White Bumps On Lips: Types, Causes, Symptoms, & Home Remedies
From a lack of hygiene to hormonal imbalances – anything can be the root of this problem.
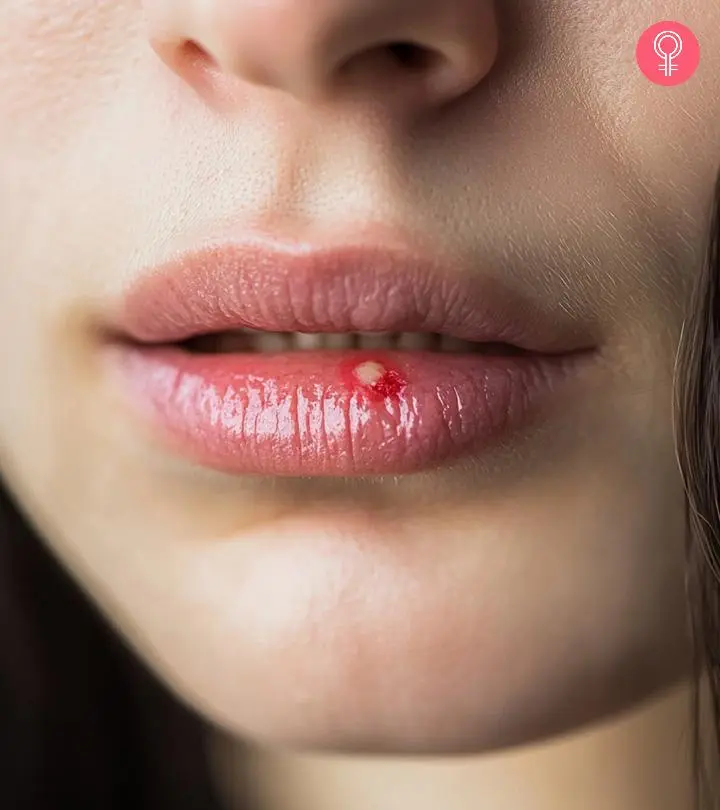

Image: Midjourney/ StyleCraze Design Team
If you have recently noticed white bumps on lips and are worried about what they are, we have the answer. These white bumps are oral ulcers and are mostly caused by factors like hormonal imbalances, poor skin hygiene, and may also indicate an underlying skin condition. They can cause great discomfort and pain, and you may have trouble opening your mouth. Therefore, consult a doctor and get them treated or try home remedies for relief and pain management. In this article, we have discussed the home remedies to minimize white bumps on the lips and preventive measures to take. Keep reading.
In This Article
What Causes White Bumps On Lips?
The sebaceous glandsi Small glands located near the second layer of the skin that produce a waxy substance called sebum, which moisturizes the skin. in the body. ” ]build up on the lips when secreted abnormally and serves as a breeding ground for viruses and bacteria. This can inflame the surrounding skin and cause white bumps.
The most common causes of white bumps on lips include:
- Hormonal imbalances (1)
- Poor personal hygiene (2)
- Allergic response to ingredients and products (anecdotal evidence)
- An injury to the area (3)
- Genetics (Anecdotal evidence)
Let us look at some of the most common conditions that may cause white bumps on lips. Keep reading.
Key Takeaways
- Hormonal imbalances, poor personal hygiene, and injury may cause white bumps on lips.
- Though these bumps may cause some pain, they are harmless. These can be treated using simple home remedies like garlic, coconut oil, and apple cider vinegar.
- White bumps may heal faster by washing your face with warm water, avoiding cosmetics, and drinking plenty of water.
Types Of White Bumps On Lips
1. Fordyce Spots
Fordyce spots are small white bumps on lips that are clusters of tiny white or yellow patches on or around the lips. These patches fade away with time and are neither contagious nor painful. These are enlarged sebaceous glands and occur mostly on vermilion (the red part of the lips) and oral mucosa. These also may occur on the penis, scrotum, and labia, though they are less common. The condition is mostly observed in middle-aged and elderly individuals (4). A study suggests that individuals with an elevated lipid profile may have the highest score of Fordyce spots (5).
 Quick Tip
Quick Tip2. Milia
These are benign (not harmful) and transient white cysts of keratini A structural protein produced by the body that is responsible for forming the nails, hair, and epidermis (the outermost layer of the skin). (a protein) on the skin. Dead skin cells get trapped under the skin and form cysts. Milia on lips is common in infants and also develops on the face (usually on the nose, chin, cheeks). Milia are classified into two types — primary milia and secondary milia. Lesions of some milia fade away on their own while others don’t. However, these white spots can be treated with simple surgical interventions and topical retinoids (6).
3. Oral Thrush
It is an infection caused by the accumulation of the Candida albicans fungus in the mouth. It affects the oral mucosa and is also referred to as oral candidiasis or oropharyngeal candidiasis (7). It is characterized by white or yellowish bumps on the inside of the cheeks, lips, and tongue.
A research study analyzed 35.5 million inpatient visits in the United States in 2018. It found that around 666,235 cases were diagnosed with fungal infections. The most commonly diagnosed fungal infections were caused by Aspergillus, Pneumocystis, and Candida, accounting for 76.3% of all cases. Further, another 6.6 million fungal infections were recorded during outpatient visits.
4. Canker Sores
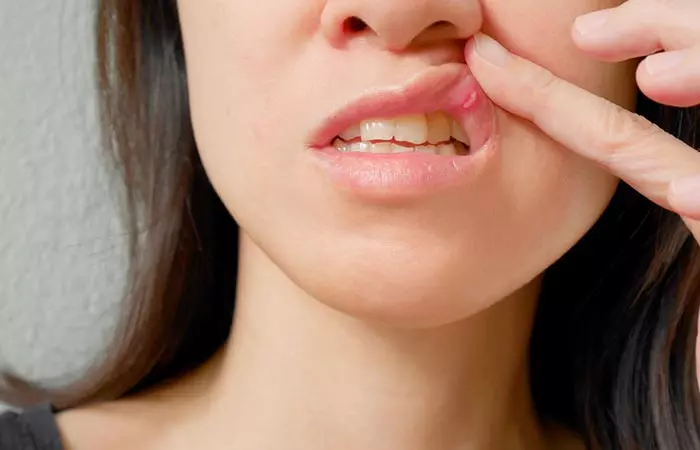

These are inflammatory white-reddish patches (mouth ulcers) on the mucous membrane lining the mouth. Usually, two to four canker sores develop at the same time. Many people start to get them when they are teens or young adults. These are more common in women than in men.
Canker sores are painful but not contagious and fade away within a week or so. Stress, oral injuries, and foods like coffee, peanuts, and tomatoes can trigger them (8), (9).
Stephen Coyner, a blogger, shared his experience about contracting canker sores in his personal blog. He said, “I use roughly a quarter cup of lukewarm water and a large spoonful of salt, then rinse for 30 seconds (i).” He explained that his doctor was hesitant to prescribe medication, as they end up weakening the immune system. He recommended washing the mouth with warm salt water after every meal to aid the healing process.
 Trivia
Trivia5. Mucoceles
Mucoceles are the most common lesions of the oral mucosa. These are caused by the accumulation of mucus secretion due to trauma, lip-biting tendencies, or changes in minor salivary glands. These occur anywhere in the oral mucosa, including the lips (most common), cheeks, and mouth (10).
6. Oral Cancer
It is characterized by a flat white bump in the mouth caused by a variety of factors, including excess exposure to the sun, excess alcohol intake, tobacco use, and the human papillomavirus (HPV). HPV is a viral infection that is spread through skin-to-skin contact (11).
7. Oral Herpes
These are cold sores on or near the mouth that may be observed in people with HIV. It is a type of herpes simplex virus (HSV) infection where the virus attacks the immune system. There are two types of HSV that cause sores – HSV-1 is usually responsible for sores near the mouth area, while HSV-2 generally infects the genitals, although it may sometimes infect the mouth and eye areas as well (12). These sores may be clear, pink, red, yellow, or white, and may be resistant to treatment. They are highly contagious and easily spread through oral sex or kissing. Oral herpes or cold sores are often mistaken for pimples. Therefore, understanding the difference between a cold sore vs. pimple can aid in the proper identification and management of the bumps.
8. Allergic Bumps
Sometimes, allergic reactions to irritants may cause inflammation around the mouth, resulting in white, itchy bumps on the lips. These irritants or allergens can be anything from pet dander to food items to harsh chemicals. A medical consultation may help in diagnosing the cause and possible treatment for the bumps.
Some types of white bumps that occur on the lips can be managed with simple home remedies. Scroll down to know more about them.
How To Treat White Bumps On Lips
Dealing with white bumps and pimples on your lips can be a hassle, but do not worry, there are ways to handle them. It is best to start with some basic home remedies. Keep reading for tips on how to manage and treat these annoying bumps effectively.
1. Garlic
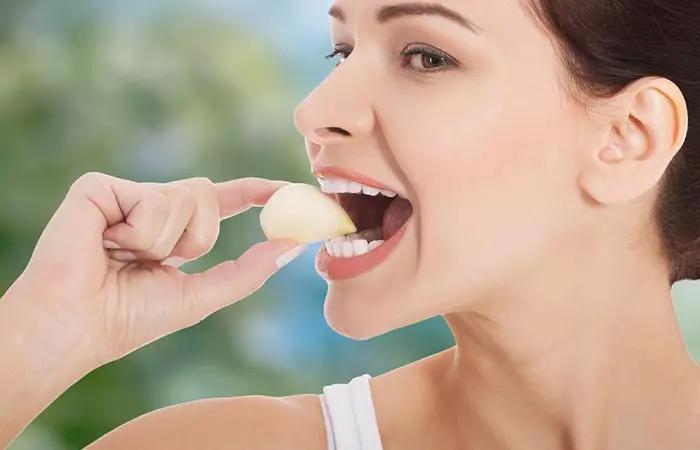

Garlic contains antimicrobiali The ability of an agent to stop the growth of microorganisms in the body, thereby preventing any infections. , anti-inflammatory, and antibacterial properties (13), (14), (15). The study shows that ajoene, a sulfur compound from garlic, stops bacteria and yeast from growing. It works better on gram-positive bacteria like Bacillus and Staphylococcus at lower doses. It can also kill microbes at slightly higher doses (14). Consuming garlic cloves daily helps you maintain dental hygiene and prevent bacterial growth.
Ingredients
- 2 garlic cloves
- 200 ml water
- 1-2 tablespoons lemon juice
Method
- Crush the garlic cloves and add water and lemon juice.
- Drink the mixture in the morning on an empty stomach.
2. Apple Cider Vinegar
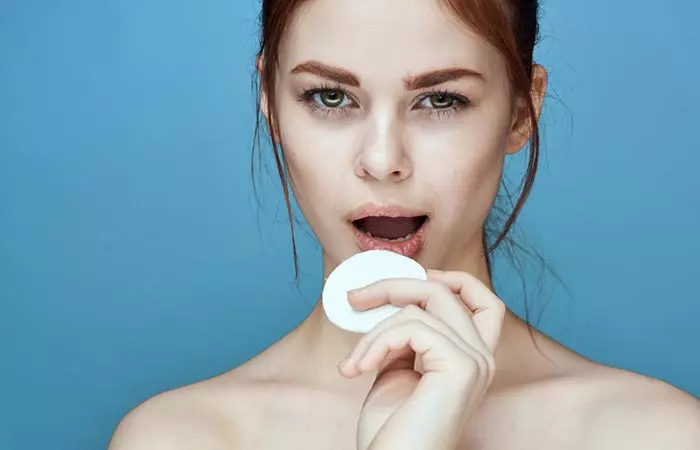

Apple cider vinegar (ACV) has antibacterial properties (16). Its astringent effect may help regulate and manage the excess sebum production on the skin. It has acetic acid that has antioxidant properties that help with wounds, infections, and itching (17).
Ingredients
- A few drops of apple cider vinegar
- A few drops of water
- Cotton sponge/ball
Method
- Mix apple cider vinegar and water in equal amounts.
- Dab the solution on the affected skin with a cotton ball.
- Rinse off with lukewarm water after a few minutes.
- Apply twice a week for better results.
3. Coconut Oil

Dehydrated skin leads to excess sebum release, which may result in white bumps. Coconut oil hydrates and moisturizes your skin (18). It has anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial properties too. Studies show it helps soothe skin and reduce inflammation. It strengthens the skin barrier, provides some UV protection, and is safe to use as it does not cause irritation (19).
Ingredients
- 2-3 tablespoons coconut oil
- A few drops of lavender essential oil
Method
- Apply warm, unrefined coconut oil to the afflicted area.
- You can also blend it with lavender oil and apply.
4. Over-The-Counter Treatments
You may also use OTC medications to treat the white bumps on your lips. However, get advice from a dermatologist first.
In case of a viral infection, look for topical antiviral creams to help reduce the duration and severity of the outbreak. Opt for antifungal creams if you identify a fungal infection. Choose topical retinoid products or chemical peels for conditions like Fordyce spots.
Maintain oral hygiene and eat a balanced diet to avoid the recurrence of white bumps. Regularly rinse your mouth with warm water and salt.
Medications and topical treatments may provide temporary relief or completely heal the condition. Visit your dentist regularly for routine checkups.
White bumps can be bothersome, but you can prevent them with a few self-care techniques. Check them out in the next section.
Self-Care Measures To Treat White Bumps On Lips
Here are a few self-care techniques that may help a lip bump heal faster and minimize any pain or discomfort.
- Wash your face with warm water until the bump goes away. Use a liquid cleanser.
- Pat the skin dry after washing the face rather than rubbing it.
- Avoid the use of tobacco.
- Avoid cosmetics, sunscreen, and face creams.
- Eat a diet rich in vitamins and minerals obtained from whole foods.
- Drink plenty of water.
- Avoid rubbing, squeezing, or touching the bumps.
- Maintain good oral health by brushing and flossing the teeth at least twice a day.
- Use lip balms with natural components and a sun-protection factor.
Do you need to seek medical attention for white bumps on the lips? If yes, when should you consult a doctor?
When To See A Doctor
White bumps on the lips are usually harmless and do not warrant medical attention. Home remedies can be effective for white spots on the lips, but it is important to use them with caution. While natural treatments may help, they are not a substitute for professional medical advice. So, it is best to consult a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and the right course of action. If symptoms persist or worsen, seek medical attention promptly. Consult a doctor only if these bumps persist longer than two weeks or cause the following symptoms:
- Pain
- Bleeding
- Difficulty chewing and swallowing
- Neck and jaw swelling
- Fever and sore throat
- Rapid-spreading rashes
- Breathing difficulties
- Numb tongue
Infographic: Medical Treatments For White Bumps On Lips
White bumps can develop on your lips due to factors such as hormonal imbalance, allergic reaction, or poor skin hygiene. Sometimes, it may also be the symptom of an underlying medical condition. While some white bumps can be managed at home with simple natural remedies, some require proper medical treatment.
Check out the infographic below to know more! Illustration: StyleCraze Design Team
White bumps on the lips, such as canker sores, usually do not require medical attention. They may cause irritation and pain, but these white bumps on lips can be relieved with easy home remedies. Try the solutions recommended in this article for yourself and see the results. White bumps are inconvenient, but they can be avoided with a few self-care practices. However, if these lip blisters linger for more than two weeks, you should see a doctor. Furthermore, it is critical to comprehend their causes to rule out any major underlying disease. They could even be a result of oral herpes, which is a contagious disease and needs quick treatment. Therefore, regular dental examinations are recommended.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is a white bump on the lip a cold sore?
A white bump on the lips could be a cold sore or fever blister if it develops into a cluster of white bumps.
How long do Fordyce spots last?
Fordyce spots are usually permanent. But, sometimes, they fade away on their own. While they may get aggravated due to stressful situations, they are usually harmless. However, you may still choose to get them removed through topical medications or laser techniques. If you are looking for less invasive options you may try home remedies to treat Fordyce spots. However, always consult a doctor before trying any home remedies.
Can lip balm or lipstick cause white bumps on the lips?
Allergies from ingredients in lip balms and lipsticks may lead to allergic contact cheilitis that is marked by peeling, redness, and inflammation of the lips but not white spots or bumps.
Discover 12 simple methods for removing white spots from your lips! Get rid of those irritating white spots and get your lips looking smooth and healthy again. Watch this video to learn more.
Personal Experience: Source
StyleCraze's articles are interwoven with authentic personal narratives that provide depth and resonance to our content. Below are the sources of the personal accounts referenced in this article.
i. How to beat debilitating canker sores; a personal guidebookhttps://medium.com/@stephencoyner/how-to-beat-debilitating-canker-sores-and-mouth-ulcers-a-personal-guidebook-e2fbc2f65f03
References
Articles on StyleCraze are backed by verified information from peer-reviewed and academic research papers, reputed organizations, research institutions, and medical associations to ensure accuracy and relevance. Read our editorial policy to learn more.
- Symptomatic changes of oral mucosa during normal hormonal turnover in healthy young menstruating women
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22665744/ - Risk factors and management of white spot lesions in orthodontics
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/labs/pmc/articles/PMC4072374/ - oral mucosal trauma and injuries
https://www.intechopen.com/chapters/65714 - Fordyce Spots
https://www.oatext.com/pdf/CCRR-1-140.pdf - Can presence of oral Fordyce\’s granules serve as a marker for hyperlipidemia?
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25426145/ - Milia
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK560481/ - Oral candidiasis: An overview
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/labs/pmc/articles/PMC4211245/ - Canker sores (mouth ulcers): Overview
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK546250/ - Guideline for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Recurrent Aphthous Stomatitis for Dental Practitioners
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/labs/pmc/articles/PMC4441245/ - Oral mucocele: Review of literature and a case report
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26538955/ - Oral Cancer: Prevention Early Detection and Treatment
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK343649/ - Herpes Virus, Oral Clinical Signs and QoL: Systematic Review of Recent Data
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6563194/ - Garlic: a review of potential therapeutic effects
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/labs/pmc/articles/PMC4103721/ - Inhibition of microbial growth by ajoene a sulfur-containing compound derived from garlic.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/labs/pmc/articles/PMC168248/ - Antimicrobial properties of allicin from garlic
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/10594976/ - Antimicrobial activity of apple cider vinegar against Escherichia coli Staphylococcus aureus and Candida albicans; downregulating cytokine and microbial protein expression
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/labs/pmc/articles/PMC5788933/ - Acetic acid and the skin: a review of vinegar in dermatology
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34350993/ - A randomized double-blind controlled trial comparing extra virgin coconut oil with mineral oil as a moisturizer for mild to moderate xerosis
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15724344/ - In vitro anti-inflammatory and skin protective properties of Virgin coconut oil
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6335493/
Read full bio of Dr. Robert S. Bader
Read full bio of Monomita Chakraborty
Read full bio of Anjali Sayee
Read full bio of Swathi E


























Community Experiences
Join the conversation and become a part of our empowering community! Share your stories, experiences, and insights to connect with other beauty, lifestyle, and health enthusiasts.