7 Serious Side Effects Of Pineapple
Your summer-favorite fruit can cause serious allergies if you aren't careful enough.

Image: Midjourney/ StyleCraze Design Team
Many of the side effects of pineapple might make you reconsider consuming this tropical treat.
There’s nothing like pineapples during the summer. Pineapples have a refreshing taste and help cool you off in the heat.
There will always be a place for pineapples, regardless of whether you slice, prepare a punch, or bake a dish with it. However, everything has some pros and cons, and even such a healthy fruit as pineapple can pose health risks when consumed in excess.
Pineapple may cause certain allergies or prevent certain medications from working properly.
This article examines the side effects of pineapples, their safety, and any potential drug interactions. Take a look below.
 Know The Flip Side: Pineapple
Know The Flip Side: PineappleShort-Term Effects
Oral allergies, throat irritation, vomiting, nausea, and skin rash.
Long-Term Effects
Tooth decay, diabetes, excessive menstruation flow, and gastrointestinal problems.
Drug Interactions
When taken with blood-thinning medicines, it can cause the risk of excessive bleeding.
When To See A Doctor
If you experience excessive stomach ache or excessive menstruation flow than usual, you may need to visit your doctor.
In This Article
Side Effects Of Pineapple
Although there are multiple health benefits of pineapples, surplus consumption can lead to serious complications. Here are some pineapple side effects you should be aware off.
1. Allergy
What?
Consumption of pineapples can lead to allergic reactions in a few people.
How?
Pineapple has ‘meat-tenderizing’ properties, which may trigger allergic reactions. Pineapple may also cause latexi A milky white liquid found in many plants that may cause an allergic reaction in some individuals. allergies in some (1). Mostly these reactions would resolve within a few hours by themselves. But if not, then a medical practitioner should be consulted immediately.
Symptoms?
Excessive tenderness or swelling on the lips, a tingling sensation in the throat.
Sarah, a mom blogger, observed a series of concerning incidents related to their child Aidan’s potential pineapple allergy. These incidents included him experiencing symptoms like vomiting, skin rashes, and general discomfort. She says, “He also had some small spots, (usual for Aidan when he has a virus) as well as some red, sore looking patches of skin on his legs (i).” Sarah’s mom suggested it may have been caused by a pineapple allergy.
2. Blood Sugar Levels

What?
This is one of the serious side effects excess intake of pineapple can cause. Overconsumption of pineapples may spike blood sugar levels in susceptible individuals. This obviously does pose complications.
How?
Pineapples are one of those fruits that contain glucose and sucrose sugars. And because of this, they may elevate blood sugar levels in our body (2). Most fruits contain carbohydrates and these can also raise the blood sugar levels. In fact, 100 grams of pineapple has 14.1 grams of carbohydrates (3).
Symptoms?
Headache, increased thirst and frequent urination (3).
3. Bromelain Reactions

What?
Bromelain is an enzyme found in the pineapple juice and stem (5). This enzyme has been found to cause reactions in our bodies. However, while natural bromelain does not seem to be toxic, taking it as a supplement may warrant precaution.
How?
Bromelain has anticoagulanti A property, chemical substance, or medication that reduces or helps prevent the clotting of blood. properties (3). It might increase the risk of bleeding when consumed with blood-thinners.
Symptoms?
Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea,abdominal pain, heartburn, and indigestion.
 Quick Tip
Quick Tip4. Drug Interactions

What?
Pineapple might even interfere or interact with certain types of medications or drugs. This might lead to heightened side effects and other problems.
How?
The bromelain in pineapple may increase the absorption of certain antibiotics like amoxicillin and tetracycline (4). This effect may cause side effects in some individuals.
Symptoms?
Chest pain, bloody nose, chills, fever, dizziness, etc.
5. Tooth Damage

What?
Though pineapple is a healthy and delicious fruit, excess intake can cause desensitizationi Damage to the nerves of your teeth that makes them non-reactive or insensitive to a particular, external stimulus. of teeth or tooth decay.
How?
Fruits like pineapple that are highly acidic in nature may initiate a chemical process in the mouth when consumed. Excess intake of pineapple, coupled with improper oral hygiene practices, may increase risk of tooth decay (5).
Symptoms?
Tooth pain and extreme sensitivity when taking hot or cold foods.
6. Oral Allergy Syndrome

What?
Oral allergy syndrome is nothing but an allergy to airborne particles like dust and pollen.
How?
This phenomenon occurs when the immune system in our body confuses the protein in pineapple with pollen or any other allergen (6). As a result of this, reactions occur within the body.
Symptoms?
Irritation or itching on the tongue for sometime after consuming a pineapple.
7. Diarrhea

What?
Some people may experience vomiting, abdominal pain, and diarrhea after consuming pineapples (8).
How?
Ripe pineapples contain natural sugars like fructose (9). Consuming large quantities of fructose may cause gastrointestinal discomfort in children and certain adults (10).
Symptoms?
You may experience diarrhea, flatulence, vomiting, abdominal pain, and bloating, sometimes as quickly as 30 minutes after consuming pineapples (8), (10). However, more studies are warranted in this regard.
 Quick Tip
Quick TipThey say no human being is perfect. Probably the same applies to fruits too. Depending upon the health conditions one has, some fruits might be desirable and healthy and some might be not.
Note: Always consult a healthcare professional for personalized advice if you experience any side effects or adverse reactions after consuming pineapple. Remember, individual responses to pineapple may vary, so professional guidance is recommended for addressing specific health concerns.
All the above mentioned are side effects of pineapple consumption! Though I don’t mean to say pineapples are ‘bad’ or ‘poisonous’, they do have their own set of side effects and should be consumed in moderation.
If you experience any side effects mentioned, it is important to consider whether you fall into one of the groups that should limit or avoid pineapple consumption. Scroll down to know more.
Who Should Avoid Pineapple?
There are quite a few people who should avoid consuming pineapples, such as:
- Those who are allergic to pineapple or similar fruits, such as kiwis, should stay away from it to avoid symptoms like swelling or itching.
- While individuals with diabetes should watch portions because of their glycemic index, people with oral sensitivity may become irritated.
- Moderate pineapple consumption is advised for pregnant women because excessive consumption may stimulate the uterus.
- If you experience adverse effects, speak with a healthcare professional.
If pineapple triggers negative reactions, consider trying other alternatives like mango, papaya, or oranges for a vitamin C boost and tropical sweetness. Melons like cantaloupe or honeydew are hydrating, while strawberries, grapes, and bananas offer milder options. While kiwi adds a tangy touch, guava and peaches give diversity; however, due to potential allergies, care should be used. These fruits ensure a healthy diet without the risks associated with pineapple.
Key Takeaways
- Certain medications may interact negatively when consuming pineapple.
- Pineapple may cause allergic reactions in some people.
- Excess pineapple consumption may cause elevated blood sugar levels or tooth damage.
- Bromelain, an enzyme found in pineapple, may increase bleeding risk if taken as a supplement.
- Pineapple may also trigger reactions from oral allergy syndrome.
Infographic: Pineapples: General Recommended Daily Intake
Pineapple is a tropical treat, which, if overindulged in, can quickly become a disaster. As every individual reacts differently to different pineapple concentrations, there are no strict limits on its intake values. However, some general recommendations can help.
Check out the infographic below to learn more about the recommended daily intake values of pineapple and its associated products. Illustration: StyleCraze Design Team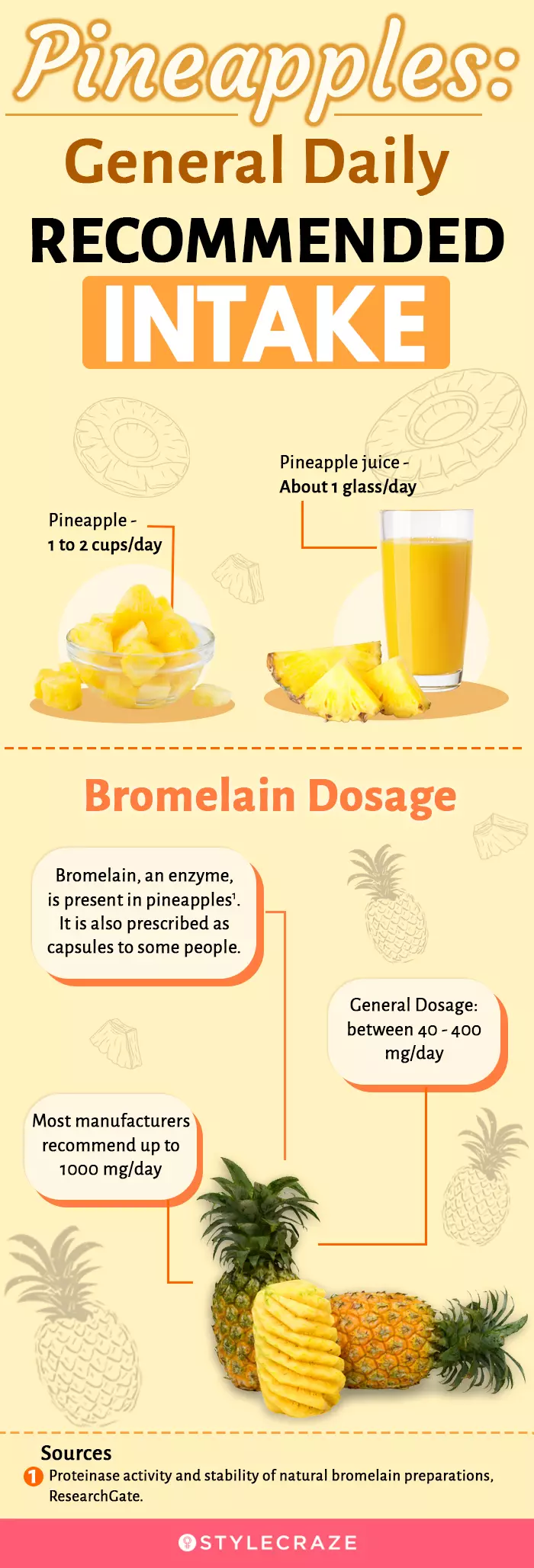
A tropical tangy-sweet fruit that is perfect for summer, pineapples are a wonderful fruit to have in the pantry. However, they should not be consumed in excess. The side effects of pineapples range from increased blood sugar levels to a high risk of dental problems. The presence of an enzyme called bromelain and its activity can also increase bleeding risk. In some cases, pineapples may trigger allergic reactions, or interfere with the functioning of certain medications, especially antibiotics. Some anecdotal evidence also suggests the possibility of skin irritation, mouth sores, and increased heart rate from overconsumption of pineapples. But such claims remain to be proved by medical research. If possible, try to limit your intake or stay away from it entirely to avoid such complications.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is it OK to eat pineapple at night?
Blanca Garcia, Registered Dietitian Nutritionist, says, “Pineapple is safe to eat at night as long as it is consumed between meals and in moderation.”
Can pineapple cause uric acid?
According to Garcia, “Although pineapple is an acidic fruit, it does not raise uric acid levels in the body; rather, it helps lower uric acid levels due to its high magnesium content.”
Can pineapple cause gas and bloating?
“No. Instead, it helps with bloating because it contains bromelain, an enzyme that breaks down protein and aids in digestion,” says Blanca Garcia.
What happens if I eat pineapple every day?
Pineapple is loaded with many beneficial nutrients that offer various benefits like boosting digestion, improving immunity, dissolving kidney stones and revving metabolism. However, having it in moderation is advised.
Does pineapple affect sperm count?
Yes, pineapple affects sperm count positively. It is rich in manganese, and B vitamins, which determine the sperm count. Therefore, including this fruit as a part of the diet helps increase the sperm count.
Can pineapple raise blood pressure?
No. Pineapple cannot cause high blood pressure. Moreover, its low potassium content helps manage blood pressure levels effectively.
What are some ways to incorporate pineapple into my diet?
You can incorporate pineapple into your diet in various ways. You may add fresh pineapple chunks to your morning smoothies or yogurt bowls. It also works well as a topping for salads or grilled chicken and fish. Pineapple can be used in homemade salsa, baked into desserts, or enjoyed as a refreshing snack on its own.
Illustration: Serious Side Effects Of Pineapple

Image: Stable Diffusion/StyleCraze Design Team
Discover the surprising dangers of excessive pineapple consumption. From tongue inflammation to digestive woes, this eye-opening video reveals the 5 side effects of consuming this tropical treat every day.
Personal Experience: Source
StyleCraze's articles are interwoven with authentic personal narratives that provide depth and resonance to our content. Below are the sources of the personal accounts referenced in this article.
i. No pina coladas at preschool…..https://happymummyhappychildhappylife.wordpress.com/tag/pineapple/
References
Articles on StyleCraze are backed by verified information from peer-reviewed and academic research papers, reputed organizations, research institutions, and medical associations to ensure accuracy and relevance. Read our editorial policy to learn more.
- “Latex-fruit syndrome”: frequency of cross-reacting IgE antibodies
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/9188921/ - Blood glucose responses of diabetes mellitus type II patients to some local fruits
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24394507/ - Pineapple raw
https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/food-details/2346398/nutrients - Comparison of proteolytic cytotoxic and anticoagulant properties of chromatographically fractionated bromelain to un-fractionated bromelain
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8205729/ - Bromelain
https://www.nccih.nih.gov/health/bromelain# - Bromelain a Potential Bioactive Compound: A Comprehensive Overview from a Pharmacological Perspective
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8067380/ - Relationship between Food Habits and Tooth Erosion Occurrence in Malaysian University Students
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3431744/ - Epidemiological study of oral allergy syndrome in birch pollen dispersal-free regions
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31708436/ - Pineapple raw all varieties
https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/169124/nutrients - Fructose malabsorption
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4755956/ - Systemic allergic reaction and diarrhoea after pineapple ingestion
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/8511816/ - Effect of Temperature on the Stability of Fruit Bromelain from Smooth Cayenne Pineapple
https://www.thaiscience.info/journals/Article/TKJN/10641696.pdf
Read full bio of Karishma Shah
- Blanca Garcia, RDN, has 8 years of experience as a nutrition specialist. She graduated from California State University of Los Angeles in 2011 and interned at the University of Puerto Rico Medical Science Campus in 2012. She services clients in both English and Spanish.
 Blanca Garcia, RDN, has 8 years of experience as a nutrition specialist. She graduated from California State University of Los Angeles in 2011 and interned at the University of Puerto Rico Medical Science Campus in 2012. She services clients in both English and Spanish.
Blanca Garcia, RDN, has 8 years of experience as a nutrition specialist. She graduated from California State University of Los Angeles in 2011 and interned at the University of Puerto Rico Medical Science Campus in 2012. She services clients in both English and Spanish.
Read full bio of Ravi Teja Tadimalla
Read full bio of Arshiya Syeda
Read full bio of Sindhu Koganti




























Community Experiences
Join the conversation and become a part of our empowering community! Share your stories, experiences, and insights to connect with other beauty, lifestyle, and health enthusiasts.