Goji Berries Side Effects: 6 Ways They May Cause Harm
Be mindful while consuming this fruit and save yourself from its adverse effects.

Image: Shutterstock
Goji berries are small fruits that are rich in nutrients and are often used in many salads and oatmeal. These slightly sweet and tart fruits are native to the Tibetan Himalayan region and China. The benefits of these tiny berries are numerous when you consume them in moderation, but with excess intake, there are also several side effects of goji berries. They may interact with certain drugs or cause an allergic reaction in some individuals (1).

Goji berries are prized for their flavor and versatility in cooking alongside their possible health advantages. They are also rich in antioxidants, vitamins A and C, and essential amino acids. While they are known for their many benefits, such as alleviating headaches and thyroid problems, you should be aware of the adverse effects they cause. In this article, we have discussed the possible side effects of goji berries. Keep reading to know more!
 Know The Flip Side: Goji Berries
Know The Flip Side: Goji BerriesShort-Term Effects
Diarrhea, allergies, lower blood sugar levels, and low blood pressure.
Long-Term Effects
Aggravates the risk of miscarriage in pregnant individuals.
Drug Interactions
It may interact with blood pressure medication and enhance the effect of anticoagulant drugs and increase bleeding.
When To See A Doctor
If you experience excessive diarrhea, very low blood sugar levels (especially if you have diabetes), and bleeding from the vagina (especially if you are pregnant).
In This Article
What Are The Side Effects Of Goji Berries?
1. May Cause Drug Interactions
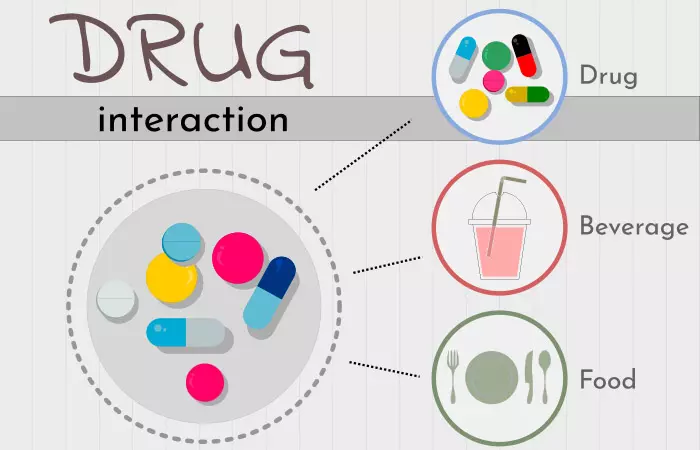
Goji berries can interact with certain blood-thinning drugs, including warfarin. In a study, a 71-year-old woman took goji berry juice while she was on warfarin therapy. The woman experienced symptoms of bruising, rectal bleeding, and bleeding from the nose (2). Her symptoms improved once she stopped taking the juice.
Goji berry juice is a popular herbal drink that can increase bleeding. It interacts with and enhances the action of drugs like warfarin, which is an anticoagulanti Chemical substances or medications that help thin the blood and prolong the process of blood clotting. (3).
 Trivia
Trivia2. May Lower Blood Sugar Way Too Much
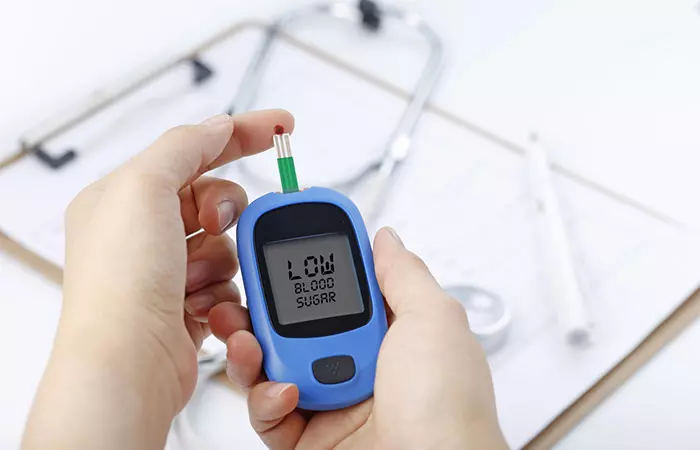
Goji berries can lower blood sugar levels. They have been identified as possible treatment options to manage diabetes (4). But if you are already on diabetes medication, they may cause your blood sugar levels to decrease way too much.
There is no direct research stating that goji berries can cause hypoglycemiai A condition in which the blood sugar level (glucose) in the body drops below the standard range. . However, it is better to exercise caution. Please check with your doctor before consuming goji berries if you are undergoing diabetes treatment.
3. May Cause Allergies
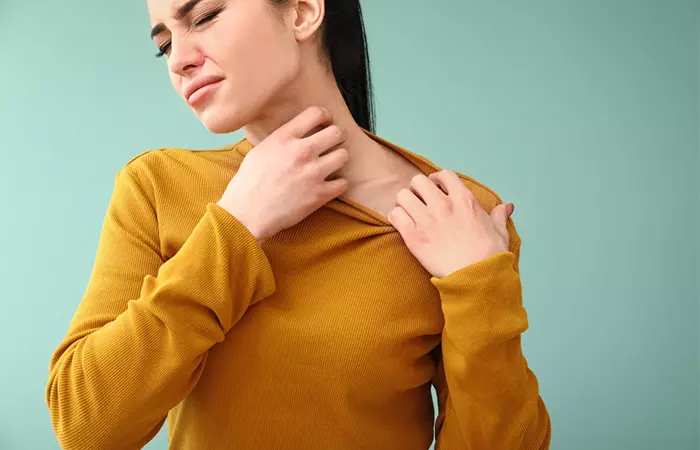
Goji berries can cause anaphylaxis, a condition in which the body becomes hypersensitive (5). The lipid transfer proteins in the berries could be responsible for these reactions.
The symptoms of anaphylaxis include skin irritation like hivesi Raised itchy rashes on the skin that are caused due to allergic reactions, medications, or stress. , airway obstruction, nausea, gastrointestinal issues, vomiting, and shock (6). Individuals at risk of food allergies must not consume goji berries until they get approval from their doctor.
4. May Cause Hypotension

Studies show that goji berries can help lower blood pressure levels (7). This may be good news, but it can cause problems if the individual is already on medications for treating high blood pressure.
Goji berries may enhance the action of medications that lower blood pressure. This can lead to hypotension or blood pressure levels plummeting to dangerously low levels.
Though there is no direct research to establish this, there is a possibility. If you are already on medication to treat hypertension, please check with your doctor before you consume goji berries.
5. May Lead To Diarrhea
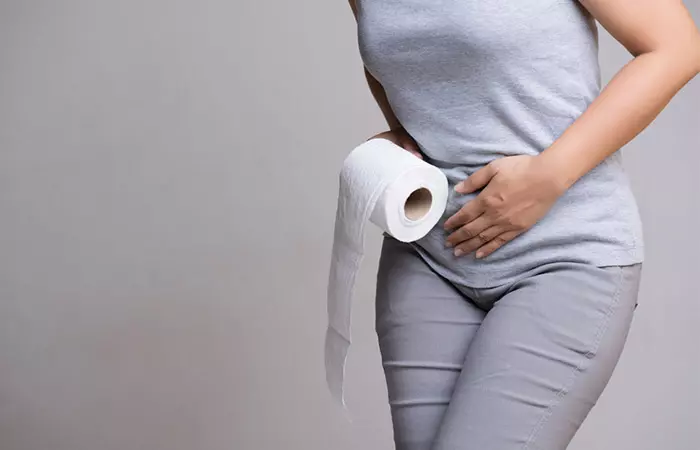

In one case report, an individual who had consumed goji berries (goji berry tea) had experienced non-bloody diarrhea and abdominal pain. The berries were found to modulate certain genes in the human body. Another possible reason for these side effects could be contamination (8).
Hence, if you have digestive issues, please check with your doctor before consuming goji berries.
6. May Cause Miscarriage
Goji berries contain betaine (9). Betaine could also be used to induce menstruation and abortion. The berries also have an estrogen-mimicking effect. Hence, they must not be used by pregnant or lactating women or anyone with diseases sensitive to estrogen (10).
 Trivia
TriviaNow that you have learned about the side effects of goji berries, take a look at some simple yet effective ways to enjoy them as part of a balanced diet while minimizing risks. Scroll down to know more.
How To Include Goji Berries In A Balanced Diet
- Opt for organic, unsulfured goji berries to avoid pesticides and preservatives.
- Make sure there are no artificial additives or any added sweeteners when purchasing dried berries.
- Consume goji berries in a small quantity if you are new to them and monitor for allergic responses.
- Add chia seeds, almonds, or Greek yogurt to reduce the absorption of sugar.
- In order to counteract their mild diuretic impact, pair them with watermelon, cucumber, or celery.
Key Takeaways
- Goji berries may lead to symptoms like bruising, rectal bleeding, and nose bleeding when in contact with certain drugs.
- They may drastically lower blood sugar levels in people who are already on medication for diabetes. So, watch out if you are a diabetic patient.
- Consuming excess goji berries may lead to digestive problems like bloating and abdominal pain.
- They contain betaine, which can cause miscarriage in pregnant women.
Infographic: What Happens If You Eat Too Many Goji Berries?
Goji berries are consumed in different forms and are very beneficial if consumed correctly, but excess intake can cause some serious side effects. It is important to identify these side effects and get treated immediately.
Check out the infographic given below to learn about the side effects of Goji berries.
Some thing wrong with infographic shortcode. please verify shortcode syntax
Goji berries are packed with beneficial compounds. However, if consumed in excess, goji berries can lead to many adverse effects. The side effects of goji berries range from diarrhea to low blood sugar levels. They may cause lower blood pressure as well. In some cases, goji berries can cause allergic reactions or interfere with the functioning of certain medications, resulting in bleeding. In severe cases, they may result in miscarriage, and therefore pregnant or lactating women should refrain from excessive consumption of these berries. Limiting or avoiding their consumption can prevent these possible unwanted effects. Lastly, it is essential that you consult medical experts before including goji berries in your diet, especially if you are on medication or have underlying medical conditions.
Frequently Asked Questions
Are goji berries carcinogenic?
Eva De Angelis, a dietitian nutritionist, says, “Goji berries have always been commonly used in traditional Chinese herbal medicine. They’ve also been labeled a superfood because of their high concentrations of bioactive compounds like polysaccharides, polyphenols, flavonoids, and carotenoids. Most of these compounds have the potential to be powerful allies in the fight against cancer.”
Do goji berries have heavy metals?
According to Eva De Angelis, a dietitian nutritionist, “Like any other crop, goji berry plants are treated with pesticides, which may be harmful to human health. Plus, some heavy metals could be absorbed by the plant, but the content is different for different areas of the world. Yet, there is insufficient evidence to suggest that this is the case, so eating goji berries does not pose a carcinogenic risk.”
Do goji berries make you sleepy?
Eva De Angelis says, “Goji berries have been linked to an improved sense of well-being and neurologic and psychological performance. Furthermore, because they are high in melatonin, the sleep hormone, they can improve our sleep quality with no side effects.” This may reduce the chance of insomnia.
How many goji berries should you eat a day?
You can eat 15 g of goji berries a day (8). This quantity is considered beneficial for eye health with 3 g of zeaxanthin in it. However, the safe daily limit of goji berries is not yet known.
Can those with diabetes eat goji berries?
Yes, they can. These berries can control blood sugar levels. From one study, goji berries have antidiabetic efficacy, which can balance glucose levels in the blood (11).
Can berries make you gain weight?
There is no evidence stating that berries may cause weight gain. Instead, they may decrease cholesterol levels in the body (12). This may help with weight loss.
Why is there a lead warning on goji berries?
Fresh and unprocessed goji berries grown in lead-free soil do not contain much lead and have no warning labels on their packaging. However, berries grown in soil with high levels of lead or berries with excessive lead added to them during the manufacturing and packaging process may have a warning label (if the quantity of lead exceeds permissible levels).
When is the best time to eat goji berries?
The best time to eat goji berries is before or after a workout session. The carbs in the berries can fuel your exercise or replenish your fuel stores effectively.
How do you remove lectins from goji berries?
Rinsing and soaking goji berries before cooking them at high temperatures can minimize their lectin content.
How much caffeine is in goji berries?
Goji berries do not contain caffeine. However, tea leaves, when included with goji berries to make tea, may impart their caffeine content to the final brew.
Is goji berry high in melatonin?
Yes, goji berries are high in melatonin – with its content ranging between 123.44 and 1600.48 ng/gFW.
Illustration: Goji Berries Side Effects: 6 Ways They May Cause Harm

Image: Stable Diffusion/StyleCraze Design Team
Learn about the side effects of goji berries in this video focused on healthy eating tips. Gain insights into potential drawbacks and considerations when consuming this superfood.
References
Articles on StyleCraze are backed by verified information from peer-reviewed and academic research papers, reputed organizations, research institutions, and medical associations to ensure accuracy and relevance. Read our editorial policy to learn more.
- Goji berries (Lycium barbarum): risk of allergic reactions in individuals with food allergy, Journal of Investigational Allergology & Clinical Immunology, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23101309/ - Probable interaction between Lycium barbarum (goji) and warfarin, Pharmacotherapy, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22392461/ - Bleeding due to a probable interaction between warfarin and Gouqizi (Lycium Barbarum L.), Toxicology Reports, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5598317/ - Goji Berry (Lycium Barbarum) in the treatment of diabetes melitus: a systematic review, Food Research, ResearchGate.
https://www.researchgate.net/publication/319200037_Goji_Berry_Lycium_Barbarum_in_the_treatment_of_diabetes_melitus_a_systematic_review - Anaphylaxis associated with the ingestion of Goji berries (Lycium barbarum), Journal of Investigational Allergology & Clinical Immunology, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22312943/ - Anaphylaxis, Canadian Family Physician.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2954079/ - Anti-hypertensive effect of Lycium barbarum L. with down-regulated expression of renal endothelial lncRNA sONE in a rat model of salt-sensitive hypertension, International Journal of Clinical & Experimental Pathology, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4525921/ - Goji Berries as a Potential Natural Antioxidant Medicine: An Insight into Their Molecular Mechanisms of Action, Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6343173/ - Goji Berry (Lycium barbarum): Composition and Health Effects – A Review, Polish Journal of Food and Nutrition Sciences, ResearchGate.
https://www.researchgate.net/publication/288630233_Goji_Berry_Lycium_barbarum_Composition_and_Health_Effects_-_A_Review - Biomolecular and Clinical Aspects of Chinese Wolfberry, Herbal Medicine, National Center for Biotechnology Information.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK92756/ - Practical Application of Antidiabetic Efficacy of Lycium Barbarum Polysaccharide in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes, Medicinal Chemistry, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25381995// - Strawberries, Blueberries, and Cranberries in the Metabolic Syndrome: Clinical Perspectives, Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22082311//
Read full bio of Madhu Sharma
- Eva De Angelis is a Dietitian Nutrionist from Argentina. She specializes in food and nutrition education, and healthy cooking. She has a Bachelor’s degree in Human Nutrition and Dietetics from ISalud University, a postgraduate certificate in Nutrition, Gastronomy, and Health, a culinary diploma, and an intermediate-level technical degree in Food Science.
 Eva De Angelis is a Dietitian Nutrionist from Argentina. She specializes in food and nutrition education, and healthy cooking. She has a Bachelor’s degree in Human Nutrition and Dietetics from ISalud University, a postgraduate certificate in Nutrition, Gastronomy, and Health, a culinary diploma, and an intermediate-level technical degree in Food Science.
Eva De Angelis is a Dietitian Nutrionist from Argentina. She specializes in food and nutrition education, and healthy cooking. She has a Bachelor’s degree in Human Nutrition and Dietetics from ISalud University, a postgraduate certificate in Nutrition, Gastronomy, and Health, a culinary diploma, and an intermediate-level technical degree in Food Science.
Read full bio of Sindhu Koganti
Read full bio of Ravi Teja Tadimalla
Read full bio of Himanshi Mahajan


























Community Experiences
Join the conversation and become a part of our empowering community! Share your stories, experiences, and insights to connect with other beauty, lifestyle, and health enthusiasts.