Types Of Hair Loss, Causes, Treatments, & Prevention Options
A comprehensive guide explaining the causes of hair loss and best treatment options for it

Image: Shutterstock
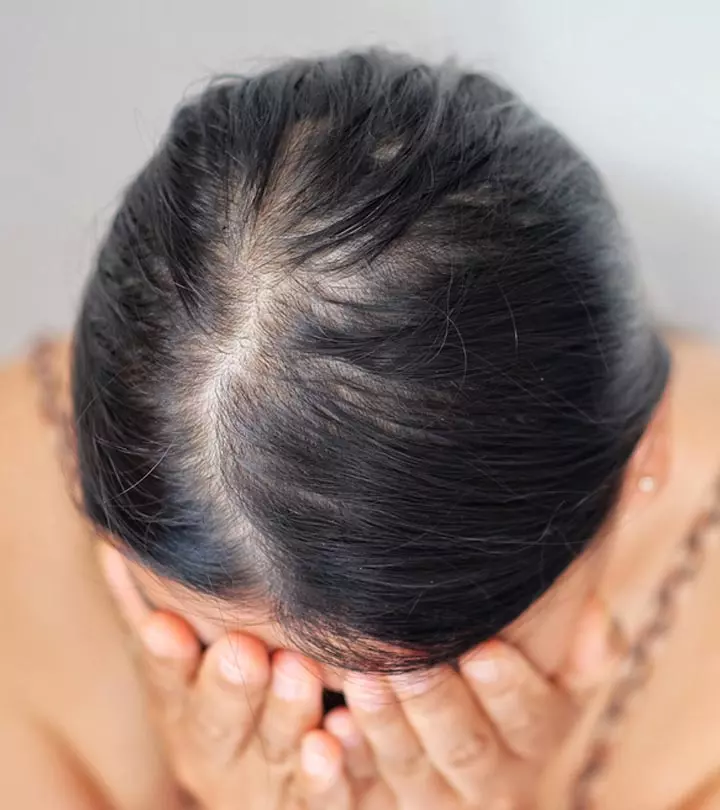
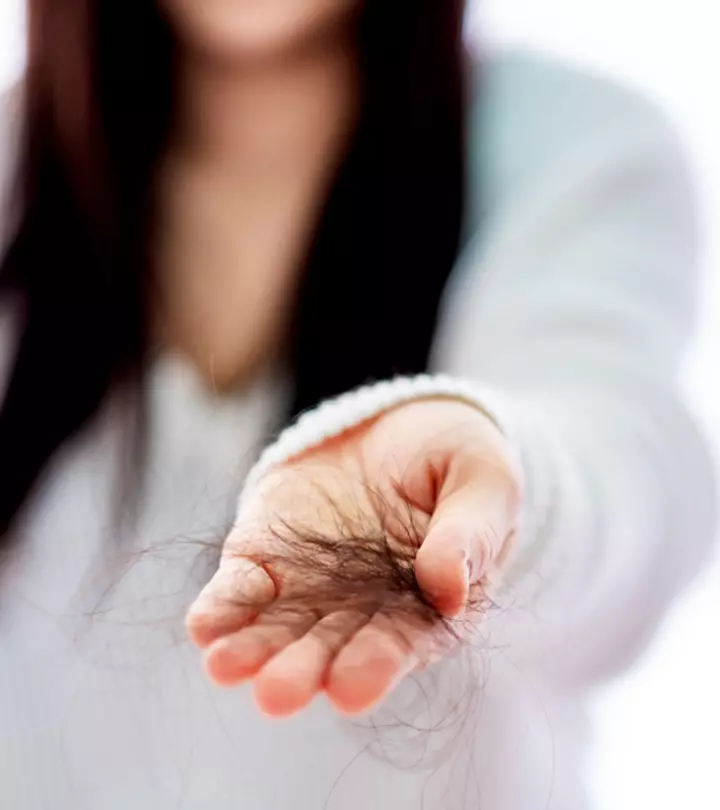
As per the American Association of Dermatology, losing about 100 hair strands every day is perfectly normal (1). But if you are losing more hair, you may be affected by one of the many different types of hair loss. These may be caused due to hormonal changes, genetics, stress, sudden and extreme weight loss or gain, etc. To recover from these conditions, you need to know which type of hair loss you have. Keep reading to understand the different hair loss types and the treatment options available.
In This Article
Different Types Of Hair Loss
- Alopecia Areata: This is an autoimmune condition resulting in hair loss on the scalp, eyebrows, eyelashes, and the face (2). It causes your hair to fall out in patches and may lead to total scalp hair loss (or even full-body hair loss). This is an autoimmune disorder that affects close to 25% of the general population. It is characterized by non-scarring hair loss that leaves a hair shaft without any growth. Several types of alopecia affect men and women the most (3), (4).
- Androgenic Alopecia: This is when hair loss occurs in patterns. Hair starts to fall when testosterone (the male sex hormone) is converted to dihydrotestosterone, which starts to attack the hair follicles and causes miniaturization, leading to hair fall. The increased activity of 5 alpha-reductase converts testosterone to DHT, leading to an increased number of DHT receptors in the follicles.
- Alopecia Areata: This is an autoimmune disorder that affects close to 25% of the general population (4). It is characterized by non-scarring hair loss that leaves a hair shaft without any growth. It can occur as patchy bald spots or could be widespread as well. Alopecia could occur in different types.
- Patchy Alopecia Areata: Hair loss occurs in distinct or joined patches.
- Alopecia Totalis: Total loss of hair on the scalp.
- Alopecia Universalis: Total loss of hair on the body.
- Alopecia Incognita: Total loss of hair in a diffused manner. It is diagnosed with a pull test, yellow dots, short and miniature hair regrowth, and lack of nail development.
- Ophiasis: Hair loss occurring in a band-like shape along the head’s circumference, specifically near the ears and back of the head.
- Sisaipho: Chronic alopecia that occurs everywhere except the border of the scalp.
- Marie Antoinette Syndrome: An “overnight” graying of hair paired with an episode of acute diffuse alopecia. This condition often occurs with pigmented hair.
- Reticular Alopecia Areata: Patches of alopecia occurring with well preserved narrow bands of hair in between (5).
- Diffuse Alopecia Areata: Widespread and acute hair loss commonly mistaken for androgenic alopecia or chronic telogen effluvium (5).
- Drug-Induced Hair Loss: Hair loss can be caused by the intake of certain drugs. Drugs can induce either anagen or telogen effluvium (6). Such conditions can lead to patterned or diffused hair loss and can be acute or chronic.
- Anagen Effluvium: Anagen effluvium occurs a few days or weeks after you start taking the drug.
- Telogen Effluvium: Drug-induced telogen effluvium normally occurs two to four months after you start taking the drug. Telogen effluvium occurs when more than 20% of your follicles suddenly go into the telogen phase, decreasing the number of actively growing hair follicles (7). This results in the loss of hair volume and, eventually, balding. Telogen effluvium is mostly induced by triggers.
Other than medications, other triggers may also cause telogen effluvium. They include:- Health triggers: Malaria, typhoid, tuberculosis, thyroid issues, organ dysfunctions, HIV, malnutrition, syphilis, autoimmune diseases, and nutrient deficiencies
- Stress Triggers: Emotional trauma, heavy labor, starvation, crash diets, severe injuries, and surgeries
- Drug Triggers: Oral retinoids, oral contraceptives, anti-thyroid drugs, anticonvulsants, hypolipidemic drugs, beta-blockers, amphetamines, captopril, and heavy metals
- Local Triggers: Hair dye allergies
- Postpartum Hair Loss: Postpartum hair loss occurs a few weeks after the mother delivers her child. It is caused by low hormone levels. An increase in progesterone and estrogen levels in the body during pregnancy puts hair in a prolonged anagen phase (8), (9).Removal of the placenta normalizes these hormone levels, causing hair loss. Postpartum hair loss can also be caused by nutrient deficiencies, stress, post-surgery stress, and hypothyroidism (8), (10).
- Stress-Related Hair Loss: Stress affects hair follicle development and can impact the hair growth cycle (11). Stress-related hair loss, when left untreated, can lead to serious hair disorders like alopecia, telogen effluvium, and baldness.
- Trichotillomania: A compulsive disorder where the patient pulls out her hair, causing hair loss (12).
- Diffuse Thinning: Hair begins thinning all over the scalp.
- Hair Loss Due To Nutrient Deficiencies: Vitamins, proteins, amino acids, or mineral deficiencies can also contribute to hair loss (13). Deficiencies in iron, vitamin D, selenium, and calcium can lead to hair loss.
 Trivia
TriviaThese are the different types of hair loss in women. Let us now briefly look into the causes for the same.
Causes Of Hair Loss That Affect Women
1. Genetic Factors
Genes play a huge role in hair loss. The most common type of hair loss, alopecia, is caused due to genetic factors. While this is more evident in men, women too are likely to develop genetically inherited alopecia.
2. Hormonal Issues
Changes in hormone levels increase hair follicle sensitivity. These changes may also weaken hair roots and cause excessive hair fall. Thyroid issues and anti-thyroid medications are another common cause of hair loss. They cause widespread hair loss that makes hair look sparse. Thyroid issues may also lead to permanent hair loss in some cases.
Menopause, ovarian cysts, hypothyroidism, and hyperthyroidism bring about major changes in the body’s hormonal balance. These changes could trigger hair loss.
3. Pregnancy
The change in hormone levels during pregnancy often causes hair loss. Hair growth should return to normal a few weeks or months after delivery. Sometimes, the drugs prescribed during pregnancy can also cause hair loss. This type of hair loss is more likely to stop following the discontinuation of the drugs.
4. Physical And Mental Stress
One of the most common causes of hair loss is stress. Physical, emotional, and mental stress increases free radical production, causing oxidative damage to hair. Stress may also make hair thin and brittle.
5. Scalp Infections
The scalp is prone to fungal and bacterial infections like dandruff and eczema. These infections weaken hair and harm scalp health. They may also cause hair breakage and thinning.
Scalp fungal infections such as tinea capitis may also cause hair damage and loss. The fungus invades the outer covering of the hair shaft and eventually targets the hair shaft. This may eventually lead to patches of hair loss. This fungal infection can also spread to the eyelashes and eyebrows (14).
6. Autoimmune Disorders
Autoimmune diseases may cause hair loss too. Alopecia are at a is an autoimmune disease where the immune system attacks the hair follicles, causing hair loss (4).
Scalp psoriasis is another autoimmune disease that affects the scalp and can even spread to the forehead, back of the neck, and inside the ears. It causes thick, itchy, and inflamed patches on the scalp. It may also cause symptoms such as itching, bleeding, burning sensation, or temporary hair loss (15).
7. Medication And Treatments
Certain medical conditions call for treatments and surgeries that may cause side effects, including hair loss. Treatments like chemotherapy, steroids, and medications for typhoid, heart disease, and depression may cause extreme hair fall. Certain other drugs may also cause hair loss as a side effect (16), (17), (18), (19).
10. Over processing And Styling
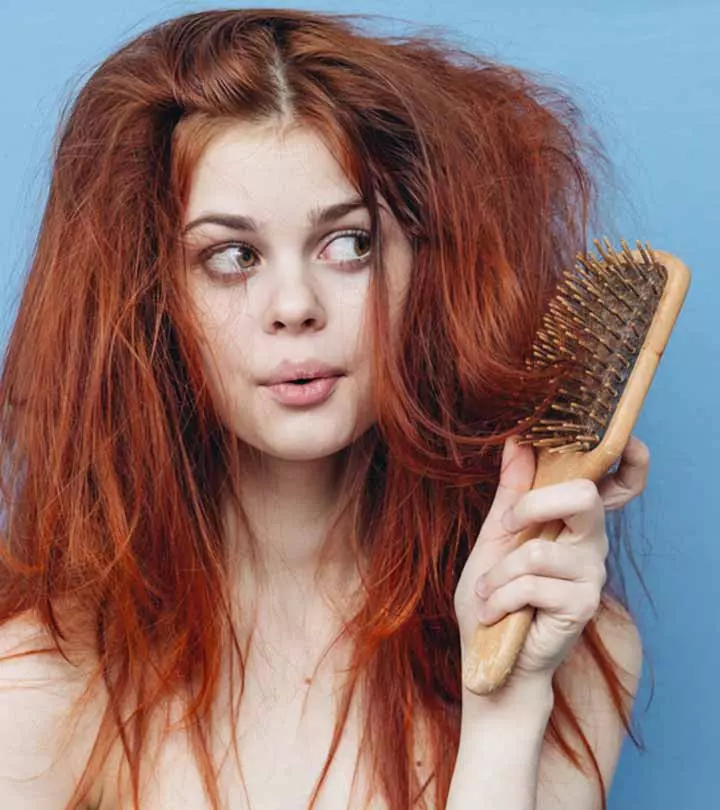
Excess use of hair products and heating tools can cause hair damage and hair loss. Hair products like shampoos and conditioners contain chemicals that might not be good for the scalp. Tight hairstyles that pull at the roots can cause follicular damage and hair loss.
11. Improper Food Habits
There is sufficient evidence to prove that vitamins and minerals play a key role in hair growth (13). Certain nutrient deficiencies due to an unbalanced diet can cause hair loss as well.
12. Over-Supplementation
Over-supplementation of a few nutrients, including vitamins A and E and selenium, may also cause hair loss (10). You may always go for real fruits and other organic foods first and take supplements only when needed.
Treatment Options
- Hair loss can be treated with drugs like minoxidil or finasteride or natural remedies like coconut oil, hair packs, etc. Anecdotal evidence suggests that using natural remedies has fewer risks than using drugs.
- Massaging the scalp with oil can stimulate hair growth by improving blood circulation (20). Opt for hot oil treatments or regular oil massages to stimulate the scalp and follicles.
- Having a healthy and balanced diet may help reduce hair loss and induce hair growth.
- Exercise, meditation, and yoga may help alleviate stress and reduce stress-induced hair loss. Tia, a blogger, shares her experience of living with alopecia from a coily hair perspective. She recounts the discovery of bald spots about 9 years ago while having relaxed hair and the subsequent journey of regrowth. She adds, “Inflammation is a culprit in this situation, so I take care not to eat too much sugar, or bring stress to myself (i)!”
- Reduce the use of heating tools.
- Have a regular hair care routine with deep conditioning treatments. Get regular trims to prevent hair from weakening at the ends.
 Trivia
TriviaWhile most types of hair loss can be treated, certain conditions could be permanent due to damaged follicles. One may have to go for hair transplantation in such cases.
Is Hair Loss Different In Women And Men
While there are common types of hair loss that affect both women and men, the causes could differ. One common cause of hair loss in women is excessive grooming and styling. Women with androgenic alopecia have hair loss caused by androgen levels that are too high or low. However, androgenic alopecia in men is caused due to an increase in DHT production.
Female-patterned hair loss is different from male-patterned hair loss. The primary symptoms of female pattern hair loss include the following:
- Hair thinning is observed mainly on the top and the crown area. Balding starts with the widening of the center hair part.
- The front hairline remains unaffected in most.
- The hair loss may be acute, but it does not lead to complete or near total baldness, as it does in men.
- More hair loss is observed during showers and while brushing hair.
Hair loss in women is also triggered by pregnancy and hormonal changes.
Treatment Options Specific For Women
With androgenic hair loss, women are prescribed anti-androgens like cyproterone-acetate, spironolactone, and flutamide that may reduce hair loss due to hormonal changes (21). Women may also require to take prenatal vitamins to treat postpartum hair loss or hair loss during pregnancy.
If you are losing more than 100 strands of hair a day, it might be because you are affected by hair loss. There are different types of hair loss caused by various factors. From hormonal changes to stress to lifestyle issues, several factors contribute to hair loss. Understanding the cause of your hair loss can help you determine the type of treatment you need. There are both medical and home remedies to treat hair loss issues. Consuming a healthy and balanced diet will also help you maintain your hair health.
Frequently Asked Questions
Does lack of sleep cause hair loss?
Lack of sleep can affect your lifestyle and cause stress leading to hair loss.
What should I eat to stop hair loss?
You should eat a balanced diet of fruits, vegetables, greens, grains, dairy, and nuts. These contain vitamins, minerals, proteins, amino acids, and fatty acids that might stimulate hair growth.
Which exercise is best for hair growth?
Exercise may not stimulate hair growth. However, you should exercise daily or live an active lifestyle to avoid hair loss.
Can inactivity cause hair loss?
Inactivity can lead to changes in your thyroid function that might lead to hair loss.
Key Takeaways
- Hair loss is a common hair problem that can be caused by autoimmune conditions, drugs, or other health conditions.
- Pregnancy, hormonal imbalances, genetics, and excess hair styling may trigger hair loss in women.
- It can be treated with the help of anti-androgens like cyproterone-acetate, spironolactone, and flutamide. It also can be minimized with coconut oil or hair packs.
Read full bio of Dr. Shruti Chavan
Read full bio of Anjali Sayee
Read full bio of Eshna Das
Read full bio of Swathi E

























Community Experiences
Join the conversation and become a part of our empowering community! Share your stories, experiences, and insights to connect with other beauty, lifestyle, and health enthusiasts.