Low Histamine Diet – Health Benefits And Side Effects
While this eating plan is not for everyone, some may really benefit from its effects on the body.

Image: Shutterstock
A low-histamine diet is recommended for people with histamine intolerance. While histamine aids in several bodily functions, excess histamine can lead to symptoms similar to an allergic reaction. Roughly 20% of the western population deals with food intolerances, with histamine intolerance being one of the most common (1). In this article, we will explore what histamine intolerance is, how a low-histamine diet is beneficial, and what foods to avoid.
 At A Glance: Low Histamine Diet
At A Glance: Low Histamine Diet- Principle: A balanced diet that includes fresh, low-histamine foods.
- Purpose: To lower the level of histamine in the body, reduce the symptoms of hives, and manage atopic dermatitis.
- Who It Is For: People with histamine intolerance or sensitivity.
- Principle: A balanced diet that includes fresh, low-histamine foods.
- Duration: Short-term
- Who Should Avoid: Pregnant and breastfeeding women, children, people with (a history of) eating disorders, and people with medical conditions that require a specific dietary approach.
- Cons: Very restrictive as it requires the elimination of processed and canned foods.
In This Article
What Is Histamine And Histamine Intolerance?
Histamine is a chemical substance released by mast cells (a type of white blood cells) that helps regulate the body’s response to foreign substances. Simply put, your body releases histamine when it perceives something as harmful. While the body gets some amount of histamine from its own cells, histamine is also found in certain foods.
According to the Food and Health Organization of the United Nations and the World Health Organization, histamine-rich foods may cause histamine intolerance in sensitive individuals who have trouble breaking down this compound (2). Similar to an allergic reaction, the symptoms of histamine intolerance are (1):
- Headaches
- Palpitationi Sensations of pounding and racing heart felt in the chest, neck, and throat.
- Redness
- Skin inflammation
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Itchy skin
- Rashes
- Diarrhea
According to the American Academy of Allergy, Asthma, and Immunologyi A study of biology and medicine that deals with the medical research of immune systems. , there is no specific test for diagnosing histamine intolerance (3). So, doctors recommend an elimination diet. This means removing histamine-rich foods for 4 weeks and gradually adding them back. This allows your doctor to determine which food is triggering the symptoms.
Note: It is important to note that histamine intolerance may affect individuals in different ways, with symptoms ranging from mild discomfort to severe reactions. Therefore, it is recommended to always consult a healthcare expert before making any dietary changes. They can help you tailor dietary choices to your specific needs and carefully monitor how your body responds to various foods. This can help manage the condition more effectively and improve your overall well-being.
How does a low-histamine diet benefit us? Let’s find out in the next section.
Key Takeaways
- Your body becomes histamine intolerant when it is unable to metabolize histamine.
- This condition manifests in the form of an allergic reaction.
- Studies suggest that diamine oxidase, a low histamine-breaking enzyme, may cause the intolerance.
- Avoid fermented foods like pickles, kimchi, yogurt, etc., while on a low-histamine diet.
Benefits Of A Low-Histamine Diet
- May Lower The Level Of Histamine In Your Body
The primary purpose of a low-histamine diet is to decrease the level of histamine in the body. Diamine oxidase is an enzymei Proteins that aid in speeding our bodies' chemical changes or metabolism. that is responsible for breaking down histamine in our bodies. Studies have suggested that low levels of diamine oxidase (DOA) may increase the levels of histamine in the body (4). In another study, patients with histamine intolerance had lower DOA activity. The same patients when asked to go on a low-histamine diet with DOA supplements saw an improvement in the symptoms (5).
- May Help Reduce The Symptoms Of Hives
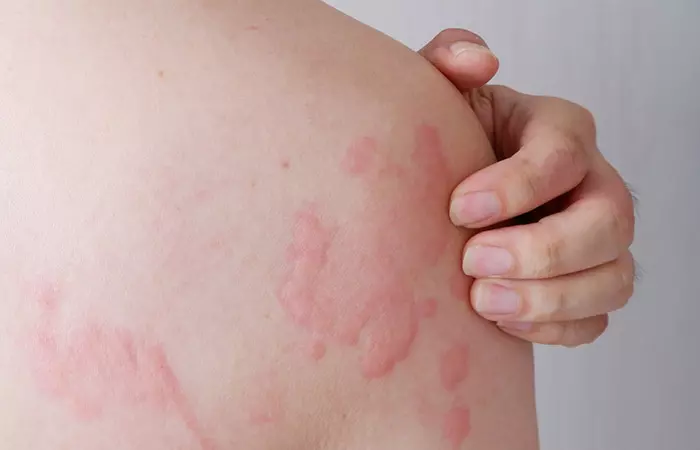
A low-histamine diet may be instrumental in reducing the symptoms of hivesi A typical skin rash caused by an allergic reaction and characterized by swollen and itchy bumps. . A study was conducted in 2018 to see the effect of a low-histamine diet on patients with chronic hives. The patients were prohibited from consuming histamine-rich food for 4 weeks. After 4 weeks, the researchers found a significant decrease in the histamine levels and severity of hive symptoms (6). Research also suggests that consuming a low-histamine diet for 3 weeks may be beneficial to patients with hives accompanied by gastrointestinali It is of or pertaining to the gut and the stomach. symptoms (7).
- May Help Manage Atopic Dermatitis
Similar to symptoms of histamine intolerance, the symptoms of atopic dermatitisi A chronic skin condition that causes inflammation, dryness, and itching. may worsen due to the intake of histamine-rich food. A study conducted on a boy with atopic dermatitis found that a low-histamine diet is instrumental in the reduction of symptoms (1), (8).
- May Reduce The Symptoms Of Irritable Bowel Syndrome
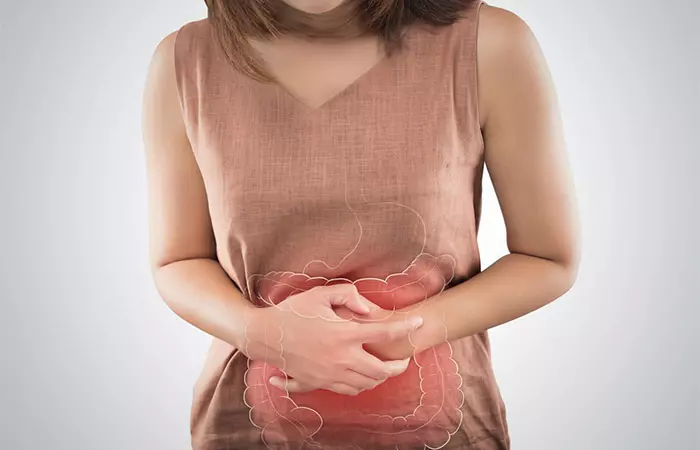
Eating a low histamine diet may reduce the symptoms of IBS. Research suggests that an effective IBS diet involves avoiding gluten-rich foods and fermented products, which may play an important role in reducing symptoms (9).
A blogger shared her experience of following a low histamine diet for a week on her blog: “It took several days to get into the groove of eating this way, and then I noticed that I had lost some weight. I started weighing myself on Day 5 and by Day 6 had lost at least eight pounds (i).”
Even though a low-histamine diet has many potential benefits, it is highly recommended that you consult a doctor before going on this diet.
Since the low-histamine can be restrictive, check out the next section for a delicious and easy recipe you can experiment with on this diet.
Easy Low Histamine Diet Recipe
Grilled Lemon Herb Chicken

Ingredients
- 2 boneless, skinless chicken breasts (approximately 250 g)
- Juice of one lemon
- 2 tablespoons of fresh parsley, chopped
- 1 tablespoon of olive oil
- Salt and pepper, to taste
Method
- Mix the lemon juice, chopped parsley, olive oil, salt, and pepper in a bowl.
- Marinate the chicken in this mixture for at least 30 minutes.
- Preheat the grill to medium-high heat and grill the chicken for about 6-8 minutes per side.
- Serve the grilled lemon herb chicken hot.
If you aren’t sure which foods are high in histamine? Check out the next section to read about which foods to avoid on a low-histamine diet.
Foods To Avoid On A Low-histamine Diet
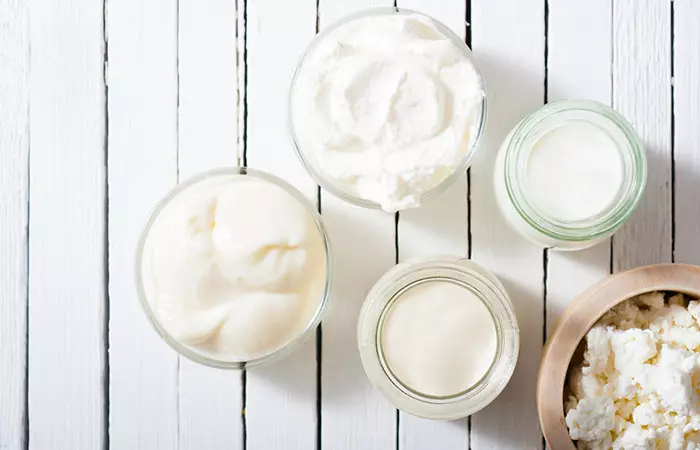

Today, due to limited evidence, it is difficult to quantify histamine levels in food. Factors such as storage time, addition of preservatives, and how old the food is can impact its histamine levels. Make sure you avoid foods labeled as “histamine liberators” as they are meant to help release histamine from other foods you consume. Here is a list of foods that may have higher levels of histamine (10):
- Cheese, sour cream, buttermilk, and yogurt
- Kimchi and sauerkraut
- Pickles or pickled veggies
- Kombucha
- Salami, sausages, and fermented ham
- Beer, wine, and champagne
- Miso, tempeh, natto, and soy sauce
- Sourdough bread
- Tomatoes
- Eggplant
- Spinach
- Frozen, salted, or canned fish such as sardines and tuna
- Vinegar
- Tomato ketchup
- Avocado
 Quick Tip
Quick TipWhile the above is a list of foods to avoid, below is a list of foods that are considered to be low in histamine.
- Herbal teas
- Quinoa, buckwheat, and rice
- Chia, flax seeds, and hemp
- Vegetables excluding spinach, eggplant, and tomato
- Freshly cooked seafood and meat
- Gluten-free products
- Cooked eggs
- Dairy-free products
- Coconut products, such as coconut milk and coconut butter
Always choose fresh foods, as they are generally considered lower in histamine compared to processed food. Research suggests that boiling foods has little influence on the histamine content of food. In some cases, it may even decrease it. However, frying and grilling are linked to increased histamine levels (11).
The next section explores the cons of eating a low-histamine diet.
Cons Of A Low-histamine Diet

While limited studies indicate that a low-histamine diet can help reduce symptoms of various diseases, more studies are warranted to confirm that.
- There is no scientific evidence currently that suggests that a low-histamine diet may improve quality of life in the long term.
- A low-histamine diet may lead to malnutrition. Before you opt for it, it is recommended to consult a doctor/nutritionist for better understanding.
- A low-histamine diet may be hard to sustain as it requires complete elimination of processed and canned foods. This may be hard for people who rely on these kinds of food for convenience.
 Quick Tip
Quick TipTo Sum It Up
Histamine intolerance is a medical condition that is difficult to diagnose, and a low-histamine diet may be essential in tackling it. especially for individuals with compromised gut health and mast cell activation syndrome. Limited scientific evidence suggests that a low histamine diet may help in the reduction of symptoms of hives and atopic dermatitis. While cutting out fermented products and other selected foods may be beneficial for a while, it may lead to malnutrition in the long run. Before you opt for this diet, consult your doctor/nutritionist to plan a balanced diet that meets all your dietary needs.
Frequently Asked Questions
How can I lower my histamine levels quickly?
Taking antihistamines, corticosteroids, and DAO enzyme supplements may help lower your histamine levels quickly, especially if you suffer from DAO deficiency. DAO deficiency is a condition where the body lacks the DAO enzyme responsible for breaking down histamine. Therefore, consult your doctor before taking these medications.
Are potatoes high in histamine?
No, potatoes are not high in histamine.
What time of day is histamine highest?
Though the histamine levels keep fluctuating throughout the day, the body releases higher levels of histamine at night and the lowest levels in the afternoon. Excessive histamine may result in itching, difficulty breathing, and lack of sleep. Therefore, it is best to consume low histamine foods after evening.
Illustration: Low Histamine Diet - Health Benefits And Side Effects

Image: Dall·E/StyleCraze Design Team
A low-histamine diet plan can help you manage your histamine intolerance. Get delicious recipes and a 5-day plan to help you feel better and reduce your symptoms from the video below.
Personal Experience: Source
StyleCraze's articles are interwoven with authentic personal narratives that provide depth and resonance to our content. Below are the sources of the personal accounts referenced in this article.
i. How did my first week on a low histamine diet go?https://mymastcells.blogspot.com/2014/05/how-did-my-first-week-on-low-histamine.html
References
Articles on StyleCraze are backed by verified information from peer-reviewed and academic research papers, reputed organizations, research institutions, and medical associations to ensure accuracy and relevance. Read our editorial policy to learn more.
- Histamine Intolerance: The Current State of the Art
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/labs/pmc/articles/PMC7463562/#B54-biomolecules-10-01181 - Public Health Risks of Histamine and other Biogenic Amines from Fish and Fishery Products
https://iris.who.int/bitstream/handle/10665/89216/9789240691919_eng.pdf - Diamine oxidase use in children
https://www.aaaai.org/allergist-resources/ask-the-expert/answers/old-ask-the-experts/diamine - Serum diamine oxidase activity in patients with histamine intolerance
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/labs/pmc/articles/PMC5806734/ - Serum diamine oxidase activity as a diagnostic test for histamine intolerance
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23579881/ - A Histamine-Free Diet Is Helpful for Treatment of Adult Patients with Chronic Spontaneous Urticaria
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/labs/pmc/articles/PMC5839887/ - A Popular myth – low-histamine diet improves chronic spontaneous urticaria – fact or fiction?
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27624921/ - Treatment of Atopic Dermatitis with a Low-histamine Diet
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/labs/pmc/articles/PMC3199434/ - A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis Evaluating the Efficacy of a Gluten-Free Diet and a Low FODMAPs Diet in Treating Symptoms of Irritable Bowel Syndrome
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30046155/ - Histamine intolerance and dietary management: A complete review
https://www.researchgate.net/publication/307600464_Histamine_intolerance_and_dietary_management_A_complete_review - Effect of different cooking methods on histamine levels in selected foods
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC5705351/
Read full bio of Dr. Pallavi Srivastava
Read full bio of Varsha Patnaik
Read full bio of Arshiya Syeda
Read full bio of Payal Karnik




























Community Experiences
Join the conversation and become a part of our empowering community! Share your stories, experiences, and insights to connect with other beauty, lifestyle, and health enthusiasts.