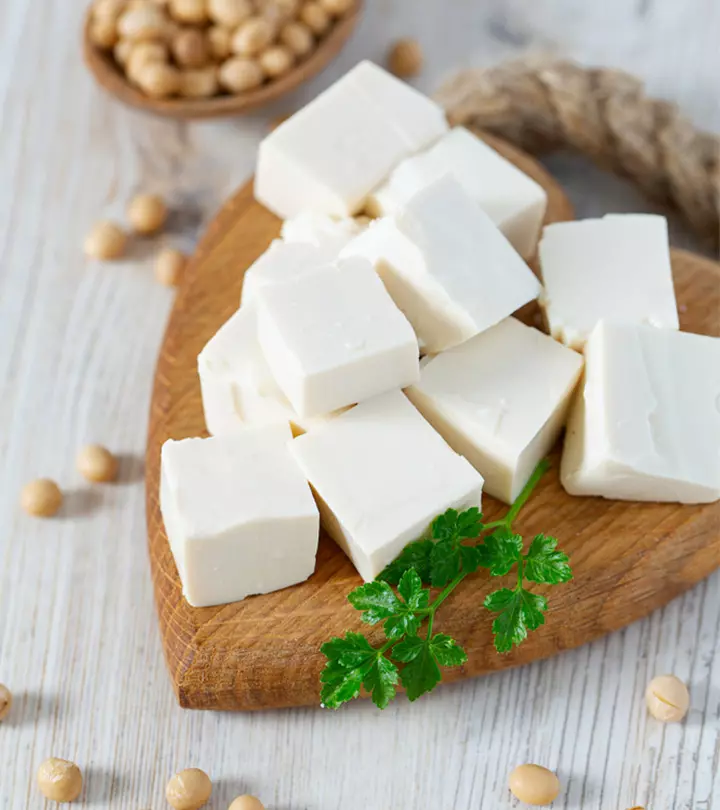
Seitan is often compared with tempeh. Both are popular plant-based alternatives to meat. But which of the two is better? Find out in the next section.
Seitan Vs. Tempeh
While seitan and tempeh are both popular plant-based proteins, they differ significantly in their composition and taste. Seitan, often called “wheat meat,” is made from gluten. It has a meaty texture and a chewy, umami flavor. It has a higher protein content than tempeh. A 100 g serving of tempeh contains about 20.3 g of protein while seitan provides about 24.7 g (8) (1).
Tempeh, on the other hand, is made from fermented soybeans. It offers a nutty flavor and has a firmer texture. It is richer in calcium and phosphorus than seitan (8). There are many benefits of tempeh, which include maintaining your gut health. You can choose either of these or both as per your dietary preferences and nutritional needs.
Infographic: Pros And Cons Of Seitan
Seitan is a healthy protein-rich substitute for meat, but that does not mean you exclude other nutrient-rich foods from your diet when consuming seitan. It is not a complete protein. Here’s a brief depiction of its pros and cons to help you make a wise decision. Check out the infographic below before switching to this plant-based meat substitute.
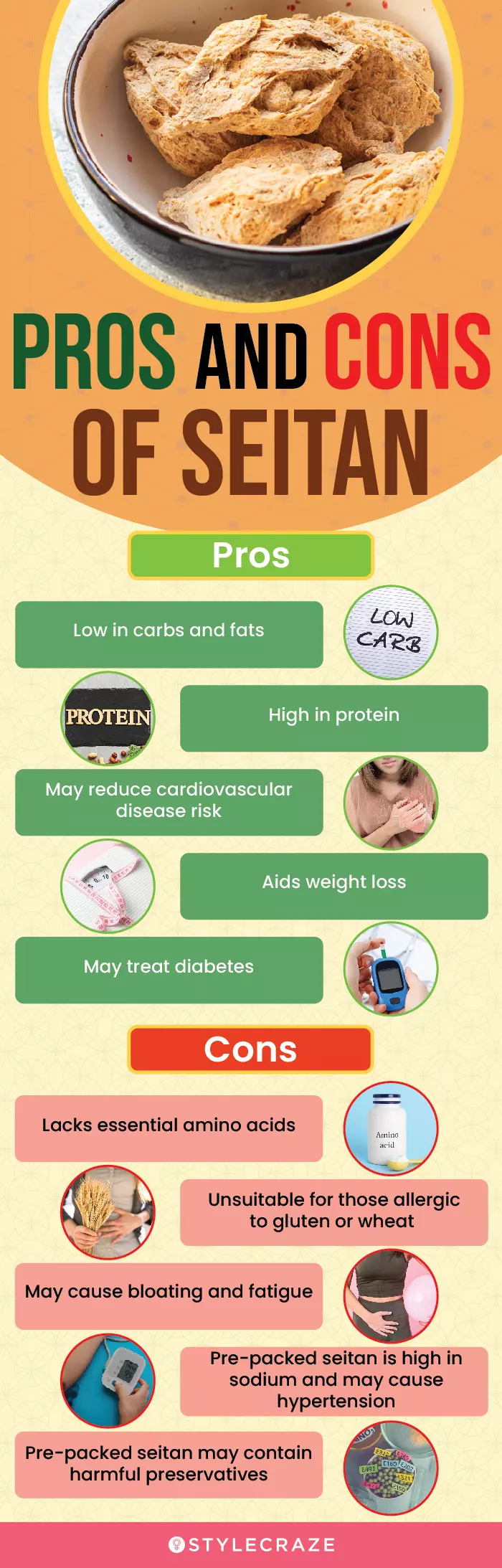
Illustration: StyleCraze Design Team
The Bottom Line
Seitan is a protein-rich ingredient that can mimic the look and taste of meat. Seitan’s nutrition profile claims to have low carbohydrates and fat, making it a healthy substitute for animal protein. However, it does not have enough amounts of some essential amino acids. Nevertheless, this plant-based protein may help you lose weight and prevent cardiovascular diseases. You can prepare it at home or buy pre-packed seitan to add to your daily diet. Regardless, ensure you do not have are not allergic to gluten or wheat products before consuming it.
Frequently Asked Questions
Which is better – seitan or tofu?
Tofu benefits are too many and the presence of certain essential nutrients makes it better than seitan. However, seitan has more protein than tofu. A 100 g serving of seitan provides about 24.7 g of protein, while tofu has only 12.7 g of protein (1) (9). Also, seitan is easier to cook with as it has a better taste and texture than tofu.
Is seitan a complete protein?
No, seitan is not a complete protein source. Though it is high in protein, it lacks essential amino acids.
What does seitan taste like?
Seitan has a dense, slightly rubbery texture and savory flavor that is akin to meat.
Is homemade seitan healthy?
Homemade seitan is comparatively healthier than pre-packed seitan, which may contain high amounts of sodium and preservatives.
Illustration: Seitan Nutrition - Benefits Side Effects & How To Make It

Image: Stable Diffusion/StyleCraze Design Team
Are you curious about the seitan’s health benefits? Check out this video to learn 5 nutritional facts about seitan and find out if it’s right for you, now!
Personal Experience: Source
StyleCraze's articles are interwoven with authentic personal narratives that provide depth and resonance to our content. Below are the sources of the personal accounts referenced in this article.
i. Beloved Seitanhttps://seesaraheat.wordpress.com/tag/seitan/
References
Articles on StyleCraze are backed by verified information from peer-reviewed and academic research papers, reputed organizations, research institutions, and medical associations to ensure accuracy and relevance. Read our editorial policy to learn more.
- Seitan wheat protein cubed, seitan
https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/food-details/2012995/nutrients - True ileal amino acid digestibility and digestible indispensable amino acid scores (DIAASs) of plant-based protein foods
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32932087/ - Effect of a 6-month vegan low-carbohydrate (‘Eco-Atkins’) diet on cardiovascular risk factors and body weight in hyperlipidaemic adults: A randomised controlled trial
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3918974/ - A plant-based diet for the prevention and treatment of type 2 diabetes
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5466941/ - Celiac disease: Prevalence, diagnosis, pathogenesis and treatment
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3496881/ - Gliadin induces an increase in intestinal permeability and zonulin release by binding to the chemokine receptor CXCR3
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/18485912/ - Sodium intake and hypertension
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC6770596/ - Tempeh
https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/food-details/174272/nutrients - Tofu, hard, prepared with nigari
https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/food-details/174291/nutrients
Read full bio of Olesya Wilson
Read full bio of Sindhu Koganti
Read full bio of Ravi Teja Tadimalla
Read full bio of Payal Karnik


























Community Experiences
Join the conversation and become a part of our empowering community! Share your stories, experiences, and insights to connect with other beauty, lifestyle, and health enthusiasts.