Shiitake Mushrooms: Nutrition, Benefits, & Side Effects
Boost your tastebuds and immunity with these rich and earthy culinary delights.

Image: Shutterstock
Shiitake is a variety of edible mushrooms native to East Asia. These mushrooms are rich in flavor, with a distinctive taste and many culinary uses. People in China first started cultivating shiitake mushrooms about 1,000 to 1,200 years ago. Shiitake mushrooms have many health benefits. They are rich in natural copper, a mineral that supports healthy blood vessels, bones, and immune health. They also have anti-inflammatory properties, and the protein they contain comprises all 18 amino acids. This article provides information about the nutritional facts, health benefits, and potential risks of shiitake mushrooms.
 Know Your Ingredient: Shiitake Mushrooms
Know Your Ingredient: Shiitake MushroomsWhat Is It?
An edible mushroom with a distinct, earthy flavor native to East Asia.
What Are Its Benefits?
It has anti-inflammatory, anti-cancer, and antioxidant properties. It may help lower cholesterol and improve heart, skin, and bone health.
Who Can Consume It?
It can be safely consumed by everyone in moderation.
How Often?
It can be safely consumed every day. However, you should limit yourself to an average amount, such as 6 to 8 mushrooms.
Caution
Eating them without cooking or in high amounts can cause allergic reactions, stomach discomfort, and blood abnormalities.
In This Article
What Are Shiitake Mushrooms?
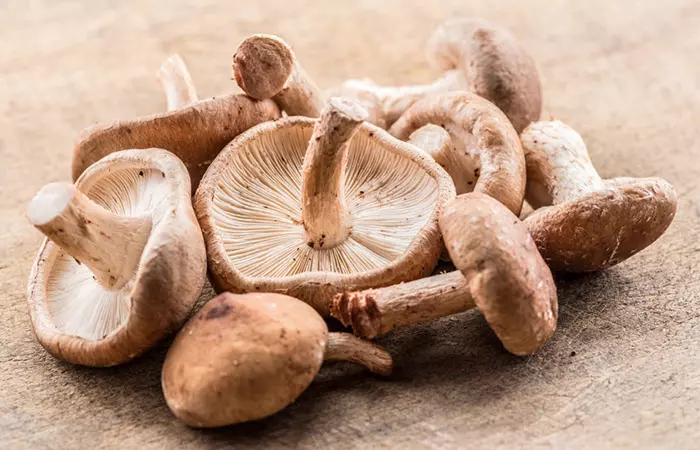

Shiitake mushrooms are smaller than regular mushrooms. Their caps measure about 10 to 20 centimeters in diameter, and are attached to thin stems. The color of the cap is light to dark brown and has a wide, umbrella-like shape with a characteristic curled rim. When cooked, shiitake mushrooms release a garlic-pine aroma and have a savory, earthy, and smoky flavor.
Shiitake mushrooms, classified as Lentinula edodes, are the second most common type of edible mushrooms in the world after the button mushrooms. They are members of the Marasmiaceae family. They have been used in traditional medicine to reduce symptoms of the common cold, increase energy, and ward off hunger.
Shiitake mushrooms were grown on deadwood logs in the olden days, which was a time-taking process. Over the past few decades, alternative techniques for cultivating shiitake mushrooms have been developed – which involve the use of waste products like corn cobs and sunflower seed hulls as the growing media.
 Trivia
TriviaShiitake mushrooms are also rich in fiber, vitamins, and minerals. They are a good source of B complex vitamins and vitamin D. They also contain polysaccharides that help reduce cholesterol and boost immunity. In the following section, we will check out the nutrition profile of shiitake mushrooms.
Key Takeaways
- The copper in shiitake mushrooms boosts immunity.
- They promote bone health as they are rich source of Vitamin D.
- However, excess intake may cause allergies and gastrointestinal issues.
- Cook and handle the mushrooms properly to avoid side effects.
Nutrition Facts Of Shiitake Mushrooms
100 grams of shiitake mushrooms contain the following nutrients (1):
| Energy | 37 kcal |
| Water | 89.7 g |
| Protein | 2.24 g |
| Fiber | 2.5 g |
| Carbohydrates | 6.79 g |
| Glucose | 2.38 g |
| Calcium | 2 mg |
| Sodium | 9 mg |
| Fatty acids, total trans | 0 g |
| Vitamin B6 | 0. 293 mg |
Shiitake mushrooms are a rich source of vitamins, minerals, and other nutrients. Hence, they offer several health benefits. Let us discuss them in the next section.
Health Benefits Of Shiitake Mushrooms
1. May Improve Immune Function
The polysaccharides in the mushrooms, the β-glucans, are well known for their biological activity related to the immune system. Fungal β-glucans are especially beneficial to humans. They stimulate the human immune system and protect against pathogenic microbes, environmental toxins, and carcinogens. They also protect us from infectious diseases (2). β-glucan has been linked to altering the immune system. Lentinan, another compound in shiitake mushrooms, can interact with macrophagesi They are specialized cells in the body that help detect and fight bacteria and other harmful pathogens. , dendritic cells, and other immune cells. Shiitake mushrooms have also been found to enhance the production of IgA (immunoglobulin A), an antibody that boosts the immune function of cellular membranes (3).
As already discussed, the copper in shiitake mushrooms is essential for optimal innate immune function. Deficiency of copper may increase one’s susceptibility to bacterial infections (4).
Anthony Puopolo, a certified physician, says shiitake mushrooms do an excellent job of reducing inflammation and supporting immune health. They are known to be high in eritadenine as well, a compound that has been found to reduce cholesterol levels. All in all, shiitake mushrooms are an excellent health choice and are easy to introduce into your diet – whether raw, roasted, sautéed, or any other way that suits your fancy.
2. May Promote Heart Health

Shiitake mushrooms contain bioactive compounds that offer antioxidant defense. They also help prevent oxidation of low-density lipoprotein (LDL, or the bad cholesterol) – and may help reduce the risk of atherosclerosis. The mushrooms also contain α-tocopherol (vitamin E), oleic acid, linoleic acid, ergosterol, and butyric acid that may function as anti-atherosclerotic agents (5).
Studies also support the beneficial impact β-glucans can have on human health (6). Edible mushroom consumption may have beneficial effects on lipid profiles too. Mushrooms may help change some metabolic markers like low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol, high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol, total cholesterol, and triglycerides, and may promote cardiovascular health. Moreover, consumption of edible mushrooms is mainly associated with reducing mean blood pressure (7).
3. May Reduce Risk Of Cancer
Mushrooms possess antioxidant, hypocholesterolemici A substance or the ability of a substance to lower cholesterol levels in the blood with potentially adverse effects. , anti-tumor, anti-cancer, immunomodulatoryi The ability to modulate immune response and exert a protective effect on the body by decreasing or increasing levels of antibodies. , anti-allergic, nephroprotectivei The ability to protect the kidneys by reducing inflammation and helping clear metabolic wastes. , and antimicrobial properties. The active components in mushrooms responsible for their anti-cancer properties are lentinan, kristin, and hispolon. Shiitake mushrooms are rich in lentinan, which is known to suppress leukemia cell proliferation. The ethanol extract of this mushroom significantly decreased the cell proliferation cancer cells (8).
Mushrooms have shown anti-cancer properties against breast, bladder, colon, lung, and prostate cancers (9). Shiitake mushrooms are regarded as medicinal foods and are used in traditional Chinese medicine for their anti-cancer and other medicinal properties.
Further research also supports the cancer prevention effects of lentinan in shiitake mushrooms (10).
4. May Promote Skin Health
Ethanolic extracts of shiitake mushrooms possess anti-inflammatory, anti-tyrosinase, antioxidant, and antibacterial properties.
These extracts are also often introduced to base cosmetic creams.
The antioxidant capacity of shiitake mushrooms can help fight oxidative stress and offer anti-aging benefits (11). For many years, people all over the world have been using wild mushrooms in their cosmetics. Today, several types of mushrooms are introduced in topical creams, lotions, ointments, serums, and facial preparations. These mushrooms include Shiitake (Lentinula edodes), Maitake (Grifola frondosa), Reishi or Lingzhi (Ganoderma lucidum), and Fu Ling (Wolfiporia extensa). They are known for their antioxidant, anti-aging, anti-wrinkle, skin whitening, and moisturizing effects (12).
Mushroom extracts, including that of shiitake mushrooms, also possess anti-irritant properties. Shiitake mushrooms contain polysaccharides, triterpenes, proteins, lipids, phenols, and cerebrosides. These serve as anti-irritants and antioxidants and stimulate the skin’s natural renewal process. They also offer protection against photoaging and help improve skin elasticity. The natural shiitake complex inhibits elastase activity and eventually slows down wrinkle formation (13).
5. May Improve Bone Health

Shiitake mushrooms contain a decent amount of vitamin D, which is known to improve bone mineral density as it has significant bioavailability (14). Vitamin D is responsible for stimulating the synthesis of calcium, helping transport proteins in the small intestine, enhancing the absorption of dietary calcium, and reducing the risk of osteomalaciai A condition in which the bones of the body become soft due to an issue with vitamin D availability or function. in adults and rickets in children (15).
A combination of extracts from L. edodes (shiitake mushrooms) and G. frondosa may reduce bone loss in the lumbar spine. L. edodes may also promote osteoblasts (cells that support new bone formation) and decrease lumbar spine bone loss. Hence, mushroom extracts can be considered a preventive treatment and/or a supplement with regard to bone health (16).
6. May Have Antiviral And Antibacterial Activity
Shiitake mushroom extract exhibited antimicrobial activity against 85% of the organisms, 50% of which were yeast and mold species (17). Mushrooms require antibacterial and antifungal compounds to survive in their natural environment. These antimicrobial compounds are isolated from many mushrooms and could be of benefit to humans (18).
Mushrooms can be used as an alternative to natural sources of new antimicrobials. Mushroom extracts have phenolic compounds that exhibit antioxidant and antimicrobial activity (19).
Mushrooms can be termed as nutritional foods with many proven benefits. But despite their health benefits, their intake may also have some potential downsides. Learn more in the next section.
Potential Side Effects Of Shiitake Mushrooms
1. May Cause Gastrointestinal Problems

Excess intake of shiitake mushroom powder may lead to eosinophiliai A condition in which a high number of white blood cells are created in the body due to an allergen or drug. and increased gastrointestinal symptoms. Many people refrain from eating shiitake mushrooms due to rashes or abdominal discomfort, and also may develop eosinophilia (20). The mushrooms may also cause bowel obstruction in a few (21).
2. May Cause Allergic Reactions
Consumption of undercooked shiitake mushrooms can cause shiitake mushroom dermatitis or flagellate dermatitis. This rash develops slowly and spreads rapidly over 24 hours. Shiitake dermatitis is a skin eruption that shows whiplash marks and occurs after consumption of raw shiitake mushrooms. It occurs due to the toxic reaction to lentinan (22).
Other allergic symptoms include linear erythematous eruptionsi A kind of skin rash that occurs if blood capillaries become inflamed or injured. It is usually mild and gets better in a few weeks. with papules. Dermatitis may occur through ingestion of mushrooms or from handling, which can result in contact dermatitis (23).
While shiitake mushrooms are generally healthy for most individuals, handling or cooking them incorrectly may result in negative side effects.
Jane, a blogger, recounts an unsettling experience after consuming a Shiitake mushroom, garlic, and sweet chili pizza. Subsequent consumption led to extreme exhaustion, followed by an itchy rash on her upper arms and scalp. She said, “On Sunday morning I woke up feeling itchy on my upper arms and scalp. Then last night when I bathed I noticed a blistery rash all over my stomach, back and lower arms etc. It is extremely itchy! And quite alarming. I am covered in this blistery rash which itches like mad!” She added, “But I have done some research and I am now pretty convinced it is Shiitake Dermatitis Syndrome (i).”
 Quick Tip
Quick TipHowever, most of the mentioned side effects are rare and mostly occur due to improper cooking methods or handling. Hence, you can enjoy these delicious mushrooms with your meal. But can you eat them daily?
Can I Eat Shiitake Mushrooms Every Day?
Yes, but in limited quantities. One can take ½ a cup of shiitake mushrooms every day to reap their benefits. Ensure the mushrooms are cooked properly. Do not microwave them (as it may increase the risk of allergic reactions).
Now that you know it is safe to enjoy shiitake mushrooms daily, the next step is to figure out easy and creative ways to incorporate them into your meals. Scroll down for some helpful tips.
How To Incorporate Shiitake Mushrooms Into Your Diet
Shiitake mushrooms can be a flavorful and nutritious addition to your meals in many ways. Here are some versatile methods for cooking and serving shiitake mushrooms:
- Toss sliced mushrooms with garlic and herbs in butter or olive oil for a richly flavored and aromatic side dish.
- Combine sliced shiitake mushrooms with bell peppers, onions, and snap peas for a delicious stir-fry mixture.
- Add shiitakes to your broths and miso soup for a deep, earthy flavor that goes well with the other components.
- Brush shiitake mushrooms with olive oil, season with salt and pepper, and grill them for a smoky flavor.
- Add sautéed shiitake mushrooms to your taco filler mixes for a delicious flavor profile.
Here is a quick and delicious recipe you can follow to discover the delights of having Shiitake mushrooms in your diet.
Shiitake Mushroom Recipe
Garlic Butter Shiitake Mushrooms
Ingredients
- 10 ounces of fresh shiitake mushrooms
- 2-3 cloves of garlic
- 2 tablespoons of unsalted butter
- Fresh parsley
- Salt to taste
- Black pepper to taste
How To Prepare
- Clean and slice the shiitake mushrooms.
- Melt butter over medium heat in a skillet.
- Mince the garlic cloves and add it. Cook until they turn fragrant.
- Toss in the mushrooms and sauté until they are tender and browned.
- Season with salt and pepper to taste.
- Garnish with freshly chopped parsley.
Mushrooms are a tasty addition to many cuisines and are known for their unique taste. There are so many variations and mushroom benefits that make them such a popular food. Amongst all the different types, East Asian shiitake mushrooms are a rich source of many beneficial nutrients that offer important health benefits. However, improper cooking methods or handling may cause allergic reactions and gastric problems in some. Excess intake may also cause side effects. Hence, caution is advised. Eating them in moderation regularly will help you reap their benefits.
Frequently Asked Questions
Are there any specific populations that should avoid shiitake mushrooms?
People with mushroom allergies should avoid shiitake mushrooms to avoid any adverse reactions. Further, although research is limited, people with autoimmune diseases or those on blood thinners should exercise caution when consuming shiitake mushrooms or consult their healthcare provider before having them.
Is Shiitake Mushroom good for weight loss?
Yes, studies show that shiitake mushrooms may help proper weight management, prevent fat deposition, and lower fat levels in your body (24).
Can you eat the entire shiitake mushroom?
Yes, you can eat the entire shiitake mushroom. Since the stem has a fibrous texture, you can cut it out or use them to create a mushroom broth.
Can shiitake be eaten raw?
Yes, fresh shiitake mushrooms can be eaten raw. However, practice caution because they may cause an allergic reaction (22).
Is shiitake good for diabetics?
Yes, shiitake mushrooms may reduce high blood sugar levels and boost insulin secretion (25). People with diabetes mellitus may add this to their diet.
Should I use shiitake stems?
Yes, you can use the stems from shiitake mushrooms to make a delicious soup, or stock.
Illustration: Shiitake Mushrooms: Nutritional Value Benefits And Side Effects

Image: Stable Diffusion/StyleCraze Design Team
Learn more about the surprising benefits of shiitake mushrooms in this enlightening video. Learn how incorporating these mushrooms in your diet can contribute to your overall well-being.
Personal Experience: Source
StyleCraze's articles are interwoven with authentic personal narratives that provide depth and resonance to our content. Below are the sources of the personal accounts referenced in this article.
i. Did you know Shiitake Mushrooms can be toxic?https://janefraser.blogspot.com/2012/09/did-you-know-shiitake-mushrooms-can-be.html
References
Articles on StyleCraze are backed by verified information from peer-reviewed and academic research papers, reputed organizations, research institutions, and medical associations to ensure accuracy and relevance. Read our editorial policy to learn more.
- Mushrooms shiitake raw
https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/169242/nutrients - Edible Mushrooms: Improving Human Health and Promoting Quality Life
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/labs/pmc/articles/PMC4320875/ - Consuming Lentinula edodes(Shiitake) Mushrooms Daily Improves Human Immunity: A RandomizedDietary Intervention in Healthy Young AdultsXiaoshuang Data Joy M. Stanilkaa Cheryl A. Rowena Elizabeth A. Estevesb Carmel
https://www.researchgate.net/publication/274901164_Consuming_Lentinula_edodes_Shiitake_Mushrooms_Daily_Improves_Human_Immunity_A_Randomized_Dietary_Intervention_in_Healthy_Young_Adults - The Role of Copper and Zinc Toxicity in Innate Immune Defense against Bacterial Pathogens*
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/labs/pmc/articles/PMC4521016/ - Lentinula edodes (shiitake mushroom): An assessment of in vitro anti-atherosclerotic bio-functionality
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1319562X16000231 - Edible Mushrooms and Beta-Glucans: Impact on Human Health
https://www.mdpi.com/2072-6643/13/7/2195 - Mushroom Consumption and Cardiovascular Health: A Systematic Review
https://www.amjmed.com/article/S0002-9343(20)31092-5/fulltext - Recent developments in mushrooms as anti-cancer therapeutics: a review
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/labs/pmc/articles/PMC3339609/ - Mushroom consumption and incident risk of prostate cancer in Japan: A pooled analysis of the Miyagi Cohort Study and the Ohsaki Cohort Study
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/labs/pmc/articles/PMC7154543/ - Astragalus and Shiitake as an Integrated Therapeutic Approach
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8401741/ - Development of Mushroom-Based Cosmeceutical Formulations with Anti-Inflammatory Anti-Tyrosinase Antioxidant and Antibacterial Properties
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/labs/pmc/articles/PMC6274557/ - Mushroom Cosmetics: The Present and Future
https://www.mdpi.com/2079-9284/3/3/22 - Cosmetic Benefits of Natural Ingredients: Mushrooms Feverfew Tea and Wheat Complex
https://jddonline.com/articles/dermatology/S1545961613S0133X - Effects of vitamin D 2-fortified shiitake mushroom on bioavailability and bone structure
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30732553/ - A Review of Mushrooms as a Potential Source of Dietary Vitamin D
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/labs/pmc/articles/PMC6213178/ - Mushroom Extracts Decrease Bone Resorption and Improve Bone Formation
https://www.researchgate.net/publication/309102411_Mushroom_Extracts_Decrease_Bone_Resorption_and_Improve_Bone_Formation - Antimicrobial properties of shiitake mushrooms (Lentinula edodes)
https://www.researchgate.net/publication/23716171_Antimicrobial_properties_of_shiitake_mushrooms_Lentinula_edodes - The Pharmacological Potential of Mushrooms
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/labs/pmc/articles/PMC1193547/ - Comparative antioxidant and antimicrobial properties of Lentinula edodes Donko and Koshin varieties against priority multidrug-resistant pathogens
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S102691852030055X - Eosinophilia and gastrointestinal symptoms after ingestion of shiitake mushrooms
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/9600497/ - Two cases of small bowel obstruction due to a shiitake mushroom
https://academic.oup.com/gastro/article/7/4/298/4037468 - A characteristic rash caused by Shiitake mushrooms – An emerging concern?
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/labs/pmc/articles/PMC8222744/ - Shiitake Mushroom Dermatitis: A Review
https://www.researchgate.net/publication/307084866_Shiitake_Mushroom_Dermatitis_A_Review - Dietary Shiitake Mushroom (Lentinus edodes) Prevents Fat Deposition and Lowers Triglyceride in Rats Fed a High-Fat Diet
https://www.researchgate.net/publication/51746881_Dietary_Shiitake_Mushroom_Lentinus_edodes_Prevents_Fat_Deposition_and_Lowers_Triglyceride_in_Rats_Fed_a_High-Fat_Diet - Shiitake Mushroom: Potential Glycemic Control Activity on Alloxan – and Glucocorticoid-Induced Diabetic Long-Evans Rats
https://www.researchgate.net/publication/284186483_Shiitake_Mushroom_Potential_Glycemic_Control_Activity_on_Alloxan_-_and_Glucocorticoid-Induced_Diabetic_Long-Evans_Rats
Read full bio of Nilofar Pendhari
Read full bio of Aparna Mallampalli
Read full bio of Ravi Teja Tadimalla
Read full bio of Sindhu Koganti


























Community Experiences
Join the conversation and become a part of our empowering community! Share your stories, experiences, and insights to connect with other beauty, lifestyle, and health enthusiasts.