Zinc For Hair Loss: 11 Proven Benefits For Strong, Thicker Hair
Learn everything about this essential nutrient and its role in your hair health.

Image: ShutterStock
Zinc for hair loss has become a potential treatment. We often see people consuming zinc supplements to improve hair loss. We know that nutrients are essential for hair growth, but do you know how zinc is beneficial and what exactly it does for hair loss? This article discusses all the benefits of zinc on hair and how zinc deficiency affects hair health. Read on.
 Trivia
Trivia Know Your Ingredient: Zinc
Know Your Ingredient: ZincWhat Is It?
A trace mineral generally found in poultry, red meat, and fish.
What Are Its Benefits?
It supports hair growth, strengthens hair follicles, and increases hair thickness.
Who Can Use It?
Zinc supplements can be consumed by all in moderation unless they are allergic to zinc.
How Often?
It can be taken every day; however, the dosage depends on the recommendation of your healthcare provider.
Caution
Excess consumption of zinc is unsafe and may cause vomiting, stomach pain, indigestion, diarrhea, and headache. It may also interact with certain medications.
In This Article
Zinc Deficiency And Hair Loss

Research shows that zinc deficiency may cause hair loss (1). Such hair loss can most often be treated with zinc supplementation. In another study, participants with male pattern hair loss, female pattern hair loss, and telogen effluviumi A temporary condition where hair begins to fall out two to three months following a stressful event or bodily change, such as childbirth or surgery. were deficient in zinc (2). Individuals with alopecia areata (an autoimmune disease that leads to patchy hair loss in a roundish configuration) were also found to have low zinc levels (3).
Along similar lines, a study found that the risk of encountering alopecia areata in a lifetime is around 2% in the general population. In addition, the study also found that alopecia areata is genetic, and those with a family history are more likely to experience it, with a probability of between 0% and 8.6%. Moreover, the study suggested that alopecia areata can increase the risk of getting other autoimmune diseases by 16%.

While zinc seems to have an important role in combating hair loss, more research is warranted. Other studies suggest no significant relationship between zinc deficiency and hair loss (1), (4), (5).
If you are unsure whether or not you have zinc deficiency, then continue reading as we explore the various symptoms that will help you understand the condition better and take action accordingly.
Key Takeaways
- Zinc is an essential nutrient for hair health, and a deficiency may lead to hair loss and damage.
- Topical and oral zinc supplementation can help improve hair growth, count, density, and keratin content.
- Oysters, red meat, poultry, beans, nuts, and vegetables are common sources of dietary zinc.
- It is recommended to consult a doctor before starting zinc supplements with any other health concerns or in combination with other medicines.
Symptoms Of Zinc Deficiency

- Hair Loss: This is the most common symptom of zinc deficiency. If you are experiencing hair thinning and frequent shedding, and notice bald patches on your scalp, it may be a result of zinc deficiency. The common hair loss symptoms have also been noticed in alopecia areata patients who have zinc deficiency (6).
- Brittle Hair: Zinc deficiency may also cause dry and brittle hair that is more prone to breakage (7).
- Scalp Issues: Insufficient serum zinc levels in the body may lead to dandruff (seborrheic dermatitis) and an itchy scalp (8).
- Premature Graying: Zinc helps maintain hair pigmentation, thus its deficiency can contribute to premature graying of the hair (9).
If you are wondering how zinc can improve your hair, here are some of its benefits.
Benefits Of Zinc For Hair

- A study showed that alopecia areata may be treated with zinc supplementation (6). Nine out of 15 participants in the study showed improved hair growth with regular intake of zinc supplements.
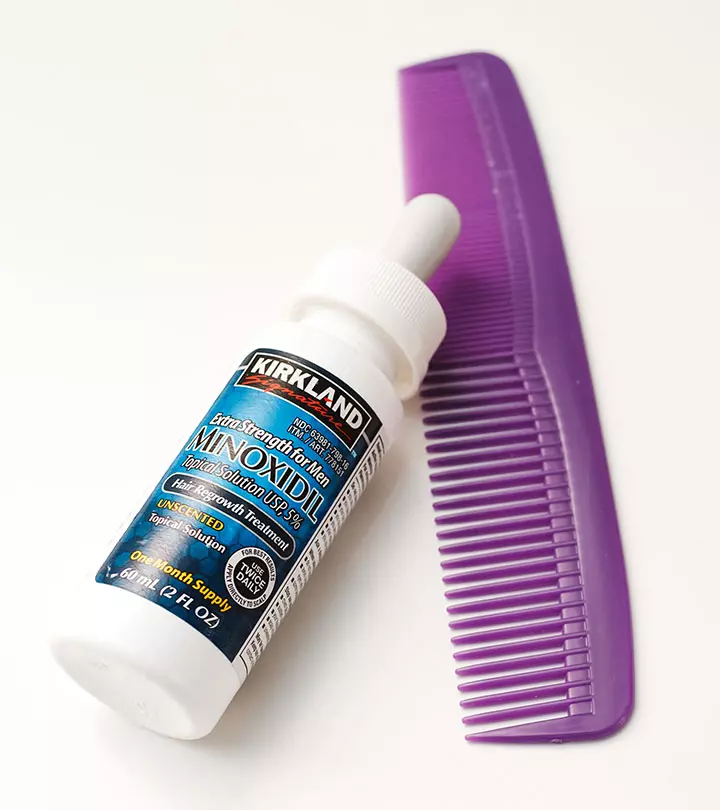
- Another study used oral supplementation of chelated zinc paired with regular applications of topical minoxidil (10). Chelated zinc played an important role in hair growth in female pattern hair loss.
- Zinc contains enzymes crucial for certain functional activities in the hair follicles (10). The nutrient also helps inhibit hair follicle regression and may accelerate the healing of hair follicles.
- Oral zinc sulfate can help treat patchy alopecia areata with a low relapse rate after cessationi A process of reducing or ending hair loss by effective medication and dietary changes to regrow hair. of the treatment (6).
- Oral L-cystinei A form of non-essential amino acid if taken as medication with zinc which promotes hair regrowth and strengthening. , when combined with zinc, can treat diffuse alopecia. It also can increase hair count, improve hair density, and boost keratin content (11).
- Topical and oral supplementation of zinc is said to impact hair loss and promote hair growth. Zinc may inhibit 5-alpha reductase, an enzyme that may disrupt hair growth. Zinc also has anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties that may promote hair growth (11).
- Zinc chelates paired with pyrithionei It is used to prepare zinc pyrithione which is antibacterial, antimicrobial, and antifungal and used to treat dandruff. may be used as a treatment for dandruff (11).
- Zinc is an enzyme activator. It activates the protein transformation necessary for hair building (12).
- Zinc deficiencies might diminish hair and scalp health and make hair brittle (7). This problem may be treated with zinc supplementation
- Free radicals cause oxidative damage and lead to hair loss. Zinc, being an antioxidant, can help balance the production of free radicals (7).
There are numerous other benefits of zinc which makes it a truly beneficial and important mineral for hair and overall health. A deficiency of this mineral can weaken the hair follicles, causing hair fall. One of the best ways to avoid a zinc deficiency is to consume more foods rich in zinc. Here are some food options you can consider adding to your everyday diet.
Foods Rich In Zinc
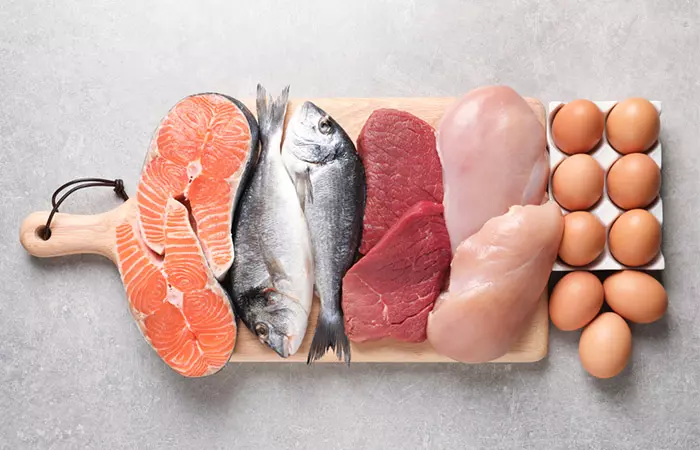

A diet low in zinc can cause hair loss and make hair brittle (7). You can counter this by consuming fish and meat, which are rich in zinc and add to hair nutrition (1). Oysters, red meat, and poultry are the best sources of zinc (13). Other zinc-rich foods include crabs, lobster, dairy products, beans, nuts, chickpeas, quinoa, hemp seeds, lentils, pumpkin seeds, cashews, chia seeds, and fortified breakfast cereals. Vegetables and grains are comparatively lower in zinc. The table below provides a comprehensive idea.
| Foods Rich In Zinc | ||
|---|---|---|
| Food | Milligrams (mg) per serving | Percent DV* |
| Oysters, cooked, breaded and fried, 3 ounces | 74 | 673 |
| Beef chuck roast, braised, 3 ounces | 7 | 64 |
| Crab, Alaska king, cooked, 3 ounces | 6.5 | 59 |
| Beef patty, broiled, 3 ounces | 5.3 | 48 |
| Lobster, cooked, 3 ounces | 3.4 | 31 |
| Pork chop, loin, cooked, 3 ounces | 2.9 | 26 |
| Baked beans, canned, plain or vegetarian, ½ cup | 2.9 | 26 |
| Breakfast cereal, fortified with 25% of the DV for zinc, 1 serving | 2.8 | 25 |
| Chicken, dark meat, cooked, 3 ounces | 2.4 | 22 |
| Pumpkin seeds, dried, 1 ounce | 2.2 | 20 |
| Yogurt, fruit, low fat, 8 ounces | 1.7 | 15 |
| Cashews, dry roasted, 1 ounce | 1.6 | 15 |
| Chickpeas, cooked, ½ cup | 1.3 | 12 |
| Cheese, Swiss, 1 ounce | 1.2 | 11 |
| Oatmeal, instant, plain, prepared with water, 1 packet | 1.1 | 10 |
| Milk, low-fat or non fat, 1 cup | 1 | 9 |
| Almonds, dry roasted, 1 ounce | 0.9 | 8 |
| Kidney beans, cooked, ½ cup | 0.9 | 8 |
| Chicken breast, roasted, skin removed, ½ breast | 0.9 | 8 |
| Cheese, cheddar or mozzarella, 1 ounce | 0.9 | 8 |
| Peas, green, frozen, cooked, ½ cup | 0.5 | 5 |
| Flounder or sole, cooked, 3 ounces | 0.3 | 3 |
The list doesn’t end here. There are numerous other foods high in zinc, which you can check out and include in your diet. While your daily intake of zinc depends on your dietary choices. However, if you are taking zinc supplements for hair, it’s better to keep it within permissible limits. Scroll down to get more information related to dosage.
Zinc Dosage For Hair

Following are the adequate zinc dosage values recommended by the Food and Nutrition Board (13):
| Recommended Dietary Allowances (RDAs) for Zinc | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age | Male | Female | Pregnancy | Lactation |
| 0 – 6 months | 2 mg* | 2 mg* | ||
| 7 – 12 months | 3 mg | 3 mg | ||
| 1 – 3 years | 3 mg | 3 mg | ||
| 4 – 8 years | 5 mg | 5 mg | ||
| 9 – 13 years | 8 mg | 8 mg | ||
| 14 – 18 years | 11 mg | 9 mg | 12 mg | 13 mg |
| 19+ years | 11 mg | 8 mg | 11 mg | 12 mg |
Zinc is hailed as one of the most important nutrients for hair growth. But did you know it may have some side effects too? Scroll down to learn more about them.
Side Effects
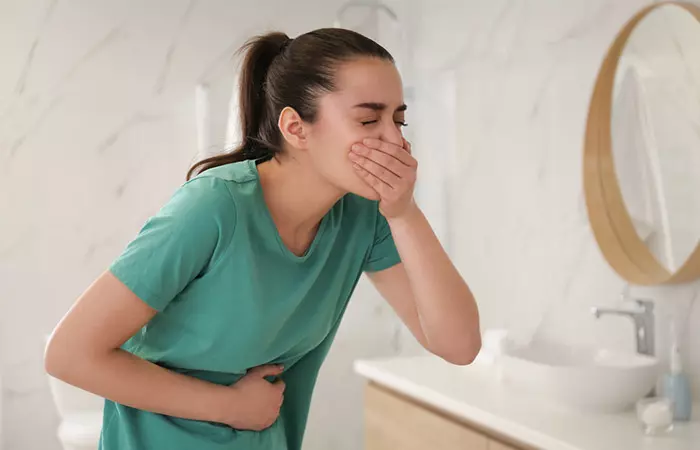

Excess intake of zinc can lead to zinc toxicity. It can cause nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, headaches, and abdominal cramps (13).
 Quick Tip
Quick TipIt is also advisable to check with a doctor before taking any hair supplements and hair vitamins with medications. Certain medications may react adversely with zinc. Antibiotics can inhibit zinc absorption. Diureticsi Any ingredient or drug that encourages diuresis (excessive urine production) to flush out excess salt and water from the body. may reduce zinc levels in the body and cause a deficiency. Zinc may also reduce the absorption and activity of penicillaminei A medication used to remove excess copper from the bloodstream and reduce swelling and pain during arthritis. , hindering rheumatoid arthritisi An autoimmune condition that causes persistent inflammation and affects the tissue on both sides of joints, especially the hands and feet, and hair loss. treatment (12).
Illustration: Zinc For Hair Loss: How It Works, Benefits, And Side Effects

Image: Dall·E/StyleCraze Design Team
Learn from a dermatologist how zinc can improve your skin and hair health! Get the facts on how to incorporate it into your routine from the video below.
Infographic: A Complete Guide To Zinc For Hair Loss
Various studies have suggested that zinc deficiency may cause hair loss. The good news is that increasing your zinc intake may help strengthen your hair follicles and boost hair growth. Check out the infographic below to know about the benefits of zinc for your hair, how to incorporate it into your diet, and more.
Some thing wrong with infographic shortcode. please verify shortcode syntaxZinc plays an important role in hair care and especially in combating hair loss. Using zinc for hair loss can be a good idea as it is proven to have treated hair loss problems in people with alopecia areata. According to anecdotal evidence, regular zinc supplementation may also improve hair growth. Consuming a zinc-rich diet like crabs, fish, nuts, beans, lobster, dairy products, and cereals may help combat hair loss issues. You may also make a few lifestyle changes and maintain a healthy sleep pattern to keep your hair issues at bay.
Frequently Asked Questions
What happens if you take zinc every day?
You can have zinc daily so long as it is within the recommended dosage. Excess intake may lead to vomiting, stomach issues, and other health problems.
When should I take zinc in the morning or night?
Zinc can be taken at any time of the day. However, you should not take it on an empty stomach as it may upset the stomach.
Can zinc cause blood clots?
Zinc deficiency may lead to blood clots and other irregularities.
Is it OK to take vitamin C and zinc together?
Yes. It is alright to consume vitamin C with zinc, provided they are within their recommended dosage.
References
Articles on StyleCraze are backed by verified information from peer-reviewed and academic research papers, reputed organizations, research institutions, and medical associations to ensure accuracy and relevance. Read our editorial policy to learn more.
- The Role of Vitamins and Minerals in Hair Loss: a Review,
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6380979/ - Analysis of Serum Zinc and Copper Concentrations in Hair Loss,
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24371385/ - The Role of Micronutrients in Alopecia Areata: a Review,
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28508256/ - Comparison of Zn, Cu, and Fe Content in Hair and Serum in Alopecia Areata Patients With Normal Group,
https://www.hindawi.com/journals/drp/2014/784863/ - Element Concentrations in Serum, Erythrocytes, Hair and Urine of Alopecia Patients,
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/2424231/ - The Therapeutic Effect and the Changed Serum Zinc Level after Zinc Supplementation in Alopecia Areata Patients Who Had a Low Serum Zinc Level
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2861201/ - Diet and hair loss: effects of nutrient deficiency and supplement use
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5315033/ - Serum zinc levels in seborrheic dermatitis: a case-control study https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7018314/
- Premature Graying of Hair: Review with Updates
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6290285/ - A Pilot Study of the Efficacy in Treatment of Female Pattern Hair Loss Using 5% Minoxidil Solution Combined With Oral Chelated Zinc Supplement,
https://www.longdom.org/open-access/a-pilot-study-of-the-efficacy-in-treatment-of-female-pattern-hair-loss-using-minoxidil-solution-combined-with-oral-chelated-zinc-supplement-2167-0951.1000113.pdf - Complementary and Alternative Treatments for Alopecia: a Comprehensive Review,
https://karger.com/sad/article/5/2/72/291462/Complementary-and-Alternative-Treatments-for - Efficacy of Alimental Components in an Oral Supplement for the Treatment of Hair Fall, Hair Growth, Skin & Nail Problems and Role of Hairvit Plus in Their Composition Upgradation,
https://www.ijsrp.org/research-paper-0318/ijsrp-p7545.pdf - Zinc,
https://ods.od.nih.gov/factsheets/Zinc-HealthProfessional/
Read full bio of Dr. Priya Gill
Read full bio of Anjali Sayee
Read full bio of Eshna Das
Read full bio of Krati Darak
























Community Experiences
Join the conversation and become a part of our empowering community! Share your stories, experiences, and insights to connect with other beauty, lifestyle, and health enthusiasts.