Winter Melon: Nutrition, Benefits, Risks, & Precautions
Make the most of this nutritious seasonal vegetable when it is available on the market.
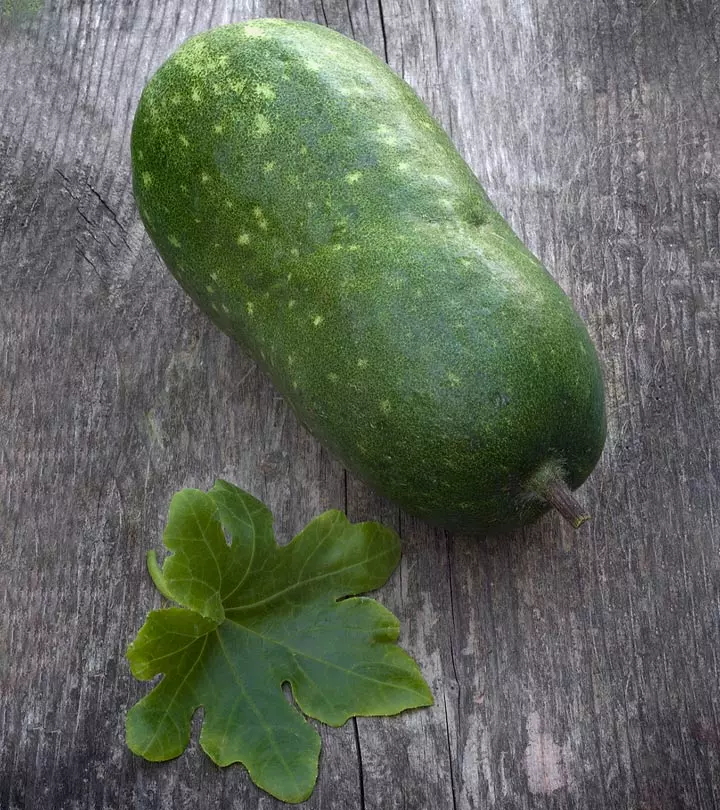

Image: ShutterStock
Winter melon, also known as Benincasa hispida, downtime melon, wax gourd, white pumpkin, ash gourd, and Chinese watermelon, is a fruit native to the corridor of Southern Asia. This versatile ingredient is commonly used in soups, stir-fries, and desserts. More recently, many people have become acquainted with the many winter melon benefits, giving rise to its sudden popularity.
It comprises 96% water and is low in calories, fat, protein, and carbs. Yet, it is rich in fiber. In addition to vitamin C, ash gourd is a good source of flavonoids and carotenoids that may help protect body against cell damage and type 2 diabetes. Learn more about the nutrition, benefits, recipes, and side effects of winter melon here.
 Know Your Ingredient: Winter Melon
Know Your Ingredient: Winter MelonWhat Is It?
A large, oblong-shaped fruit that belongs to the Cucurbitaceae family.
What Are Its Benefits?
Helps manage type-2 diabetes, reduces the risk of cancer, improves eye health, and promotes skin health.
Who Can Use It?
People experiencing constipation and fluctuating blood sugar levels.
How Often?
Two to three times per week.
Caution
Due to its high fiber content, some people may experience mild digestive discomfort, such as gas and bloating.
In This Article
What Is Winter Melon?
Winter melons, botanically known as Benincasa hispida, are ancient fruits that grow on creeping vines belonging to the Cucurbitaceae family. The large fruits are native to Asia and are a medicinal and culinary component favored for their neutral flavor. Winter melons are known by numerous names worldwide. Some experts believe the fine, white coating on the melon, which reminded consumers of snow, is another explanation for the melon’s name. Though they’re botanically a fruit, winter melons are cooked and consumed as vegetables and are prevalently seen in curries stir-fries in many Asian cuisines such as Indian and Chinese.
Key Takeaways
- Winter melon consumption may reduce blood sugar levels.
- It may improve eyesight and protect the eyes from damage due to aging.
- It helps reduce dark spots and wrinkles on your skin.
- Winter melon is rich in potassium that, when eaten in excess, causes gastrointestinal discomfort and nausea.
Taste Of Winter Melon
The seeds of winter melon, once cooked, have a nutty and neutral taste. The flesh itself isn’t typically eaten raw. It has a mild, subtly grassy flavor that becomes transparent and soft when cooked. If cooked for a longer time, it develops a mellow taste. Because of its milder, less sweet flavor, winter melon serves as an excellent base for more flavorful dishes compared to other melons. Its texture allows it to absorb spices and seasonings well, enhancing the overall flavor of the meal.
Winter melon is nutrient-dense. Learn more about its nutrients from the section below.
Nutritional Value Of Winter Melon
Winter melon is rich in vitamins, minerals, and organic compounds. It is low in sodium and saturated fat. Following are the nutrients present in 100 grams of winter melon (1):
| Water | 96.1 g |
| Energy | 13 kcal |
| Protein | 0.4 g |
| Carbohydrates | 3 g |
| Fibre | 2.9 g |
| Calcium | 19 mg |
| Vitamin C | 13 mg |
| Vitamin B2 | 1.3 mg |
| Magnesium | 10 mg |
Its nutrient profile is responsible for the many benefits of winter melons. Let us discuss them in the next section.
Health Benefits Of Winter Melons
1. May Help Manage Type 2 Diabetes
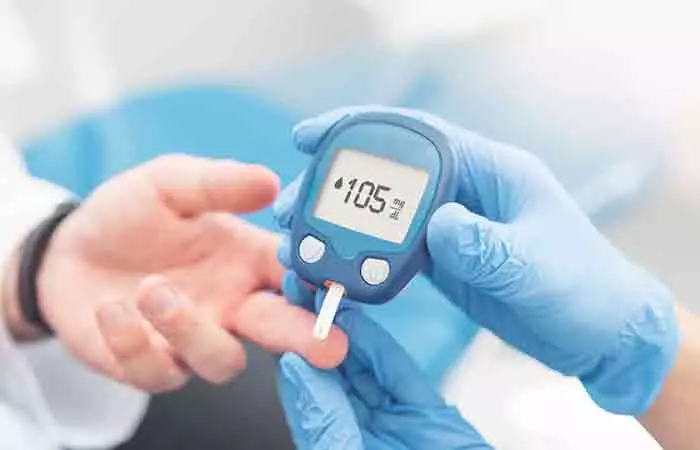
Winter melons are low in calories and are ideal for people aiming for weight loss and those with diabetes.
In studies, winter melons could help reduce blood sugar in those with type 2 diabetes mellitusi A group of diabetes caused by high blood glucose, including prediabetes, type 1, and type 2 diabetes. (2). In addition, vegetables from the Cucurbitaceae family offer beneficial fibers, β-carotene (pro-vitamin A), potassium, and vitamin C. Regularly consuming these can help manage diabetes mellitusi A group of diabetes caused by high blood glucose, including prediabetes, type 1, and type 2 diabetes. (3).
Other research also suggests that regular winter melon intake may help reduce blood sugar levels in patients with diabetes mellitusi A group of diabetes caused by high blood glucose, including prediabetes, type 1, and type 2 diabetes. (4).
2. May Help Reduce Cancer Risk
Winter melon may reduce the threat of several types of cancers.
The biochemical components in this fruit inhibit the action of carcinogensi Any agent or substance that has the potential to cause cancer and damage healthy cells in the body. and also keep the malignant cells from spreading. The melon also contains carotenoids that reduce colon cancer risk (5).
In addition, winter melon seed extracts had shown significant antioxidant capacity. They help combat the harmful action of free radicals, which may otherwise elevate cancer risk (6). The seeds of winter melon are also rich in polyunsaturated fatty acids that may reduce cancer risk (7).
3. May Improve Eye Health

The antioxidants in winter melons help reduce oxidative stressi It occurs when cells are damaged due to an imbalance between antioxidants and free radicals in the body. in the retina. Also, with age, the vitamin C levels in the eye lens may diminish and lead to potential vision issues. Consumption of fresh winter melons may increase vitamin C levels in the lens (8).
However, numerous studies on the potential of vitamin C as a cataract curative have produced mixed results (9).
Winter melons also contain riboflavin, whose deficiency may cause night blindness. Adequate riboflavin intake can help prevent the condition (10).
4. May Promote Skin Health

Winter melons are a rich source of vitamin C and antioxidants that improve skin health. Vitamin C can be used topically in dermatology to treat and help changes associated with photoagingi The condition of premature skin aging by damage from harmful UV rays, which can also lead to the risk of skin cancer. . It can also be used for the treatment of hyperpigmentation. This nutrient in winter melons protects the skin from oxidative stressi It occurs when cells are damaged due to an imbalance between antioxidants and free radicals in the body. . Ascorbic acid is the most abundant antioxidant in the skin and is the biologically active form of vitamin C (11). Vitamin C also exhibits skin brightening effects (12).
5. May Promote Heart Health

The vitamin C in winter melons reduces cardiovascular complaints by fighting free radicals. Antioxidants like vitamin C inhibit LDL oxidation and reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease (13). Vitamin C deficiency is associated with an increased risk of cardiovascular conditions. In addition, vitamin C may slightly improve endothelial function (endothelium is the cellular tissue over the heart and blood vessels) (14).
Apart from the above- mentioned benefits, anecdotal evidence suggests that winter melon juice may help in cooling down the body during summer. However, more research is needed to support this claim.
Pooja, a health and lifestyle blogger, consumed winter melon daily and saw remarkable results. She said, “For me, lack of hydration was causing constant severe headaches and after 3 months of regular consumption, I can see the headaches almost disappeared (i).”
 Did You Know?
Did You Know?These are the important benefits of winter melons. However, one must also consider their potential downsides. Learn more in the next section.
Side Effects And Allergic Reactions Of Winter Melons
May Aggravate Cold:
Winter melon has a cold potency as per Ayurveda (15). Anecdotal evidence suggests that this may aggravate cold in some individuals. Hence, avoid their intake when you have a cold and consult your doctor.
May Aggravate Gastrointestinal Discomfort: Winter melon is rich in potassium. If consumed in excess, it may aggravate gastrointestinal discomfort and lead to nausea, diarrhea, and abdominal pain (16).
Though uncommon, some people may have allergic reactions to winter melon, leading to symptoms like itching or swelling. If you experience any negative effects after eating the fruit, consult a healthcare professional immediately.
However, these side effects are associated with excess consumption of the melons, and usually subside on their own. Eating them in moderation helps reap the benefits. Know how to eat winter melon from the section below.
How To Eat Winter Melon
Winter melon can be cooked in stews, mists, and stir-fried and coddled dishes. Because the melon itself tastes plain and its texture absorbs flavor well, it’s frequently cooked with pork, funk, and other explosively seasoned constituents. It can be a great addition to salads and smoothies.
 Did You Know?
Did You Know?Selection And Storage
Always choose a winter melon with no bruises. Fresh winter melons are green with firm rinds. For storage, cut the melon, remove the white part containing the seeds, and place it in a vegetable storehouse vessel and store in the refrigerator. You can store it in the refrigerator for up to 4 days.
Winter melon can be cooked in different ways. Learn some tasty recipes from the section below.
Recipes
1. Chinese Winter Melon Soup
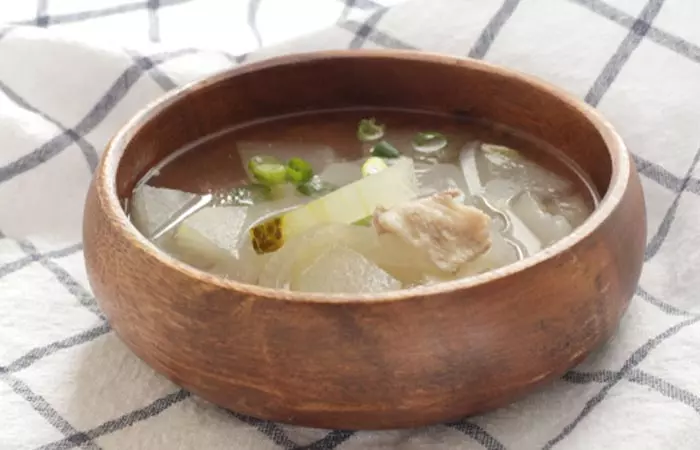

- ½ pound of winter melon
- 4 dried shiitake mushrooms
- 2 cups of chicken broth
- 2 to 3 slices of ginger
- 1/4 mug of diced cooked ham
- Salt, to taste
- Pepper, to taste
- 1 green onion
Method
- Wash the melon thoroughly. Gently remove the skin, seeds, and pulp. Cut the melon into small pieces.
- Place the melon in a pot of water and bring it to a boil. Reduce heat until the melon is tender.
- Soak the dried shiitake mushrooms in a bowl of cold water for at least 10 minutes.
- Squeeze out any redundant water from the mushrooms and set them aside.
- To the pot, add the mushrooms, gusto, funk broth, and cooked ham. Add salt and pepper to taste.
- Simmer for 20 minutes and serve hot.
2. Ash Gourd Curry
What You Need
- 200 grams of winter melon
- 1 medium onion, diced finely
- 1 green chili, diced finely
- ½ tablespoon of mustard seeds
- ½ tablespoon of cumin seeds
- ½ tablespoon of turmeric
- 2 shoots of curry leaves
- ¾ cup of grated coconut
- ¼ teaspoon of coconut powder
Method
- Wash the winter melon and keep it ready with the diced onions and green chili.
- In a frying pan, toast the coconut powder for 20 seconds. Add the mustard seeds, and when they pop, add the cumin seeds. When the cumin seeds sizzle, add the onions. Fry the onions until they are transparent.
- Add the curry leaves and green chili.
- Now add the winter melon.
- Add the turmeric and sauté for a second.
- Cover with a lid and let the ash gourd steam slowly. Don’t add water as the ash gourd has enough water in it. Cook for 7 to 8 minutes till the winter melon is nearly done.
- Mix the coconut well with the veggie.
- Switch off the flame after 2 minutes.
3. Winter Melon Tea
What You Need
- 800 grams of winter melon
- 220 grams of brown sugar
- 4-5 cups of water
- Ice cubes
Method
- Peel the winter melon, remove the spongy center with seeds, and cut it into small pieces.
- Add the pieces to a bowl and mix them with brown sugar.
- Stir well and let it sit for 2 hours.
- Then, boil the mixture on low heat for 1 hour, stirring continuously.
- Strain it using a cloth strainer and transfer the syrup to a glass jar.
- Mix 1 part syrup with 3 parts of water to make tea.
- Add ice cubes and serve cold.
Note:
You can also mix the syrup with warm water and drink it.
4. Winter Melon Salad
What You Need
- 1 cup of winter melon, diced
- 1/2 cup of dried cucumber, diced
- 1/4 cup of red onion, thinly sliced
- Fresh mint leaves
For Dressing:
- 2 tablespoons of olive oil
- 1 tablespoon of lemon juice
- Salt and pepper to taste
Method
- Mix together the winter melon, cucumber, and red onion in a bowl.
- In another bowl, whisk together the olive oil, lemon juice, salt, and pepper.
- Drizzle the dressing over the salad and toss it gently.
- Garnish with fresh mint leaves and serve chilled.
Infographic: 5 Must-Know Benefits Of Winter Melons
Winter melons have a mild taste that is quite similar to cucumber, and their fleshy part is used in various Chinese and Indian delicacies. They are rich in antioxidants and essential nutrients that are highly beneficial for your health and well-being. Check out the infographic below for the top five reasons to start consuming winter melons today.

Illustration: StyleCraze Design Team
Conclusion
Winter melon is an ancient fruit frequently eaten as a vegetable. If included as a part of the diet, it can help manage diabetes, reduce the risk of cancer, maintain bodily hydration levels and promote eye, skin, and heart health. It can be an easy addition to any dish because of its nutty taste. You can easily add winter melon to soups, salads, and smoothies. However, if consumed in excess, winter melon may aggravate cough and cold and may also cause issues with digestion. Hence, caution is advised. However, moderate consumption can offer benefits.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is winter melon the same as honeydew?
Yes, honeydew is a type of winter melon. It ripens slower than other types of melons. One of the most well-known benefits of the honeydew melon is its high water content that aids hydration. You can slice it and eat it with salt and pepper.
How can you tell when a winter melon is ripe?
If the stem is brown and it has an ashy appearance, these are indicators that the winter melon is ripe.
Are winter melons bitter?
No, winter lemons have a very mild and neutral taste. You can easily incorporate any flavor into the winter melons.
Is winter melon good for detox?
Yes, winter melon is known as a detoxificant. It helps detox the body and eliminate toxins through urine (17).
Is winter melon good for kidneys?
Yes, studies suggest that winter melon may help prevent the growth and formation of kidney stones (18).
Illustration: Is Winter Melon Good For You? Benefits And Side Effects

Image: Stable Diffusion/StyleCraze Design Team
Quench your thirst and boost your health with the refreshing goodness of ash gourd juice, also known as winter melon juice. Watch this easy recipe video and learn its incredible benefits
Personal Experience: Source
StyleCraze's articles are interwoven with authentic personal narratives that provide depth and resonance to our content. Below are the sources of the personal accounts referenced in this article.
i. 5 Daily Habits For Mind and Bodyhttps://allthewhiletilltoday.blogspot.com/2022/11/5-daily-habits-for-mind-and-body.html
References
Articles on StyleCraze are backed by verified information from peer-reviewed and academic research papers, reputed organizations, research institutions, and medical associations to ensure accuracy and relevance. Read our editorial policy to learn more.
- Winter Melon
https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/170069/nutrients - Revisiting “Vegetables” to combat modern epidemic of imbalanced glucose homeostasis
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4078339/ - Therapeutic Benefits of Commercially Available Gourd Family in Improvement and Sustainability of Human Health
https://www.researchgate.net/publication/326703774_Therapeutic_Benefits_of_Commercially_Available_Gourd_Family_in_Improvement_and_Sustainability_of_Human_Health - Different Parameters for Drying of Winter Melon
https://www.jpsr.pharmainfo.in/Documents/Volumes/vol11issue04/jpsr11041953.pdf - A Literature-Based Update on Benincasa hispida (Thunb.) Cogn.: Traditional Uses, Nutraceutical and Phytopharmacological Profiles
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8683187/ - Antioxidant activity of winter melon (Benincasa hispid) seeds using the conventional soxhlet extraction technique
http://www.ifrj.upm.edu.my/19%20(01)%202011/(30)IFRJ-2011-161%20Mandana.pdf - Nutritional composition and oil fatty acids of Indian winter melon Benincasa hispid (Thunb).Seeds
http://www.ifrj.upm.edu.my/20%20(03)%202013/16%20IFRJ%2020%20(03)%202013%20Rayees%20(338).pdf
- Vitamin C and the Lens: New Insights into Delaying the Onset of Cataract
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/labs/pmc/articles/PMC7602486/ - Vitamin C and the Lens: New Insights into Delaying the Onset of Cataract
https://www.mdpi.com/2072-6643/12/10/3142 - Riboflavin (vitamin B-2) and health
https://academic.oup.com/ajcn/article/77/6/1352/4689829 - Vitamin C in dermatology
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3673383/ - Anti‐aging and brightening effects of a topical treatment containing vitamin C, vitamin E, and raspberry leaf cell culture extract: A split‐face, randomized controlled trial
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7027822/ - Vitamins E and C in the Prevention of Cardiovascular Disease in Men
https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jama/fullarticle/1028653#24631875 - Vitamin C and Heart Health: A Review Based on Findings from Epidemiologic Studies
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27529239/
- A COMPREHENSIVE REVIEW ON THE NUTRITIONAL AND MEDICINAL SIGNIFICANCE OF KUSHMANDA OR ASH GOURD AS PER AYURVEDA
https://www.researchgate.net/publication/358045158_International_Journal_of_Ayurveda_and_Pharma_Research_Review_Article_A_COMPREHENSIVE_REVIEW_ON_THE_NUTRITIONAL_AND_MEDICINAL_SIGNIFICANCE_OF_KUSHMANDA_OR_ASH_GOURD_AS_PER_AYURVEDA_Nimmy_V_S - Potassium
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK539791/ - Ash gourd and its applications in the food, pharmacological and biomedical industries
https://www.researchgate.net/publication/337854043_Ash_gourd_and_its_applications_in_the_food_pharmacological_and_biomedical_industries - ANTIUROLITHIATIC POTENTIAL OF THE EDIBLE PLANTS AQUEOUS EXTRACT OF RADISH, WINTER MELON AND PSEUDOSTEM OF BANANA TREE: IN VITRO STUDY
https://www.researchgate.net/publication/351576947_ANTIUROLITHIATIC_POTENTIAL_OF_THE_EDIBLE_PLANTS_AQUEOUS_EXTRACT_OF_RADISH_WINTER_MELON_AND_PSEUDOSTEM_OF_BANANA_TREE_IN_VITRO_STUDY
Read full bio of Dr. Pallavi Srivastava
Read full bio of Aparna Mallampalli
Read full bio of Ravi Teja Tadimalla
Read full bio of Payal Karnik




























Community Experiences
Join the conversation and become a part of our empowering community! Share your stories, experiences, and insights to connect with other beauty, lifestyle, and health enthusiasts.