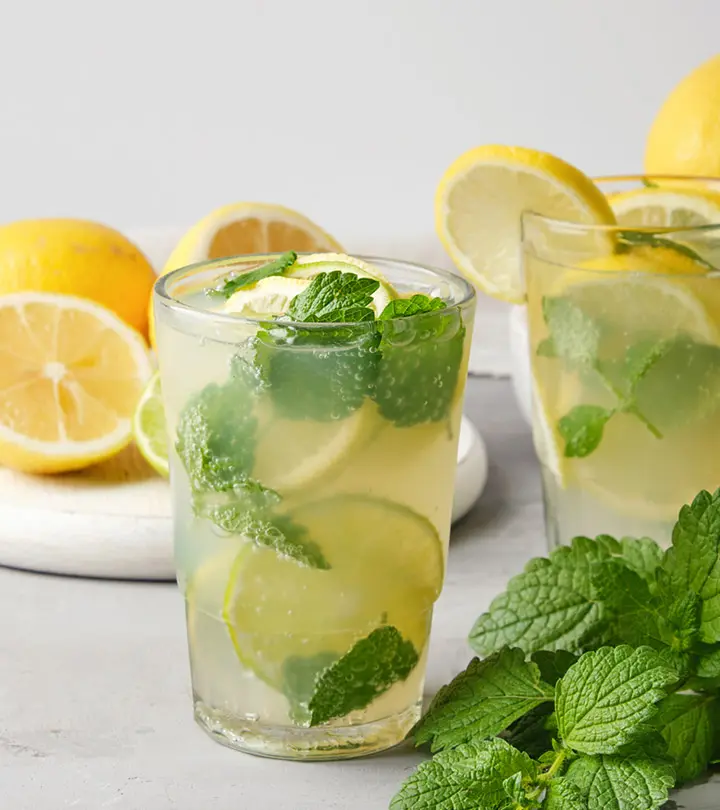
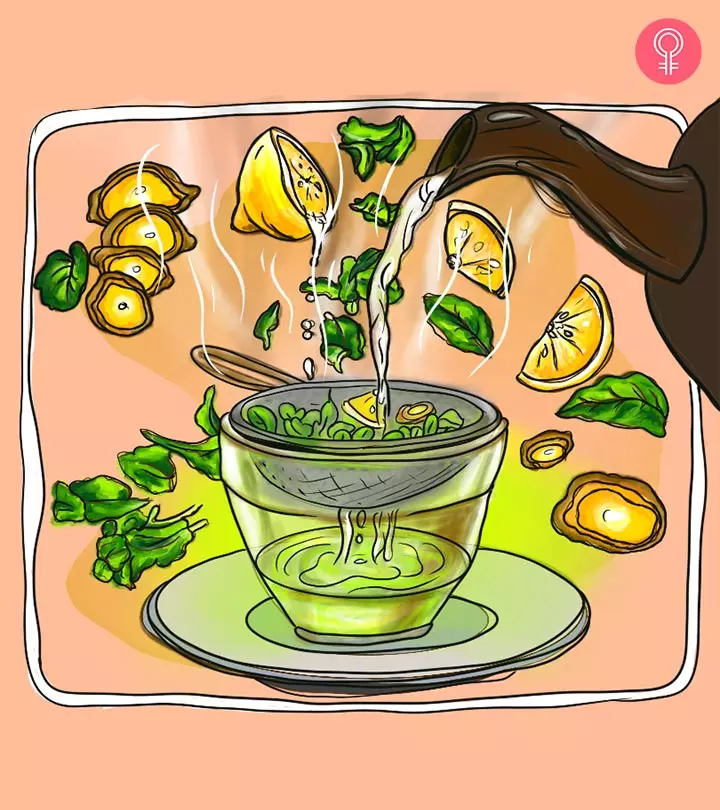
6 Side Effects Of Drinking Too Much Lemon Water
Lemon water is refreshing but can affect your health in ways you haven’t thought of.

Image: Shutterstock
Lemon water is consumed by many for its refreshing taste. But, because of its acidic nature, excess intake of lemon water may harm the tooth enamel. Many people consume it as a detox drink to aid in weight loss or maintain their hydration levels. However, there are also some other side effects of lemon water you should be aware of if you plan to consume it regularly. Know what research says about these negative effects and how you can prevent them. Read on.
 Know The Flip Side: Lemon Water
Know The Flip Side: Lemon WaterShort-Term Effects
Stomach cramps, nausea, vomiting, acidity, sunburn, canker sores, and an upset stomach.
Long-Term Effects
Mouth ulcers, tooth enamel decay, migraines, heartburn, and other gastroesophageal reflux issues.
Drug Interactions
Lemon juice should be avoided when on any medication, especially when taking calcium antagonists medicines.
When To See A Doctor
If you experience any severe short term effects like chronic nausea or unbearable stomach cramps.
In This Article
What Are The Side Effects Of Too Much Lemon Water?
Although there are several lemon water benefits, overconsumption may cause adverse reactions. Allyson Brigham, MS, RDN, says, “ It is common for tooth enamel to deteriorate due to the citric acid in lemon juice. There are also side effects, such as stomach cramps and gastrointestinal problems.” She adds, “The body’s reaction to too much acidity in the stomach can be very painful and cause serious problems if left untreated. If you experience this symptom, stop drinking lemon water immediately.”
Listed below are some potential disadvantages of drinking lemon water daily and in excess amounts. Take a look!
1. May Decay Tooth Enamel

A study discusses a female patient (smoker) who experienced erosion of the enamel and dentinal hypersensitivityi A sharp, transient tooth pain resulting from an exposed dentin surface reacting to stimuli that cannot be linked to a dental disorder. following the frequent consumption of lemon juice (lemon water). Excess intake of lemon water may lead to acidic demineralization of the tooth enamel (1).
Another Brazilian study proved the same. Lemon juice displayed corrosive effects on the teeth similar to that of soft drinks. All of them are equally acidic (2).
Brushing your teeth immediately after consuming lemon water may help prevent erosion. You may also start brushing and flossing twice a day for better results and improved oral health (3).
You may also drink lemon water using a straw to prevent tooth decay.
2. May Cause Sunburns
Certain studies indicate that heading out into the sun after applying lemon juice to your skin can cause blisters and dark spots.
This condition is called phytophotodermatitis and is a worse form of sunburn.
Allyson Brigham says,“ Lemons sting or even burn the skin because they are highly acidic.”
The culprits are the chemicals in lemon juice, called psoralens, which interact with sunlight and cause burn (4).
In another study, citrus consumption was linked to an increased risk of melanoma (skin cancer). The effect was attributed to the presence of psoralens in most citrus fruits. However, further studies are needed to better understand the effects of citrus fruit/juice on skin health (5).
3. May Aggravate Canker Sores
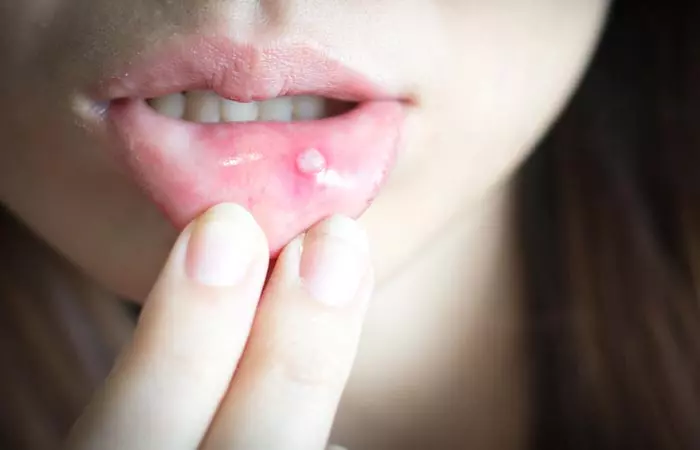
Canker sores are a form of mouth ulcers. These are shallow sores inside the mouth (or the base of the gums), and they are painful. Some research states that citric acid may provoke mouth ulcers (6). The mechanism of how citric acid may lead to this is yet to be understood.
The citric acid in lemons can worsen your sores and also cause more. Hence, ensure you don’t take lemons (or any citrus fruit) if you have canker sores. Wait for them to heal completely.
 Did You Know?
Did You Know?4. May Aggravate Heartburn
While consuming lemon juice may boost metabolism and digestion, some research considers citrus fruits to be causing heartburn or acid reflux. In studies, patients who complained of similar gastrointestinal symptoms were found to be consuming more of citrus fruits and juices (7).
However, the information in this aspect is mixed. Anecdotal evidence suggests that lemon water can both hurt and help heartburn symptoms. If you have heartburn symptoms, it is best to check with your doctor before consuming lemon water (or other citrus foods/fluids).
It is also thought that lemon may activate pepsin, which is a stomach enzyme that breaks down proteins. Reflux of the digestive juices in the stomach is believed to activate the inactive pepsin molecules in the throat and esophagus, leading to heartburn. More research is needed to substantiate this.
Lemon juice may also decrease the effectiveness of the lower esophageal sphincter muscle and instead allow the stomach acid to splash up the esophagus. The juice may also worsen peptic ulcers. Ulcers are formed by excessively acidic digestive juices. Drinking lemon juice (and eating other acidic foods) can only make things worse and affect the digestion process.
Certain experts speculate that lemon juice can also trigger GERDi A chronic condition that develops when bile or stomach acid enters the esophagus and irritates the cell walls. symptoms. Hence, avoid lemons if these symptoms are triggered, as the response varies.
The intake of lemon water on an empty stomach is also thought to trigger GERD symptoms, although there is no evidence to support this.
5. May Trigger Migraine In Patients

There is some research that citrus fruits may trigger migraines. The fruits may induce a migraine attack through an allergic reaction. Tyramine, a specific substance in citrus fruits, could be the culprit (8).
6. May Lead To Frequent Urination

Drinking lemon water is generally considered safe for most people. However, some possible side effects of lemon water for females may include frequent urination. Though there is no research that proves that excess lemon water may lead to frequent urination, women may experience the same due to excess intake of lemon water. It may have more to do with the water, and not the lemon itself.
Some believe that lemon juice, especially in a glass of warm water, can act as a diuretic. It can increase urine output, and if this goes overboard, you may end up feeling dehydrated. This is because the juice from lemon rids your body of the excess water. In the process, it can also flush out excess amounts of electrolytes and sodium through urine. At times, it can flush out too much of them and cause dehydration. However, research is lacking in this aspect.
It also is believed that acidic fruits like lemons can irritate the bladder. This may increase the urge to urinate more often. Though there is no evidence to support this, you can avoid lemon water and other acidic fruits for about a week and see if your symptoms improve. If not, consult your doctor.
Lemon water is also believed to cause excess iron content in the blood, although there is no research to support this. The vitamin C in lemon water may increase iron absorption, but this was only found to help with iron deficiency anemia (in rat studies) (9).
It also is believed that lemon water may trigger nausea or vomiting. This may be attributed to its vitamin C content. There also have been cases of vomiting following excess intake of lemon water (more than 2 lemons or 3 cups of diluted lemon juice). Theories suggest that the body would flush out the excess vitamin C, triggering the symptoms. However, there is no evidence to support this.
Most of the side effects attributed to lemon water are yet to be studied. Excess intake of the beverage can erode the tooth enamel and may aggravate sunburns or trigger migraines. The other side effects need more research to substantiate the findings.
Note: Be aware that technically you can eat an entire raw lemon, it is not recommended as the high acidity can irritate your mouth, throat, and stomach and it has a very sour taste that may not suit your taste buds.
Is there a way to drink lemon juice and avoid the side effects? Is there a safe dosage?
Key Takeaways
- Excess consumption of lemon juice may lead to tooth erosion.
- The psoralens present in lemon may interact with sun rays and burn the skin.
- Overconsumption of lemon juice may cause heartburn and migraines.
- Lemon may reduce the movement of calcium through calcium channels in the body, which is essential for treating hypertension.
What Is The Recommended Dosage Of Lemons/Lemon Juice?

The ideal dosage of lemon water depends on the user’s age, health, etc. There is not enough scientific information to determine the ideal dosage of lemon/lemon water. But from anecdotal evidence, about a glass or two of lemon water (about 120 ml) per day seems to be safe. In moderate amounts, lemon tea can also be beneficial.
 Fun Fact
Fun FactDo Lemons Have Any Interactions With Medications?
Though lemons don’t severely interact with any medications, certain studies shed light on the interactions of other citrus fruits (grapefruit juice) with calcium antagonists (medications that disrupt the movement of calcium through calcium channels, which are used for treating hypertensioni High blood pressure; blood pressure over 140/90 indicates the blood exerts too much force on the artery walls. ) (10).
Though the citrus juice could increase the bio availability of the medication, its effects on the human body may not be desirable.
Another Japanese study recommends that patients avoid the intake of citrus juice while on medications as the juice might interact with them, causing potential hazards (11).
There is insufficient information on the interactions lemon water might have with herbs.
However, people taking blood thinners should be cautious about consuming lemon juice, as it may increase the risk of bleeding. Consult a healthcare provider to assess the potential risks and benefits of adding lemon juice to your diet.
While it is mistaken to be alkaline due to its high mineral content, it actually is acidic in nature. The highly acidic nature of lemon juice may affect the pH balance of the blood. However, there is limited research to support this claim.
While lemons may interact with some medications, there are several creative ways to enjoy their refreshing taste without compromising health. Scroll down to know more.
Alternate Ways To Enjoy Lemon
- To lessen acidity, use ½ to 1 lemon juice with 8–16 ounces of water.
- Slice lemons and let them infuse in cold water for a refreshing drink.
- Incorporate a few drops of lemon juice into mint, ginger, or chamomile tea.
- Add grated zest to baked products, yogurt, marinades, and salads.
- Mix lemon juice with olive oil and herbs for a mild salad dressing.
- Blend with bananas, berries, yogurt, or greens to balance the acidity.
Infographic: Side Effects Of Overconsumption Of Lemon Water
It is not just refreshing to drink lemon water, it’s also very beneficial to your health as it contains Vitamin C and minerals like potassium, calcium and magnesium. But lemon water can also have some serious side effects if consumed above a limit.
Check out the infographic given below to know about the side effects caused by the overconsumption of lemon water.

Illustration: StyleCraze Design Team
Lemon water is known for its refreshing taste and antioxidant properties. The phenolic compounds and nutrients present in lemon water may boost liver function and immunity and reduce body inflammation. However, excess intake of lemon water may cause side effects like tooth decay, sunburns, canker sores, heartburn or acid reflux, migraine, and frequent urination. Though there are no listed dosage levels of lemon water, consuming one or two glasses of lemon water a day is considered safe.
Frequently Asked Questions
Does lemon affect female fertility?
Allyson says, “Citric acid is a natural antiseptic that can help balance your body’s pH levels, which can help reduce vaginal alkalinity. In addition to fighting infertility-causing bacteria, citric acid also aids in the treatment of a number of other health conditions.”
Does the intake of lemon water every morning weaken your bones?
There is no research that supports this. Hence, you can go for it. But if you have come across someone facing such issues due to the intake of lemon water in the mornings, do consult your doctor.
What are the side effects of lemons on hair? Does it decolorize hair?
Side effects of lemons on the hair, if frequently used, may include damage to the scalp, given the acidic nature of the fruits. This nature of lemons can also turn your hair gray. To avoid this, use lemon juice along with some warm hair oil. This ensures your scalp doesn’t get dried up.
Can you drink lemon water at night?
Yes. There are no known adverse effects of drinking lemon water at night.
Does lemon water harm your kidneys?
The citric acid in lemon water may help treat kidney stones. There is no evidence if lemon water may harm the kidneys.
Illustration: Side Effects Of Drinking Too Much Lemon Water

Image: Stable Diffusion/StyleCraze Design Team
Learn about the potential side effects of drinking too much lemon water. Click on this video to know more about different tips and precautions you should keep in mind when consuming lemon water.
References
Articles on StyleCraze are backed by verified information from peer-reviewed and academic research papers, reputed organizations, research institutions, and medical associations to ensure accuracy and relevance. Read our editorial policy to learn more.
- Particular dental erosion, The Pan African Medical Journal, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6235510/ - In vitro study of enamel erosion caused by soft drinks and lemon juice in deciduous teeth analysed by stereomicroscopy and scanning electron microscopy, Caries Research, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/8877092/ - When life gives you lemons, make lemon water, University of Florida.
https://podcasts.ufhealth.org/when-life-gives-you-lemons-make-lemon-water/ - A tropical skin eruption, The Canadian Journal of Infectious Diseases, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2094864/ - Citrus Consumption and Risk of Cutaneous Malignant Melanoma, Journal of Clinical Oncology, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4979231/ - Canker sores from allergy to weak organic acids (citric and acetic): Case report and clinical study, Journal of Allergy, ScienceDirect.
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/002187075690154X - Risk factors for gastroesophageal reflux disease: the role of diet, Przeglad Gastroenterologiczny, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4223119/ - Diet and migraine, Revista de neurologia, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/8681169/ - Effects of Citric Acid and Lemon Juice on Iron Absorption and Improvement of
Anemia in Iron-Deficient Rats, Food, Science, and Technology Research, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
https://www.jstage.jst.go.jp/article/fstr/18/1/18_127/_pdf - Interaction of citrus juices with pranidipine, a new 1,4-dihydropyridine calcium antagonist, in healthy subjects, European Journal of Clinical Pharmacology, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/9923580/ - Undesirable effects of citrus juice on the pharmacokinetics of drugs: focus on recent studies, Drug Safety, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16048354/ - Fermented Citrus Lemon Reduces Liver Injury Induced by Carbon Tetrachloride in Rats, US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
https://www.hindawi.com/journals/ecam/2018/6546808/
Read full bio of Julie Freeman
- Allyson Brigham, MS, RDN, has three years of experience in nutritional counseling and meal prep. She has a master's degree from the University of Saint Joseph.
 Allyson Brigham, MS, RDN, has three years of experience in nutritional counseling and meal prep. She has a master's degree from the University of Saint Joseph.
Allyson Brigham, MS, RDN, has three years of experience in nutritional counseling and meal prep. She has a master's degree from the University of Saint Joseph.
Read full bio of Ravi Teja Tadimalla
Read full bio of Arshiya Syeda
Read full bio of Sindhu Koganti


























Community Experiences
Join the conversation and become a part of our empowering community! Share your stories, experiences, and insights to connect with other beauty, lifestyle, and health enthusiasts.